Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 15 Computers and Basic Psychological Science in Testing
Uploaded by
Ruby Jinn Makinano BarreteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 15 Computers and Basic Psychological Science in Testing
Uploaded by
Ruby Jinn Makinano BarreteCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 15 COMPUTERS AND BASIC PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE IN TESTING
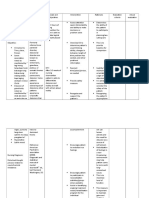
NAME OF TEST ACRONYM AGE DESCRIPTION MEASURES/ASSESS… STRENGTH/LIMITATION
AUTHOR/PUBLISHER APPLICABLE
The Fear Survey FSS Children as the oldest and most researched of the measuring specific has been subjected to anything
Schedule well as adults cognitive-behavioral self-report procedures phobias close to an adequate
Akutagawa (1956) Items are typically related to situations that attempts to identify psychometric analysis
involve fear and avoidance behaviors those situations that
elicit fear and thus
avoidance
The Assertive Behavior ABSS Self-report questionnaire for assertiveness
Inventory Schedule
Self-Report Battery
Cautela and Upper
(1976)
The Dysfunctional DAS Identifies beliefs that The validity of the scale is
Attitude Scale might interact with a supported by a variety of factor
A. T. Beck’s (1967, 1976, stressor to produce analytic data.
2002) psychopathology
Irrational Beliefs Test IBT 100-item to measure irrational widespread use in clinical setting
The IBT requires subjects to indicate their beliefs and has received considerable
R.A. Jones level of agreement or disagreement with each attention
of the 100 items on a 5-point scale (e.g., “I test-retest coefficients for short
frequently worry about things over which I intervals ranging from .48 to .90
have no control”). Half of the items indicate for individual scales and .88 for full
the presence of a particular irrational belief; scale
the other half, its absence. The validity documentation is
weak, both related to anxiety and
depression
Irrational Beliefs IBI To improve upon some of the weaknesses of Irrational beliefs Consistent psychometric
Inventory the IBT properties across several cultures
Measures cognition rather than affect Internal consistency is acceptable,
Uses a 5-point scale and consists of five and the five subscales were found
subscales: worrying, rigidity, need for to be independent of each other.
approval, problem avoidance, and emotional Useful in clinical and research
irresponsibility settings when exploring the role of
irrational beliefs in obsessive-
compulsive disorder, social
phobias, and therapy for
depression
Chapter 16 Testing in Counseling Psychology
NAME OF TEST ACRONYM AGE DESCRIPTION MEASURES/ASSESS… STRENGTH/LIMITATION
AUTHOR/PUBLISHER APPLICABLE
Strong Vocational SVIB Created after the criterion-group approach method patterns of interest
Interest Blank Items in the SVIB were weighted according to how
frequently an interest occurred in a particular
occupational group as opposed to how frequently
it occurred in the general population.
399 items were related to 54 occupations for men.
A separate form presented 32 different
occupations for women.
Strong-Campbell SCII New version of SVIB Occupational Interest
Interest Inventory response to the shortcomings of the SVIB
most widely used interest inventory today
D. P. Campbell. 1974 Items from both the men’s and women’s forms of
the SVIB were merged into a single form that
included scales devoid of gender bias
The SCII in its current form is divided into seven
parts has 325 items, to which a person responds
“like,” “dislike,” or “indifferent”
Score Summaries (4 scales):
[1] general themes based on Holland’s six
personality types (Realistic, Investigative, Artistic,
Social, Enterprising, Conventional),
[2] administrative indexes, [3] Person’s basic
interests, [4] Occupational Scales
The SCII is no longer used very much because it
has been replaced by newer tests
The Campbell Interest CISS Degree of interest and shorter and more efficient than
and Skill Survey Degree of skill the older SCII.
Campbell, 1992 Uses the theoretical structure of
Holland
Extensive evidence of reliability
and validity
New evidence continues to
support the validity of the CISS
Strong Interest SII Interest Substantial concurrent validity
Inventory (new) for variety of college major
choices
The basic interest scales were
the best predictors of selection
of major
The Kuder KOIS High school Previously known as the Kuder Preference Survey Occupational interest Psychometric properties are
Occupational Interest age Second most widely used interest inventory today very good
Survey one of several interest scales that grew out of the Short-term reliabilities tend to
original Kuder Preference Survey published in be high
1939 Scores are stable as long as 30
offered a unique alternative to the SVIB, SCII, and years
CISS Predictive validity for college
Presents the test taker with 100 triads (sets of majors is good
three) of alternative activities. For each triad, the Maybe quite useful for guidance
test taker selects the most preferred and the least decisions for high school and
preferred alternatives. Scoring of the KOIS scales college students
gives the same information yielded by the earlier
Kuder Preference Surveys—data on 10 general
occupational interests (e.g., outdoor interests
versus social service interests).
separate norms for men and women; separate
scales for college Majors
the National Career Assessment Service became
the international distributor for the KOIS
The report is divided into four sections:
[1] summarizes the dependability of the results,
[2] rank orders interest patterns in comparison to
the normative sample of men and women,
[3] ranks the test taker in relation to men and
women who are employed in different occupations
and are satisfied with their career choices,
[4] matches patterns of interests to those of
students who have selected different college
majors.
