Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BM229 - Strategic Business Mangament
Uploaded by
John Paul PrestonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BM229 - Strategic Business Mangament
Uploaded by
John Paul PrestonCopyright:
Available Formats
Subject: BM229 – Strategic Business Management Top management attempts to program future success
Reporter: John Paul G. Preston through detailed analysis of:
Professor: Dr. Terry L. Andaya o Profitability / Prices
o Efficiency / Costs
o Market Share / Growth
CHAPTER 2. THE STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
o Market demands
PROCESS
o Utilization of Resources
2.3 Strategizing for Competitive Advantage: How is Strategy o Contribution of Stakeholders
Made? o Reputation and Survival
Five year plans and correlated budgets
FRAMEWORK FOR FORMULATING STRATEGIES
Just like people, organizations are different and unique AFI FRAMEWORK FOR TOP-DOWN STRATEGIC PLANNING
from each other.
Strategies, and ultimately the competitive advantage, are
derived from Mission, Vision, Values, and Goals of the
organizations.
To guide us in formulating strategies, the following
framework is to be considered:
SHORTCOMINGS OF THE TOP-DOWN APPROACH
May not adapt well to change
Formulation separate from implementation
Information flows top-down (one-way)
The leader’s future vision can be wrong
2.5 Scenarios
SCENARIO PLANNING
Uses a top-down approach
Generates a dominant plan, that is, must implement
the most probable option
Asks “WHAT-IF” questions
o Top management envisions different
scenarios
o Then they derive strategic responses
Consider optimistic and pessimistic futures
Examples:
Three Approaches to Strategize for Competitive Advantage o New laws restrict carbon emissions
o Strategic Planning – a formal, top-down o Demographic shifts
approach o Changing economic conditions
o Technological advances
o Scenario Planning – a formal, top-down
planning approach
AFI FRAMEWORK FOR SCENARIO PLANNING
o Strategy as planned emergence – begins with
a strategic plan, less formal
2.4 Strategic Planning
TOP-DOWN STRATEGIC PLANNING
Rational, data-driven strategy process
Define mission, vision and goals (strategic intent)
External analysis of opportunities and threats
Internal analysis of strengths and weaknesses
Create strategic fir through SWOT
Formulate appropriate strategy
Implement chosen strategy
Monitor performance and modify if necessary
BM 229 Strategic Business Management
Chapter 2, The Strategic Management Process
John Paul G. Preston
FORMULATION & IMPLEMENTATION USING SCENARIO o Allows for new emerging ideas to become
PLANNING realize
Formulation stage o Resources-allocation process (RAP)
o Identify strategic options o Serendipity can have dramatic effects
o Develop contingency plans
o Use analytical tools Strategy as Planned Emergence relies on data, plus:
o Build future options o Personal experience
Implementation stage o Deep domain expertise
o Execute dominant strategic plan o Front line employee insights
The option that best matches the
current reality KEY POINTS ABOUT STRATEGY
Modifications made as needed Intended Strategy
o Determine if alternate scenario should be o The outcome of a rational and structured top-
used down strategic plan
Emergent Strategy
STRATEGY AS PLANNED EMERGENCE: TOP DOWN AND o Any unplanned strategic initiative
BOTTOM-UP o Bubbles up from the bottom of the
Strategic Initiative organization
o Any activity a firm pursues to explore and o Can influence and shape a firm’s overall
develop: strategy
New products and processes Realized Strategy
New markets o Combination of intended and emergent
New ventures strategy
o Can bubble up from deep within a firm
through: 2.6 Implications for the Strategist
Autonomous actions
Strategic initiatives TWO FOUNDATIONAL INGREDIENT FOR COMPETITIVE
undertaken by employees ADVANTAGE
In response to unexpected 1. Inspiring vision and mission statement
external or internal o Backed by ethical values
opportunities o Customer-oriented / problem-defining
Serendipity Correlated with success
Random events, surprises, o Allow for strategic flexibility to change
coincidences To meet changing customer needs
Has an effect on strategic To exploit external opportunities
initiatives 2. An effective Strategic Management Process
Resource-allocation process (RAP)
How a firm allocates THE THREE STRATEGY PROCESSES HAVE STRENGTHS &
resources based on policy WEAKNESSES
Mintzberg's Planning Framework Effectiveness dependent on rate of change
o Reflects, if strategies can be planned or can o Slow / stable firms would choose top-down
emerge from the bottom-up Effectiveness dependent on firm size
o Provides more integrative and complete o Large firms would choose top-down or
framework scenario planning
o Relies on the assumption, that planning
should start with a rational structured, top- ALL EMPLOYEES SHOULD BE INVOLVED IN MISSION/VISION
down strategic plan (intended strategy) STATEMENT CREATION
o Mintzberg’s Planning Framework: Belief in the vision and mission is motivating.
