Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ap European History Timeline: Dylan Graves, Mcavoy, Period 8
Uploaded by
Connor MunroeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ap European History Timeline: Dylan Graves, Mcavoy, Period 8
Uploaded by
Connor MunroeCopyright:
Available Formats
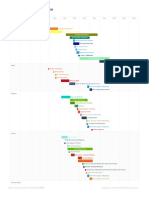
AP European History Timeline
Dylan Graves, McAvoy, Period 8
1300 1350 1400 1450 1500 1550 1600 1650 1700 1750 1800 1850 1900
Large Scale Events and
Movements
Hundred Years War
The Black Death
Itialian Renaissance
Northerern Renaissance
Commercial Revolution
Reformation
Scientific Revolution
Agricultural Revolution
Enlightenment
Industrial Revolution
French Revolution
Small Scale Events and
Movements
Petrach
Avignon Papacy
Boccaccio
Jacquerie
John Hus and the Hussites
Council of Constance
Erasmus
Copernicus
Columbian Exchange
Witch Hunts
Rule of King Henry VIII of England
German Peasant Revolts
King William of Orange the Silent
Council of Trent
Tycho Brahe
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
Rule of Mary I of England
French Wars on Religion
Shakespeare
Rule of James I of England
Dutch Revolt
Dutch Golden Age
Rule of King Henry IV of France
Rule of Louis XIII
Thirty Years' War
Blaise Pascal
Rule of Charles I of England
John Locke
English Civil War
Rule of Louis XIV
Mississippi Bubble
Voltaire
War of Spanish Succession
Rousseau
Rule of Fredrick the Great of Prussia
War of Austrian Succession
Seven Years' War
Rule of King Louis XVI of France
American Revolution
The Great Fear
National Convention
Reign of Terror
The Directory
Individual Dates
The Golden Bull
John Wycliffe
Invention of the Printing Press
Ferdinand and Isabella marry
Columbus's Discovery of the New World
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
Luthers posts his 95 Thesis
Diet of Worms
John Calvin and the Calvinists
The Prince is Published
Peace of Augsburg
St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre
Spanish Armada attacks
Edict of Nantes
Assassination of Henry IV of France
Principa Mathematica is published
Pragamatic Sanction
Treaty of Utrecht
Diplomatic Revolution
Estates General is Called and Meets
Nobles renounce feudal priveledge
Formation of the National Assembly
Tennis Court Oath
Storming of Bastille
Declaration of Rights of Man and Citizen
Women's March on Versailles
Constitution of the Year III
Napoleon becomes Emperor
Types of
Art
Mannerism
Dutch Golden Age Art
Boroque
Neoclassicalism
Rococo
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
Large Scale Events and Movements
Hundred Years War The Hundred Year's War was a war between England and France over
1337 - 1453 feudal disputes that lasted 116 years, with fighting divided over the course
of that time.
The Black Death A plague from rats imported from ships from Asia that caused the death of
1346 - 1400 1/3 of Europe
Itialian Renaissance Period of relative peace and intellect throughout Italy that lead to a great
1350 - 1527 deal of art and culture, ending with the sacking of Rome
Northerern Renaissance Until 1450, the Italian Renaissance had little effect on Northern Europe.
1450 - 1648 However, ideas began to spread, leading to a Renaissance period in
northern Europe and ending after the Thirty Years' War
Commercial Revolution Period of European colonization and mercantilism which lasted from 1488
1488 - 1776 with the first European sailing around the Cape of Good Hope and ended
around the time of the American Revolution in 1776
Reformation The Protestant Reformation began with Luther's posting of his 95 thesis
1517 - 1648 and lasted until 1648, after the Thirty Years' War
Scientific Revolution Period of Scientific Growth where many 'natural philosophers' studied and
1543 - 1789 learned a great deal about astronomy, biology, and other fields of science.
Agricultural Revolution Period where efficiency of agriculture allowed for better quality of life and
1600 - 1750 eventually lead to the Industrial Revolution
Enlightenment A period of enlightened growth and education leading into more modern
1700 - 1800 society, many philosopher's debated what an ideal society was and what
rights should exist.
Industrial Revolution A period in Europe of economic and technological expansion, resulting
1750 - 1900 from increase life expectancy and health caused by the Agricultural
revolution. Inventions such as the Spinning Jenny, the Water Frame, and
the Steam Engine helped progress this period.
