Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Steam Water Circulation Design
Uploaded by
Thoni Lackner0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views18 pagesGiu
Original Title
4. Steam Water Circulation Design
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGiu
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views18 pagesSteam Water Circulation Design
Uploaded by
Thoni LacknerGiu
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
As presented in the previous chapter, boilers can be
classified by their combustion method, by their
application or by their type of steam/water
circulation.
This chapter will describe the different types of
steam/water circulation in boilers.
Steam boiler types according to steam/water circulation
Shell type boilers
Shell type boilers are boiler that are built
similarly to a shell and tube heat exchanger.
In large volume type boilers a burner or a grate is
situated inside a big tube, called chamber.
The chamber is surrounded by water in a pressure
vessel that functions as the outer boiler wall.
Thus, the water absorbs the heat and some of the
water is converted to saturated steam.
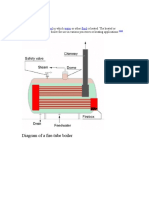
Shell type boiler: Höyrytys TTKV-fire tube boiler
Fire tube boilers
Modern fire tube boilers are used in applications that
require moderate pressures and moderate demand.
As the name implies, the basic structure of a fire tube
boiler consists of tubes, where fuel is burned and flue
gas is transported, located in a pressurized vessel
containing water.
Usually boilers of this type are customized for liquid
or gaseous fuels, like oil, natural gas and biogases.
Fire tube boilers are used for supplying steam or
warm water in small-scale applications.
Large volume boilers
Schematic of the Höyrytys TTKV-fire tube hot-water boiler
Large volume boilers
Schematic of the Höyrytys TTK fire tube steam boiler
Water tube boilers
In contrast to large volume boilers, the steam/water
mixture is inside the tubes in water tube boilers, and
is heated by external combustion flames and flue
gases.
The water tube boilers are classified by the way of
the water/steam circulation: natural circulation,
forced or assisted circulation, once-through and
combined circulation type boilers.
Natural circulation boilers
The natural circulation is one of the oldest principles for
steam/water circulation in boilers.
Natural circulation principle is usually implemented on small
and medium sized boilers.
Typically the pressure drop for a natural circulation boiler is
about 5-10 % of the steam pressure in the steam drum and the
maximum steam temperature varies from 540 to 560 °C
Natural circulation boilers
Natural circulation principle
Assisted or forced circulation boilers
In contrast to natural circulation boilers, forced circulation is
based on pump-assisted internal water/steam circulation.
The circulation pump is the main difference between natural
and forced circulation boilers.
Practically the maximum operation pressure for a forced
circulation boiler is 190 bar and the pressure drop in the boiler
is about 2-3 bar.
Assisted or forced circulation boilers
Principle of forced/assisted circulation
Once-through boiler types
There are three main types of once through boilers:
1. Benson design
2. Sulzer design
3. Ramzin design.
Once-through boiler types
Benson design once-through boiler
Once-through boiler types
Sulzer design once-through boiler. The separation bottle is marked
with an arrow
Once-through boiler types
Ramzin once-through boiler
Combined circulation boilers
Simplified principle of combined circulation.
