Professional Documents
Culture Documents
18 Round The Year Cultivation
Uploaded by
Abhijit Jadhav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pages1) The document discusses round-the-year cultivation of different mushrooms in India based on their temperature requirements and seasonal variations.
2) It provides temperature ranges for spawning and cropping of various mushrooms like white button, oyster, milky, paddy straw etc.
3) Models for mushroom cultivation in different agro-climatic zones of North India like plains, medium elevation and high elevation areas show possibilities of cultivating different mushrooms throughout the year based on season.
Original Description:
18 Round the year cultivation
Original Title
18 Round the year cultivation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document discusses round-the-year cultivation of different mushrooms in India based on their temperature requirements and seasonal variations.
2) It provides temperature ranges for spawning and cropping of various mushrooms like white button, oyster, milky, paddy straw etc.
3) Models for mushroom cultivation in different agro-climatic zones of North India like plains, medium elevation and high elevation areas show possibilities of cultivating different mushrooms throughout the year based on season.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pages18 Round The Year Cultivation
Uploaded by
Abhijit Jadhav1) The document discusses round-the-year cultivation of different mushrooms in India based on their temperature requirements and seasonal variations.
2) It provides temperature ranges for spawning and cropping of various mushrooms like white button, oyster, milky, paddy straw etc.
3) Models for mushroom cultivation in different agro-climatic zones of North India like plains, medium elevation and high elevation areas show possibilities of cultivating different mushrooms throughout the year based on season.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Round the Year Cultivation of Mushrooms
The practice of taking crops alternatively to utilize the principles of crop
rotation can also be implemented in mushroom cultivation. However the
cultivation of different mushrooms in rotation is not yet popular because of
mushroom being a non-traditional crop. Majority of the farmers are cultivating
mushrooms only during particular seasons. Farmers in the plains of North India
cultivate white button mushrooms during winter only and stop the mushroom
cultivation during summer and dismantle their temporary growing houses. It is
also paradoxical to note that India is largely a tropical country and we mainly
cultivate temperate mushroom. The tropical and sub tropical mushrooms like
oyster (Pleurotus spp), paddy straw (Volvariella sp), milky (Calocybe sp), reishi
(Ganoderma sp), wood ear (Auricularia spp) etc are not cultivated on a larger
scale. To cultivate different types of mushrooms based on different seasons and
prevailing climate one should know the requirement of specific temperature and
humidity of different edible mushrooms. Since mushrooms contain about 90%
water it is desirable to grow them under a relative humidity of above 85-90%. The
temperature requirements of some important mushrooms are given in Table 1.
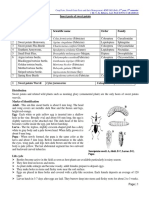
Table 1: temperature requirements of some important mushrooms
S.N Scientific name Common name Temperature
. of Mushroom requirement
Spawning Cropping
1 Agaricus bisporus White button mushroom 22-25 14-16
2 Agaricus bitorquis Summer white button 28-30 25
mushroom
3 Auricularia sp Black ear/ Wood ear 20-34 12-30
mushroom
4 Lentinula edodes Shiitake mushroom 22-27 15-20
5 Pleurotus erangii Kabul Dhingri 18-22 14-18
6 P. flabilatus Dhingri (flavillatus) 25-30 22-26
7 P. florida Dhingri (Florida) 25-30 18-22
8 P. sajor caju Dhingri 25-32 22-26
9 Vovariella Paddy straw/ Parali 32-34 28-32
volvacea mushroom
10 Calocybe indica Milky/ Dudhiya 25-30 30-35
mushroom
From the Table 1 it is cleat that mushrooms can also be cultivated round
the year based on season like other field crops. In the plains of North India white
button mushroom can be cultivated during winter. In summer, the sub tropical or
tropical mushroom species like high temperature tolerant white button
mushroom, milky, oyster or paddy straw mushroom can be cultivated. It is also
worth mentioning the fact that even the various Pleurotus spp (Oyster
mushroom) alone offers scope to cultivate it through out the year in many parts
of India. A model for round the year cultivation of different mushrooms in north
India is depicted below (Fig.1).
