Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Latent Heat
Uploaded by
rohitOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Latent Heat
Uploaded by
rohitCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat Flow 21
Latent Heat
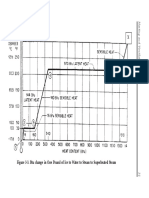
The definition of latent or hidden heat is: heat that is known
to be added to or removed from a substance but no temperature
change is recorded.” The heat released by boiling water is an
example of latent heat. Once water is brought to the boiling point,
adding more heat only makes it boil faster; it does not raise the
temperature of the water. The level of latent heat is measured in
degrees Fahrenheit (°F) and it is indicated as dew point (dp) tem-
perature (for example, 60°Fdp). Enthalpy is in Btu/lb°F. People,
water equipment, and outdoor air are examples of substances that
give off latent heat. A seated person in an office gives off approxi-
mately 225 Btuh of latent heat into the conditioned space.
Total Heat
Total heat is the sum of sensible heat and latent heat. It is
measured in degrees Fahrenheit (°F) and it is indicated as wet
bulb (wb) temperature. For example, 54°Fwb. Total heat level is
measured with an ordinary thermometer; however, the thermom-
eter tip is covered with a sock made from a water-absorbing
material. The sock is wetted with distilled water and the ther-
mometer is placed in the air stream in the air handling unit or
duct. As air moves across the wet sock, some of the water is
evaporated. Evaporation cools the remaining water in the sock
and cools the thermometer. The decrease in the temperature of the
wet bulb thermometer is called “wet bulb depression.” For room
wet bulb temperature the wet bulb thermometer is typically in an
instrument such as a sling- or power-psychrometer along with a
dry bulb thermometer. Enthalpy is in Btu/lb°F. A seated person
gives off approximately 450 Btuh of total heat (225 Btuh sensible
heat plus 225 Btuh latent heat).
HEAT TRANSFER EQUATIONS
AIR SYSTEMS - SENSIBLE HEAT TRANSFER EQUATION
Btuh = cfm × 1.08 × TD
22 HVAC Fundamentals
Where:
Btuh = Btu per hour (sensible heat) also written Btuhs
cfm = volume of airflow, cubic feet per minute
1.08 = constant:
60 min/hr × 0.075 lb/cf (density of air) × 0.24 Btu/lb°F (spe-
cific heat of air)
TD = dry bulb temperature difference of the air entering and
leaving a coil EAT – LAT or LAT – EAT (Entering Air Temperature
and Leaving Air Temperature). TD (temperature difference) is of-
ten written as delta T or ∆T. In applications where cfm to the con-
ditioned space needs to be calculated, the TD is the difference
between the supply air temperature dry bulb and the room tem-
perature dry bulb.
To find volume: cfm = Btuh ÷ (1.08 × TD)
To find temperature difference: TD = Btuh ÷ (1.08 × cfm)
AIR SYSTEMS - TOTAL HEAT TRANSFER EQUATION
Btuh = cfm × 4.5 × ∆h
Where:
Btuh = Btu per hour (total heat) also written Btuht
cfm = volume of airflow, cubic feet per minute
4.5 = constant: 60 min/hr × 0.075 lb/cf
∆h = Btu/lb change in total heat content (enthalpy) of the air
The total heat content of the air is determined from a wet
bulb and dry bulb temperature, and a psychrometric chart. For
example, the air temperature leaving a typical commercial cooling
coil might be 55°Fdb and 54°Fwb. Plotting these temperatures on
a psychrometric chart gives an enthalpy (total heat content) of the
air at 22.627 Btu/lb.
