Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAP-2 Architecture Guide
Uploaded by
MuhammadHaque0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views19 pagesOriginal Title
Lecture Note 06
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views19 pagesSAP-2 Architecture Guide
Uploaded by
MuhammadHaqueCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
SAP-2
Navila Rahman Nadi
What is New?
• The SAP-2 adds a lot of functionality to the SAP-1
hardware, but the important additions are to the
instruction set.
• Data path is bigger, but operation remains the
same means the accumulator is 8 bit.
• The RAM is 64k now, so huge memory address
area of 65,536 bytes
• Control sequencer is much bigger as a result of all
the extra registers we added, but we won’t worry
about what’s inside.
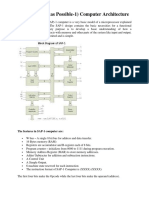
Architecture
Input port
• Hexadecimal keyboard encoder -receives the
data from outer environment and converts it
into hexadecimal form.
• The system can understand and send them to
the input port 1.
• It has two input ports.( port 1 and 2)
Program Counter
• 16 bit address, thus can count from
PC= 0000 0000 0000 0000 (0000H)
to
PC= 1111 1111 1111 1111(FFFFH)
• Before each computer run, a low CLR signal
resets the PC so that the data processing
starts with the instruction stored in memory
location 0000H
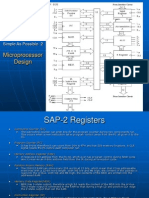
Memory Address Register(MAR) and
MEMORY
• MAR Receives 16- bit address from PC.
• MAR’s output addresses the desired memory
location.
• Memory is 64K (1,024 × 64 = 65,536 bytes).
• With 2K ROM ( addresses of 0000H to 07FFH)
• 2K ROM(addresses from 0000H-07FFH)
• 62K RAM(addresses from 0800H-FFFFH)
Memory Data Register (MDR)
• 8-bit Register
• it stores the data or operand that is fetched
from the memory which is needed for
computation.
Instruction Register
• holds the complete format of the Instruction
that is to be executed.
• 8-bit op code for each instruction
• SAP 2 consists of total 42 instructions
Controller Sequencer
• It provides necessary timing signals like T0, T1,
T2, ….. and control signals providing the
direction for executing the program.
• Generates the control words
(microinstructions)
• Control Word is bigger (CON)
Accumulator
Same as SAP-1
• The result of all the mathematical operations
is stored in accumulator.
• It is one of the operand of ADD, OUT, SUB
instruction.
• It is also known as processor register.
ALU and Flags
• ALU :- Includes both arithmetic and logical
operation
• Flag: Represent the status of the arithmetic
and logical operation.
• Zero Flag(Z)= When the accumulator content
becomes zero.
• Sign Flag(S)= When the accumulator contents
become negative during the execution of the
instructions
TMP, B and C registers
• Temporary register (TMP).
• They are the second operand of the
mathematical operations.
• Register B and C are used to move data during
program run.
• The register B and C is accessible to the
programmer.
Output Ports
2 output ports(3 and 4)
Port 3 : Drives Hexadecimal display- processed
data.
Port 4: sends ACKNOWLEDGE signals used to
hexadecimal encoder.(Handshaking)
Memory Reference Instruction
• LDA ( Load the accumulator)
LDA 2000H means to load the accumulator with the contents of memory location
of 2000H
• STA (Store the accumulator)
STA 7FFFH means to store the accumulator contents at memory location of 7FFFH
If Acc=8AH then the execution of 7FFFH stores 8AH at address 7FFFh
3 byte instruction
• MVI (Move Immediate)
It tells the computer to load a designated register with the byte that immediate
follows the opcode.
MVI A, 37H tells the computer to load the accumulator with 37H , After this
instruction has been executed the binary contents of the accumulator are:
Acc=0011 0111
2 byte instruction
Opcodes
Register Instruction
• MOV
The mnemonic for MOVE. It tells the computer
to move data from one register to another.
MOV A,B
Tells the computer to move the data in the B
register to the accumulator.
The operation is nondestructive, meaning that
the data in B register is copied but not erased.
1 byte instruction
Register Instruction
• ADD and SUB
ADD stands for add the data in the designated register to
the accumulator.
ADD B means to add the contents of the B register to the
accumulator.
If A= 04H and B=02H then the execution of ADD B results in
A=06H
Similarly SUB means subtract the data in the designated
register from the accumulator.
