Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Y 10 WK 5 L 1 Xlink
Uploaded by
api-450306740Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Y 10 WK 5 L 1 Xlink
Uploaded by
api-450306740Copyright:
Available Formats
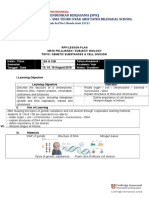
Lesson Plan
Lesson Topic: Sex linked traits Year Level: 10
9 Time: Monday P1 Date: 27/05/19
08:30 - 09:32
Learning Area: Science (Genetics) Students’ Prior Knowledge:
Year 10: Structure of DNA, mitosis, meiosis, punnet
Strand/Substrand/Content Descriptor from the squares, heredity, incomplete & co-dominance.
West Australian Curriculum:
Biological sciences:
Transmission of heritable characteristics
from one generation to the next involves
DNA and genes (ACSSU184)
General Capabilities
Literacy Numeracy ICT competence Critical and Ethical behaviour Personal and Intercultural
creative Social understanding
thinking competence
Cross-curriculum priorities
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Asia and Australia’s engagement Sustainability
histories and cultures with Asia
Lesson Objectives
As a result of this lesson, students will be able to:
• Recall that humans have autosomes and sex chromosomes
• Compare the four patterns of inheritance (autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, X-linked
recessive)
• Explain why sex-linked recessive traits are more likely to affect males
Teacher’s Prior Preparation/Organisation: Provisions for Learner diversity (G&T, SWD, EALD,
Roll set up on computer
SAER)
Book projected on board
SWD Direct questions according to students abilities
SAER Write large on board, worked examples
LESSON EVALUATION (to be completed AFTER the lesson)
Assessment of Lesson Objective and Suggestions for Improvement:
Teacher self-reflection and self-evaluation:
[OFFICIAL USE ONLY] Comments by classroom teacher, HOPP, supervisor:
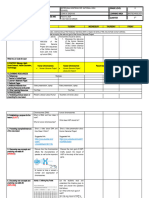
LESSON DELIVERY (attach worksheets, examples, marking key, etc, as relevant)
Time Stages of the Lesson Resources
10mins
Stage 1 Introduction YouTube
08:30- Video to start:
08:40 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=veB31XmUQm8&t=90s
Recaps where DNA is found, shows the pairs and that only 1 pair is sex chromosomes,
explains that Y chromosomes code for important male traits whereas lots of useful
information is contained on the X.
Don’t need to know anything about X inactivation which is explained but if anyone was
wondering why identical twins don’t have the same DNA or what happens to the DNA that
isn’t expressed it will still be interesting.
Video explains at the end that while females have 2 genes and could inherit a dominant,
because males only have one copy of the X chromosome, if they inherit the affected X from
their mother they will also be affected.
50mins
Stage 2 Body of lesson Oxford
8:40 - Use Oxford notes:
Science 10
9:30 Define autosomes, sex chromosomes, relate XX, XY genotypes to female, male phenotype.
p.18-21
Saw in video that Y chromosome mostly contains male specific genes, it is smaller.
X chromosome carries genes for sexual characteristics but because it is larger also carries
other non-sexual information (examples)
Traits carried on a sex chromosome are called sex-linked
There are four main patterns of inheritance: autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-
linked dominant, X-linked recessive
Table with similarities and differences, explain each point (punnet sq. if needed)
How to write sex linked traits
Haemophilia example, punnet squares showing Queen Victoria’s family.
Q.1,6,7,8
If lots of time (>10min): explain that a pedigree is an easy way to show this without having to
do a punnet square every time.
Then Q. 2,3,4.
If short amount of time left:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kMWxuF9YW38 (5:45)
Video recaps human sex determination then shows how animals have different systems
2mins
Stage 3: Conclusion
9:30- pack up 2 mins before end of class
9:32
Transition:
Pack books away.
Assessment strategies:
Checking understanding in class discussion, completing written questions.
References
Silvester, H., Yap, S. (2016). Oxford Science 10 Western Australian Curriculum. South Melbourne, VIC: Oxford
University Press.
