Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rehabilitation of Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH) Complicated With Localized Tooth Surface Loss 2014
Uploaded by
player osamaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rehabilitation of Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH) Complicated With Localized Tooth Surface Loss 2014
Uploaded by
player osamaCopyright:
Available Formats
Q U I N T E S S E N C E I N T E R N AT I O N A L
RESTORATIVE DENTISTRY
Walter Y.H. Lam
Rehabilitation of molar-incisor hypomineralization
(MIH) complicated with localized tooth surface loss:
A case report
Walter Y.H. Lam, BDS, MDS (Pros)1/Edward H.T. Ho, BDS, MClinDent (Pros)2/
Edmond H.N. Pow, BDS, MDS (Pros Dent), PhD3
Molar-incisor hypomineralization (MIH) is a developmental report describes the management of a patient with MIH com-
enamel hypomineralized condition characteristically involving plicated with localized TSL and lack of occlusal clearance due
the first permanent molars and sometimes also the incisors. to dentoalveolar compensation. The atypical TSL pattern
The affected teeth are predisposed to tooth surface loss (TSL) involved all anterior teeth and required the placement of Dahl
which may not only compromise the esthetics and function appliances on both arches. (Quintessence Int 2014;45:377–379;
but also endanger the pulp and longevity of the teeth. This doi: 10.3290/j.qi.a31540)
Key words: Dahl concept, erosion, minor axial tooth movement, molar-incisor hypomineralization, tooth surface
loss, tooth wear
Molar-incisor hypomineralization (MIH) is the demar- affected tooth to mechanical breakdown. Tooth surface
cated enamel porosity of systemic origin, affecting one loss (TSL) is the loss of surface tooth substance caused
or more permanent molars (usually the first molars) by mechanical and chemical (erosion) factors. A strong
with or without involvement of the incisors and relationship between the presence of acid erosion and
canines.1 Its prevalence varies widely from 2.5% to enamel hypomineralization has also been reported.3
40.2%.2 It is believed that both hereditary and develop- The hypomineralized enamel may be susceptible to TSL
mental factors are contributory. It usually compromises processes.
the enamel hardness and therefore predisposes the MIH teeth might be associated with pathologic TSL,
and a case of linear enamel hypoplasia combined with
TSL has been reported.4 MIH complicated with TSL may
1 Postgraduate Student, Discipline of Oral Rehabilitation, Faculty of Dentistry, The not only compromise the esthetics and function but
University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, People’s Republic of China. also endanger the pulp and longevity of the affected
2 Part-time Clinical Lecturer, Discipline of Oral Rehabilitation, Faculty of Dentistry,
The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, People’s Republic of China. teeth. TSL might be complicated by eruption of the
3 Associate Professor, Discipline of Oral Rehabilitation, Faculty of Dentistry, The teeth with its dentoalveolar processes which obliterate
University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, People’s Republic of China.
the space for any restorations.5 This report describes
Correspondence: Dr Edmond Pow, 4/F, Oral Rehabilitation, Prince the rehabilitation of a patient suffering from MIH com-
Philip Dental Hospital, 34 Hospital Road, Sai Ying Pun, Hong Kong SAR,
People’s Republic of China. Email: ehnpow@hku.hk plicated with localized TSL.
VOLUME 45 • NUMBER 5 • MAY 2014 377
Q U I N T E S S E N C E I N T E R N AT I O N A L
L am et al
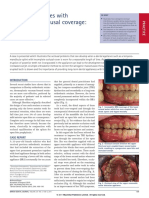
a b c
Figs 1a to 1c Preoperative views showing localized tooth surface loss and enamel defects.
Figs 2a and 2b Diagnostic wax-up on
the articulated casts and Dahl appliances
a b in situ.
a b c
Figs 3a to 3c Postoperative views showing the definitive restorations.
CASE REPORT Preventive measures were instituted and TSL pro-
gression was evaluated to be stable for 6 months.