SUB C will subtract the contents of the C register from the
accumulator.
1 byte instruction
Register Instruction
• INR and DCR
INR means increment the contents of the register
DCR means decrement the contents of the
register
If B=56H and C=8AH the execution of INR B results
in B= 57H
And the execution of a DCR C produces
C=89H
1 byte instruction
You might also like
- MICROPROCESSOR-Unit IIDocument38 pagesMICROPROCESSOR-Unit IIgiri dipeshNo ratings yet
- Basic SAP-1 Computer Architecture ExplainedDocument9 pagesBasic SAP-1 Computer Architecture ExplainedAshna100% (1)
- MCS-51 Instruction Set SummaryDocument50 pagesMCS-51 Instruction Set SummaryAli ShanNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 Comp OperationDocument32 pagesLecture2 Comp Operationimran_84No ratings yet
- Sap 2Document35 pagesSap 2Michael Vincent B. Nierva88% (8)
- Simple As Possible Computer (SAP-1) : Lecture-3Document44 pagesSimple As Possible Computer (SAP-1) : Lecture-3Tawhid KhondakarNo ratings yet
- Csa Mte2Document88 pagesCsa Mte2DEVCON EVENTNo ratings yet
- 8051 NotesDocument24 pages8051 Notessreedhar_vkNo ratings yet
- Embedded Microprocessor Lecture 2Document15 pagesEmbedded Microprocessor Lecture 2ojasbhosale07No ratings yet
- Sap 1Document15 pagesSap 1Nahin Amin100% (1)
- CoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design Hardware SummaryDocument164 pagesCoE3DJ4 Digital Systems Design Hardware SummaryhossamalsherbinyNo ratings yet
- Co&a Module 5 Part 1Document25 pagesCo&a Module 5 Part 1BOBAN05No ratings yet
- Micro ControllersDocument141 pagesMicro ControllersBiswajit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller SeriesDocument14 pagesMicrocontroller SeriesmasindedaddyNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Design SAP-1 ExplainedDocument33 pagesMicroprocessor Design SAP-1 Explainedvester sampanaNo ratings yet
- 8085 Processor Unit I: Mr. S. VinodDocument52 pages8085 Processor Unit I: Mr. S. VinodVinod SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 4 Bit Cpu ReportDocument16 pages4 Bit Cpu ReportHarshil LodhiNo ratings yet
- Coa HW2Document6 pagesCoa HW2Mohammed AyadNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Experiments List and Code for Finding Smallest NumberDocument21 pagesMicroprocessor Experiments List and Code for Finding Smallest NumbermajorjawarpartapNo ratings yet
- TMS320LF2407Document90 pagesTMS320LF2407Polumuri RamanaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Timing and Execution in 8085Document50 pagesInstruction Timing and Execution in 8085rahul agarwalNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor Architecture OverviewDocument39 pages8085 Microprocessor Architecture OverviewSana KhanNo ratings yet
- Coa Unit III FinalDocument136 pagesCoa Unit III FinalDewashish Shankar TaraleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Data ManipulationDocument42 pagesChapter 2 Data ManipulationRidoy zzamanNo ratings yet
- SAPDocument21 pagesSAPdanielcasayuranNo ratings yet
- SSSCDocument28 pagesSSSCMahesh KoliNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineering B.E III Year System Designing With MicrocontrollerDocument18 pagesBiomedical Engineering B.E III Year System Designing With MicrocontrollerREKHA SENCHA gs0801bm161043No ratings yet
- LECTURE2 - MiceroprocessorDocument18 pagesLECTURE2 - Miceroprocessor47b363575eNo ratings yet
- SAP-1 (Simple As Possible-1) Computer ArchitectureDocument8 pagesSAP-1 (Simple As Possible-1) Computer ArchitecturesaikotNo ratings yet
- MC 68hc11Document72 pagesMC 68hc11hulavanyaNo ratings yet
- Understanding the ARM Processor ArchitectureDocument54 pagesUnderstanding the ARM Processor ArchitectureRobin SinghNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Question BankDocument26 pagesMicrocontroller Question Bankraj_vis321No ratings yet
- 8051 Instruction Set GuideDocument19 pages8051 Instruction Set Guideharshad lokhandeNo ratings yet
- Pic16f FeaturesDocument40 pagesPic16f Featuresveeramaniks408No ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document49 pagesLecture 02Colesha BarukaNo ratings yet