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
French Revolution Period of French Revolt which lead to the Rise of Napolean Bonaparte and
1789 - 1799 utilized many Enlightenment ideas to attempt to formulate a new
government,
Small Scale Events and Movements
Petrach Considered father of Humanism for his humanistic papers and essays.
1304 - 1374
Avignon Papacy A time when the popes (Seven total) resided in Avignon, part of France,
1309 - 1376 and were under influence of France. Lasted until Gregory XI moved the
papacy to Rome.
Boccaccio Humanist who wrote much in agreement with Petrach.
1313 - 1375
Jacquerie Revolt during the summer of 1358 in France, Part of the Hundred Years'
March 1358 - July 1358 War
John Hus and the Hussites The Hussites were followers of the ideas of John Hus and were one of the
1403 - 1431 forerunner groups for the reformation
Council of Constance The council held to resolve the dispute over who the pope was. Resolved
1414 - 1418 in decision that Pope Martin V was the true pope.
Erasmus Humanist writer who supported religious toleration.
1466 - 1534
Copernicus Copernicus was a natural philosopher who was one of the first to propose
1473 - 1543 a formula for a heliocentric ideology.
Columbian Exchange Vast exchange of goods, culture, diseases, and ideas between Europe and
1492 - 1776 the New World, caused by the Commercial Revolution
Witch Hunts Period of 'Hunting Witches' in small towns, using witches as excuses for
1500 - 1750 bad things.
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
Rule of King Henry VIII of England Henry VIII of England separated the Church of England from the Roman
1509 - 1547 Catholic Church and established himself as the Supreme Head of the
Church of England.
German Peasant Revolts German peasants, inspired by Martin Luther, tried and failed to revolt.
1524 - 1527
King William of Orange the Silent Main leader of the Dutch revolt, excellent politique
1544 - 1584
Council of Trent Catholic attempt to stop the Protestant religion and to reform the Catholic
1545 - 1563 church.
Tycho Brahe Astronomer who accurately observed the heavens
1546 - 1601
Rule of Mary I of England "Bloody Mary". Very catholic ruler who was disliked in the public view
1553 - 1558 because of her Catholic faith that caused her to execute protestants.
French Wars on Religion Period of fighting within France between Catholics and Protestants
1562 - 1598 (Huguenots) that results in the Edict of Nantes
Shakespeare Codified English Language, wrote many plays and sonnets
1564 - 1616
Rule of James I of England
1567 - 1625
Dutch Revolt The revolts of the protestant Dutch against the Catholic Spain ending in
1568 - 1648 Dutch separation from Spain.
Dutch Golden Age After the Dutch Revolts, dutch trade, science, and are were superior to
1570 - 1650 nearly everyone else's at the time.
Rule of King Henry IV of France Politique who changed his religion and alter policies numerous times in
1589 - 1610 order to keep good control of his citizens. Is rumored to have said, "Paris is
well worth a Mass"
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
Rule of Louis XIII Along with Cardinal Richelieu, one of the first absolute monarchs,
1610 - 1643 removed rights of Huguenots, and was involved in the Thirty Years' War
against the Hapsburg.
Thirty Years' War The War that ended the Reformation with the Treaty of Westphalia. It had 4
1618 - 1648 stages and was between Catholics and Protestants.
Blaise Pascal Natural Philosopher who studied mathematics and physics.
1623 - 1662
Rule of Charles I of England Levied taxes without parliamentary consent, was considered tyrannical by
1625 - 1649 many, partially responsible for the English Civil War.
John Locke Enlightened thinker who urged that the role of government is to protect
1632 - 1704 the people from themselves. Used idea of Natural Rights, or rights that
everyone should be granted, an idea embraced by the French Revolution.
English Civil War Civil war in England which ended with the execution of King Charles, and
1642 - 1651 the establishment of the Commonwealth by Oliver Cromwell.
Rule of Louis XIV Centralized French government by building and maintaining nobles in
1643 - 1715 Versailles, waged successful wars, revoked the Edict of Nantes
Mississippi Bubble An economic bubble of Denmark that burst when the bank was forced to
1684 - 1720 stop payment on paper noted, destroying their economy.
Voltaire Cynical enlightened thinker who wrote much about the evils of the church
1694 - 1778 and advocated freedom of religion and expression.