You might also like
- Original Autel Ikey For MaxiIM KM100 IM508 IM608 PRO - Jack Wu +8615606013298Document4 pagesOriginal Autel Ikey For MaxiIM KM100 IM508 IM608 PRO - Jack Wu +8615606013298Wu JackNo ratings yet
- Turbine ManualDocument190 pagesTurbine Manualtrungdtd711100% (21)
- Power Industry Appl GuideDocument38 pagesPower Industry Appl GuidePetrovich1No ratings yet
- JPT RMP C1Document24 pagesJPT RMP C1HaRriet De Guzman Villanueva100% (1)
- 10th and Yampa Hotel Planning CommissionDocument54 pages10th and Yampa Hotel Planning CommissionEleanor HasenbeckNo ratings yet
- PPR PPRCT Installation Manual PDFDocument31 pagesPPR PPRCT Installation Manual PDFAn BuiNo ratings yet
- Idronics 27 Hot Water HeatpumpDocument84 pagesIdronics 27 Hot Water HeatpumpHuynh Le DuyenNo ratings yet
- IVT Heat PumpsDocument12 pagesIVT Heat Pumpskushik9781No ratings yet
- A ResortDocument4 pagesA ResortDisha ShahNo ratings yet
- Pool Side Equipment PDF Document Aqua Middle East FZCDocument20 pagesPool Side Equipment PDF Document Aqua Middle East FZCAdolfsmith69No ratings yet
- Pex InstallDocument37 pagesPex Installtincanandstring987No ratings yet
- Commercial thermal storage technologies - Molten salts vs steam accumulatorsDocument9 pagesCommercial thermal storage technologies - Molten salts vs steam accumulatorsYousef SalahNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump Catalog - AIROSD EvaDocument24 pagesHeat Pump Catalog - AIROSD EvaEmil EremiaNo ratings yet
- Drainage-Systems-Installation-Guide - OffsetDocument72 pagesDrainage-Systems-Installation-Guide - OffsetPaqui MorentNo ratings yet
- Pdfanddoc 714255 PDFDocument83 pagesPdfanddoc 714255 PDFArmin MerjaNo ratings yet
- Lift Pit Sump PumpDocument1 pageLift Pit Sump PumpAkhil VijaiNo ratings yet
- Types of Boilers PDFDocument5 pagesTypes of Boilers PDFJosé RubioNo ratings yet
- 0il Extracting MachineDocument26 pages0il Extracting MachineDagi TewanayNo ratings yet
- Boiler Book PDFDocument44 pagesBoiler Book PDFmpgzyah100% (5)
- Pool Hydraulic Analysis FormDocument6 pagesPool Hydraulic Analysis FormtonyonlyNo ratings yet
- Technical Guide for Heat PumpsDocument399 pagesTechnical Guide for Heat PumpsszaszdeziderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SteamGeneratorsDocument156 pagesChapter 3 SteamGeneratorssam afiNo ratings yet
- Design and Thermal Analysis of CFB and Simple BoilersDocument89 pagesDesign and Thermal Analysis of CFB and Simple Boilersbharathkumar0310No ratings yet
- Topic 1sanitation System SlideDocument66 pagesTopic 1sanitation System Slidedhevashini narayananNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Regenerative Feed Water HeatersDocument5 pagesOptimization of Regenerative Feed Water Heatersphanipavan2687No ratings yet
- Water Recycle and Reuse NIMMS University PDFDocument8 pagesWater Recycle and Reuse NIMMS University PDFDennis KorirNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument38 pagesRefrigeration SystemAdrian Derek IvashkoveNo ratings yet
- NTPC PresentationDocument222 pagesNTPC PresentationReaderRRGHT100% (2)
- Harvia Products For Steam Room: Natural Well-BeingDocument4 pagesHarvia Products For Steam Room: Natural Well-BeingAhmadSalaimehNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Renewal Proposal V2.3Document17 pagesKitchen Renewal Proposal V2.3moses kisakyeNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument178 pagesUntitledapi-108818349No ratings yet
- Proposal (Autosaved) KKDocument5 pagesProposal (Autosaved) KKAmilin HatiaraNo ratings yet
- Fascination Sheet Metal Chapter 1 PDFDocument10 pagesFascination Sheet Metal Chapter 1 PDFknizamNo ratings yet
- Pepperell Mill Campus Business Prospectus & Project OverviewDocument46 pagesPepperell Mill Campus Business Prospectus & Project OverviewPepperellMillNo ratings yet
- Clearing Clogged Drains - Snake or HydrojetDocument3 pagesClearing Clogged Drains - Snake or Hydrojetcrystal_drain_plumbingNo ratings yet
- Application Notes Hot Water Circuit IDL Midleton 052016Document4 pagesApplication Notes Hot Water Circuit IDL Midleton 052016nascasNo ratings yet