Fig. 1:Possibility of mushroom cultivation in plains
From the above figure it is clear that white button mushroom can be
cultivated during winter months of October to February. High temperature
tolerant button mushroom can be cultivated from September to April except
during peak winter. Black ear mushroom during February to April, dhingri from
September to May, paddy straw mushroom from July to September and milky
mushroom from February to April and July to September.
In medium elevated lands, white button mushroom can be cultivated from
September to March while the summer white button mushroom can be cultivated
during July to August and
Fig 2: Possibility of mushroom cultivation at medium elevated lands
also during March to May. Shiitake can be cultivated from October to February,
while milky mushroom from April to June. The oyster mushroom can be
cultivated almost through out the year in medium elevated lands. Model for
mushroom cultivation in these lands is depicted in fig. 2
The high-elevated lands are suitable for white button and shiitake for most
part of the year while the dhingri can be taken up during the summer season in
these areas. Fig.3 indicates the scope of mushrooms in the high-elevated lands.
Fig. 3: Possibility of mushroom cultivation in high elevation/hilly areas
By following the round the year cultivation of different edible mushrooms
depending on the season, the farmers can achieve the following benefits
Round the year economic returns
Round the year employment opportunities for farm labour
Round the year resource utilization in the farm
Continuous nutrition to family members
Break in the chain of epidemics of pests and diseases.
Hence, looking at the opportunities various mushrooms offers to
cultivate them through our the year, farmers should practice round the year
cultivation to reap maximum benefits.
You might also like
- Small-Scale Mushroom Cultivation (Autosaved)Document349 pagesSmall-Scale Mushroom Cultivation (Autosaved)amphreyevansNo ratings yet
- Mushroomrite 170620054116Document103 pagesMushroomrite 170620054116keithNo ratings yet
- Mushroomm NotesDocument74 pagesMushroomm NotesEmma WatsonNo ratings yet
- Oyester Mushroom CultivationDocument8 pagesOyester Mushroom CultivationkibriyaNo ratings yet
- Puccinia Graminis IDocument10 pagesPuccinia Graminis IJoy BengeNo ratings yet
- FungosementesDocument7 pagesFungosementesAlessandra silvaNo ratings yet
- Technology For Hybrid Seed Production: Oyster Mushroom CultivationDocument13 pagesTechnology For Hybrid Seed Production: Oyster Mushroom CultivationFerri GunawanNo ratings yet
- Mushrooms Plants Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide Carbohydrates Cellulose Sunlight EnergyDocument29 pagesMushrooms Plants Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide Carbohydrates Cellulose Sunlight EnergyAbisinuola OlapadeNo ratings yet
- Edodes and Tremella Fuciformis Was First Recorded in China in The YearsDocument23 pagesEdodes and Tremella Fuciformis Was First Recorded in China in The YearsSamuel DavisNo ratings yet
- FAQ Paddy Straw MushroomDocument2 pagesFAQ Paddy Straw MushroomchampakNo ratings yet
- 8 Plant Clinic Management in Different Crops of RajasthanDocument19 pages8 Plant Clinic Management in Different Crops of RajasthanSamuel DavisNo ratings yet
- Business Plan of MushroomsDocument29 pagesBusiness Plan of MushroomsMahamudul Hasan80% (5)
- Disease Competitor Moulds Dr. S.R. Sharma PDFDocument86 pagesDisease Competitor Moulds Dr. S.R. Sharma PDFIndra-Astral PemulaNo ratings yet
- Maize Northern Leaf Blight 226Document2 pagesMaize Northern Leaf Blight 226Shaik Gouse BashaNo ratings yet
- Small-Scale Mushroom CultivationDocument172 pagesSmall-Scale Mushroom CultivationDrdorko Drdorko100% (2)
- Round The Year Mushroom & EconomicsDocument22 pagesRound The Year Mushroom & EconomicsShivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Winged Bean-422Document6 pagesWinged Bean-422Zared Patricia de PaduaNo ratings yet
- What Is MushroomDocument4 pagesWhat Is MushroomDhanraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Ajay AgriDocument10 pagesAjay Agrilakadia taylorNo ratings yet