TED-Ed. (2012, April 23). Sex Determination: More Complicated Than You Thought [Video file]. Retrieved from https://
www.youtube.com/watch?v=kMWxuF9YW38
TED-Ed. (2017, April 18). Secrets of the X chromosome - Robin Ball [Video file]. Retrieved from https://
www.youtube.com/watch?v=veB31XmUQm8&t=90s
You might also like
- Y 10 WK 7 L 1 EvidenceDocument2 pagesY 10 WK 7 L 1 Evidenceapi-450306740No ratings yet
- Y 10 WK 5 L 3 PedigreeDocument2 pagesY 10 WK 5 L 3 Pedigreeapi-450306740No ratings yet
- Race To The Double HelixDocument9 pagesRace To The Double Helixapi-246410580No ratings yet
- Y 10 WK 7 L 3 CompanatomyDocument2 pagesY 10 WK 7 L 3 Companatomyapi-450306740No ratings yet
- Meiosis Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMeiosis Lesson Planapi-350432337No ratings yet
- Burton 14te802 Gltunit2Document12 pagesBurton 14te802 Gltunit2api-257192598No ratings yet
- Biology Science For Life With Physiology 5Th Edition Belk Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesBiology Science For Life With Physiology 5Th Edition Belk Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFCassieYangiosx100% (12)
- Y 10 WK 8 L 1 PressuresDocument2 pagesY 10 WK 8 L 1 Pressuresapi-450306740No ratings yet
- S9Q1L17Document3 pagesS9Q1L17ronnie dela cruzNo ratings yet
- 10.5 Modern Evidence of Evolution PDFDocument4 pages10.5 Modern Evidence of Evolution PDFAngela Foulger-RichardsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sex InfluencedDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Sex InfluencedQueencess Ara Torres100% (1)
- DLP 5Document2 pagesDLP 5Marlow LowkeyNo ratings yet
- Modern Drama Course OutlineDocument10 pagesModern Drama Course OutlineSamah ElsaidNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.002.10s Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)Document7 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.002.10s Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- ElicitDocument5 pagesElicitJoan Dadivas AmancioNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson Plan GeneticsDocument10 pagesCot Lesson Plan GeneticsPrincess Ronquillo - DuqueNo ratings yet
- Anth 202 2018 SyllabusDocument11 pagesAnth 202 2018 SyllabusngyubingNo ratings yet
- April 8-12 Lesson Plans Cycle 3 2024Document22 pagesApril 8-12 Lesson Plans Cycle 3 2024Erlinda CalNo ratings yet
- Y 10 WK 6 L 3 NatselectlabDocument2 pagesY 10 WK 6 L 3 Natselectlabapi-450306740No ratings yet
- 2 eDocument8 pages2 eapi-239239720No ratings yet
- Learning Plan Genbio 2 Week 1Document5 pagesLearning Plan Genbio 2 Week 1Albert Rosete100% (1)
- ELC 411 - Language and GenderDocument12 pagesELC 411 - Language and GenderIan Paul Hurboda DaugNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare Syllabus Fall 2020 PDFDocument9 pagesShakespeare Syllabus Fall 2020 PDFMatthew NathanNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.001.07s Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)Document7 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.001.07s Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.001.07f Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)Document8 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.001.07f Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.002.10s Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)Document7 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.002.10s Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- LP #1 Physical ScienceDocument3 pagesLP #1 Physical ScienceShellis TorrefrancaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 - EndocrineDocument4 pagesWEEK 3 - EndocrineFrancis CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Acquiring LanguageDocument7 pagesAcquiring LanguageAdrianNo ratings yet
- Stetson University Department of Education Daily Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesStetson University Department of Education Daily Lesson Planapi-509272747No ratings yet