- 8085 MICROPROCESSOR: BUS ORGANIZATION AND PIN FUNCTIONSDocument38 pages8085 MICROPROCESSOR: BUS ORGANIZATION AND PIN FUNCTIONSAkshit MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture: Chapter Two/ Microprocessor 8086 Lecture FourDocument23 pagesComputer Architecture: Chapter Two/ Microprocessor 8086 Lecture FourSorensenNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Microprocessor of 8085 - 2024Document77 pages1.introduction To Microprocessor of 8085 - 2024sanchita4586No ratings yet
- Introduction To 8085 MicroprocessorDocument37 pagesIntroduction To 8085 MicroprocessorAmit BeheraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 68HC11 MICROCONTROLLERDocument72 pagesIntroduction To 68HC11 MICROCONTROLLERNarasimha Murthy Yayavaram100% (3)
- Unit 4Document53 pagesUnit 4subithavNo ratings yet
- Imp 22Document31 pagesImp 22Panku RangareeNo ratings yet
- Co Unit2 Part1Document11 pagesCo Unit2 Part1Manjushree N.SNo ratings yet
- PIC 16f877a Memory OrganizationDocument33 pagesPIC 16f877a Memory OrganizationTarek BarhoumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Notes Computer OrganizationDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Notes Computer OrganizationsriNo ratings yet
- NEC 022 External Paper SolutionDocument13 pagesNEC 022 External Paper SolutionSachin PalNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Microoperations in RegistersDocument79 pages4 Types of Microoperations in RegistersSriram MurthyNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer OrganizationDocument23 pagesBasic Computer OrganizationKibrom HaftuNo ratings yet
- SAP Report Group 2Document14 pagesSAP Report Group 2Chanel Hooper0% (1)
- Simple As Possible ComputersDocument16 pagesSimple As Possible ComputersMd. Jahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller - PDF 1411210674Document27 pagesMicrocontroller - PDF 1411210674Anney RevathiNo ratings yet
- Computer Applications and ManagementDocument11 pagesComputer Applications and ManagementParag PaliwalNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocess or ArchitectureDocument39 pages8085 Microprocess or ArchitectureAbhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- MI Chapter 1Document29 pagesMI Chapter 1DANIEL ABERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2Sameer SharmaNo ratings yet
- Processor Organization: Module-3 Part-2Document88 pagesProcessor Organization: Module-3 Part-2Khushi MahawarNo ratings yet
- CPU Design Documentation SampleDocument27 pagesCPU Design Documentation SampleJoseph Kerby J. NavaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- FARMĀN: Royal Decrees in Persian HistoryDocument23 pagesFARMĀN: Royal Decrees in Persian HistoryMuhammadHaqueNo ratings yet
- Turkey's ConstitutionDocument92 pagesTurkey's ConstitutionMuhammadHaqueNo ratings yet
- The Consti Tuti ON Ofthe Republi C Ofkorea: PreambleDocument43 pagesThe Consti Tuti ON Ofthe Republi C Ofkorea: PreambleROK ChannelNo ratings yet
- Design of Single Stage Buck and Boost CoDocument6 pagesDesign of Single Stage Buck and Boost CoMuhammadHaqueNo ratings yet
- The Constitution of The United States - PDFDocument10 pagesThe Constitution of The United States - PDFMuhammadHaqueNo ratings yet
- The Constitution of The Russian FederationDocument30 pagesThe Constitution of The Russian Federationestafa_russoNo ratings yet
- Copyblogger Copywriting 101 2 PDFDocument91 pagesCopyblogger Copywriting 101 2 PDFamirNo ratings yet
- E Brand PrinciplesDocument6 pagesE Brand PrinciplesImran AlamNo ratings yet
- Constitution of NorwayDocument28 pagesConstitution of NorwayMuhammadHaqueNo ratings yet
- Python 3 Cheat Sheet v3Document13 pagesPython 3 Cheat Sheet v3Nilay Chauhan100% (3)
- Parents' Rights On ChildrenDocument2 pagesParents' Rights On ChildrenM HawkNo ratings yet
- My - Cb.magnetic Headlines 2 2Document56 pagesMy - Cb.magnetic Headlines 2 2Mohammed SaqlainNo ratings yet