- Small Scale MushroomDocument87 pagesSmall Scale MushroomSolomon Oduro100% (1)
- Squash ProductionDocument7 pagesSquash ProductionSo Young100% (1)
- Major Diseases of Sorghum and Bajra.: C O Llege of Agriculture, RaipurDocument14 pagesMajor Diseases of Sorghum and Bajra.: C O Llege of Agriculture, RaipurVed MehraNo ratings yet
- PipliDocument8 pagesPipliSachin PatilNo ratings yet
- Revised Crop Diseases - FormattedDocument98 pagesRevised Crop Diseases - FormattedMona ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Phaseolus VulgarisDocument13 pagesPhaseolus Vulgarisunveiled2004100% (4)
- Mid Term Exam AGR-401 Section (B)Document10 pagesMid Term Exam AGR-401 Section (B)esha raniNo ratings yet
- Paddy Straw Mushroom ProdnDocument44 pagesPaddy Straw Mushroom ProdnmiradewiNo ratings yet
- Diseases of PotatoDocument8 pagesDiseases of PotatoAkash RoyNo ratings yet
- Diseases of PotatoDocument8 pagesDiseases of PotatoAkash RoyNo ratings yet
- Squash PlANTINGDocument3 pagesSquash PlANTINGatriyo salise100% (1)
- Ampalaya Production GuideDocument10 pagesAmpalaya Production Guideapo_mallariNo ratings yet
- Lab Report On Mushroom Production (Autorecovered)Document6 pagesLab Report On Mushroom Production (Autorecovered)karugusam0% (1)
- A Simple Method For Culture Conservation of Some Commercial MushroomsDocument4 pagesA Simple Method For Culture Conservation of Some Commercial MushroomsAhmed BadrNo ratings yet
- Ent-354 - Notes Cum Manual YTJ - FDocument66 pagesEnt-354 - Notes Cum Manual YTJ - FNiraj GurjarNo ratings yet
- An Overview of White Rot Disease Management in Small OnionDocument5 pagesAn Overview of White Rot Disease Management in Small OnionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ostreatus, Ganoderma Lucidum and Calocybe Indica)Document6 pagesOstreatus, Ganoderma Lucidum and Calocybe Indica)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Training Material ICRISAT CompDocument131 pagesTraining Material ICRISAT CompsaravananNo ratings yet
- (Big Picture) Oyster-Mushroom-Cultivation-Book-1Document36 pages(Big Picture) Oyster-Mushroom-Cultivation-Book-1Bismo AnggoroNo ratings yet
- Morphological VariabilityDocument16 pagesMorphological Variabilityraj cyberboyNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Science Education)Document41 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Science Education)Tahirullah KhanNo ratings yet
- 17-ARID-2935 (Hafiz Muhammad Zahid) 1Document5 pages17-ARID-2935 (Hafiz Muhammad Zahid) 1Ch WadiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Factors Affecting MushroomsDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Factors Affecting MushroomsGlaiza Lacson100% (1)
- MushroomDocument7 pagesMushroomKapil DangauraNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Diseases Rice 2015Document13 pagesBacterial Diseases Rice 2015Teguh PratamaNo ratings yet
- Mushroom CultivationDocument9 pagesMushroom CultivationShalmali ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 3RD Term S2 Agricultural ScienceDocument24 pages3RD Term S2 Agricultural ScienceFootball FlameNo ratings yet
- Disease Competitor Moulds Dr. S.R. SharmaDocument86 pagesDisease Competitor Moulds Dr. S.R. SharmaAntoni GandiaNo ratings yet
- University of Agricultural Sciences, GKVK Bangalore-65: Flower Visitors in Pollination and Pod Set of PigeonpeaDocument8 pagesUniversity of Agricultural Sciences, GKVK Bangalore-65: Flower Visitors in Pollination and Pod Set of PigeonpeaMahendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Bridge1977 PDFDocument9 pagesBridge1977 PDFAni ArdNo ratings yet
- (Volvariella Volvacea) : Cultivation Technology of Paddy Straw MushroomDocument44 pages(Volvariella Volvacea) : Cultivation Technology of Paddy Straw Mushroomlulay1974No ratings yet
- ZZZZZDocument15 pagesZZZZZMULUKEN TILAHUNNo ratings yet
- Mushroom Growers Handbook 1 Mushworld Com Chapter 8 3Document3 pagesMushroom Growers Handbook 1 Mushworld Com Chapter 8 3ian7thNo ratings yet
- Paddy Straw MushroomDocument38 pagesPaddy Straw MushroomShivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Sweet Potato PestsDocument6 pagesSweet Potato PestsHarihara PadhiNo ratings yet