- Science9 q1 Slk4 Heredity-Inheritance-And-Variation v1Document23 pagesScience9 q1 Slk4 Heredity-Inheritance-And-Variation v1Saffira CameroNo ratings yet
- NT 1655334640Document3 pagesNT 1655334640fabiana meloNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.002.10s Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)Document7 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Nats2332.002.10s Taught by Homer Montgomery (Mont)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- What Makes You, You? (Genetics, Heredity, DNA Structure) 10 Grade Biology Biology)Document8 pagesWhat Makes You, You? (Genetics, Heredity, DNA Structure) 10 Grade Biology Biology)Mariah KeagyNo ratings yet
- The Myth of Language Universals: Language Diversity and Its Importance For Cognitive ScienceDocument65 pagesThe Myth of Language Universals: Language Diversity and Its Importance For Cognitive ScienceMichael LiuNo ratings yet
- 5e Heredity Genetics Unit Portfolio CrespoDocument6 pages5e Heredity Genetics Unit Portfolio Crespoapi-247308630No ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP For Evidence of Evolution Prepared by Jessa S. Eleazar 1Document10 pagesSemi Detailed LP For Evidence of Evolution Prepared by Jessa S. Eleazar 1Jay Rodren IbitaNo ratings yet
- Content Standard: The Evidence For Evolution (60 Mins.)Document3 pagesContent Standard: The Evidence For Evolution (60 Mins.)bhojoNo ratings yet
- Satuan Pendidikan Kerjasama (SPK) SD - SMP - Sma Teuku Nyak Arif Fatih Bilingual SchoolDocument8 pagesSatuan Pendidikan Kerjasama (SPK) SD - SMP - Sma Teuku Nyak Arif Fatih Bilingual SchoolyunimuliaNo ratings yet
- edTPA Lesson Segment 5Document2 pagesedTPA Lesson Segment 5Danielle Wilson100% (1)
- Model Fitxa DactivitatsDocument12 pagesModel Fitxa DactivitatstriplelouNo ratings yet
- Bruton-Annotated Lesson PlanDocument22 pagesBruton-Annotated Lesson Planapi-489727615No ratings yet
- 045 Lesson Plan Genetic DiversitiesDocument4 pages045 Lesson Plan Genetic DiversitiesbayangatkizzyNo ratings yet
- Ijells202110 (3) 224 235Document12 pagesIjells202110 (3) 224 235VŨ KIÊNNo ratings yet
- MCB 121 SyllabusDocument3 pagesMCB 121 SyllabusBrett PikeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Form # - 2 - : I. DescriptionDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Form # - 2 - : I. DescriptionAlex VarNo ratings yet
- Fairy Tales Around The World: Grade 3 Integrated Unit Plan: ELA, Social, Science, Art Miss KenneyDocument26 pagesFairy Tales Around The World: Grade 3 Integrated Unit Plan: ELA, Social, Science, Art Miss Kenneyapi-420344817No ratings yet
- ELECT2 Mythology & FolkloreDocument7 pagesELECT2 Mythology & FolkloreAdalyn Cullanan-SorianoNo ratings yet
- SDLP DAY - Biodiversity 3Document7 pagesSDLP DAY - Biodiversity 3Jessica SudioNo ratings yet
- 5E'S-Engage (1-2 Lessons) : Bvk5Ptp80My&T 19SDocument14 pages5E'S-Engage (1-2 Lessons) : Bvk5Ptp80My&T 19Sapi-451062387No ratings yet
- Hansen Video Art Spring 2019 Syllabus PDFDocument10 pagesHansen Video Art Spring 2019 Syllabus PDFAnonymous 8DDZujNo ratings yet
- W1 DLLDocument5 pagesW1 DLLJoan Dadivas AmancioNo ratings yet
- EDUC9 Module 4Document10 pagesEDUC9 Module 4Jomarc Cedrick GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson PlanMadiyar KospekovNo ratings yet
- How Whales Hear - PBS LearningMediaDocument4 pagesHow Whales Hear - PBS LearningMediaCarita HemsleyNo ratings yet
- Whaley Multicultural Changes EvolutioniiDocument11 pagesWhaley Multicultural Changes Evolutioniiapi-419020914No ratings yet
- Unit Plan Template: Objectives/OutcomesDocument4 pagesUnit Plan Template: Objectives/Outcomesapi-546993307No ratings yet
- Y 10 WK 8 L 1 PressuresDocument2 pagesY 10 WK 8 L 1 Pressuresapi-450306740No ratings yet
- Y 10 WK 7 L 3 QuestionsDocument2 pagesY 10 WK 7 L 3 Questionsapi-450306740No ratings yet
- Y 10 WK 6 L 3 NatselectlabDocument2 pagesY 10 WK 6 L 3 Natselectlabapi-450306740No ratings yet
