Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction & Epidemiology Clinical Features: End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
Uploaded by
Nikki VillanuevaOriginal Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIntroduction & Epidemiology Clinical Features: End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
Uploaded by
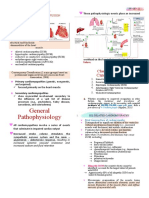
Nikki VillanuevaINTRODUCTION & CLINICAL FEATURES
EPIDEMIOLOGY Uremia is a clinical syndrome
- no single symptom/sign/laboratory will reflect all
End-stage Renal Disease (ESRD) aspects
- irreversible loss of renal function
- BUN & creatinine are inaccurate markers of
- results to accumulation of toxins, and loss of
internal homeostasis
clinical syndrome of uremia
- fatal unless given renal replacement therapy:
- Reason for emergency dialysis: hyperK, severe
- Renal transplant
acid-base disturbances, pulmonary edema
- Dialysis (hemo or peritoneal)
resistant to usual tx
Uremia - ↑ urea, BUN w/ ssxs
Non-specific: anorexia, vomiting, lassitude
Azotemia - ↑ N, BUN w/o ssxs
(subtle; attributed to other things)
Severe: tremors (asterixis), altered sleep-wake
Hemodialysis cycles, disorientation, seizures or convulsions
- initial therapy in majority of adults
(severe), bleeding diathesis (platelet abnormality)
- 1/2 alive 3 years post therapy
- cardiac cause as cause of death in 1/2
Leads to death unless toxins removed by RRT
Renal transplant & Peritoneal Dialysis
- more common in children
Neurologic
- Uremic encephalopathy: cognitive defects,
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY memory loss, decreased attentiveness, slurred
speech, reversal of sleep-wake cycle, asterixis,
1. Excretory Failure
seizure, coma, symptomatic improvement with
• elevated levels of >70 chemicals in uremic dialysis
plasma cause uremic organ dysfunction
- Dialysis dementia: progressive neurologic decline,
• Urea is not the major toxin
failure to improve with dialysis, fatal
• Toxins: cyanate, guanidine, polyamines and - Subdural hematoma: headache, FND, seizure,
B2-microglobulin
coma
• most toxins are protein bound —> non- - Peripheral neuropathy: singultus (hiccups),
dialyzable
restless leg syndrome, sensorimotor neuropathy,
2. Biosynthetic Failure autonomic neuropathy
• loss of renal hormones 1,25(OH)2-vit D3 and
EPO
Cardiovascular
• 1a-hydroxylase converts Vit D to active form
- coronary artery disease
• ↓EPO —> anemia - HTN: essential htn, glomerulonephritis, renal
• ↓Vit D3 —> ↓GI Ca absorption —> artery stenosis, fluid overload
secondary hyperparathyroidism —> renal - Heart failure: fluid overload, uremic
bone disease (aka bone resorption) cardiomyopathy, high output AVF
3. Regulatory Failure - Pericarditis: uremic, dialysis related, pericardial
• oversecretion of hormones —> disruption of tamponade
normal feedback mechanism
• Uremic State
Hematologic
- ↑hormone ↓ feedback ↑ ROS
- Anemia, decreased RBC survival, decreased EPO
- ROS interacting w/ CHO, lipids, AA —> - bleeding diathesis
atherosclerosis & amyloidosis
- Immunodeficiency (humoral & cellular)
- amyloid - insoluble protein
4. [TRANS]: progressive inflammation & GI
consequences - anorexia, metallic taste, N/V
- GI bleeding
- Diverticulosis, diverticulitis
- Ascites
Renal bone disease
- Metastatic calcification (calciphylaxis)
- Hyperparathyroidism (osteitis fibrosa cystica)
- Vit D3 deficiency & aluminim intoxication
(osteomalacia)
phantasmagory 2020 Nephro Lec 2019 x Tintinalli x UpToDate 1 of 2
Stage 1-2 : still reversible
Stage 3-5: point of no return
NEUROLOGIC COMPLICATIONS
Stroke - subdural hematoma - in dialysis
patients
Uremic encephalopathy - after eliminating
structural, vascular, infectious, toxic &
metabolic causes; improves with dialysis
Dialysis dementia - progressive, evident after
2 years of dialysis. Evident after at least 2
years of dialysis therapy
Peripheral neuropathy - m/c neurologic; LE >
UE. Large fiber involvement + paresthesias
↓DTR, imapired vibration sense, muscle
wasting & weakness
CARDIOVASCULAR
COMPLICATIONS
HEMATOLOGIC COMPLICATIONS
GI COMPLICATIONS
RENAL BONE DISEASE
B2-MICROGLOBULIN
AMYLOIDOSIS
HEMODIALYSIS
phantasmagory 2020 Nephro Lec 2019 x Tintinalli x UpToDate 2 of 2
You might also like
- Nephrology NewDocument93 pagesNephrology Newsaeedassaf97No ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Volume Depletion VascularDocument7 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Volume Depletion VascularJennyu YuNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument47 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseSaowda HussainNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Uremia SyndromeDocument8 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Uremia SyndromeMartien Silviandy SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument47 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseTamzid Rabby TanmoyNo ratings yet