A 44-year-old man complained of shortened anterior Based on the diagnostic wax-ups, 3 mm of interocclusal
teeth deteriorating his appearance. No erosive factors space was required. A nickel-chromium bite plane and
or parafunctional habits were found. Normal facial provisional composite crowns (Sinfony, 3M Espe) were
height with freeway space of 2 mm was noticed. Mild fabricated and luted (Ketac Cem, 3M Espe) on maxillary
TSL confined to enamel was detected on the occlusal and mandibular anterior teeth respectively (Fig 2). Six
surface of all first premolars. Severe TSL exposing den- months later, simultaneous posterior occlusal contacts
tin and/or pulp was found on all the anterior teeth, and were reestablished uneventfully. The appliances were
the left maxillary and right mandibular first molars. removed and all anterior teeth were provisionalized for
Enamel opacity was observed on the remaining first 6 weeks. Full ceramic crowns (IPS e.max Press, Ivoclar
molars. A provisional restoration was found on the cin- Vivadent) were fabricated and luted (Calibra, DeTrey,
gulum of the discolored left maxillary central incisor. Dentsply). The left maxillary and right mandibular first
Compensatory eruption of the anterior teeth and the molars were prepared for gold onlay and crown re-
alveolar process complicated with deepened incisal spectively. The left maxillary central incisor was man-
plane was observed. No interocclusal space was aged nonsurgically and surgically, but the fistula
observed between the anterior teeth in centric occlu- remained unresolved. It was replaced by an implant of
sion (Fig 1). A diagnosis of MIH, and localized anterior 4.0 × 13 mm (Astra Tech Implant System, Dentsply)
TSL with dentoalveolar compensation was made. with a screw-retained metal-ceramic restoration. The
378 VOLUME 45 • NUMBER 5 • MAY 2014
Q U I N T E S S E N C E I N T E R N AT I O N A L
L am et al
patient had been followed for 6 months. All teeth, res- CONCLUSION
torations, and the implant-supported crown were
intact and firm (Fig 3). The patient was satisfied with MIH may predispose to TSL. With severe TSL and a lack
the esthetics and function. of interocclusal space, the Dahl concept can be utilized
to facilitate the rehabilitation.
DISCUSSION
In the present case, localized TSL was observed mainly
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
on the occlusal surfaces of the incisors and first molars, The authors thank John Lo, Assistant Professor of Oral and Maxillofa-
cial Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, The University of Hong Kong, for
which suggested that the affected teeth were first com-
performing the implant surgery; and Mr Sam Tang for the dental la-
promised by MIH followed by attrition and dentoalveo- boratory work.
lar compensation over time.
Dahl appliance was used to correct the dentoalveo-
lar compensation, by intruding the teeth in contact REFERENCES
with the appliance and eruption of nonoccluded teeth, 1. Lygidakis NA, Wong F, Jälevik B, Vierrou AM, Alaluusua S, Espelid I. Best Clinical
Practice Guidance for clinicians dealing with children presenting with Molar-
and recreating the lost interocclusal space for restor- Incisor-Hypomineralisation (MIH): An EAPD Policy Document. Eur Arch Paedi-
ations. The amount of space required was determined atr Dent 2010;11:75–81.
2. Jälevik B. Prevalence and diagnosis of Molar-Incisor-Hypomineralisation
by esthetics and diagnostic wax-ups. The increase in (MIH): A systematic review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 2010;11:59–64.
occlusal vertical dimension (OVD) of less than 4 mm has 3. Kazoullis S, Seow WK, Holcombe T, Newman B, Ford D. Common dental
conditions associated with dental erosion in schoolchildren in Australia.
been shown to be well adapted in dentate subjects.6 It Pediatr Dent 2007;29:33–39.
has been recommended to place the appliance on the 4. Boston DW, Al-bargi H, Bogert M. Abrasion, erosion, and abfraction combined
with linear enamel hypoplasia: a case report. Quintessence Int 1999;30:683–
arch with TSL,5 but the atypical TSL pattern in this case 687.
entailed its placement on both arches. After Dahl ther- 5. Poyser NJ, Porter RW, Briggs PF, Chana HS, Kelleher MG. The Dahl Concept:
past, present and future. Br Dent J 2005;198:669–676.
apy, the OVD was restored and the dentition was reha- 6. Dahl BL, Krogstad O. The effect of a partial bite raising splint on the occlusal
bilitated by contemporary full coverage restorations face height. An x-ray cephalometric study in human adults. Acta Odontol
Scand 1982;40:17–24.
and an implant-supported crown.