War of Spanish Succession War for Spain and France to unite against most of Europe, ended with
1701 - 1714 decision that Philip could be King of Spain, but not of France as well.
Rousseau Possibly the most important figure in the Enlightenment, many of his ideas
1712 - 1779 on the Social Contract influenced French peasantry during the French
Revolution
Rule of Fredrick the Great of Prussia Brilliant military strategist who lead Prussia in any successful campaigns
1740 - 1786 during his reign
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
War of Austrian Succession War over whether Maria Theresa should keep the Austrian Throne. Ends
1740 - 1748 with Maria Theresa keeping the Austrian Throne.
Seven Years' War Ended with the Treaty of Paris of 1763, marking the beginning of British
1754 - 1763 Dominance outside Europe.
Rule of King Louis XVI of France King of France under whom the Revolution of France occurred, eventually
1774 - 1792 leading to his downfall.
American Revolution American colonies separated from Great Britain.
1775 - 1783
The Great Fear A period in the French Revolution where rumors spread that an armed
July 17, 1789 - August 5, 1789 group of peasants were roaming the countryside as part of the Revolution
National Convention French revolutionary committee which organized the Revolution and the
1792 - 1794 Committee of Public Safety.
Reign of Terror A time when the Committee of Public Safety was executing anyone who
September 5, 1793 - July 28, 1794 they though didn't support the Revolution... Which was about 25,000
people.
The Directory Frances revolutionary government
1795 - 1799
Individual Dates
The Golden Bull Established centralization of Holy Roman Empire, gave much power to
1356 Prussia.
John Wycliffe John Wycliffe, founder of the Lollards, translated the Bible into vernacular
1382 English, which sets up some basis for the Protestant reformation.
Invention of the Printing Press Printing press is invented by Gutenberg, revolutionizing the ability to print
1440 books, and spurring the Northern Renaissance.
Ferdinand and Isabella marry King Ferdinand, king of Spain, and Isabella, Queen of Castile, marry to end
October 18, 1469 hostilities between the nations.
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
Columbus's Discovery of the New World Columbus discovers America
1492
Luthers posts his 95 Thesis Martin Luther posts his 95 thesis on a church door, arguing that
October 31, 1517 indulgences are morally wrong. Begins Reformation
Diet of Worms A diet in the Holy Roman Empire which produced the Edict of Worms, that
1521 declared Martin Luther and his following to be outlaws, and his religion
banned.
John Calvin and the Calvinists John Calvin creates Calvinism, a Protestant religion based on pre-
1530 destination
The Prince is Published The Prince, by Machiavelli, is published, explaining what a good ruler
1532 should be.
Peace of Augsburg The decree that the leader of a region may choose between Lutheranism
1555 and Catholic. Cuius regio, eius religio in the Holy Roman Empire.
St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre Date when Roman Catholic mobs, during the French Religious War, killed
August 23, 1572 5,000 to 30,000 protestants.
Spanish Armada attacks The failed Spanish attack on England using naval forces. Because of a
August 8, 1588 storm and new technology and tactics, England won decisively.
Edict of Nantes Issued by Henry IV that allowed Calvinists of France many rights in
1598 attempt to promote civil unity.
Assassination of Henry IV of France Henry IV is assassinated by a Catholic fanatic.
May 14, 1610
Principa Mathematica is published Book by Isaac Newton during the Scientific Revolution stating Newton's
1687 Laws of Motion
Pragamatic Sanction An edict issued by Holy Roman Emperor Charles VI to insure his daughter
1713 inherited his land.
Treaty of Utrecht The treaty ending the War of Spanish Succession allowing for Philip to
1713 remain King of Spain, but not King of France.
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
Diplomatic Revolution Shift of support between England and France over Austria and Prussia,
1756 from Austria sided with England and Prussia sided with France to the
reverse.
Estates General is Called and Meets The Estates General meets in Versailles, and ends in the Tennis Court
1789 oath, sparking the French Revolution
Nobles renounce feudal priveledge In order to support the French Revolution and to avoid being persecuted
1789 by the peasants, Franh nobles revoke their feudal power.
Formation of the National Assembly The pivotal group of Third Estates Generals formed a group against the
June 17, 1789 French Monarchy, eventually beginning a revolution.
Tennis Court Oath One of the meetings of the National Convention, the group that began the
June 20, 1789 French Revolution. Happened after the National Convention was forced to
use a Tennis Court after being locked out of their meeting place.