In its current form KOIS examines the similarity
between a test taker’s interests and those of
people employed in various occupations in a
manner much like that of the SCII and CISS.
Suggesting which occupational group might work
best with a test taker’s interests
May help students choose a Major
Contains non-traditional occupations for men and
women
Jackson Vocational Used for career education and counselling of high Occupational interest Reliability for 10 general
Interest Survey (JVIS) school and college students occupational themes is
Used to plan careers for adults including those approximately .89 and that the
Douglas Jackson who want to make midlife career changes. test-retest stability of the 44
Consists of 289 statements describing job-related basic interest scales ranges
activities from .84 to .88
It takes 45 minutes to complete and the scoring Validity studies that JVIS
yields 34 basic interest scales predicts university and
The test construction carefully avoided gender academic majors more
bias accurately than do most other
Employ forced choice formats in which the interest inventories.
respondent must indicate a preference between
two equally popular interests.
Hand-scored and machine scored
Career Assessment CAI designed for people not oriented toward careers Career choice Has a desirable psychometric
Inventory requiring college or professional training properties
written at the sixth-grade reading level and is Scores tend to be stable
designed for the 80% of U.S. citizens who have Culturally fair, eliminate gender
Charles B. Johansson fewer than four years of postsecondary education bias
Each test taker is evaluated on Holland’s six
occupational theme scales: realistic, investigative,
artistic, social, enterprising, and conventional.
The second portion of the CAI report describes
basic interests. Each test taker is evaluated in 22
specific areas, including carpentry, business, and
food service. The third section of the report is a
series of occupational scales. Scores for the 89
occupational scales on the CAI were obtained by
using a criterion-keying method. The interests of
the test takers are matched to the interests of
truck drivers, secretaries, waitpersons, and so
forth.
Somewhat the working person’s working survey
The Self-Directed SDS self-scored, and self-interpreted vocational Career interest Test takers can score their own
Search interest inventory Readiness for career test
attempts to simulate the counseling process by decision making and Allow test taker to interact with
J. L. Holland allowing respondents to list occupational readiness to obtain computer-assisted guidance
aspirations, indicate occupational preferences in guidance system
six areas, and rate abilities and skills in these Available on-line and users
areas appear to be more satisfied
personal career theorythe test takers can score than those who respond to the
their own inventory and calculate six summary paper-and-pencil version
scores, which they can use
to obtain codes that reflect the highest areas of
interest linked to an occupational finder
Includes 228 items. Six scales with 11 items each
describe activities. Another 66 items assess
competencies, with six scales of 11 items each.
Occupations are evaluated in six scales of 14
items each. Self-estimates are obtained in two
sets of six ratings.
Chapter 17 – Testing in Health Psychology and Health Care
NAME OF TEST ACRONYM AGE DESCRIPTION MEASURES/ASSESS… STRENGTH/LIMITATION
AUTHOR/PUBLISHE APPLICABLE
R
Halstead-Reitan Adults The process of habilitation available in different versions for
Neuropsychological (different requires at least seven steps: children and adults
Battery version for (1) assessment of the child, (2) Disadvantage: requires 8 to 12
children) assessment of the hours to administer
Ward Halstead and environment, (3) predictions A large number of studies validate
Ralph M. Reitan about short- and long-term the Halstead and Reitan
outcomes, (4) development of procedures
an ideal plan, (5) assessment The battery can assist in localizing
of resources, (6) development injury in either the left or right
of a realistic intervention plan, hemisphere of the brain.
and (7) ongoing assessment. New methods of brain imaging (MRI
Patients assessed by the and CT scan) may be more efficient
Halstead-Reitan battery often for locating injury
receive the full Minnesota
Multiphasic Personality
Inventory (MMPI) to evaluate
their emotional state in
response to a medical
situation.
The battery also includes a full
WAIS.
Most of the studies show that
performance on specific
subtasks of the Halstead-
Reitan battery is associated
with dysfunction in one of the
two hemispheres of the brain.
Components of the Halstead-
Reitan Neuropsychological
Battery for Adults: [1] Halstead
category test [2] Tactual test
(time, memory, localization) [3]
Rhythm test [4] Speech-
sounds perception test [5]
Finger oscillation test [6]
Related Procedures [7] Trail-
making test [8] Strength-of-grip
test [9] Sensory–perceptual
examination
Luria-Nebraska Adults Luria did not acknowledge that neuropsychological assessment
Neuropsychological (different any single area was solely intuitive judgments about deficits in
Battery version for responsible for any particular functional systems
children) behavior. Instead, Luria saw estimate the area of the brain
Luria, 1966, 1973 the brain as a functional damaged by a tumor or lesion
system, with a limited number
of brain areas involved in each
behavior. Each area in the
functional system might be
considered a necessary link in
a chain. If any link is injured,
the total system will break
down.
