Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Air Conditioning Formulas PDF
Uploaded by
towiwaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Air Conditioning Formulas PDF
Uploaded by
towiwaCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Air Conditioning
Figure 5
Formulas
Basic Air Conditioning Formulas
Application
EXPRESSED
TO DETERMINE AS COOLING HEATING and/or HUMIDIFYING
NT V NT V
Guide
Total Airflow CFMT 1. CFMT = 1. CFMT =
60 min./hr. 60 min./hr.
NO V No V
Infiltration or Ventilation CFMo 2. CFMo = 2. CFMo =
60 min./hr. 60 min./hr.
Number of Air Changes CFMT (60 min./hr.) CFMT (60 min./hr.)
NT 3. NT = 3. NT =
Per Hour – Total V V
Number of Air Changes CFMo (60 min./hr.) CFMo (60 min./hr.)
Per Hour – Outdoor Air No 4. No = 4. No =
V V
Total Heat (HT) Btuh 5. HT = CFMT x 4.5 x (h1 – h2) = Btuh 6. HT = CFMT x 4.5 x (h2 – h1) = Btuh
Sensible Heat (HS) Btuh 7. HS = CFMT x 1.08 x (T1 – T2) = Btuh 8. HS = CFMT x 1.08 x (T2 – T1) = Btuh
Latent Heat (HL) Btuh 9. HL = CFMT x .68 x (W1 – W2) = Btuh 10. HL = CFMT x .68 x (W2 – W1) = Btuh
CFMo CFMo
Entering Air Temperature (T1) °F. D.B. 11. T1 = t1 + x (t2 – t1) = °F.D.B. 1 12. T1 = t1 – x (t1 – t2) = °F.D.B. 2
CFMT CFMT
(Mixed Air)
1 If duct heat gain is a factor, add to T1: 2 If duct heat loss is a factor, subtract from T1:
Duct Heat Gain (Btuh) Duct Heat Loss (Btuh)
CFMT x 1.08 CFMT x 1.08
Leaving Air D.B. HS HS
°F. D.B. 13. T2 = T1 – = °F.D.B. 14. T2 = T1 + = °F.D.B.
Temperature (T2) CFMT x 1.08 CFMT x 1.08
HS (total) HS
Required Airflow CFMT 15. CFMT = = CFM 16. CFMT = = CFM
1.08 x (T1 – T2) 1.08 x (T2 – T1)
OR
HS (internal)3
CFMT = = CFM
1.08 x (t1 – T2)
3 Sensible load of outside air not included
Btu/lb. HT HT
Enthalpy – Leaving Air (h2) 17. h2 = h1 – = Btu/lb. dry air 18. h2 = h1 + = Btu/lb. dry air
dry air CFMT x 4.5 CFMT x 4.5
19. Refer to Enthalpy Table and read W.B. temperature 20. Refer to Enthalpy Table and read W.B. temperature
Leaving Air W.B. Temperature °F.W.B.
corresponding to enthalpy of leaving air (h2) (see #17). corresponding to enthalpy of leaving air (h2) (see #18).
Heat Required to Evaporate
Water Vapor Added to Btuh 21. HL = CFMo x .68 (W3 – Wo) = Btuh 22. HL = CFMo x .68 (W3 – Wo) = Btuh
Ventilation Air
Excess Latent Capacity
( ) ( )
Lbs. Make up = of System x % Run Time HL loss Btuh (see #22)
Humidification Requirements 23. = lbs./hr. 24. Make up = = lbs./hr.
water/hr. Moisture 1060 Btu/lb. Moisture 1060 Btu/lb.
(Industrial Process Work)
LEGEND DERIVATION OF AIR CONSTANTS
CFMT = Total airflow cubic feet/min. The air constants below apply specifically to standard air which is
CFMo = Outdoor air cubic feet/min. defined as dry air at 70°F and 14.7 P.S.I.A. (29.92 in. mercury column).
NT = Total air changes per hour They can, however, be used in most cooling calculations unless extremely
No = Outdoor air, air changes per hour precise results are desired.
V = Volume of space cubic feet 4.5 (To convert CFM to lbs./hr.)
HT = Total heat Btuh
HS = Sensible heat Btuh 60 min./hr.
4.5 = or 60 X .075
HL = Latent heat Btuh 13.33
* h1 = Enthalpy or total heat of entering air Btu/lb. Where 13.33 is the specific volume of standard air (cu.ft./lb.) and
* h2 = Enthalpy or total heat of leaving air Btu/lb. .075 is the density (lbs./cu.ft.)
T1 = Temperature of entering air .24 X 60
T2 = Temperature of leaving air 1.08 = or .24 X 4.5
13.33
Tadp = Apparatus dewpoint °F.D.B.