Storming of Bastille Bastille is captured by peasants, rebellion begins
July 14, 1789
Declaration of Rights of Man and Citizen The documents that was influenced by the idea of 'Natural Rights' and
August 26, 1789 declared what rights every human should have.
Women's March on Versailles Paris women rioted over high bread prices and so they ransacked the
October 5, 1789 Palace of Versailles, which ended with King Louis XVI to return to Paris
with them.
Constitution of the Year III Constitution ratified by the National Convention to establish the Directory
August 22, 1795
Napoleon becomes Emperor Napoleon becomes Emperor, and that ends Semester 1!
May 18, 1804
Types of Art
Mannerism A type of art associated with the Italian Renassaince
1500 - 1580
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
Dutch Golden Age Art Art that highlights daily life using still lives, or paintings of inanimate
1560 - 1650 objects that emphasized peasant life.
Boroque Style of art that was very grand and furnished. Very ornate.
1580 - 1800
Neoclassicalism Art that was painted in the classical Greek and Roman style, depicting
1750 - 1800 contemporary scenes.
Rococo French style similar to the ornate baroque.
1750 - 1800
https://www.preceden.com/timelines/39150 Create your own timelines at Preceden.com.
You might also like
- English Radicals and the American RevolutionFrom EverandEnglish Radicals and the American RevolutionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- AP European History Review TimelineDocument16 pagesAP European History Review TimelinePriscilla RayonNo ratings yet
- AP Euro DBQ DatabaseDocument108 pagesAP Euro DBQ Databasenahuether4100% (1)
- Enlightened DespotsDocument19 pagesEnlightened Despotsapi-261847896100% (1)
- AP Euro Syllabus 2017-2018Document17 pagesAP Euro Syllabus 2017-2018Armin Chicherin100% (1)
- Ap Euro Study GuideDocument78 pagesAp Euro Study GuideArianna Hunter0% (1)
- AP European History Terms Chambers)Document73 pagesAP European History Terms Chambers)RebeccaDealNo ratings yet
- WH9 Enlightenment UnitHandoutDocument5 pagesWH9 Enlightenment UnitHandoutAdam NeblockNo ratings yet
- AP Euro WWIIDocument11 pagesAP Euro WWIIMatthew SamilowNo ratings yet
- European Exploration TestDocument6 pagesEuropean Exploration Testapi-336784766No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Reformation and Religious Warfare in The Sixteenth CenturyDocument12 pagesChapter 13 Reformation and Religious Warfare in The Sixteenth Centurybella___rose0% (1)
- Scientific Revolution QuestionsDocument3 pagesScientific Revolution QuestionsGideonRichterNo ratings yet
- APEC Chapter 15 NotesDocument12 pagesAPEC Chapter 15 NotesSteven ChenNo ratings yet
- AP European History Anchor Dates PDFDocument4 pagesAP European History Anchor Dates PDFramya100% (1)
- AP Euro Chapter 11 Study GuideDocument6 pagesAP Euro Chapter 11 Study Guide3l39h4ntNo ratings yet
- The Mongol Impact On China - Europe - and The Middle EastDocument39 pagesThe Mongol Impact On China - Europe - and The Middle Eastinsightsx100% (1)
- Questions 1-3 Refer To The Image Below by Casper David Friedrich Entitled A Walk at Dusk, C. 1830-1835Document22 pagesQuestions 1-3 Refer To The Image Below by Casper David Friedrich Entitled A Walk at Dusk, C. 1830-1835Kool BeansNo ratings yet
- French RevolutionDocument57 pagesFrench RevolutionAvinash TietlerNo ratings yet
- World History & Geography (1st Tri) - 2011 Study GuideDocument5 pagesWorld History & Geography (1st Tri) - 2011 Study GuideJosh KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Palmer, Colton, A History of The Modern WorldDocument21 pagesPalmer, Colton, A History of The Modern Worldmsalgueiro98330550% (2)
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Michael ChiuNo ratings yet
- AP European History 2004 MC Exam AnswersDocument1 pageAP European History 2004 MC Exam AnswersresilientnightNo ratings yet
- Absolutism and Constitutional IsmDocument24 pagesAbsolutism and Constitutional IsmTin LuuNo ratings yet