To find volume: cfm = Btuh ÷ (4.5 × ∆h)
To find enthalpy difference: ∆h = Btuh ÷ (4.5 × cfm)
You might also like
- Understanding Memory Loss and Saying GoodbyeDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Memory Loss and Saying GoodbyeStoenica ElenaNo ratings yet
- Evaporative Cooling Technical Handbook - MuntersDocument20 pagesEvaporative Cooling Technical Handbook - MuntersradiopascalgeNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Principles and ConceptsDocument64 pagesAir Conditioning Principles and ConceptsILYAS AHMED100% (1)
- Samuel C. Sugarman - HVAC Fundamentals-Fairmont Press - Distributed by Marcell Dekker - CRC Press (2005) - 3Document2 pagesSamuel C. Sugarman - HVAC Fundamentals-Fairmont Press - Distributed by Marcell Dekker - CRC Press (2005) - 3rohitNo ratings yet
- CHE 436 MODULE 6 - Psychrometry (Humidification, Dehumidification, Cooling TowDocument48 pagesCHE 436 MODULE 6 - Psychrometry (Humidification, Dehumidification, Cooling TowEirell SandersNo ratings yet
- HVAC Glossary of TermsDocument2 pagesHVAC Glossary of TermsCamilo Enrique Monroy CardenasNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric ProcessDocument24 pagesPsychrometric ProcessmechgokulNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 51Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 51rohitNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument19 pagesAir ConditioningNurul AkmamNo ratings yet
- Mass and Energy Balance of Cooling TowerDocument4 pagesMass and Energy Balance of Cooling TowerJohn Lenin100% (1)
- Chap # 07 Psychrometry-03Document18 pagesChap # 07 Psychrometry-03Aleena Amin KhuwajaNo ratings yet
- HVAC Cooling Load CalculationDocument98 pagesHVAC Cooling Load CalculationVishnupriya B.100% (1)
- HVAC Cooling Load CalculationDocument98 pagesHVAC Cooling Load CalculationVishnupriya B.100% (3)
- Psychrometric Processes of Air ConditioningDocument37 pagesPsychrometric Processes of Air ConditioningEphraim MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument72 pagesAir ConditioningNIKNo ratings yet
- Gas - Vapor Mixtures & Air - ConditioningDocument27 pagesGas - Vapor Mixtures & Air - ConditioningElena Romero ArandaNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Chart CalculationsDocument1 pagePsychrometric Chart CalculationsMc Jason LaureteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Psychrometric ChartDocument41 pagesChapter 2 Psychrometric ChartMuhammad Abdullah93% (14)
- BS-3 Unit 1Document116 pagesBS-3 Unit 1Pavithra SivasankaranNo ratings yet
- Lecture No.1 Part 2 (Psychrometerc)Document3 pagesLecture No.1 Part 2 (Psychrometerc)Mohsen HassanNo ratings yet
- The Theory and Operation of Evaporative CoolersDocument9 pagesThe Theory and Operation of Evaporative CoolersMichael ZhangNo ratings yet
- Marley Perfomance Cooling Tower CTII-01ADocument4 pagesMarley Perfomance Cooling Tower CTII-01ApiolinwallsNo ratings yet
- PSYCHROMETRIC GraphDocument31 pagesPSYCHROMETRIC GraphEnemona ShellengNo ratings yet
- Dew-Point Temperature and Air Conditioning ProcessesDocument18 pagesDew-Point Temperature and Air Conditioning ProcessesShariq SalahudeenNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Processes GuideDocument5 pagesPsychrometric Processes GuidetubelineNo ratings yet
- Pysch Rome TryDocument65 pagesPysch Rome Tryvinayaka93No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning-Principles and ConceptsDocument64 pagesAir Conditioning-Principles and ConceptsAbhishek Venkitaraman Iyer98% (40)
- PsychrometricesDocument9 pagesPsychrometriceskawsar_002No ratings yet
- AHU CalculationsDocument2 pagesAHU CalculationsTusshar KNo ratings yet
- AIR HANDLING SYSTEM: PSYCHROMETRICS AND PROCESSESDocument58 pagesAIR HANDLING SYSTEM: PSYCHROMETRICS AND PROCESSESAndy MakNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of Moist AirDocument7 pagesEnthalpy of Moist AirRahul PatelNo ratings yet
- FME Notes Unit3Document7 pagesFME Notes Unit3vishal shuklaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Cooling ExplainedDocument25 pagesRefrigeration and Cooling ExplainedGeorge MarkasNo ratings yet