- Parents' Rights On ChildrenDocument2 pagesParents' Rights On ChildrenM HawkNo ratings yet
- Addressing Modes of 8086: Navila Rahman NadiDocument19 pagesAddressing Modes of 8086: Navila Rahman NadiMuhammadHaqueNo ratings yet
- Peasant Revolt PDFDocument8 pagesPeasant Revolt PDFMuhammadHaqueNo ratings yet
- Lect 4 Boolean AlgebraDocument19 pagesLect 4 Boolean AlgebraMuhammadHaqueNo ratings yet
- ECR – 209: Understanding the Intel 8086 MicroprocessorDocument32 pagesECR – 209: Understanding the Intel 8086 MicroprocessorMuhammadHaqueNo ratings yet
- Manual Tooling CatalogDocument70 pagesManual Tooling CatalogGuillaume JaNo ratings yet
- RecurDyn For BeginnersDocument295 pagesRecurDyn For BeginnersautocratNo ratings yet
- Avery E-1310Document4 pagesAvery E-13106612poolNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Introduction To CommunicationDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 1 Introduction To CommunicationadibNo ratings yet
- CCA Script JhoDocument6 pagesCCA Script JhoJefferson GomezNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA and RACDocument13 pagesOracle DBA and RACSandhyaSeoNo ratings yet
- Oracle9i Client: Installation and Administration Guide Release 2 (9.2.0.4.0) For Stratus Contiuum 600 and 1200 SeriesDocument44 pagesOracle9i Client: Installation and Administration Guide Release 2 (9.2.0.4.0) For Stratus Contiuum 600 and 1200 SeriesMohan Kumar GNo ratings yet
- Syntec CNC Application Manual v10.0Document155 pagesSyntec CNC Application Manual v10.0Ga Bicho De SavorNo ratings yet
- General Description: Multiservice SwitchDocument66 pagesGeneral Description: Multiservice SwitchJatinder Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Hitachi EX200-1 Parts CatalogueDocument109 pagesHitachi EX200-1 Parts Cataloguemikkoms100% (2)
- VLSI Semi Custom Design Methodologies GuideDocument25 pagesVLSI Semi Custom Design Methodologies GuidePraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Xerox C35 Style Copier RepairsDocument12 pagesXerox C35 Style Copier RepairsSean Reilly0% (1)
- Pipelined Quadratic Function Core Computes y=ax^2+bx+cDocument2 pagesPipelined Quadratic Function Core Computes y=ax^2+bx+cDurga MiniNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Deh-2950mp 2990mp PDFDocument70 pagesPioneer Deh-2950mp 2990mp PDFAxl Mendoza100% (3)
- Acatistier Colectie de Acatiste Si Paraclise PDFDocument3 pagesAcatistier Colectie de Acatiste Si Paraclise PDFAlinutza Alina0% (4)
- Triac PDFDocument4 pagesTriac PDFgopu705204No ratings yet
- Man4359b Punch2ch ManDocument72 pagesMan4359b Punch2ch ManAntonio Perez PerezNo ratings yet
- Projec Report Guide Line To Prepare A Project Report and Format of ReportDocument12 pagesProjec Report Guide Line To Prepare A Project Report and Format of ReportManish BhartiNo ratings yet
- Telemedicine Through The Internet and IntranetDocument14 pagesTelemedicine Through The Internet and Intranetalexhuq2010100% (1)
- 50X01-LT - QT-Budgetary - 220308Document6 pages50X01-LT - QT-Budgetary - 220308Ricardo Jose Vazquez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Apw5u La-C401p (Rev 1.0) PDFDocument78 pagesApw5u La-C401p (Rev 1.0) PDFjuan jose BalderramaNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual EX-M02: Test Unit For Electronic ModulesDocument4 pagesInstallation Manual EX-M02: Test Unit For Electronic Modulesmehdi810No ratings yet
- Moglix Material PendencyyDocument12 pagesMoglix Material Pendencyylucky sharmaNo ratings yet
- Finished PosterDocument1 pageFinished Posterapi-396402491No ratings yet
- MDocument16 pagesMHugo LoureiroNo ratings yet
- Voltage Sag and Anti IslandingDocument10 pagesVoltage Sag and Anti IslandingDramebaaz SandeepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Stepper MOTOR PracticalDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Stepper MOTOR PracticalmfmprofNo ratings yet
- Jobber JR DetailsDocument2 pagesJobber JR DetailsUrvish PatelNo ratings yet
- Manual TI-500SLDocument22 pagesManual TI-500SLjuanjo100% (1)
- Electro PenDocument12 pagesElectro Pengivens201No ratings yet