- A History of Western Society - Chapter 13 NotesDocument13 pagesA History of Western Society - Chapter 13 Notesmattlcordell100% (1)
- The Protestant ReformationDocument3 pagesThe Protestant Reformationdeez IINo ratings yet
- Modern World TimelineDocument3 pagesModern World Timelineapi-327452561No ratings yet
- AP Euro Wars ChartDocument5 pagesAP Euro Wars ChartLilaa Lee100% (1)
- AP Europe Cram Packet 09Document139 pagesAP Europe Cram Packet 09Perry01No ratings yet
- AP World History Unit Three: 1450-1750 Homework Sheet #7 MondayDocument4 pagesAP World History Unit Three: 1450-1750 Homework Sheet #7 Mondaykqmurphy100% (1)
- AP Euro Ch. 15 NotesDocument2 pagesAP Euro Ch. 15 NotesJSun YiNo ratings yet
- European Exploration and ColonizationDocument47 pagesEuropean Exploration and ColonizationHenrJT1728100% (7)
- AP Euro Chp. 12 PacketDocument12 pagesAP Euro Chp. 12 PacketJohan AriasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 Scientific Revolution-1Document4 pagesWorksheet 1 Scientific Revolution-1Khue TiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Packet - History French RevolutionDocument64 pagesAssignment Packet - History French RevolutionAnthony TanNo ratings yet
- AP Euro History Review ChartsDocument12 pagesAP Euro History Review ChartsJakBlackNo ratings yet
- Comparing Imperialism in AfricaDocument1 pageComparing Imperialism in Africaapi-276669719100% (1)
- Spice ChartDocument10 pagesSpice Chartapi-296326751No ratings yet
- Ap World History Course OutlineDocument5 pagesAp World History Course Outlineapi-293851161100% (1)
- APWH CH 10-12 Test Review With AnswersDocument3 pagesAPWH CH 10-12 Test Review With Answersmelissa_chow_1No ratings yet
- AP European History 2004 MC ExamDocument18 pagesAP European History 2004 MC Examresilientnight100% (4)
- AP Euro - Ch. 13 OutlineDocument8 pagesAP Euro - Ch. 13 OutlineStephanie Chiu71% (7)
- Bentley CH 20 - Western Europe During The High Middle AgesDocument11 pagesBentley CH 20 - Western Europe During The High Middle Agesapi-242081192100% (1)
- AP Euro Study Guide Pack 2021 v2Document18 pagesAP Euro Study Guide Pack 2021 v2LittlenessimsNo ratings yet
- AP Euro Writing PacketDocument32 pagesAP Euro Writing Packetjoero51No ratings yet
- Keck's AP European SyllabusDocument9 pagesKeck's AP European SyllabusJonathan Daniel KeckNo ratings yet
- Ch. 20 Brinkley 14Document34 pagesCh. 20 Brinkley 14baashii4No ratings yet
- Making Europe2Document963 pagesMaking Europe2Negar SBNo ratings yet
- AP European OutlineDocument19 pagesAP European Outlinemr3lusiveNo ratings yet
- Absolutism & Enlightenment 2Document41 pagesAbsolutism & Enlightenment 2IsabellaNo ratings yet
- AP Euro Chapter 1 Section 1 NotesDocument5 pagesAP Euro Chapter 1 Section 1 Noteskelly100% (1)
- AP European History: Free-Response QuestionsDocument14 pagesAP European History: Free-Response QuestionsAnitaNo ratings yet
- Malcolm H. SternDocument4 pagesMalcolm H. SternGregory HooNo ratings yet
- Sovereignty and PartitionDocument31 pagesSovereignty and PartitionThomas KNo ratings yet
- Sciensctist ChartDocument4 pagesSciensctist ChartWillSmithNo ratings yet
- 4.1 The Divisive Politics of SlaveryDocument12 pages4.1 The Divisive Politics of SlaveryAPTeacherNo ratings yet
- 3 Siglo XVIIDocument16 pages3 Siglo XVIIjewiki7470No ratings yet
- Essential Vocabulary From The AP European History Key ConceptsDocument8 pagesEssential Vocabulary From The AP European History Key Conceptsise eggfNo ratings yet
- History of FranceDocument496 pagesHistory of FrancevNo ratings yet
- First Draft MindmapDocument1 pageFirst Draft Mindmapapi-335646206No ratings yet
- Heart of Darkness Full CH 1Document4 pagesHeart of Darkness Full CH 1Connor MunroeNo ratings yet
- Heart of Darkness VocabularyDocument2 pagesHeart of Darkness VocabularyConnor MunroeNo ratings yet
- Heart of Darkness Chapter 1 QuestionsDocument2 pagesHeart of Darkness Chapter 1 QuestionsConnor MunroeNo ratings yet
- Heart of Darkness Chapter 1 Questions - ContinuedDocument3 pagesHeart of Darkness Chapter 1 Questions - ContinuedConnor MunroeNo ratings yet