Pluripotentiality: states that
any one center in the brain can
be involved in several different
functional systems. Multiple
systems might be responsible
for the same behavior. Thus, if
a child’s injury affects one
system, another system may
take over.
includes 269 items that are
divided into 11 subsections:
Motor Functions, Rhythm,
Tactile, Visual, Receptive
Speech, Expressive Speech,
Reading, Arithmetic Skills,
Memory, Intellectual
Processes
Golden (1981) developed a
standardized version of Luria’s
procedures.
California Verbal CVLT Adults a relatively new approach to determines how errors are made in Versions for both the PC and the
Learning Test clinical neuropsychology that learning tasks Macintosh are available
builds on research in identify different strategies, one can administer it either in a
psychological testing, cognitive processes, and errors that are paper-and-pencil form or with a
psychology, and computer associated with specific deficits microcomputer
science attempts to link memory deficits with In the computer-assisted form of
includes other features derived impaired performance on specific the test, the examiner can enter
from experimental cognitive tasks for people who have known responses directly into the
psychology neurological problems computer using a single key or a
assesses various variables, including light pen to touch the words on a
levels of recall and recognition, monitor screen. This greatly
semantic and serial strategies, serial facilitates and speeds up the
position effects, learning rates across scoring process.
trials, consistency of item recall the test correlates with other
across trials, degree of vulnerability measures such as the Wechsler
to proactive and retroactive memory scale
interference, retention of information factor analysis studies of the CVLT
over short and long delays, and suggest independent factors for
learning errors in recall and learning strategy, acquisition rate,
recognition serial position, discriminability, and
learning performance.
The diversity of deficits identified by
the CVLT could not be identified
using more-traditional psychometric
tests
The CVLT has been used to
compare patients with Alzheimer’s
disease, Korsakoff’s syndrome, and
Huntington’s disease.
it allows a more precise evaluation
of the nature of the problems than
do other tests.
California Verbal CVLT-C Children aged individually administered can be used to evaluate mild to The test was standardized on a
Learning Test—C 5–16 In a typical testing session, the severe learning disabilities, attention large national sample.
child may receive a list of 15 deficit disorder (ADD), mental Internal consistency and alpha
words on Monday and an retardation, and other neurological reliabilities for the test are generally
interference list of 15 words on disorders high (usually above .80 for all age
Tuesday. After the interference provides information for the levels).
list, the child is tested on the diagnosis of psychiatric disorders provides substantially more
Monday list. After a 20-minute assesses both recall and recognition diagnostic information
delay, a nonverbal test is of words It is beginning to find a variety of
administered, followed by tests clinical uses. For example, recent
of long-delay free recall and studies suggest that the CVLT can
long-delay cued recall, then a be used to detect whether patients
test designed to assess are faking head injury in order to
recognition of the words that gain benefits
were administered the day
before.
Produce several different
scores including total recall,
learning strategy, serial
position effect, learning rate,
consistency of item recall,
proactive and retroactive
interference, and retention
over long and short delays.
Automated ANAM quick computerized The measure has now been used in
Neuropsychological interpretation of a variety of clinical populations
Metrics neuropsychological tests including studies of patients with
ANAM can efficiently screen multiple sclerosis, lupus,
people with cognitive changes Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s
includes a variety of different disease, brain injury, and migraine
tasks including code headache.
substitution, code substitution responsive to cognitive changes
recognition, matching two that result from neurological
samples, mathematics, disorders
running memory, and logical The reliability of performance on
reasoning. these tasks tends to be in the
moderate range with few
coefficients above .8. Studies have
suggested that the math and
running memory tasks are
associated with measures that
would be expected to correlate with
cognitive functioning. These include
performances on time limited
attention tasks and working
memory tasks. Overall, there is
reasonably good evidence for the
validity of the ANAM
The State-Trait STAI provides two separate scores: the two components clearly assess STAI trait scale correlates well with
Anxiety Inventory one for state anxiety (A-State) different aspects of anxiety other measures of trait anxiety
and another for trait anxiety Good evidence exists for the
(A-Trait) validity and the reliability of the
The STAI A-Trait scale STAI. Test–retest reliabilities range
consists of 20 items. On a 4- from .73 to .86 for the trait scale.
point scale, subjects indicate The state scale, which is supposed
how they generally feel about to be inconsistent over time, indeed
each item. A similar set of has low test–retest reliability (.16
items is used to evaluate the to .54).
A-State. Other scales that attempt to
The STAI trait scale has been measure trait anxiety do not do so
correlated with the Taylor well.