Every employee plays a strategic role.
Any employee can have great ideas.
Strategy Can Come from Top Down and Bottom Up
o Bottom-up strategic initiatives emerge
o Evaluated and coordinated by management
o Some intended strategies drop off in the
process
BM 229 Strategic Business Management
Chapter 2, The Strategic Management Process
John Paul G. Preston
You might also like
- V16 Event 63 Cover Letter HelpDocument2 pagesV16 Event 63 Cover Letter HelprelonzNo ratings yet
- Lean Simplified: The Fast Eat The Slow! Key ToolsDocument2 pagesLean Simplified: The Fast Eat The Slow! Key ToolsVelangini Papi Reddy ThummaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Answering Case Study From My LecturerDocument7 pagesGuidelines For Answering Case Study From My LecturerBenny KhorNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis for Linear Programming SolutionsDocument40 pagesQuantitative Analysis for Linear Programming SolutionsAhmed HusseinNo ratings yet
- Demand and Elasticities PDFDocument4 pagesDemand and Elasticities PDFHaroon ZafarNo ratings yet
- Ch 2 Inv Appraisal IntroDocument5 pagesCh 2 Inv Appraisal IntroTeresaBachmannNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Assessment Scheme: Attendance, Participation, Assignments, ExamDocument2 pagesAcademic Writing Assessment Scheme: Attendance, Participation, Assignments, ExamNehal NabilNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) : DefinitionDocument5 pagesJob Safety Analysis (JSA) : DefinitionJude LichyNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 2020 For Cs StudentDocument112 pagesPhysics 1 2020 For Cs StudentSamNo ratings yet
- Use Cost and Volume Price Anlysis To Increase ProfitDocument2 pagesUse Cost and Volume Price Anlysis To Increase ProfitChristopher Raj0% (1)
- Student's CaseDocument11 pagesStudent's Caseremon4hr100% (1)
- Modern Project Management Strategies for SuccessDocument2 pagesModern Project Management Strategies for SuccessTri ArdhiansaNo ratings yet
- Corn Oil Analysis H-32Document4 pagesCorn Oil Analysis H-32Arief RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis Lab Manual PDFDocument20 pagesChemical Analysis Lab Manual PDFSundar SkNo ratings yet
- Earned Value AnalysisDocument1 pageEarned Value AnalysisMohamad CharafNo ratings yet
- Basic Mud Reportv1.5Document21 pagesBasic Mud Reportv1.5Anonymous MxwCc4No ratings yet
- Math Conversion Chart - Lengths: Metric ConversionsDocument5 pagesMath Conversion Chart - Lengths: Metric ConversionsJulhamEfendiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Saponification ValueDocument2 pagesDetermination of Saponification Valuetrs22No ratings yet
- ELECSDocument37 pagesELECSIra CervoNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Acid Value in OilDocument20 pagesEstimation of Acid Value in OilSundar SkNo ratings yet
- Session 2 Kotler - Mm15eDocument12 pagesSession 2 Kotler - Mm15eNehal NabilNo ratings yet
- Drilling Engineering - PE 311Document49 pagesDrilling Engineering - PE 311Adnan JadoonNo ratings yet
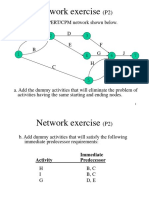
- Network exercise PERT/CPM solutionsDocument5 pagesNetwork exercise PERT/CPM solutionsNehal NabilNo ratings yet
- Question Paper - OR Quiz 1 PDFDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper - OR Quiz 1 PDFAdit ShahNo ratings yet
- Buss1040 Exam NotesDocument39 pagesBuss1040 Exam NotespiethepkerNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic Tableapi-312162583No ratings yet
- Xanthani GummiDocument2 pagesXanthani GummiLaurentiu DinuNo ratings yet
- Barashale™ Lite Fluid System: For Fields With Salt Formations and Low Fracture PressuresDocument2 pagesBarashale™ Lite Fluid System: For Fields With Salt Formations and Low Fracture PressuresLuis Romer Soliz AndiaNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument155 pagesLab ManualKieu Phuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Improving The Rheological Properties of Drilling Mud Using Local Based MaterialsDocument6 pagesImproving The Rheological Properties of Drilling Mud Using Local Based MaterialsPratham ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet EssentialsDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet EssentialsFrancis C FrancisNo ratings yet
- Driss PresentationDocument8 pagesDriss PresentationAmine MimoNo ratings yet
- Potassium Formate DryDocument2 pagesPotassium Formate DryYamamoto_KZNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Mud Engineering & Chemicals Company: Page 1 of 1Document1 pageEgyptian Mud Engineering & Chemicals Company: Page 1 of 1GPCNo ratings yet
- Mud Motor Operation Key PointsDocument3 pagesMud Motor Operation Key Pointssanjeet giriNo ratings yet