- 332 Theory Material RevisedDocument152 pages332 Theory Material RevisedDada PeerNo ratings yet
- Soil Borne Diseases of Major Pulses and Their Biological Management PDFDocument11 pagesSoil Borne Diseases of Major Pulses and Their Biological Management PDFSp SarathyNo ratings yet
- NEMATOLOGY Assignment Group 1Document7 pagesNEMATOLOGY Assignment Group 1jaahbless8No ratings yet
- Mushrooms in Biodiversity and Food Security of Sikkim: Tasvina R. Borah and H. RahmanDocument15 pagesMushrooms in Biodiversity and Food Security of Sikkim: Tasvina R. Borah and H. RahmanAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Spawn Production TechnologyDocument8 pagesSpawn Production TechnologythosampaNo ratings yet
- Cultivation Technology of Reishi Mushroom: SearchDocument7 pagesCultivation Technology of Reishi Mushroom: SearchAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution DefinitionDocument4 pagesAir Pollution DefinitionAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Mycobiology 3822010 ADocument6 pagesMycobiology 3822010 AAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Biofloc Technology Short Coures at WA17Document2 pagesBiofloc Technology Short Coures at WA17Mohamed SadekNo ratings yet
- Indianphyto2012 PDFDocument6 pagesIndianphyto2012 PDFAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Calocybe Indica (P & C) in Konkan Region of Maharashtra, IndiaDocument6 pagesCultivation of Calocybe Indica (P & C) in Konkan Region of Maharashtra, IndiaAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Sanjeevan Agrotech PDFDocument3 pagesSanjeevan Agrotech PDFAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Reishi MushroomDocument6 pagesCultivation of Reishi MushroomvliesNo ratings yet
- Mushrooms in Biodiversity and Food Security of Sikkim: Tasvina R. Borah and H. RahmanDocument15 pagesMushrooms in Biodiversity and Food Security of Sikkim: Tasvina R. Borah and H. RahmanAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Sanjeevan Agrotech PDFDocument3 pagesSanjeevan Agrotech PDFAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Reishi MushroomDocument6 pagesCultivation of Reishi MushroomvliesNo ratings yet
- Spawn Production TechnologyDocument8 pagesSpawn Production TechnologythosampaNo ratings yet
- M. Prameela and G. Uma DeviDocument4 pagesM. Prameela and G. Uma DeviAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Hadoop Streaming: For Live Customized Hadoop Training (Including Prep For The Cloudera Certification Exam), Please EmailDocument10 pagesHadoop Streaming: For Live Customized Hadoop Training (Including Prep For The Cloudera Certification Exam), Please EmailAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Pipe Materials and Types of JointsDocument35 pagesPipe Materials and Types of JointsAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument31 pagesTutorialCrispus KimingichNo ratings yet
- Creating Home-Based Edible Gardening Projects!Document2 pagesCreating Home-Based Edible Gardening Projects!Abhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Mech Elect CSR 2018-19 0 PDFDocument113 pagesMech Elect CSR 2018-19 0 PDFAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PDFDocument271 pagesTutorial PDFAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Testwww - Creating A Custom Java Desktop Database Application - NetBeans 6.5 TutorialDocument22 pagesTestwww - Creating A Custom Java Desktop Database Application - NetBeans 6.5 TutorialzballestaNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument13 pagesOverviewAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- 07 Hive 01Document22 pages07 Hive 01ArunKumarNo ratings yet
- 07 Hive 01Document22 pages07 Hive 01ArunKumarNo ratings yet
- 01 Overview HadoopDocument22 pages01 Overview Hadoopalekh_mitsNo ratings yet
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)Document14 pagesHadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)Manikantan GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- PigDocument25 pagesPigAbhijit JadhavNo ratings yet
- Implementing So ADocument65 pagesImplementing So Arahulkatarey100% (1)