Manifest Anxiety Scale; it was Each component of the STAI
also associated with another appears to measure what it is
trait-anxiety scale known as supposed to measure, and the two
the Institute for Personality components (A-State and A-Trait)
and Ability Testing (IPAT) clearly assess different aspects of
Anxiety Scale for the same anxiety.
groups of college students and The STAI is useful because
psychiatric patients. behavior is influenced by both
situations and personality traits.
Evidence suggests that the STAI is
reliable and that most items perform
well, even when the test takers are
in extremely stressful situations
Recent factor analysis studies have
continued to show the two-factor
(A-State and A-Trait) structure.
The STAI has been translated into
many different languages and is
available in both adult and
children’s versions.
There are good psychometric
evaluations of many of these forms.
There are also comparisons
showing modest evidence for the
validity of parent reports of their
children’s anxiety. The STAI has
been validated for older adults and
has been shorted for use in special
populations, such as critically ill
adults.
The Test Anxiety TAQ The grandparent of all test- assesses a person’s predisposition Over the years, people have
Questionnaire anxiety measures to think or act in a way that interferes discovered some inadequacies with
outgrowth of the Mandler and with the completion of a task this questionnaire and have
Seymour Sarason Sarason (1952) test-anxiety measure assesses anxiety transformed it into other measures
theory associated with situations such as the Test Anxiety Scale
The theory distinguishes The reliability of the TAQ is high.
between two different drives Early studies using a group of 100
(Learned Task Drive and Yale students demonstrated that
Learned Anxiety Drive), or the split-half reliability was .99, and
motivational states, that a coefficient of .82 was obtained in
operate in test-taking a test–retest study over a 6-week
situations. period.
37-item questionnaire
The Test Anxiety TAS Irwin Sarason, the brother of determines which people are highly One early criticism of the TAQ was
Scale Seymour Sarason (the original test anxious that it dealt with state anxiety rather
co-developer of test-anxiety than trait anxiety.
Irwin Sarason, 1958 theory), rewrote the TAQ items The first revision of the TAQ began
in a true–false format to create to consider individual or personality
the 21-item Test Anxiety Scale differences in test anxiety.
(TAS). Since the introduction of the TAS,
the focus on the test-anxiety Sarason has accumulated
problem shifts from the convincing evidence of a
situation in the TAQ to the meaningful distinction between
person in the TAS more and less test-anxious
individuals.
TAS makes meaningful distinctions
among people; they also suggest
that school performance may be
associated with personality
characteristics other than
intelligence.
An extensive array of the literature
supports the validity of the TAS as
a measure of personality. The TAS
shows that a combination of high
trait anxiety and high environmental
anxiety produce the most test
anxiety.
Achievement AAT An 18-item scale that gives measurement of test anxiety
Anxiety Test scores for two different
components of anxiety:
Alpert and Haber facilitating and debilitating.
(1960). [facilitating anxiety is helpful,
and debilitating anxiety is
harmful]
Test Anxiety TAICA younger well validated measure newer measure
Inventory students who directed toward younger
for Children and may also students who may also have
Adolescents have learning learning disabilities
disabilities
Ways of Coping A 68-item checklist.
Scale The scale includes seven
subscales for problem solving,
Lazarus, 1995; growth, wishful thinking,
Lazarus & Folkman, advice seeking, minimizing
1984 threat, seeking support, and
self-blame. (can be divided
into problem-focused and
emotion-focused strategies)
Ways of Coping one of the most widely used Some researchers have offered
questionnaire measures in health psychology criticism. For example, some
studies have failed to replicate the
basic factor structure.
Coping Inventory 33-item measure derived from
clinical interview data
Horowitz & Wilner, 3 categories of items: [1]
1980 describes activities and
attitudes that people use to
avoid stress. [2] involves items
that characterize strategies for
working through stressful
events. [3] considers
socialization responses, or
how each strategy would help
the respondent cope with a
specific stressful event.
Outcome Study SF-36 outcome measure The SF-36 grew out of work by the
Short Form-36 includes eight health concepts: RAND Corporation and the Medical
physical functioning, role- Outcomes Study (MOS)
physical, bodily pain, general The SF-36 can be either
health perceptions, vitality, administered by a trained
social functioning, role- interviewer or self-administered.
emotional, and mental health it is brief, and there is substantial
evidence for its reliability and
validity.
The SF-36 can be machine-scored
and has been evaluated in large
population studies.