- VideorubricDocument1 pageVideorubricapi-450306740No ratings yet
- FPD IctDocument4 pagesFPD Ictapi-450306740No ratings yet
- Content and Context Analysis of Selected Primary SourccesDocument3 pagesContent and Context Analysis of Selected Primary SourccesToshi CodmNo ratings yet
- Technical EnglishDocument7 pagesTechnical EnglishGul HaiderNo ratings yet
- Breaking News EnglishDocument13 pagesBreaking News English32. Nguyễn OanhNo ratings yet
- Defining The Christian Faith PaperDocument8 pagesDefining The Christian Faith Paperlin tongNo ratings yet
- Examiners' Report Principal Examiner Feedback January 2018Document9 pagesExaminers' Report Principal Examiner Feedback January 2018RafaNo ratings yet
- SFC PresentationDocument51 pagesSFC PresentationjmtriggerzNo ratings yet
- M 3 Nceog 2Document110 pagesM 3 Nceog 2Bharti SinghalNo ratings yet
- Norman Gulley: A Christ-Centered Approach To Last-Day EventsDocument35 pagesNorman Gulley: A Christ-Centered Approach To Last-Day EventsJorge Luis Echeverry González100% (1)
- Education and Its LegitimacyDocument4 pagesEducation and Its LegitimacySheila G. Dolipas100% (6)
- Irjet V3i7146 PDFDocument6 pagesIrjet V3i7146 PDFatulnarkhede2002No ratings yet
- Engine Interface ModuleDocument3 pagesEngine Interface ModuleLuciano Pereira0% (2)
- 02 Height and Distance - NIMCET Free Study MatrerialDocument2 pages02 Height and Distance - NIMCET Free Study MatrerialIshang VashishthaNo ratings yet
- Business English IDocument8 pagesBusiness English ILarbi Ben TamaNo ratings yet
- Kibera Mirror JULYDocument8 pagesKibera Mirror JULYvincent achuka maisibaNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University Mba - Thesis 060517Document2 pagesFar Eastern University Mba - Thesis 060517Lex AcadsNo ratings yet
- Performace Task 2 Electric Field LinesDocument31 pagesPerformace Task 2 Electric Field LinesStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Kumleben Commission ReportDocument232 pagesKumleben Commission ReportJulian Rademeyer100% (2)
- Comparative Analysis of State Bank of India With Other Credit SchemesDocument97 pagesComparative Analysis of State Bank of India With Other Credit SchemesVKM2013No ratings yet
- The Role of Leadership On Employee Performance in Singapore AirlinesDocument42 pagesThe Role of Leadership On Employee Performance in Singapore Airlineskeshav sabooNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Mental Workload LiteratureDocument36 pagesA Review of The Mental Workload LiteratureArlene LaguaNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 3 Practice Test Dynamics5Document5 pagesPhysics Unit 3 Practice Test Dynamics5StephanieNo ratings yet
- Obat Keras N0vember 2021Document137 pagesObat Keras N0vember 2021antonNo ratings yet
- SocialPolitical and Cultural ChangeDocument8 pagesSocialPolitical and Cultural ChangeChristine Mae BeramoNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Measurement Uncertainty For Electrical Conductivity in WaterDocument4 pagesEstimation of Measurement Uncertainty For Electrical Conductivity in WaterMaruthi KNo ratings yet
- Lux Level Calculation: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Document1 pageLux Level Calculation: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Wilson (Electrical Engineer)No ratings yet
- UW Mathematics Professor Evaluations For Fall 2011Document241 pagesUW Mathematics Professor Evaluations For Fall 2011DPNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Patient Flow: Innovation Series 2003Document16 pagesOptimizing Patient Flow: Innovation Series 2003Jeff SavageNo ratings yet
- Culture NegotiationsDocument17 pagesCulture NegotiationsShikha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Elaborare Modele de Rating in Conformitate Cu IFRS 9Document8 pagesElaborare Modele de Rating in Conformitate Cu IFRS 9MstefNo ratings yet
- Boonton Radio Corporation - The Notebook 12Document8 pagesBoonton Radio Corporation - The Notebook 12Luiz Roberto PascotteNo ratings yet