Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHNG3805 HW9 3 PDF
Uploaded by
Nur AnissaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHNG3805 HW9 3 PDF
Uploaded by
Nur AnissaCopyright:
Available Formats
Homework 9
Q1 Non-Newtonian flow
(1) Rheological test on milk of magnesia provides the following data. Calculate the consistency
coefficient (K) and the flow index (m).
Shear rate, s-1 7.2 16 64 320 720
Shear stress, Pa 7.0 9.1 14.3 24.2 31.6
(2) This suspension is pumped 2.11 m down a pipe of radius 6.95 mm. Mean suspension density is
1300 kg/m3. Complete the tables below. (show you calculation step for one as example)
For Laminar flow:
Pressure drop, ∆P, kPa Flow rate, m3/s Velocity, m/s Re*
5
15
30
40
80
For Turbulent flow:
Velocity, m/s Re* f –1/2 (method 1) f –1/2 (method 2)
4.66
7.64
Method 1 uses the general formula for friction factor
Method 2 uses the correlation for power-law fluids
Q2 Minimum fluidising velocity
Based on lecture notes, please derive the formula for minimum-fluidising velocity (Umf) as a function
of g, ρs, ρ, μ, ε, and particle diameter x.
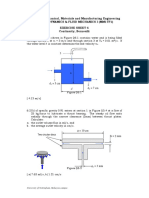
Q3 Fluidisation
A packed bed consisting of 1.96 kg of solids of density 2.8 g/cm3 is contained in a cylindrical vessel
of 10 cm internal diameter, and the bed height is 20 cm.
(1) What is the volume of the vessel occupied by the bed is (mL)?
(2) What is the volume of the solids in the vessel (mL)?
(3) What is the porosity of the bed?
(4) The particle size is 500 μm, and the liquid density and viscosity are 1000 kg/m3 and 0.001 Pa∙s,
what is the minimum fluidising velocity (m/s)?
(5) Was the use of the Kozeny-Carman equation justified?
(6) What type of fluidisation likely to occur?
You might also like
- Problems Collection-2018Document19 pagesProblems Collection-2018calvinNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Coulson Ingles Cap 5 y 6 PDFDocument20 pagesSolucionario Coulson Ingles Cap 5 y 6 PDFDARIONo ratings yet
- Momentum Transfer: Sison, Kelly Sheine O. 4Che-CDocument16 pagesMomentum Transfer: Sison, Kelly Sheine O. 4Che-CKelly SisonNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation HWDocument2 pagesSedimentation HWTariq DNo ratings yet
- Tutorial #5 On Centrifugal Settling and CyclonesDocument2 pagesTutorial #5 On Centrifugal Settling and CyclonesTinaNu67% (3)
- Che 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Document7 pagesChe 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Bao-Ngoc HoangNo ratings yet
- B48BB Tutorial Questions v3Document16 pagesB48BB Tutorial Questions v3aidaNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations Tutorial 2015-2016Document13 pagesUnit Operations Tutorial 2015-2016hazimraad0% (1)
- SatopDocument31 pagesSatopUcu KhoerunisaNo ratings yet
- Membrane Separation ProcessDocument30 pagesMembrane Separation ProcessPradeep Aneja50% (2)
- Isro Scientist Me 2020 Paper 80c39244Document20 pagesIsro Scientist Me 2020 Paper 80c39244Elsa PoirotNo ratings yet
- Question Papers 2011Document9 pagesQuestion Papers 2011Ebenaza GodsonNo ratings yet
- CE570 Final Exam Fall 2023Document4 pagesCE570 Final Exam Fall 2023farajelmabroukNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: University of Pune Polymer/Petroleum/Petrochemical) Momentum TransferDocument42 pagesInstructions:: University of Pune Polymer/Petroleum/Petrochemical) Momentum TransferEkugum Pascal ChinedumNo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet 6Document4 pagesExercise Sheet 6Gonçalo GuerreiroNo ratings yet
- Saet 1 BDocument9 pagesSaet 1 BnaefmubarakNo ratings yet
- CHE4162 Particle Technology November 2010 Exam SolutionsDocument14 pagesCHE4162 Particle Technology November 2010 Exam SolutionsPa1 Kumar MNo ratings yet
- 8-Sediment Transport Rate 1 PDFDocument18 pages8-Sediment Transport Rate 1 PDFMursaleenNo ratings yet
- In A Quality Control TestDocument5 pagesIn A Quality Control TestHarry Frianota IDNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1Marie Angeline BautistaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Question Bank @Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics Question Bank @AnujNo ratings yet