VOLUME 45 • NUMBER 5 • MAY 2014 379
You might also like
- Recipe Booklet PRINT VERSIONDocument40 pagesRecipe Booklet PRINT VERSIONjtsunami815100% (1)
- Transaction AnalysisDocument34 pagesTransaction AnalysisSunil Ramchandani100% (1)
- Hematology SOPsDocument99 pagesHematology SOPssalamon2t100% (1)
- Restoration of The Worn Dentition. Part 2Document7 pagesRestoration of The Worn Dentition. Part 2Isharajini Prasadika Subhashni GamageNo ratings yet
- "Facial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Parts IDocument14 pages"Facial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Parts ILeonardo Lamim80% (5)
- ABGD Written Study Questions 2007Document291 pagesABGD Written Study Questions 2007Almehey NaderNo ratings yet
- Allnex Powder BrochureDocument28 pagesAllnex Powder BrochureandreathomeNo ratings yet
- Full Mouth Rehabilitation of The Patient With Severly Worn Out Dentition A Case Report.Document5 pagesFull Mouth Rehabilitation of The Patient With Severly Worn Out Dentition A Case Report.sivak_198100% (1)
- Testing of Semifinished Products of Thermoplastics Bases - Indications Directive DVS 2201-1Document4 pagesTesting of Semifinished Products of Thermoplastics Bases - Indications Directive DVS 2201-1OscarNo ratings yet
- Pulverizers: By: G. RamachandranDocument140 pagesPulverizers: By: G. Ramachandranshivshankar prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Standard Into-Plane Fueling Service Levels and SafetyDocument8 pagesStandard Into-Plane Fueling Service Levels and SafetyPrekelNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Digestion in Stomach and Intestines Grade 4Document3 pagesLesson Plan On Digestion in Stomach and Intestines Grade 4jaydalene saga macay100% (5)
- Zachrisson2004 Management of Missing Maxillary Anterior Teeth With Emphasis On AutotransplantationDocument5 pagesZachrisson2004 Management of Missing Maxillary Anterior Teeth With Emphasis On AutotransplantationplsssssNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Premolar Transplantation To Replace Missing Maxillary Anterior Teeth: A Multidisciplinary ApproachDocument14 pagesMandibular Premolar Transplantation To Replace Missing Maxillary Anterior Teeth: A Multidisciplinary ApproachRicha AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment in A Periodontal Patient With Pathologic Migration of Anterior TeethDocument9 pagesOrthodontic Treatment in A Periodontal Patient With Pathologic Migration of Anterior TeethMárcio LMSNo ratings yet
- 724 2683 4 PB PDFDocument2 pages724 2683 4 PB PDFCristi GaidurNo ratings yet
- Internal ResorptionDocument4 pagesInternal ResorptionmaharaniNo ratings yet
- CANINEDocument10 pagesCANINEHarish Kumar.THOTANo ratings yet
- Abutment Evaluation in FPD 2Document5 pagesAbutment Evaluation in FPD 2ahmad955mlsNo ratings yet
- Mcevoy 05 04Document3 pagesMcevoy 05 04wafasahilahNo ratings yet
- Pulp Treatment of Triple Tooth in Primary Dentition: Two Case ReportsDocument8 pagesPulp Treatment of Triple Tooth in Primary Dentition: Two Case ReportsDelia Guadalupe Gardea ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Kjod 53 2 125Document12 pagesKjod 53 2 125khiemnguyen13No ratings yet
- Dens Invaginatus, Clinically As Talons Cusp: An Uncommon PresentationDocument4 pagesDens Invaginatus, Clinically As Talons Cusp: An Uncommon PresentationYulinda PrimilisaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Removable ProstheTicsDocument9 pagesFixed Removable ProstheTicsSumi AliNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Prosdent 2014 12 024Document6 pages10 1016@j Prosdent 2014 12 024kinoNo ratings yet
- Functional Occlusion in Orthodontics: ClinicalDocument11 pagesFunctional Occlusion in Orthodontics: ClinicalNaeem MoollaNo ratings yet
- Impacted Mandibular Second Molars. A Retrospective..Document6 pagesImpacted Mandibular Second Molars. A Retrospective..Anibal LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Canino Ectopico A Nivel de Incisivo LateralDocument12 pagesCanino Ectopico A Nivel de Incisivo Lateralangianny_cdNo ratings yet
- Asds 02 0215Document3 pagesAsds 02 02156mf9jf6h99No ratings yet
- Alternativas A TotalesDocument12 pagesAlternativas A TotalesJuan Jose Stuven RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 140115092530 Phpapp02Document131 pagesPresentation1 140115092530 Phpapp02Ana LucaNo ratings yet