.24 BTU = specific heat of standard air (BTU/LB/°F)
t1 = Indoor design temperature °F.D.B.
t2 = Outdoor design temperature °F.D.B. 60 1060 1060
.68 = X or 4.5 X
W1 = Grains of water/lb. of dry air at entering condition Grains/lb. 13.33 7000 7000
W2 = Grains of water/lb. of dry air at leaving condition Grains/lb.
Where: 1060 = Average Latent Heat of water vapor (BTU/LB.).
W3 = Grains of water/lb. of dry air at indoor design conditions Grains/lb.
Wo = Grains of water/lb. of dry air at outdoor design conditions Grains/lb. 7000 = Grains per lb.
* See Enthalpy of air (Total Heat Content of Air) Table for exact values.
For complete equipment / combination selections,
installation instructions and warranty information,
please refer to Product Data/Ratings and/or Installers Effective 4/4/11
Guides and Limited Warranty Handbooks. AC/IN-13 14-1011-26
You might also like
- Hvac Formulas PDFDocument25 pagesHvac Formulas PDFSaraswatapalit0% (1)
- Equations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbDocument21 pagesEquations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbzodedNo ratings yet
- CFM and Capacity Calcs 4.5Document9 pagesCFM and Capacity Calcs 4.5hvacrmedicNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry Part-2Document11 pagesPsychrometry Part-2Tushar Sharma100% (1)
- One Btu Equals 1.055 KJ.: Joule (J)Document3 pagesOne Btu Equals 1.055 KJ.: Joule (J)suboo0678No ratings yet
- 1-Internal Heat GainDocument15 pages1-Internal Heat GainWunNa100% (1)
- Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipDocument2 pagesBasic HVAC Formulas - Tech Tipgauravgujar24100% (1)
- Humidification Load Calculator GuideDocument22 pagesHumidification Load Calculator GuideAnvar Pa100% (1)
- HVAC Thermal Load EstimatingDocument28 pagesHVAC Thermal Load EstimatingIntisar Ali SajjadNo ratings yet
- Experimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %Document31 pagesExperimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %JayZx WayNo ratings yet
- RAC 32 Important QuestionDocument10 pagesRAC 32 Important QuestionBalvinderNo ratings yet
- شرح مروحة الدخانDocument6 pagesشرح مروحة الدخانZiyad AwaliNo ratings yet
- #HVAC - Five Easy Steps To Estimate External Static Pressure Drop in HVAC Ducts Using Equal Friction MethodDocument5 pages#HVAC - Five Easy Steps To Estimate External Static Pressure Drop in HVAC Ducts Using Equal Friction MethodAbdulHakeemSKNo ratings yet
- Psych Rome TricsDocument46 pagesPsych Rome TricsDenitta D'RoseNo ratings yet
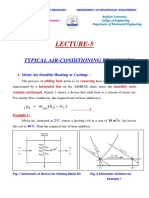
- Lecture-5: Typical Air-Conditioning ProcessesDocument10 pagesLecture-5: Typical Air-Conditioning Processesabrar alhadadNo ratings yet
- Heatload Calculation 2Document44 pagesHeatload Calculation 2Mustansir Pancha50% (2)
- HAP Thermal Load Cal - FormulaDocument19 pagesHAP Thermal Load Cal - Formulamajortay100% (1)
- Cooling Load EstimationDocument4 pagesCooling Load Estimationk.vikasNo ratings yet
- Design Example - WorkshopDocument4 pagesDesign Example - WorkshoplaichmailNo ratings yet
- Psychrometrics ProblemDocument7 pagesPsychrometrics ProblemPraveenkumar KashyabNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric ChartDocument7 pagesPsychrometric ChartSyarifah Humaira Al'mudhirNo ratings yet
- Calculating Cooling LoadsDocument2 pagesCalculating Cooling LoadsHerman SubagioNo ratings yet
- Heat Gain CalculationsDocument17 pagesHeat Gain CalculationsPrabu RajaNo ratings yet
- Chiller Plant Calculation & Raw Data RequiredDocument1 pageChiller Plant Calculation & Raw Data RequiredBudi IswahyudiNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric ProcessesDocument14 pagesPsychrometric ProcessesKabin BoraNo ratings yet
- HVAC Monthly Schedule - 2013Document6 pagesHVAC Monthly Schedule - 2013MuhammadIqbalMughalNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas and ValuesDocument13 pagesHvac Formulas and ValuesRamadan RashadNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Charge CalculatorDocument1 pageRefrigerant Charge CalculatorBala Krishna GallaNo ratings yet
- Fgas Refrigerant CalculatorDocument12 pagesFgas Refrigerant CalculatorKhadija MirajNo ratings yet