The reliability and validity of the SF-
36 are well documented
Disadvantage: it does not have
age-specific questions, and one
cannot clearly determine whether it
is equally appropriate across age
levels
Nottingham Health NHP has two parts: The first The NHP is consumer-based and
Profile includes 38 items divided into arises from definitions of health
six categories: sleep, physical offered by individuals in the
mobility, energy, pain, community.
emotional reactions, and social this scale uses language that is
isolation. The second part of easily interpreted by people in the
the NHP includes seven community and conforms to
statements related to the minimum reading requirements.
areas of life most affected by Substantial testing has been
health: employment, performed on the NHP; however,
household activities, social life, the NHP does not provide relative-
home life, sex life, hobbies and importance weightings across
interests, and holidays dimensions. As a result, it is difficult
to compare the dimensions directly
with one another
Medical College MCAT a rite of passage for entrance identify students who are most likely administered by computer
Admission Test into medical school. to succeed with a difficult medical The test is quite demanding and it
Starting in 2015, the MCAT will school curriculum takes 5.5 hours to complete.
undergo a significant change. the current version tests physical and Analysis of data
The most important series of biological sciences, verbal reasoning, from older MCATs had suggested that the
changes will involve a new and writing skills writing samples were not valid predictors of
section focusing on several The new psychological, social, and medical school success.
conceptual areas from the biological foundations of behavior The new critical analysis and
behavioral and social sciences. section of the test assesses a wide reasoning skills section
The change in the MCAT follows range of knowledge and draws upon uses traditional test formats and presents
a comprehensive review by a concepts from psychology, sociology, passages that need to be read.
series of prestigious groups biology, research methods, and
including the Institute of statistics.
Medicine of the National Test items then assess the test
Academy of Sciences and the takers ability to comprehend the
American Association of Medical topics in the passages. These topics
Colleges. include ethics and philosophy, cross-
The new MCAT also includes a cultural studies, and population
section on critical analysis and health.
reasoning. This section was
added to replace the writing
samples sections.
The plan for the new MCAT was
released in 2011, but the new
test will not be used until 2015.
Chapter 18 – Testing in Business and Industrial Settings
NAME OF TEST ACRONYM AGE DESCRIPTION MEASURES/ASSESS… STRENGTH/LIMITATION NAME OF TEST
AUTHOR/PUBLISHE APPLICABLE AUTHOR/PUBLISHER
R
Taylor-Russell To use this you must personnel selection The Taylor-Russell tables also
Tables have the following help reveal the futility of
information: [1] Definition certain types of assessment
of success [2] procedures.
Determination of base
rate [3] Definition of
selection ratio [4]
Determination of validity
coefficient
give the likelihood that a
person selected on the
basis of the test score will
actually succeed
The Myers-Briggs MBTI I. B. Myers to determine where people fall The MBTI is widely used and
Type Indicator and K. C. on the introversion-extroversion has been extensively
Briggs dimension and on which of the researched
four modes they most rely on review of studies published
I. B. Myers and K. C. between 1996 and 2000
Briggs revealed literally hundreds of
studies that have used the
MBTI in creative ways to study
human personality and its
correlates
Wonderlic Personnel WPT/ WRT-R adults Based on another a quick (12-minute) test of
Test popular instrument, the mental ability
Otis Self-Administering Normative data are available
Tests of Mental Ability on more than 50,000 adults 20
a quick and stable paper- to 65 years old.
and-pencil intelligence Odd–even reliability
test with extensive norms coefficients are also excellent,
Widely used for with a range of .88 to .94
employee-related reported in the manual.
decisions in industry The main drawback of the
WPT is its validity
documentation, although
available studies tend to
support it
In the absence of local data,
test scores must be
interpreted with some caution.
In 2007, a new version of the
Wonderlic, known as the
Wonderlic Personnel Test–
Revised (WRT-R) was
released. The newer version
updates the traditional
Wonderlic and uses newer
technologies for test
administration and scoring.
For most test takers, the new
version can be completed in
about 12 minutes.
Differential Aptitude DAT assessing clerical competence,
Test such as speed, accuracy, and
grammar
Bennett two popular measures of
Mechanical mechanical ability
Comprehension Test
and the Revised
Minnesota Paper
Form Board
Tests
Accounting Accounting skills
Orientation
Test
Admission Test to assess business skills and
for Graduate Study in readiness for graduate study in
Business business
Occupational O*NET The system includes one can understand divergent O*NET continues to evolve.
Information Network three categories: (1) occupations in relation to tasks The entire database is
worker requirements, and skills that generalize across available to the public at no
such as skills, occupational categories cost (see ONETCENTER.
knowledge, and abilities; job analysis ORG). The 2012 data base
(2) experience includes thousands of
requirements, including occupational definitionand the
training and licensure; system is continually updated.
