100% found this document useful (1 vote)
398 views5 pagesProject Management Information Systems
A Project Management Information System (PMIS) is an integrated system for managing and distributing project information. It contains information needed for all project stages from initiating to closing. The PMIS framework collects, organizes, stores, processes, and disseminates project information to assess project status. It provides essential cost, schedule, and performance data to support project planning, execution, and control. An effective PMIS adapts to user needs and provides standardized, decision-oriented information.
Uploaded by
محمد محمود مهديCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
398 views5 pagesProject Management Information Systems
A Project Management Information System (PMIS) is an integrated system for managing and distributing project information. It contains information needed for all project stages from initiating to closing. The PMIS framework collects, organizes, stores, processes, and disseminates project information to assess project status. It provides essential cost, schedule, and performance data to support project planning, execution, and control. An effective PMIS adapts to user needs and provides standardized, decision-oriented information.
Uploaded by
محمد محمود مهديCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
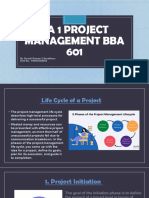
- Introduction to PMIS: Provides an overview of Project Management Information Systems (PMIS), outlining the necessary functions and benefits of implementing such systems in managing projects.
- Closing and Outcome Review: Describes the closing phase of a project and the subsequent review activities to document outcomes and learned lessons.
- Project Execution, Management, and Control: Focuses on methods and practices for executing and managing projects effectively while maintaining control over processes.
- Integration and Data Creation within PMIS: Explains how PMIS supports integration of management processes and the creation of data throughout project life cycles.
- Benefits of Computer-based PMISs: Discusses the advantages of utilizing computer-based PMISs, focusing on speed, ease of use, and efficiency improvements.