- Interact Club ConstitutionDocument9 pagesInteract Club Constitutionapi-366663480No ratings yet
- Duane Banks Stadium RenovationDocument3 pagesDuane Banks Stadium RenovationGazetteonlineNo ratings yet
- Commercial Hot Water (Reference)Document2 pagesCommercial Hot Water (Reference)binhjukiNo ratings yet
- Bank Clerks: Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesBank Clerks: Job DescriptionAnuradha ShettyNo ratings yet
- Wavin Pilsa PPR Technical Manual - March 2016Document52 pagesWavin Pilsa PPR Technical Manual - March 2016George SobhyNo ratings yet
- Gorenje Highlights HDocument32 pagesGorenje Highlights Hjamppajoo2No ratings yet
- Regulations For Sanitary InstallationsDocument207 pagesRegulations For Sanitary Installationsyusuf100% (1)
- Company Profile For ErolDocument4 pagesCompany Profile For ErolREGINo ratings yet
- Wilo Star z1Document20 pagesWilo Star z1Jovisa MaricNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Layout Design GuideDocument20 pagesPharmacy Layout Design Guidehumag143No ratings yet
- Heat Pump Sizing FormDocument1 pageHeat Pump Sizing FormDenver RumneyNo ratings yet
- Laser Cutting Business InformationDocument75 pagesLaser Cutting Business InformationParag HadkeNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Solar Water Heating Basics PDFDocument111 pagesHandbook - Solar Water Heating Basics PDFmnt6176No ratings yet
- Plumbing System AnalysisDocument3 pagesPlumbing System AnalysisAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- Home Water Supply SystemDocument49 pagesHome Water Supply Systemragani ramadasNo ratings yet
- BIM For Renovation ProjectsDocument3 pagesBIM For Renovation ProjectssacinNo ratings yet
- Flow Cytometry Basic TrainingDocument89 pagesFlow Cytometry Basic TrainingPotini AdityaNo ratings yet
- Stone Processing Machine Operator SPO.147152600Document14 pagesStone Processing Machine Operator SPO.147152600swami061009No ratings yet
- Hot Water SupplyDocument17 pagesHot Water SupplyBRAIN OF AN ARCHITECTNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank Purpose - FunctionDocument35 pagesSeptic Tank Purpose - FunctionMasnun Rahman100% (2)
- Asd Reinforcement Detailing Manual Eng 2010Document222 pagesAsd Reinforcement Detailing Manual Eng 2010Cristian Gonzalo Fiorilo BravoNo ratings yet
- Hafele All Appliance BrandsDocument8 pagesHafele All Appliance BrandsMichael RojasNo ratings yet
- Unvented Calorifiers Installation & Commissioning GuideDocument10 pagesUnvented Calorifiers Installation & Commissioning GuidePaul KwongNo ratings yet
- Dryroom Basement Waterproofing PDFDocument4 pagesDryroom Basement Waterproofing PDFKevin BallNo ratings yet
- Swimming Pool Ozone SystemDocument21 pagesSwimming Pool Ozone SystemPragnesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- 2014-4966-1M-1008 Rev D Hot Water Circulation Pump DatasheetDocument10 pages2014-4966-1M-1008 Rev D Hot Water Circulation Pump DatasheetSamuel JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Boilers: The Pressure Vessel in A Boiler Is Usually Made of Steel (Or Alloy Steel)Document21 pagesBoilers: The Pressure Vessel in A Boiler Is Usually Made of Steel (Or Alloy Steel)Sampath KumarNo ratings yet
- #Lecture 3 - Steam GeneratorsDocument22 pages#Lecture 3 - Steam Generatorsmohamed EldesokyNo ratings yet
- Boiler: Diagram of A Fire-Tube BoilerDocument4 pagesBoiler: Diagram of A Fire-Tube BoilerMd ShahidNo ratings yet
- Steam BoilerDocument7 pagesSteam BoilerVishnu VardhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Jurnal TeknologiDocument7 pagesJurnal TeknologiThoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Steam GenerationDocument26 pagesThe Basics of Steam GenerationThoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- Journal of Refrigeration, Air Conditioning, Heating and Ventilation Design of A Compressed Air VehicleDocument7 pagesJournal of Refrigeration, Air Conditioning, Heating and Ventilation Design of A Compressed Air VehicleThoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- Solar Powered Air Conditioning System: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesSolar Powered Air Conditioning System: SciencedirectMedo HamedNo ratings yet