- DrilplexDocument6 pagesDrilplexLoganBohannonNo ratings yet
- Gitman 12e 525314 IM ch11rDocument22 pagesGitman 12e 525314 IM ch11rAnn!3100% (1)
- What Is ECD ? - GSR/WGP/WGO - G Fletcher Jan 2008Document9 pagesWhat Is ECD ? - GSR/WGP/WGO - G Fletcher Jan 2008Joaquin Dix'sNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Important Terms and Concepts: PhasesDocument71 pagesChapter-1 Important Terms and Concepts: PhasesAccount AccountNo ratings yet
- Sample Mid Semester Exam With AnswersDocument15 pagesSample Mid Semester Exam With AnswersjojoinnitNo ratings yet
- Vdocument - in LPP With SolutionsDocument21 pagesVdocument - in LPP With SolutionsShital GuptaNo ratings yet
- Iodine Value SOPDocument3 pagesIodine Value SOPsuresh kumarNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)Document40 pagesSupply Chain Management (SCM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)Abdur RajakNo ratings yet
- IADC/SPE 87139 Reformulating An Oil-Based Drilling Fluid With Especially Selected Chemicals Lead To Development of A Low-Viscosity High-Sag Stability Drilling FluidDocument11 pagesIADC/SPE 87139 Reformulating An Oil-Based Drilling Fluid With Especially Selected Chemicals Lead To Development of A Low-Viscosity High-Sag Stability Drilling FluidmsmsoftNo ratings yet
- Abdf - Novel ApplicationsDocument6 pagesAbdf - Novel ApplicationsVamsee KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Technical: & Letter WritingDocument50 pagesTechnical: & Letter WritingFarhan Khan NiaZiNo ratings yet
- Conversion TableDocument2 pagesConversion TablemnjnasirNo ratings yet
- All About Supply, Demand, Elasticity, UtilityDocument11 pagesAll About Supply, Demand, Elasticity, Utilityantara nodiNo ratings yet
- Sanju Marketing NotesDocument39 pagesSanju Marketing NotesSanjiv Gautam100% (1)
- What Are The Main Steps of Quantitative Analysis?Document9 pagesWhat Are The Main Steps of Quantitative Analysis?Nehal NabilNo ratings yet
- Packing List Rig-882 (Ver 05-31-19) Pics Final 05-05-19Document14 pagesPacking List Rig-882 (Ver 05-31-19) Pics Final 05-05-19Imatsu International BusinessNo ratings yet
- Simplex Method in ORDocument10 pagesSimplex Method in ORAli MemonNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer Flow and Pipe Network AnalysisDocument18 pagesBoundary Layer Flow and Pipe Network AnalysisnkchandruNo ratings yet
- A Day in The Life of Frederic GodeDocument6 pagesA Day in The Life of Frederic GodeRachelle AndradeNo ratings yet
- BM229 - Strategic Business MangamentDocument2 pagesBM229 - Strategic Business MangamentJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Process ExplainedDocument43 pagesStrategic Management Process ExplainedJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy Concepts & The Is/It Strategy ImplicationsDocument74 pagesBusiness Strategy Concepts & The Is/It Strategy ImplicationsMoon 131415No ratings yet
- Chap 2Document71 pagesChap 2Jaka SeptiadiNo ratings yet
- 1A Introduction and Strategic Management EssentialsDocument25 pages1A Introduction and Strategic Management EssentialsJoyce Wong100% (2)
- 2022 - ER - Additional Slides What Is Strategy ManagementDocument9 pages2022 - ER - Additional Slides What Is Strategy Managementevelynn ellmaNo ratings yet
- Content For Chapter 6Document20 pagesContent For Chapter 6John Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- ABM Work Immersion Option C Online Marketing and Industry PartnershipDocument2 pagesABM Work Immersion Option C Online Marketing and Industry PartnershipJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Marketing PlanDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The Marketing PlanJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Checklist For 4th BizConDocument1 pageChecklist For 4th BizConJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- 4th Virtual Business Conference Educating for a VUCA WorldDocument3 pages4th Virtual Business Conference Educating for a VUCA WorldJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Up WorkDocument1 pageUp WorkJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Testing: How Is The Test Done?Document3 pagesAuditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Testing: How Is The Test Done?John Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Testing: How Is The Test Done?Document3 pagesAuditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Testing: How Is The Test Done?John Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- ABM WI Industry PartnershipDocument2 pagesABM WI Industry PartnershipJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Content For Chapter 6 NEWDocument4 pagesContent For Chapter 6 NEWJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- MGT 