- HVAC FormulasDocument7 pagesHVAC Formulasisaiaspaula80No ratings yet
- HVAC ConstantsDocument6 pagesHVAC ConstantsWilliam Greco100% (8)
- Humidification Load Calculation Armstrong PDFDocument3 pagesHumidification Load Calculation Armstrong PDFsyedNo ratings yet
- Sample Calculations of Boiler Pumps and IDDocument5 pagesSample Calculations of Boiler Pumps and IDMasih BelajarNo ratings yet
- Heat LoadDocument53 pagesHeat Loadabdul azizNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Design - Psychrometrics & Coil Load CalculationDocument13 pagesAir Conditioning Design - Psychrometrics & Coil Load Calculationvsajv83% (6)
- Cooling Load CalculationDocument33 pagesCooling Load CalculationJodin Alido Mahinay100% (1)
- Calculation Sheet Document No. Page No. Revision No. Date Prepared by Approved by Plant PlaceDocument22 pagesCalculation Sheet Document No. Page No. Revision No. Date Prepared by Approved by Plant PlaceSwapnil Pratap Singh100% (1)
- Exhaust Air Heat - Recovery SystemsDocument4 pagesExhaust Air Heat - Recovery SystemsBiya ZainNo ratings yet
- Example 6 - Cal Supply Air Quantity FCUDocument11 pagesExample 6 - Cal Supply Air Quantity FCUHo Dac ThanhNo ratings yet
- Chillers TraneDocument52 pagesChillers TranesnakelostNo ratings yet
- 4 ACMV SystemsDocument293 pages4 ACMV SystemsMorgan HengNo ratings yet
- Jet Fan CatalogueDocument10 pagesJet Fan Catalogueabc3579No ratings yet
- HVAC System Load CalculationDocument7 pagesHVAC System Load CalculationMohammed MujahedNo ratings yet
- Precooled Ahu CalculationDocument3 pagesPrecooled Ahu CalculationEdmund YoongNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Calculation For Inverter RoomDocument1 pageVentilation Calculation For Inverter RoomHoney TiwariNo ratings yet
- Air-Conditioning Load EstimationDocument23 pagesAir-Conditioning Load Estimationtkm2004No ratings yet
- Heat Load Estimation MS1525 DesignDocument10 pagesHeat Load Estimation MS1525 Designhans weemaesNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load1111 PDFDocument43 pagesCooling Load1111 PDFJason PaquibulanNo ratings yet
- Duct DesignDocument35 pagesDuct DesignAnonymous 8LOtly9100% (5)
- Psychrometry For Air ConditioningDocument59 pagesPsychrometry For Air ConditioningPraveenkumar KashyabNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry. Heat Recovery Air Handling Unit (Ahu) - by Ömer Faruk DDocument13 pagesPsychrometry. Heat Recovery Air Handling Unit (Ahu) - by Ömer Faruk DKarl WeierstrassNo ratings yet
- DEWALT HVACR Professional Reference Master EditionDocument24 pagesDEWALT HVACR Professional Reference Master EditionLorenc Hysa100% (1)
- Latent HeatDocument2 pagesLatent HeatrohitNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument1 pageFormulasYoesof HilabyNo ratings yet
- Equations, Data and Rules ThumbDocument3 pagesEquations, Data and Rules Thumbsripriya01No ratings yet
- HVAC Supply Airflow Calculation SampleDocument7 pagesHVAC Supply Airflow Calculation Sampletankimsin100% (4)
- Azucar HojaDocument9 pagesAzucar HojaJorge PerezNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredDocument5 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredkarthickNo ratings yet
- AirFlowFormulas PDFDocument4 pagesAirFlowFormulas PDFGurunathan AmmasaiNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger - ChE GuideDocument5 pagesAir Cooled Heat Exchanger - ChE GuideAnonymous KpVxNXsNo ratings yet
- Problems On SFD & BMDDocument43 pagesProblems On SFD & BMDmal201182% (11)
- Tech. Spec. For VesselsDocument6 pagesTech. Spec. For Vesselssanjay421No ratings yet
- Piping ComponentsDocument39 pagesPiping Componentsbvenky991100% (1)
- List Mep Contractors Company Dubai6 PDFDocument10 pagesList Mep Contractors Company Dubai6 PDFsojuiype50% (8)
- Data Bank Consult LoadingDocument151 pagesData Bank Consult Loadingravirawat15No ratings yet
- Ibr FormsDocument117 pagesIbr Formsshivabtowin3301No ratings yet
- Jigs and Fixtures: A Basic LookDocument16 pagesJigs and Fixtures: A Basic Lookravirawat15No ratings yet
- Caesar II TrainingDocument61 pagesCaesar II TrainingReaderRRGHT86% (7)