- HVAC Cooling WaterDocument54 pagesHVAC Cooling WaterShiyamraj Thamodharan100% (1)
- Lecture 2 HvacDocument38 pagesLecture 2 HvacJohn BennettNo ratings yet
- Basics of Steam System DesignDocument5 pagesBasics of Steam System Designarun89000100% (1)
- Steam TheoryDocument44 pagesSteam TheoryProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Evaporative CoolerDocument12 pagesProject Report On Evaporative Coolersourabh singh tomerNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Chart Analysis and Cooling Coil CalculationsDocument6 pagesPsychrometric Chart Analysis and Cooling Coil CalculationsMohsen HassanNo ratings yet
- Antoine'sDocument3 pagesAntoine'sGarcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric ReviewDocument27 pagesPsychrometric ReviewfarinNo ratings yet
- WBTDocument5 pagesWBTnagsraviNo ratings yet
- ءاوهلا فييكت تاموُظنم Air-Conditioning Systems - Mee51413 سماخلا فصلاDocument25 pagesءاوهلا فييكت تاموُظنم Air-Conditioning Systems - Mee51413 سماخلا فصلاali awadNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Refrigeration Reviewer Chapter 1Document65 pagesMechanical Engineering Refrigeration Reviewer Chapter 1Marcial Jr. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Basic Air Conditioning FormulasDocument1 pageBasic Air Conditioning Formulasravirawat15100% (3)
- Navigating the Psychrometric ChartDocument11 pagesNavigating the Psychrometric ChartmohdkamalhaziqNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Properties and ProcessesDocument11 pagesPsychrometric Properties and ProcessesKarthik HarithNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning FundamentalsDocument69 pagesAir Conditioning FundamentalsPaul KwongNo ratings yet
- Experimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %Document31 pagesExperimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %JayZx WayNo ratings yet
- Cooling and Dehumidifying AirDocument5 pagesCooling and Dehumidifying AirFaquruddin AliNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument37 pagesAir Conditioningfirst lastNo ratings yet
- Slide Metoda EORDocument60 pagesSlide Metoda EORMaysithah ZahraNo ratings yet
- 1 - AC Lecture NoteDocument32 pages1 - AC Lecture Notefutsy dailyNo ratings yet
- Thermo L10Document26 pagesThermo L10Pronto P ChirinkaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- The Home Owner's Guide to HVAC: The Envelope and Green TechnologiesFrom EverandThe Home Owner's Guide to HVAC: The Envelope and Green TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 33Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 33rohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamDocument2 pagesFigure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 25Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 25rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 57Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 57rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 27Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 27rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
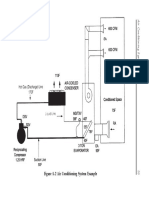
- Figure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExampleDocument2 pagesFigure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExamplerohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 35Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 35rohitNo ratings yet
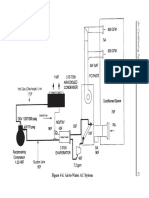
- Figure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesFigure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 1Document2 pagesHVAC Systems 1rohitNo ratings yet
- Btuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23Document2 pagesBtuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)rohitNo ratings yet
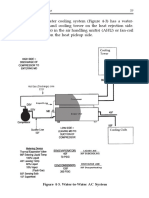
- Air Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 55Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 55rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerrohitNo ratings yet
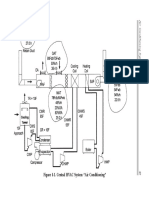