- Discuss 3Document7 pagesDiscuss 3Zaid DewachiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dental Anatomy: Learning Objec TivesDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Dental Anatomy: Learning Objec Tivesbalkiz mahamedNo ratings yet
- The Stressed Pulp Condition An Endodontic RestorativeDocument2 pagesThe Stressed Pulp Condition An Endodontic RestorativeChris TayNo ratings yet
- Management of Ectopically Erupting MaxillaryDocument7 pagesManagement of Ectopically Erupting MaxillaryLiliana Aguilar VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Attempted Traction of Impacted and Ankylosed Maxillary Canines.Document9 pagesAttempted Traction of Impacted and Ankylosed Maxillary Canines.Maria Fernanda CáceresNo ratings yet
- ARTICAL1Document7 pagesARTICAL1Aseel AnesNo ratings yet
- Lyu 2018Document7 pagesLyu 2018Andres CoboNo ratings yet
- 3 Badr2016Document22 pages3 Badr2016Daniel Espinoza EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Ehrlich. Various Methods in Achieving Anterior Guidance. (1989)Document5 pagesEhrlich. Various Methods in Achieving Anterior Guidance. (1989)Erika Stephany ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Fusion of Mandibular Second Molars With Supernumerary Teeth: Case ReportDocument5 pagesBilateral Fusion of Mandibular Second Molars With Supernumerary Teeth: Case ReportUcc Ang BangarenNo ratings yet
- Molar Impactions: Etiology, Implications and Treatment Modalities With Presentation of An Unusual CaseDocument3 pagesMolar Impactions: Etiology, Implications and Treatment Modalities With Presentation of An Unusual Casemagus davilaNo ratings yet
- Correcting Severe Scissor Bite in An Adult: Case ReportDocument12 pagesCorrecting Severe Scissor Bite in An Adult: Case ReportLikhita ChNo ratings yet
- Dens Evaginatus Case ReportDocument2 pagesDens Evaginatus Case ReportPurwita NurwidyastutiNo ratings yet
- Rescue Therapy With Orthodontic Traction To Manage Severely Impacted Mandibular Second Molars and To Restore An Alveolar Bone DefectDocument12 pagesRescue Therapy With Orthodontic Traction To Manage Severely Impacted Mandibular Second Molars and To Restore An Alveolar Bone DefectNathália LopesNo ratings yet
- Extrusion Splint Technique in Management of Dental Trauma: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesExtrusion Splint Technique in Management of Dental Trauma: A Case ReportdrvarunmalhotraNo ratings yet
- Shanjiang 2016Document6 pagesShanjiang 2016systematic reviewNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Lateral Incisor With Four Root CanalsDocument5 pagesMaxillary Lateral Incisor With Four Root Canalsdentace1No ratings yet
- Multimodal Imaging of Dental Pulp Healing PatternsDocument15 pagesMultimodal Imaging of Dental Pulp Healing PatternsamaferuasNo ratings yet
- Factors Associated With Post Core Correction of Malpositioned TeethDocument3 pagesFactors Associated With Post Core Correction of Malpositioned TeethM Ghazy FajruyumaNo ratings yet
- 35 Predicting Pulpectomy SuccessDocument7 pages35 Predicting Pulpectomy SuccessveronicaonggaNo ratings yet
- PdeoDocument4 pagesPdeounaNo ratings yet
- SJ BDJ 2011 46Document2 pagesSJ BDJ 2011 46Destya Sandra DewiNo ratings yet
- Vincent Trapozzano, New Portrichey, Fla.,And Gordon Winter, PhiladelphiaDocument7 pagesVincent Trapozzano, New Portrichey, Fla.,And Gordon Winter, PhiladelphiaNajeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- ReferensiDocument4 pagesReferensiluluNo ratings yet
- 01 A Method For Positioning The Premaxilla During Impression MakingDocument4 pages01 A Method For Positioning The Premaxilla During Impression MakingalonsoNo ratings yet
- Delayed Formation of Multiple Supernumerary TeethDocument6 pagesDelayed Formation of Multiple Supernumerary TeethsauriuaNo ratings yet
- The 2 X 4 Appliance McKeown SandlerDocument4 pagesThe 2 X 4 Appliance McKeown Sandlervefiisphepy83312No ratings yet
- Liaw 2018Document131 pagesLiaw 2018tâm nguyễnNo ratings yet
- 3.lower Lip Sucking Habit Treated With A Lip Bumper ApplianceDocument7 pages3.lower Lip Sucking Habit Treated With A Lip Bumper ApplianceRahma IskNo ratings yet