- UsfdaDocument10 pagesUsfdaravirawat15No ratings yet
- IBRDocument37 pagesIBRravirawat15No ratings yet
- Team BMM Presents! Greetings SMS!Document6 pagesTeam BMM Presents! Greetings SMS!ravirawat15No ratings yet
- Piping Material SpecificationDocument36 pagesPiping Material Specificationravirawat15100% (2)
- MC-8002 Mixer 2Document1 pageMC-8002 Mixer 2JAIDEV KUMAR RANINo ratings yet
- Salon Building Guidelines PDFDocument8 pagesSalon Building Guidelines PDFtsnie toNo ratings yet
- Copper For BusbarDocument60 pagesCopper For BusbarSunil Gadekar100% (3)
- POLAR BEARS-Biology ProjectDocument16 pagesPOLAR BEARS-Biology Projectserwaa21No ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 1Document48 pages08 - Chapter 1danfm97No ratings yet
- AQAR-Report 2018-19 Tilak VidyapeethDocument120 pagesAQAR-Report 2018-19 Tilak VidyapeethAcross BordersNo ratings yet
- 2400 8560 PR 8010 - A1 HSE Management PlanDocument34 pages2400 8560 PR 8010 - A1 HSE Management PlanMohd Musa HashimNo ratings yet
- Infoblatt Skischulen Trends Port eDocument18 pagesInfoblatt Skischulen Trends Port eAustrian National Tourism BoardNo ratings yet
- Good Data Won't Guarantee Good DecisionsDocument3 pagesGood Data Won't Guarantee Good DecisionsAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Price List Printer HP Per November 2017Document14 pagesPrice List Printer HP Per November 2017anthony_prawiraNo ratings yet
- Sequence Analytical and Vector Geometry at Teaching of Solid Geometry at Secondary SchoolDocument10 pagesSequence Analytical and Vector Geometry at Teaching of Solid Geometry at Secondary SchoolJuan S. PalmaNo ratings yet
- Inner DriveDocument51 pagesInner DriveShaurya VajhulaNo ratings yet
- Rawtani 2019Document9 pagesRawtani 2019CutPutriAuliaNo ratings yet
- Practical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Test BankDocument27 pagesPractical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Test Bankdavidhallwopkseimgc100% (28)
- Water Quality MonitoringDocument3 pagesWater Quality MonitoringJoa YupNo ratings yet
- Symbolic Interaction Theory: Nilgun Aksan, Buket Kısac, Mufit Aydın, Sumeyra DemirbukenDocument3 pagesSymbolic Interaction Theory: Nilgun Aksan, Buket Kısac, Mufit Aydın, Sumeyra DemirbukenIgor Dutra BaptistaNo ratings yet
- FORM 2 Enrolment Form CTU SF 2 v.4 1Document1 pageFORM 2 Enrolment Form CTU SF 2 v.4 1Ivy Mie HerdaNo ratings yet
- New Admission Form Short CourseDocument4 pagesNew Admission Form Short CourseSyed badshahNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Dada and SurrealismDocument5 pagesDifference Between Dada and SurrealismPro FukaiNo ratings yet
- PWC - Digital Pocket Tax Book 2023 - SlovakiaDocument52 pagesPWC - Digital Pocket Tax Book 2023 - SlovakiaRoman SlovinecNo ratings yet
- A A ADocument5 pagesA A ASalvador__DaliNo ratings yet
- Foreign Affairs May June 2021 IssueDocument216 pagesForeign Affairs May June 2021 IssueSohail BhattiNo ratings yet
- File Server Resource ManagerDocument9 pagesFile Server Resource ManagerBùi Đình NhuNo ratings yet
- Rubber Stamp BusinessDocument4 pagesRubber Stamp BusinessvasantsunerkarNo ratings yet
- VukcevicEtAl GhostFluidMethodInPolyhedralFV AnnotatedDocument19 pagesVukcevicEtAl GhostFluidMethodInPolyhedralFV AnnotatedputhenkulamNo ratings yet
- Removal of Chloride in The Kraft Chemical Recovery CycleDocument8 pagesRemoval of Chloride in The Kraft Chemical Recovery CycleVeldaa AmiraaNo ratings yet
- 33kV BS7835 LSZH 3core Armoured Power CableDocument2 pages33kV BS7835 LSZH 3core Armoured Power Cablelafarge lafargeNo ratings yet
- Rights of An Accused Under Custodial InvestigationDocument17 pagesRights of An Accused Under Custodial Investigationadrianfrancis9100% (1)
- Accuracy of Transferring Analog Dental Casts To A Virtual ArticulatorDocument9 pagesAccuracy of Transferring Analog Dental Casts To A Virtual ArticulatorNetra TaleleNo ratings yet
- I. Errors, Mistakes, Accuracy and Precision of Data Surveyed. A. ErrorsDocument53 pagesI. Errors, Mistakes, Accuracy and Precision of Data Surveyed. A. ErrorsJETT WAPNo ratings yet