- Examples 6 - Continuity and BernoulliDocument4 pagesExamples 6 - Continuity and Bernoulli27061988No ratings yet
- PDFDocument2 pagesPDFSärîtå GôßwámîNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Corrected ExercisesDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics - Corrected Exercisesug2319311No ratings yet
- SNS College of Technology, Coimbatore-35Document4 pagesSNS College of Technology, Coimbatore-35Arul NNo ratings yet
- CHNG3805 HW7 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesCHNG3805 HW7 2020 PDFNur AnissaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesTutorial Questionsjohns ndegeNo ratings yet
- Secret FileDocument12 pagesSecret FileLucifer MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Further Problems On Fluid Dynamics (Reyonlds Number) : (1906 4000, Turbulent)Document2 pagesFurther Problems On Fluid Dynamics (Reyonlds Number) : (1906 4000, Turbulent)Cool DouglasNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Tutorial4 6Document4 pagesTutorial4 6Chinmay JoshiNo ratings yet
- Multiphase Flow - TutorialsDocument7 pagesMultiphase Flow - TutorialsOlusegun OyebanjiNo ratings yet
- Geo TechnicalDocument105 pagesGeo TechnicalSigue Ramel HinayasNo ratings yet
- 980806Solutons Manual (1 2章) 修正搞Document46 pages980806Solutons Manual (1 2章) 修正搞reidNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics ProblemsDocument16 pagesFluid Mechanics Problemsphhgphuc158No ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document6 pagesTutorial Chapter 1dhiauddinfarhiNo ratings yet
- WHITE - Buku TextDocument11 pagesWHITE - Buku TextNameis GhoffarNo ratings yet
- TD1 Plasturgie IDocument6 pagesTD1 Plasturgie Iismail mbarkiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1.docx (ME-102)Document13 pagesAssignment 1.docx (ME-102)umair rasheedNo ratings yet
- Presentation ProblemsDocument2 pagesPresentation ProblemsARFarryNo ratings yet
- DR M Aziz - Pty261s - Tutorial 7 - 2022Document1 pageDR M Aziz - Pty261s - Tutorial 7 - 2022hanzthehomeyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Ash DisposalDocument26 pagesHydraulic Ash Disposalami miaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Sample QuestionsDocument4 pagesFluid Sample Questionstfkthe46No ratings yet
- Tutorial On Flowmeters Nov17Document2 pagesTutorial On Flowmeters Nov17Ranjan Kumar100% (1)
- 2020 Exercises For Membrane TechnologyDocument2 pages2020 Exercises For Membrane Technologyanitha100% (1)
- Topic 2 - A: F M M Multiphase Flow Tutorial QuestionsDocument7 pagesTopic 2 - A: F M M Multiphase Flow Tutorial QuestionsAnjo VasquezNo ratings yet
- Thermo 1 Quality Work No.1Document16 pagesThermo 1 Quality Work No.1Mico AndresNo ratings yet
- ChE Boards Common ProblemsDocument25 pagesChE Boards Common ProblemsJan Abanes-DatingNo ratings yet
- Koiranen Paper - PDDocument6 pagesKoiranen Paper - PDBashar Al ZoobaidiNo ratings yet
- Rr410801 Transport PhenomenaDocument8 pagesRr410801 Transport PhenomenaSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Examples (Sediment Transport) AUTUMN 2018Document6 pagesExamples (Sediment Transport) AUTUMN 2018orlaandoNo ratings yet
- FM-Assignment 1680339329419Document4 pagesFM-Assignment 1680339329419Hasan javedNo ratings yet
- Novel Separation ProcessesDocument1 pageNovel Separation Processesgundogan21No ratings yet
- FM Question BankDocument5 pagesFM Question BankManoj MuNo ratings yet
- Presentation ProblemsDocument4 pagesPresentation ProblemspangiastikaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CHNG3805 HW3 2 PDFDocument1 pageCHNG3805 HW3 2 PDFNur AnissaNo ratings yet
- CHNG3805 HW7 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesCHNG3805 HW7 2020 PDFNur AnissaNo ratings yet
- Picon Nunez Et Al 2009 PDFDocument8 pagesPicon Nunez Et Al 2009 PDFNur AnissaNo ratings yet
- Lab Air 06032019Document10 pagesLab Air 06032019Nur AnissaNo ratings yet