- Controlled Tooth Movement To Correct An Iatrogenic Problem: Case ReportDocument8 pagesControlled Tooth Movement To Correct An Iatrogenic Problem: Case ReportElla GolikNo ratings yet
- A Simple Method For Correction of Buccal Crossbite of Maxillary Second MolarDocument5 pagesA Simple Method For Correction of Buccal Crossbite of Maxillary Second MolarJavier Farias VeraNo ratings yet
- Surgicalexposureof Impactedteeth: Pamela L. AlbertoDocument10 pagesSurgicalexposureof Impactedteeth: Pamela L. AlbertoDANTE DELEGUERYNo ratings yet
- Miyahira2008 - Miniplates As Skeletal Anchorage For Treating Mandibular Second Molar ImpactionsDocument4 pagesMiyahira2008 - Miniplates As Skeletal Anchorage For Treating Mandibular Second Molar ImpactionsNathália LopesNo ratings yet
- Occlusal Interference After Tooth LossDocument6 pagesOcclusal Interference After Tooth LossNiaz AhammedNo ratings yet
- Fixed Pros Test 1Document5 pagesFixed Pros Test 1Rob SegrestNo ratings yet
- 2003.john H. Warford JR - Prediction of Maxillary Canine Impaction UsingDocument5 pages2003.john H. Warford JR - Prediction of Maxillary Canine Impaction UsingLuis HerreraNo ratings yet
- Afrand Et Al 2017 AJODODocument11 pagesAfrand Et Al 2017 AJODOplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- 2003.john H. Warford JR - Prediction of Maxillary Canine Impaction UsingDocument5 pages2003.john H. Warford JR - Prediction of Maxillary Canine Impaction UsingLuis HerreraNo ratings yet
- Delayed Tooth Eruption Pa Tho Genesis, Diagnosis and Treatment.Document14 pagesDelayed Tooth Eruption Pa Tho Genesis, Diagnosis and Treatment.DrFarhana AfzalNo ratings yet
- 2002 Ericson Does The Canine Dental Follicle Cause Resorption ofDocument10 pages2002 Ericson Does The Canine Dental Follicle Cause Resorption ofplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Rizell Predictive Factors For Canine Position in Patients With Unilateral Cleft Lip and PalateDocument7 pages2020 Rizell Predictive Factors For Canine Position in Patients With Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palateplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- A New Guide Using CBCT To Identify TheDocument6 pagesA New Guide Using CBCT To Identify Theplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Eruption of The Maxillary Canine On CephalometDocument8 pagesEctopic Eruption of The Maxillary Canine On CephalometyeiNo ratings yet
- 2000 RichardsonDocument5 pages2000 Richardsonplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Surgical Exposure Technique, Age, andDocument11 pagesEffect of Surgical Exposure Technique, Age, andplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Palatally Impacted Canines A NewDocument9 pagesPalatally Impacted Canines A Newplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- AJODO-2013 (First Author) 143 5 A10Document1 pageAJODO-2013 (First Author) 143 5 A10player osamaNo ratings yet
- 2000 Ericson Resorption of Incisors AfterDocument9 pages2000 Ericson Resorption of Incisors Afterplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- A Treatment Difficulty Index For Unerupted Maxillary CaninesDocument4 pagesA Treatment Difficulty Index For Unerupted Maxillary Caninesplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Bone and Cartilage Changes After Injection of Botulinum Toxin - 2016 - American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial OrthopedicsDocument1 pageBone and Cartilage Changes After Injection of Botulinum Toxin - 2016 - American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedicsplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- AJODO-2013 143 4 446 UmesanDocument2 pagesAJODO-2013 143 4 446 Umesanplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- 2009 Kau A Novel 3D ClassificationDocument6 pages2009 Kau A Novel 3D Classificationplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Letters To The Editor: Bone and Cartilage Changes After Injection of Botulinum ToxinDocument3 pagesLetters To The Editor: Bone and Cartilage Changes After Injection of Botulinum Toxinplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Boneceramic Graft Regenerates Alveolar Defects But Slows Orthodontic Tooth Movement With Less Root ResorptionDocument10 pagesBoneceramic Graft Regenerates Alveolar Defects But Slows