- Cavour and Garibaldi Italian UnifcationDocument12 pagesCavour and Garibaldi Italian UnifcationConnor MunroeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8.1 Homework Answers PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 8.1 Homework Answers PDFConnor MunroeNo ratings yet
- NYS 50-A - Letter From Mayor Steve NobleDocument3 pagesNYS 50-A - Letter From Mayor Steve NobleDaily FreemanNo ratings yet
- 3 RDDocument758 pages3 RDArun Pravin APNo ratings yet
- Del PilarDocument3 pagesDel PilarGeroldo 'Rollie' L. Querijero100% (1)
- SAN JUAN DE DIOS Emp Association Vs NLRCDocument2 pagesSAN JUAN DE DIOS Emp Association Vs NLRCBest KuroroNo ratings yet
- Kolom Hitung Nilai Raport Semester 1Document2 pagesKolom Hitung Nilai Raport Semester 1Muthia Amelia PutriNo ratings yet
- Rise of Dictatorships and Beginnings of WWIIDocument19 pagesRise of Dictatorships and Beginnings of WWIIAnuradha MayanikarNo ratings yet
- Veer Kunwar Singh University, Ara (Bihar) : Under-Graduate (UG) Admission Registration FormDocument2 pagesVeer Kunwar Singh University, Ara (Bihar) : Under-Graduate (UG) Admission Registration FormSanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Micro Chapter 2 Study Guide Questions 14eDocument6 pagesMicro Chapter 2 Study Guide Questions 14eBeauponte Pouky MezonlinNo ratings yet
- Europe Plunges Into War: Chapter 29, Section 2Document50 pagesEurope Plunges Into War: Chapter 29, Section 2Eftichia KatopodiNo ratings yet
- Animal Wellness Action ReportDocument31 pagesAnimal Wellness Action Reportkbarrier214No ratings yet
- Roque Benitez V Santa Fe Moving and Relocation SevicesDocument3 pagesRoque Benitez V Santa Fe Moving and Relocation SevicesbrendamanganaanNo ratings yet
- Essay OutlineDocument4 pagesEssay OutlineAyaz Muhammad100% (1)
- Helmut ReisenDocument3 pagesHelmut ReisenheiNo ratings yet
- Twitter FilingDocument32 pagesTwitter Filingjeff_roberts881100% (1)
- Delos Santos V IAC DigestDocument1 pageDelos Santos V IAC DigestglainarvacanNo ratings yet
- Website Evaluation ED517 Module 6Document3 pagesWebsite Evaluation ED517 Module 6Erin WhitneyNo ratings yet
- Japan Visa Application FormDocument2 pagesJapan Visa Application FormShruti SinghNo ratings yet
- Federalism in The PhilippinesDocument43 pagesFederalism in The PhilippinesAgustinVillareal100% (3)
- Ded Order 77 S 2009Document5 pagesDed Order 77 S 2009Mia Luisa EnconadoNo ratings yet
- Class Program Sy 2019 2020Document5 pagesClass Program Sy 2019 2020Harold HusayanNo ratings yet
- Marriage Is The Process by Which Two People Make Their Relationship PublicDocument2 pagesMarriage Is The Process by Which Two People Make Their Relationship PublicKendall JennerNo ratings yet
- HL - g01 - readerPRINT - Lev1 - bk2 - My First Book - EnglishDocument28 pagesHL - g01 - readerPRINT - Lev1 - bk2 - My First Book - EnglishBukelwa MabuyaNo ratings yet
- Body Image Report EnglsihDocument25 pagesBody Image Report EnglsihnownowNo ratings yet
- Makalah Seminar Di Bogor 16-17 JUni 2010 RevisiDocument5 pagesMakalah Seminar Di Bogor 16-17 JUni 2010 RevisiRahmat PramulyaNo ratings yet
- Most Corrupt 2011: Rep. David Rivera (R-FL)Document9 pagesMost Corrupt 2011: Rep. David Rivera (R-FL)CREWNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Adjoining OwnersDocument1 pageAffidavit of Adjoining Ownersred ramos75% (4)
- Harvard Model United Nations: A Background Guide For The Special Session On TerrorismDocument40 pagesHarvard Model United Nations: A Background Guide For The Special Session On TerrorismRenzo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Washington D.C. Afro-American Newspaper, February 20, 2010Document28 pagesWashington D.C. Afro-American Newspaper, February 20, 2010The AFRO-American NewspapersNo ratings yet
- Application Form For International Students: 宗教信仰 ReligionDocument3 pagesApplication Form For International Students: 宗教信仰 ReligionTRUST ZHOUNo ratings yet
- Education From A Gender Equality PerspectiveDocument18 pagesEducation From A Gender Equality Perspectiveapi-254645679No ratings yet