and (3) job requirements,
such as work activities,
work context, and
characteristics of the
organization
You might also like
- TOP Reviewer-ElmiieDocument31 pagesTOP Reviewer-ElmiieCriselda Reloba CabailoNo ratings yet
- Psychology of Perception 2016Document162 pagesPsychology of Perception 2016Yerko Ivánovic100% (4)
- Mental Status Examination Psychiatric Nursing Assessment SpeechDocument2 pagesMental Status Examination Psychiatric Nursing Assessment SpeechElaine Louise O. Foronda100% (1)
- Theories of Personality ComparisonDocument5 pagesTheories of Personality Comparisontoffee capitulo100% (1)
- AbPsy ReviewerDocument70 pagesAbPsy ReviewerAdam VidaNo ratings yet
- Free ConvectionDocument4 pagesFree ConvectionLuthfy AditiarNo ratings yet
- Shelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesShelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions Manualjuanlucerofdqegwntai100% (10)
- Assessing Regulatory Emotional Self-Efficacy in Three CountriesDocument21 pagesAssessing Regulatory Emotional Self-Efficacy in Three CountriesMuchamad Umar Chatab Nasserie100% (1)
- All About TarlacDocument12 pagesAll About TarlacAnonymous uLb5vOjXNo ratings yet
- 3 - Clinical Assessment, Diagnosis, and Research MethodsDocument12 pages3 - Clinical Assessment, Diagnosis, and Research Methodsapi-3855346100% (1)
- Hopelessness: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesHopelessness: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJasmineNo ratings yet
- Bret Moore Fundamentals 2Document2 pagesBret Moore Fundamentals 2THERESE MARIE B ABURQUEZNo ratings yet
- (Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesDocument196 pages(Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesAmbrose66No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Situational Low SelfDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Situational Low SelfChar Perea100% (1)
- Defensive Coping Related To Perceived Lack of Self-Efficacy As Evidenced by Denial of Obvious ProblemsDocument2 pagesDefensive Coping Related To Perceived Lack of Self-Efficacy As Evidenced by Denial of Obvious ProblemsJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Letter SDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Letter Sapi-317303624100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPCharles Mallari Valdez100% (1)
- Fdar - Schizophrenia Jan 11-13Document2 pagesFdar - Schizophrenia Jan 11-13Grape Juice100% (1)
- NCP - AnxietyDocument4 pagesNCP - AnxietyRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Document3 pagesDisturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Charles Mallari ValdezNo ratings yet
- NCP Low Self Esteem DreiDocument5 pagesNCP Low Self Esteem DreiEllenare RacionNo ratings yet
- Steel 2007 - La Naturaleza de La Procrastinación - Una Revisión Teorica y de Metanalisis de La Falla AutoreegulatoriaDocument30 pagesSteel 2007 - La Naturaleza de La Procrastinación - Una Revisión Teorica y de Metanalisis de La Falla AutoreegulatoriaMartin Ruíz100% (1)
- Chapter 15 Computers and Basic Psychological Science in TestingDocument16 pagesChapter 15 Computers and Basic Psychological Science in TestingRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 JeopardyDocument4 pagesExam 3 JeopardyDiya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - OutlineDocument8 pagesChapter 15 - OutlineJusa Aldrea PratoNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Yalues: Anxiety As Caused by The Frustration of A Major Value: ReligionDocument7 pagesAnxiety and Yalues: Anxiety As Caused by The Frustration of A Major Value: ReligionRui SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To PsychologyDocument11 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To PsychologyRoselle GerobinNo ratings yet
- Butler 1991Document16 pagesButler 1991Stijn VanheuleNo ratings yet
- Nlah BlahDocument2 pagesNlah BlahACOB, Jamil C.No ratings yet
- Bantolo Bsn305 NCPDocument4 pagesBantolo Bsn305 NCPIrish BantoloNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Defusion For Psychological Distress, Dysphoria, and Low Self-Esteem: A Randomized Technique Evaluation Trial of Vocalizing StrategiesDocument22 pagesCognitive Defusion For Psychological Distress, Dysphoria, and Low Self-Esteem: A Randomized Technique Evaluation Trial of Vocalizing StrategiesBilo BiloNo ratings yet
- Aprilia Putri Rahmadini, M.Psi ., PsikologDocument12 pagesAprilia Putri Rahmadini, M.Psi ., PsikologReffa Rizkyani IrawanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Personality Assessment Volume 47 Issue 1 1983 (Doi 10.1207/s15327752jpa4701 - 8) Leary, Mark R. - Social Anxiousness - The Construct and Its MeasurementDocument11 pagesJournal of Personality Assessment Volume 47 Issue 1 1983 (Doi 10.1207/s15327752jpa4701 - 8) Leary, Mark R. - Social Anxiousness - The Construct and Its MeasurementMilosNo ratings yet
- Matrix - Week5 - (Eysenck, Buss)Document16 pagesMatrix - Week5 - (Eysenck, Buss)Ina Mikaela RecioNo ratings yet