Orthodontic Tooth Movement With Less Root Resorptionplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Reproducibility of 2 Regions of Reference For Maxillary Regional Registration With Cone-Beam Computed TomographyDocument10 pagesComparison and Reproducibility of 2 Regions of Reference For Maxillary Regional Registration With Cone-Beam Computed Tomographyplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- AJODO-2013 (First Author) 143 5 A14 PDFDocument1 pageAJODO-2013 (First Author) 143 5 A14 PDFplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- AJODO-2013 (First Author) 143 5 A2Document4 pagesAJODO-2013 (First Author) 143 5 A2player osamaNo ratings yet
- AJODO-2013 (First Author) 143 5 752Document1 pageAJODO-2013 (First Author) 143 5 752player osamaNo ratings yet
- AJODO-2013 143 4 446 KaramiDocument1 pageAJODO-2013 143 4 446 Karamiplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Corticotomy Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion - 2016 - American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial OrthopedicsDocument2 pagesCorticotomy Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion - 2016 - American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedicsplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Three Different Orthodontic Wires For Bonded Lingual Retainer FabricationDocument8 pagesComparison of Three Different Orthodontic Wires For Bonded Lingual Retainer Fabricationosama-alaliNo ratings yet
- Zachrisson Am J Orthod 2011Document9 pagesZachrisson Am J Orthod 2011player osamaNo ratings yet
- PracticalTechforAchiev PDFDocument4 pagesPracticalTechforAchiev PDFosama-alaliNo ratings yet
- SDJ 3 2013Document61 pagesSDJ 3 2013player osamaNo ratings yet
- Factorial Dimensions of Employee Engagement in Public and Private Sector BanksDocument5 pagesFactorial Dimensions of Employee Engagement in Public and Private Sector BanksCma Pushparaj KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Philosophy For Management and DisciplineDocument8 pagesPhilosophy For Management and Disciplineapi-300120362No ratings yet
- 2.2 WaterDocument32 pages2.2 WaterHelena GlanvilleNo ratings yet
- Test Unit 2 Urbanisation L P 12Document9 pagesTest Unit 2 Urbanisation L P 12Xuân NguyenNo ratings yet
- Serbia Malta & Bermuda Medical Instructions PDFDocument3 pagesSerbia Malta & Bermuda Medical Instructions PDFGISI KeyBOarD0% (1)
- Publication PDFDocument152 pagesPublication PDFAlicia Mary PicconeNo ratings yet
- PFA Vs PTFE in InstrumentationDocument5 pagesPFA Vs PTFE in InstrumentationArif HakimNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesDocument57 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Radfet DatasheetDocument6 pagesRadfet DatasheetNicholas EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Feasibility Report: at Plot No. 15/B-3, Jigani Industrial Area Anekal Taluk, Bangalore South District Karnataka byDocument41 pagesPre-Feasibility Report: at Plot No. 15/B-3, Jigani Industrial Area Anekal Taluk, Bangalore South District Karnataka by12mchc07No ratings yet
- Ship Captain's Medical Guide - 22nd EdDocument224 pagesShip Captain's Medical Guide - 22nd EdcelmailenesNo ratings yet
- OSCE Pediatric Dentistry Lecture-AnswersDocument40 pagesOSCE Pediatric Dentistry Lecture-AnswersR MNo ratings yet
- Types of Business OwnershipDocument2 pagesTypes of Business Ownershipprelovedseller bnNo ratings yet
- How To Make Panna CottaDocument3 pagesHow To Make Panna CottaBintNo ratings yet
- IGACOS Marine Sanctuary Park and ResortDocument74 pagesIGACOS Marine Sanctuary Park and ResortPlusNo ratings yet
- FF Recipe BookDocument17 pagesFF Recipe BookElectrox3dNo ratings yet
- What Is Aerobic Exercise?Document27 pagesWhat Is Aerobic Exercise?Zedy GullesNo ratings yet
- BS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctDocument60 pagesBS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctRamiAl-fuqahaNo ratings yet
- Crew Resource Management Phil O'DonnellDocument39 pagesCrew Resource Management Phil O'DonnellMostafaNo ratings yet
- Elephantgrass Bookchapter PDFDocument22 pagesElephantgrass Bookchapter PDFMuhammad rifayNo ratings yet
- Les Essences D'amelie BrochureDocument8 pagesLes Essences D'amelie BrochuresayonarasNo ratings yet