7 - Environmental Management Systems MW 5:00 - 6:30 Midterm ExamDocument1 pageMGT 7 - Environmental Management Systems MW 5:00 - 6:30 Midterm ExamJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Letter For CEFBEXDocument4 pagesLetter For CEFBEXJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- BM203B - Rating SheetDocument1 pageBM203B - Rating SheetJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- University of Cebu Graduate School Business ProcessesDocument3 pagesUniversity of Cebu Graduate School Business ProcessesJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Filipino Entrepreneurs and Role of EntrepreneurshipDocument13 pagesChallenges of Filipino Entrepreneurs and Role of EntrepreneurshipJohn Paul PrestonNo ratings yet
- Souvenir in Tourism Research. A Literature Review Andfuture AgendaDocument13 pagesSouvenir in Tourism Research. A Literature Review Andfuture AgendaCasmil BoniphaceNo ratings yet
- 061B Jsa Land Clearing 0+00Document10 pages061B Jsa Land Clearing 0+00sas13No ratings yet
- Refund LetterDocument2 pagesRefund LetterThierry GohoNo ratings yet
- Assignment PA 324Document18 pagesAssignment PA 324Mohammad Al-AminNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Logistics from Pre-Manufacturing to DeliveryDocument9 pagesContemporary Logistics from Pre-Manufacturing to Deliverymqjari2001100% (1)
- HSG THPT Mock Exam 01Document17 pagesHSG THPT Mock Exam 01nhưNo ratings yet
- 04 PM-Tricks - CostDocument27 pages04 PM-Tricks - CostMahmoud HagagNo ratings yet
- MCQS Chapter 8 Company Law 2017Document14 pagesMCQS Chapter 8 Company Law 2017BablooNo ratings yet
- Building A Data-Driven OrganizationDocument14 pagesBuilding A Data-Driven Organizationandini eldanantyNo ratings yet
- Laa 2 Donald Gunns 12 Types Codes Conventions of PrintsDocument13 pagesLaa 2 Donald Gunns 12 Types Codes Conventions of Printsapi-544028479No ratings yet
- Creating Strategic Advantages for NespressoDocument14 pagesCreating Strategic Advantages for NespressoAnkitpandya23No ratings yet
- Pricing Strategies - FinalDocument4 pagesPricing Strategies - FinalSirJason AnaloNo ratings yet
- SKAND Business and Management Paper 2 HL MarkschemeDocument3 pagesSKAND Business and Management Paper 2 HL MarkschemeSesión Plenaria Asamblea GeneralNo ratings yet
- One To One MarketingDocument22 pagesOne To One MarketingSamuel HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Rantai Pasok Daging KambingDocument9 pagesRantai Pasok Daging Kambingdian dwi cahyaniNo ratings yet
- Impact of Eco-Friendly Household Products On CustomersDocument4 pagesImpact of Eco-Friendly Household Products On CustomersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 1 - 2 - (06.10.2022, 13.10.22) TOPIC: Basic Cost Terms and Concepts, Cost Classification Ex. 1Document3 pagesTutorial - 1 - 2 - (06.10.2022, 13.10.22) TOPIC: Basic Cost Terms and Concepts, Cost Classification Ex. 1Tomas SanzNo ratings yet
- 2023 January 303 Financial Controls and Audit TaDocument17 pages2023 January 303 Financial Controls and Audit Taimabrar190No ratings yet
- Cost & Management Accounting - MGT402 Power Point Slides Lecture 22Document10 pagesCost & Management Accounting - MGT402 Power Point Slides Lecture 22AnsariRiazNo ratings yet
- Career Objective Sample Guide Under 40Document2 pagesCareer Objective Sample Guide Under 40shagun sharmaNo ratings yet
- INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT LectureDocument4 pagesINDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT LectureHlengy ZwaneNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Kit (HB 7000) Lower Breaker Part BronzeDocument4 pagesMaintenance Kit (HB 7000) Lower Breaker Part BronzedrmassterNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment OshmsDocument16 pagesGroup Assignment OshmsimanNo ratings yet
- Drive 1 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesDrive 1 Multiple Choice Questionsshankar_missionNo ratings yet
- Nature of ConsultancyDocument8 pagesNature of ConsultancyNalyanya50% (2)
- FSA - Ch06 - Liquidity of Short-Term Assets Related Debt-Paying AbilityDocument46 pagesFSA - Ch06 - Liquidity of Short-Term Assets Related Debt-Paying AbilityAmine AbdesmadNo ratings yet
- Ita Imia 2023 BDDocument28 pagesIta Imia 2023 BDKishor YenepalliNo ratings yet
- Assessment 3 Choice and Change (Presentation)Document5 pagesAssessment 3 Choice and Change (Presentation)Vladimir Losenkov100% (1)
- GTPPL Company Profile and CertificationsDocument12 pagesGTPPL Company Profile and CertificationsGtppl Green Thermo PowerNo ratings yet
- SOB - Accounting For Business Combinations - M1 PDFDocument40 pagesSOB - Accounting For Business Combinations - M1 PDFRyana ConconNo ratings yet