- Figure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"Document2 pagesFigure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 47Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 47rohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×rohitNo ratings yet
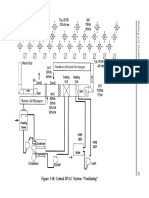
- Figure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"Document2 pagesFigure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"rohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 19Document2 pagesHeat Flow 19rohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 13: VentilatingDocument2 pagesHVAC Systems 13: VentilatingrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 17: ConductionDocument2 pagesHeat Flow 17: ConductionrohitNo ratings yet
- Samuel C. Sugarman - HVAC Fundamentals-Fairmont Press - Distributed by Marcell Dekker - CRC Press (2005) - 4Document2 pagesSamuel C. Sugarman - HVAC Fundamentals-Fairmont Press - Distributed by Marcell Dekker - CRC Press (2005) - 4rohitNo ratings yet
- New PPL Bifa ProflightDocument512 pagesNew PPL Bifa ProflightThomas AmisimNo ratings yet
- Numerical Data AnalysisDocument71 pagesNumerical Data AnalysisDedhia Vatsal hiteshNo ratings yet
- Kresley Cole - The Dark CallingDocument308 pagesKresley Cole - The Dark CallingFattyNo ratings yet
- IJOSBIE Template and GuidelinesDocument6 pagesIJOSBIE Template and Guidelinesekky firmansyahNo ratings yet
- Skill3: Unstated Detail QuestionsDocument15 pagesSkill3: Unstated Detail QuestionsHan Hye MinNo ratings yet
- Assignment HisDocument6 pagesAssignment Hisshajid chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- MHE RDG Wonders LVRDR G3 ELL U3W5 15Document24 pagesMHE RDG Wonders LVRDR G3 ELL U3W5 15Kenneth N AngelineNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument13 pagesProbabilityJoseph Christopher ButaslacNo ratings yet
- Answers To Think TanksDocument1 pageAnswers To Think TanksRonalie Dava100% (1)
- Phosphorus CycleDocument6 pagesPhosphorus CycleMarlyn P LavadorNo ratings yet
- The DivinersDocument109 pagesThe DivinersBrayden JakeNo ratings yet
- Hazard Assessment Results - Banlag FMRDocument5 pagesHazard Assessment Results - Banlag FMRArnel Bautista ArregladoNo ratings yet
- Language Worksheets: Unit 1 AnswersDocument17 pagesLanguage Worksheets: Unit 1 Answerseddie zhouNo ratings yet
- Geography Grade 6 November 2023 Memo 17 10 2023Document6 pagesGeography Grade 6 November 2023 Memo 17 10 2023Kalungi creatos37No ratings yet
- Kindergarten Unit - 201309251141177040Document3 pagesKindergarten Unit - 201309251141177040donkorernest300No ratings yet
- Part I. Phonetics: Unit 9 - Preserving Environment Worksheet No. 3Document6 pagesPart I. Phonetics: Unit 9 - Preserving Environment Worksheet No. 3Thien Duc VanNo ratings yet
- Thực hành kỹ năng đọcDocument5 pagesThực hành kỹ năng đọcTiên MỹNo ratings yet
- Quantifying The Seasonal Cooling Capacity of Green Infrastr 2020 LandscapeDocument21 pagesQuantifying The Seasonal Cooling Capacity of Green Infrastr 2020 Landscape熙槃No ratings yet
- TU6 Diagnostic TestDocument2 pagesTU6 Diagnostic TestMANYI ARBOLEDA SOLORZANONo ratings yet
- 3.1 Hazards and Hazard Type What Is A Hazard?Document2 pages3.1 Hazards and Hazard Type What Is A Hazard?YURI ISHIDANo ratings yet
- Jeff Long - Angels of LightDocument216 pagesJeff Long - Angels of LightCarlos Guevara PalauNo ratings yet
- Different Methods and Substrate Have Been Introduced and Develop For Mushroom CultivationDocument3 pagesDifferent Methods and Substrate Have Been Introduced and Develop For Mushroom CultivationGlaiza Lacson100% (1)
- ClimateDocument26 pagesClimateJenny ManagoNo ratings yet
- STC-MWC SC Grade 2Document6 pagesSTC-MWC SC Grade 2Perihan SayedNo ratings yet
- Q4 - 1ST Summative Test Science 7Document2 pagesQ4 - 1ST Summative Test Science 7Aj De CastroNo ratings yet
- The Book Thief: by Markus ZusakDocument38 pagesThe Book Thief: by Markus ZusakeightNo ratings yet
- Weather Climate QuizDocument8 pagesWeather Climate QuizJeremie M. CruzNo ratings yet
- Footing and FTB DetailsDocument1 pageFooting and FTB DetailsJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- Ib Mock TestDocument13 pagesIb Mock Testnwho0200No ratings yet