- Ghosts, Ufos, and Magic: Positive Affect and The Experiential SystemDocument15 pagesGhosts, Ufos, and Magic: Positive Affect and The Experiential SystembinzeggerNo ratings yet
- Implicit Bias Training ImageryDocument14 pagesImplicit Bias Training ImageryEstela MedinaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis, Assessment of Mental DisordersDocument22 pagesDiagnosis, Assessment of Mental DisordersJana Marie CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Personalit Y Disorder: Group 6Document30 pagesPersonalit Y Disorder: Group 6Kyra RMNo ratings yet
- Forms and Functions of The Self ConsciouDocument15 pagesForms and Functions of The Self ConsciouAlexis N. IbarraNo ratings yet
- Kernis Et Al - Master of One's Psychological Domain, Not Likely If One's Self-Esteem Is UnstableDocument9 pagesKernis Et Al - Master of One's Psychological Domain, Not Likely If One's Self-Esteem Is UnstableSofi AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Behaviour Therapy of Schizophrenia The Amenability of Delusions and Hallucinations To ReasoningDocument7 pagesCognitive Behaviour Therapy of Schizophrenia The Amenability of Delusions and Hallucinations To Reasoningyunita murfhiNo ratings yet
- Emotionality, Repression-Sensitization, and Maladjustment: Brie. 3. Psychiat. (1965), Iii, 399-404Document7 pagesEmotionality, Repression-Sensitization, and Maladjustment: Brie. 3. Psychiat. (1965), Iii, 399-404dodoNo ratings yet
- ++++visla PAIDDocument4 pages++++visla PAIDAdina CarterNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Hopelessness NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hopelessness NCPRammiel Saylo CarlosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Personality PsychologyDocument7 pagesChapter 5 - Personality Psychologyaloysius quitaligNo ratings yet
- Do Positive Illusions Foster Mental Health - (Randall Colvin, Jack Block)Document18 pagesDo Positive Illusions Foster Mental Health - (Randall Colvin, Jack Block)fiva.vcNo ratings yet
- Teach Man 2003Document10 pagesTeach Man 2003Blabla BlaNo ratings yet
- Interoceptive-Exposure Lang Eng-Gb Format ProfessionalDocument10 pagesInteroceptive-Exposure Lang Eng-Gb Format ProfessionalMissDee515No ratings yet
- Beck Thinking and Depression Idiosyncratic Content and Cognitive DistortionsDocument10 pagesBeck Thinking and Depression Idiosyncratic Content and Cognitive DistortionsFrancisco GaravagliaNo ratings yet
- Klein, Horney, MurrayDocument7 pagesKlein, Horney, MurrayJo Hannah Naranjo SullanoNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Callous-Unemotional Traits For Extending The Concept of Psychopathy To ChildrenDocument6 pagesThe Importance of Callous-Unemotional Traits For Extending The Concept of Psychopathy To ChildrenDiane MxNo ratings yet
- Personality Development: TRAIT THEORIES - Personality TheoriesDocument5 pagesPersonality Development: TRAIT THEORIES - Personality TheoriesJulianeMarieAbellaNo ratings yet
- Emotions, Rationality, and Mind/Body: Patricia GreenspanDocument18 pagesEmotions, Rationality, and Mind/Body: Patricia GreenspanGABRIEL ALEJANDRO GOMEZ SOLARTENo ratings yet
- Psychology, Sociology, and AnthropologyDocument29 pagesPsychology, Sociology, and AnthropologyArviNo ratings yet
- Psychopathy in A Noninstitutional SampleDocument17 pagesPsychopathy in A Noninstitutional SampleAleksandar VučićNo ratings yet
- Team Matrix Week 2 Psy 405Document3 pagesTeam Matrix Week 2 Psy 405Erdanx Sanchez100% (1)
- Revised. NCP. Jam 1Document3 pagesRevised. NCP. Jam 1ACOB, Jamil C.No ratings yet
- DASPS A Database For Anxious States Based On ADocument11 pagesDASPS A Database For Anxious States Based On AAbhinandan ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Individualistic Theories of CrimeDocument1 pageIndividualistic Theories of Crimemah1kh4tunNo ratings yet
- The Functional Architecture of Human Empathy PDFDocument30 pagesThe Functional Architecture of Human Empathy PDFpratolectusNo ratings yet
- The Sensations ofDocument13 pagesThe Sensations ofLuisa duenasNo ratings yet
- ACT For Psychosis Workshop BABCP 2008 Eric Morris Gordon Mitchell Amy McArthurDocument11 pagesACT For Psychosis Workshop BABCP 2008 Eric Morris Gordon Mitchell Amy McArthurjlbermudezc100% (1)
- Neural Mechanisms Underlying SchizophreniaDocument12 pagesNeural Mechanisms Underlying SchizophreniammimcNo ratings yet