- The History of Steam GenerationDocument16 pagesThe History of Steam GenerationThoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- 2 PBDocument14 pages2 PBThoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877705813014914 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S1877705813014914 Mainthasarathanr1993_939No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877705813014914 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S1877705813014914 Mainthasarathanr1993_939No ratings yet
- 082 092 PDFDocument11 pages082 092 PDFsonchemenNo ratings yet
- Equipment Maintenance Log Template 03Document2 pagesEquipment Maintenance Log Template 03Thoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- KomponenDocument7 pagesKomponenThoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- 082 092 PDFDocument11 pages082 092 PDFsonchemenNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0959652619315872 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0959652619315872 MainThoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Faiz FathoniDocument6 pagesJurnal Faiz FathoniThoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- Cis WSH Excavator Backhoe Inspreport 146494 7Document2 pagesCis WSH Excavator Backhoe Inspreport 146494 7Thoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2212017314003788 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S2212017314003788 MainThoni LacknerNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument4 pagesAcknowledgementEndalkachew AddisNo ratings yet
- TPPPSQ- Thermal Power Plant Question BankDocument5 pagesTPPPSQ- Thermal Power Plant Question BankPatel KetanNo ratings yet
- Solar CSP Plant Stores 15 Hours of EnergyDocument1 pageSolar CSP Plant Stores 15 Hours of EnergyJames AhnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 LectureDocument29 pagesChapter 9 Lectureinam vf100% (6)
- 2014 AmCham Haiti Membership DirectoryDocument28 pages2014 AmCham Haiti Membership DirectoryjeremylambethNo ratings yet
- Split Cycle EngineDocument2 pagesSplit Cycle EngineNani KotaNo ratings yet
- Intake ProcessDocument9 pagesIntake ProcessHizanorhuda ZurghibaNo ratings yet
- Company File SPPS Co.,Ltd ( ) PDFDocument47 pagesCompany File SPPS Co.,Ltd ( ) PDFrobby dedyNo ratings yet
- Fuel injection system components diagramDocument1 pageFuel injection system components diagramAuto-Moto ZS.K.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Home Heating SystemsDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Home Heating Systemshoussem houssemNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Question BankDocument3 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Question BankRohit GhulanavarNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 13 Mini-HydropowerDocument13 pagesLecturer 13 Mini-HydropowerjishnuNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbines: Prepared by Maaz Ahamd 09-ME-01Document37 pagesWind Turbines: Prepared by Maaz Ahamd 09-ME-01Javaria SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Power SystemDocument31 pagesHybrid Power SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Ece Solar Mobile Charger ReportDocument19 pagesEce Solar Mobile Charger Reportfolagtech50% (2)
- N0 Tahun Chemical Engineering Plant Cost IndexDocument18 pagesN0 Tahun Chemical Engineering Plant Cost IndexIlham Kiki ShahilaNo ratings yet
- Assign. 1 MPDE - QuestionDocument4 pagesAssign. 1 MPDE - QuestionNur Luqman DzulkifliNo ratings yet
- Solar MPPT Hybrid Charge ControllerDocument3 pagesSolar MPPT Hybrid Charge Controllermian_adnan_aslamNo ratings yet
- Ar Cycle 2Document4 pagesAr Cycle 2ELEONOR TABLINGONNo ratings yet
- LIST of GTDocument5 pagesLIST of GTSonali BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- E2876Document3 pagesE2876criveraNo ratings yet
- The Boiler Book On Line - Chapter 1 Introduction To BoilersDocument6 pagesThe Boiler Book On Line - Chapter 1 Introduction To BoilersDavid Jose Quintero VelascoNo ratings yet
- Differences Between SI Engine and CI EngineDocument4 pagesDifferences Between SI Engine and CI EngineSyifaprilia NNo ratings yet