- Discovering Daniel: Finding Our Hope in God’s Prophetic Plan Amid Global ChaosFrom EverandDiscovering Daniel: Finding Our Hope in God’s Prophetic Plan Amid Global ChaosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Habits for a Sacred Home: 9 Practices from History to Anchor and Restore Modern FamiliesFrom EverandHabits for a Sacred Home: 9 Practices from History to Anchor and Restore Modern FamiliesNo ratings yet
- The Freedom of Self-Forgetfulness: The Path to True Christian JoyFrom EverandThe Freedom of Self-Forgetfulness: The Path to True Christian JoyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (195)
- The Overcomers: God's Vision for You to Thrive in an Age of Anxiety and OutrageFrom EverandThe Overcomers: God's Vision for You to Thrive in an Age of Anxiety and OutrageNo ratings yet
- The Well-Watered Woman: Rooted in Truth, Growing in Grace, Flourishing in FaithFrom EverandThe Well-Watered Woman: Rooted in Truth, Growing in Grace, Flourishing in FaithRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (66)
- High Road Leadership: Bringing People Together in a World That DividesFrom EverandHigh Road Leadership: Bringing People Together in a World That DividesNo ratings yet
- Power Moves: Ignite Your Confidence and Become a ForceFrom EverandPower Moves: Ignite Your Confidence and Become a ForceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Becoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonFrom EverandBecoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1484)
- Imagine the God of Heaven: Near-Death Experiences, God’s Revelation, and the Love You’ve Always WantedFrom EverandImagine the God of Heaven: Near-Death Experiences, God’s Revelation, and the Love You’ve Always WantedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (31)
- Bait of Satan: Living Free from the Deadly Trap of OffenseFrom EverandBait of Satan: Living Free from the Deadly Trap of OffenseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (314)
- The Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYFrom EverandThe Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- His Needs, Her Needs: Building a Marriage That LastsFrom EverandHis Needs, Her Needs: Building a Marriage That LastsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (100)
- I Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionFrom EverandI Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionNo ratings yet
- Conversations with God: An Uncommon Dialogue, Book 1From EverandConversations with God: An Uncommon Dialogue, Book 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (68)
- Now and Not Yet: Pressing in When You’re Waiting, Wanting, and Restless for MoreFrom EverandNow and Not Yet: Pressing in When You’re Waiting, Wanting, and Restless for MoreRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- For Women Only, Revised and Updated Edition: What You Need to Know About the Inner Lives of MenFrom EverandFor Women Only, Revised and Updated Edition: What You Need to Know About the Inner Lives of MenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (274)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Tired of Being Tired: Receive God's Realistic Rest for Your Soul-Deep ExhaustionFrom EverandTired of Being Tired: Receive God's Realistic Rest for Your Soul-Deep ExhaustionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Captive in Iran: A Remarkable True Story of Hope and Triumph amid the Horror of Tehran's Brutal Evin PrisonFrom EverandCaptive in Iran: A Remarkable True Story of Hope and Triumph amid the Horror of Tehran's Brutal Evin PrisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (141)
- Create a Life You Love: How to Quiet Outside Voices So You Can Finally Hear Your OwnFrom EverandCreate a Life You Love: How to Quiet Outside Voices So You Can Finally Hear Your OwnNo ratings yet
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Forgotten God: Reversing Our Tragic Neglect of the Holy SpiritFrom EverandForgotten God: Reversing Our Tragic Neglect of the Holy SpiritRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (530)