- NCP PsychmainDocument8 pagesNCP PsychmainMichelle Kathleen EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ItcDocument7 pagesReviewer ItcGwen Mendoza SanglayNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Professional EmailDocument2 pagesHow To Write A Professional EmailRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- PCS IO PPT Part 3 Designing and Evaluating TrainingDocument91 pagesPCS IO PPT Part 3 Designing and Evaluating TrainingRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- SAT 2007 Jan Form Codes DEON EWON FFOQOG N2Document52 pagesSAT 2007 Jan Form Codes DEON EWON FFOQOG N2Ruby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- Six Steps For Writing Professional EmailsDocument2 pagesSix Steps For Writing Professional EmailsRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- The "Peril" of Overpopulation: ModernizationDocument3 pagesThe "Peril" of Overpopulation: ModernizationRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- Training and Developing EmployeesDocument24 pagesTraining and Developing EmployeesRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- PCS IO PPT Part 3 Designing and Evaluating TrainingDocument91 pagesPCS IO PPT Part 3 Designing and Evaluating TrainingRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- Preconventional Level (Age 4-10)Document1 pagePreconventional Level (Age 4-10)Ruby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- Key TermsDocument5 pagesKey TermsRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document28 pagesCH 10Shahid MashhoodNo ratings yet
- Kelly's Philosophical PositionDocument6 pagesKelly's Philosophical PositionRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- Key TermsDocument5 pagesKey TermsRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- Symptom of The Strong Feeling of Fear. He Described Fear As Being Related To All Living Creatures in Response To Perceived DangerDocument5 pagesSymptom of The Strong Feeling of Fear. He Described Fear As Being Related To All Living Creatures in Response To Perceived DangerRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- Letter of InvitationDocument1 pageLetter of InvitationRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- Authorization Letter Sample For ClaimingDocument1 pageAuthorization Letter Sample For ClaimingJovit Samaniego100% (1)
- RRL For Procrastination FinalDocument4 pagesRRL For Procrastination FinalRuby Jinn Makinano BarreteNo ratings yet
- CESCOM 10 - Aircraft Status Report: Maintenance InspectionsDocument78 pagesCESCOM 10 - Aircraft Status Report: Maintenance InspectionsAlejandro BarradasNo ratings yet
- Effects of Corneal Scars and Their Treatment With Rigid Contact Lenses On Quality of VisionDocument5 pagesEffects of Corneal Scars and Their Treatment With Rigid Contact Lenses On Quality of VisionJasmine EffendiNo ratings yet
- NA ReadingStrategies U5M11L03Document1 pageNA ReadingStrategies U5M11L03Lila AlwaerNo ratings yet
- Shoshana Bulka PragmaticaDocument17 pagesShoshana Bulka PragmaticaJessica JonesNo ratings yet
- UpdateJul2007 3julDocument10 pagesUpdateJul2007 3julAnshul SinghNo ratings yet
- Mossbauer SpectrosDocument7 pagesMossbauer SpectroscyrimathewNo ratings yet
- World BankDocument28 pagesWorld BankFiora FarnazNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Computer Science ASDocument194 pagesPaper 1 Computer Science ASLailaEl-BeheiryNo ratings yet
- Ortho TechnologyDocument196 pagesOrtho Technologyr3doc3No ratings yet
- Lecture BouffonDocument1 pageLecture BouffonCarlos Enrique GuerraNo ratings yet
- DIY Toolkit Arabic Web VersionDocument168 pagesDIY Toolkit Arabic Web VersionAyda AlshamsiNo ratings yet
- 한국항만 (영문)Document38 pages한국항만 (영문)hiyeonNo ratings yet
- Very Hungry Caterpillar Clip CardsDocument5 pagesVery Hungry Caterpillar Clip CardsARTGRAVETO ARTNo ratings yet
- Nascsa - Sponsor Solicitation List: January 06, 2021Document35 pagesNascsa - Sponsor Solicitation List: January 06, 2021Prasoon SimsonNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Strategic Management BarbosaDocument11 pagesSustainable Strategic Management BarbosapurwawardhaniNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Short-Circuit Current (Isc) at Any Point Within A LV Installation - Electrical Installation GuideDocument6 pages3-Phase Short-Circuit Current (Isc) at Any Point Within A LV Installation - Electrical Installation GuideYuukinoriNo ratings yet
- School Activity Calendar - Millsberry SchoolDocument2 pagesSchool Activity Calendar - Millsberry SchoolSushil DahalNo ratings yet
- PedagogicalDocument94 pagesPedagogicalEdson MorenoNo ratings yet
- P D P: C I D, C M: Design of Coastal RoadsDocument55 pagesP D P: C I D, C M: Design of Coastal RoadsMohammedNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesISMAEL KRIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- RS-All Digital PET 2022 FlyerDocument25 pagesRS-All Digital PET 2022 FlyerromanNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte Ga b85m Ds3h A r10 PDFDocument30 pagesGigabyte Ga b85m Ds3h A r10 PDFMartha Lorena TijerinoNo ratings yet
- Teaching PowerPoint Slides - Chapter 5Document19 pagesTeaching PowerPoint Slides - Chapter 5Azril ShazwanNo ratings yet
- Aman Singh Rathore Prelms Strategy For UPSCDocument26 pagesAman Singh Rathore Prelms Strategy For UPSCNanju NNo ratings yet
- Aex-Kissan KeralaDocument25 pagesAex-Kissan Keralabsh08070No ratings yet