- Parasitoid and Its Hosts PDFDocument16 pagesParasitoid and Its Hosts PDFJerwin VirgoNo ratings yet
- MFW May Portfolio UpdateDocument42 pagesMFW May Portfolio UpdatejasonmalumedNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log DLL TLE 7 Week 1 June 3 - 7, 2019Document4 pagesDaily Lesson Log DLL TLE 7 Week 1 June 3 - 7, 2019LEANDRO BOTALON100% (2)
- The Medieval English Landscape, 1000-1540Document294 pagesThe Medieval English Landscape, 1000-1540Antonio avilaNo ratings yet
- Faiz Habib and Irfan Habib, Mapping Neolithic IndiaDocument9 pagesFaiz Habib and Irfan Habib, Mapping Neolithic IndiaKumar KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 01 ACPC Jojo Badiola Agricultural - MicrofinanceDocument10 pages01 ACPC Jojo Badiola Agricultural - MicrofinanceMicrofinanceCouncil OfthePhilsNo ratings yet
- Soil Security: Dominique Arrouays, Vera Leatitia Mulder, Anne C. Richer-de-ForgesDocument2 pagesSoil Security: Dominique Arrouays, Vera Leatitia Mulder, Anne C. Richer-de-ForgesMoezselmi.12 SelmiNo ratings yet
- Economic Security Assessment in Catubig Northern Samar PhilippinesDocument6 pagesEconomic Security Assessment in Catubig Northern Samar PhilippinesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- AgriNext Conference Agenda 2024Document4 pagesAgriNext Conference Agenda 2024Climatology UAFNo ratings yet
- Ethnomedicinal-Plant-Names-and-Translations-may 7 Edit Co ChaliqueDocument6 pagesEthnomedicinal-Plant-Names-and-Translations-may 7 Edit Co ChaliqueMelissa Joy DollagaNo ratings yet
- Analysis The Potential of Malang Regency As A Center For Oil Palm Plantations in East JavaDocument7 pagesAnalysis The Potential of Malang Regency As A Center For Oil Palm Plantations in East JavaMamta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- A Survey Paper On Plant Disease Identification Using Machine Learning ApproachDocument4 pagesA Survey Paper On Plant Disease Identification Using Machine Learning ApproachDrawing n RockingNo ratings yet
- Livestock and Products Annual Cairo Egypt 09-01-2021Document17 pagesLivestock and Products Annual Cairo Egypt 09-01-2021karan kambojNo ratings yet
- JHS 3Document2 pagesJHS 3abdulrahmanabdulhakeem2017No ratings yet
- Dhenu Milk Dairy FarmDocument26 pagesDhenu Milk Dairy FarmArdhendu SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument31 pagesAgricultureMickaelaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Integrated Pest ManagementDocument8 pagesLiterature Review On Integrated Pest Managementea4gaa0g100% (1)
- Agra CasesDocument23 pagesAgra CasesDanyNo ratings yet
- Q4 AFA Agricrop 10 Week 8Document4 pagesQ4 AFA Agricrop 10 Week 8Eden SumilayNo ratings yet
- Pechay Production GuideDocument3 pagesPechay Production GuideJulie Anne Uy Autentico67% (6)
- Climate Change and Sustainable Development: Ethical Perspectives On Land Use and Food ProductionDocument528 pagesClimate Change and Sustainable Development: Ethical Perspectives On Land Use and Food ProductionAndreea Cătălina TacheNo ratings yet
- Seal Acon Evo PetDocument58 pagesSeal Acon Evo PetHamzah HamzahNo ratings yet
- At A Potato Digging by Seamus Heaney AnalysisDocument3 pagesAt A Potato Digging by Seamus Heaney AnalysisTabish203900% (1)
- Economic Study of Binadhan-14 Production inDocument10 pagesEconomic Study of Binadhan-14 Production inKrishibid Syful IslamNo ratings yet
- RTL Feasibiliry StudyDocument6 pagesRTL Feasibiliry StudyrudygootNo ratings yet
- Avocado Fruit Farming - PDFDocument11 pagesAvocado Fruit Farming - PDFJames WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 1991 Reforms in Agricultural SectorDocument8 pages1991 Reforms in Agricultural SectorTabrez AlamNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The Mining IndustryDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of The Mining IndustrylucianNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Contingency Plan For District: Mungeli State: ChhattisgarhDocument27 pagesAgriculture Contingency Plan For District: Mungeli State: ChhattisgarhRavi S. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Afa ModuleDocument12 pagesAfa ModuleFrancisco C. ArianNo ratings yet