- Renal Osmosis HY Pathology Notes ATF - ATFDocument109 pagesRenal Osmosis HY Pathology Notes ATF - ATFTran Thai Huynh NgocNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Anemia: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Prima IndonesiaDocument24 pagesClinical Approach To Anemia: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Prima IndonesiaDzil FikriNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument62 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryIvan HensonNo ratings yet
- Cute and Hronic: Renal FailureDocument31 pagesCute and Hronic: Renal FailureEhab S. AlHarbiNo ratings yet
- Renal Exam Class TestDocument8 pagesRenal Exam Class Test1fleetingNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument20 pagesAcute and Chronic Kidney DiseaseCabdi WaliNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Ch. 31 Hematologic ProblemsDocument36 pagesAnemia: Ch. 31 Hematologic Problemshops23100% (3)
- CKD AweDocument25 pagesCKD AweMunawwar AweNo ratings yet
- O LiguriaDocument4 pagesO LiguriaxmwdataNo ratings yet
- Approach To Acute Renal FailureDocument40 pagesApproach To Acute Renal FailureMochammad Fariz AmsalNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocument7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- 4 Kidney Diseases TogleMDDocument1 page4 Kidney Diseases TogleMDMarianneNo ratings yet
- Uptodate: Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument13 pagesUptodate: Chronic Kidney DiseaseAtiqah ShahNo ratings yet
- Blood FunctionsDocument3 pagesBlood FunctionshelloaNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument6 pagesAcute Renal FailureSNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemLeigh Maxenne IcoNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Document7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- Acute Renal Failure - Dr. Wael Omar (AQH) : Functions of The KidneyDocument3 pagesAcute Renal Failure - Dr. Wael Omar (AQH) : Functions of The KidneyasdddNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Sumit Kumar, MD, MPH Presbyterian Hospital, Dallas, TXDocument47 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Sumit Kumar, MD, MPH Presbyterian Hospital, Dallas, TXAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument20 pagesRenal SystemRahul DasNo ratings yet
- Too Little Insulin: Chronic ComplicationsDocument3 pagesToo Little Insulin: Chronic ComplicationsMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- ElectrolyteDocument4 pagesElectrolyteRon Vien'sNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 CKDDocument53 pagesLecture 3 CKDPharmswipe KenyaNo ratings yet
- MNT Penyakit GinjalDocument41 pagesMNT Penyakit GinjalNurfitriana DwiNo ratings yet
- Anemia - Aortic Stenosis B5Document8 pagesAnemia - Aortic Stenosis B5Aila HinlogNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: 1. Reduction in FunctionDocument6 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: 1. Reduction in FunctionKelebogile NkomoNo ratings yet
- CCRNPart 2Document164 pagesCCRNPart 2Paolo Vega100% (5)
- Triệu Chứng - Hội Chứng Bệnh Thận Y3Document58 pagesTriệu Chứng - Hội Chứng Bệnh Thận Y3trungNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument61 pagesRenal FailureEdward XiamNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Clinical Approach and Management: Dairion Gatot, Savita Handayani, Heny Syahrini, Andri MardiaDocument22 pagesAnemia: Clinical Approach and Management: Dairion Gatot, Savita Handayani, Heny Syahrini, Andri MardiarubyniNo ratings yet
- Long Cases Key TopicsDocument109 pagesLong Cases Key TopicsXu PeihaoNo ratings yet
- AKI in OBSTETRICSDocument41 pagesAKI in OBSTETRICSDebajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Diana's Renal DiseasesDocument9 pagesDiana's Renal DiseasesdhyltonNo ratings yet
- (Study Group) Diabetic Nephropathy, Hypertensive NephropathyDocument7 pages(Study Group) Diabetic Nephropathy, Hypertensive NephropathyZarif IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- Hematology Anemia & Bleeding Zorko2015Document6 pagesHematology Anemia & Bleeding Zorko2015Rishi Sharma100% (1)
- SGD - Polyuria in Pediatrics: Clinical ExaminationDocument1 pageSGD - Polyuria in Pediatrics: Clinical ExaminationREnren ConsolNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyBella Cy LopezNo ratings yet
- Renal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi SharmaDocument36 pagesRenal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi Sharmanidhi261987No ratings yet
- SGD - Polyuria in Pediatrics: Clinical ExaminationDocument1 pageSGD - Polyuria in Pediatrics: Clinical ExaminationREnren ConsolNo ratings yet
- Anti HypertensionDocument4 pagesAnti HypertensionMuhammad Zeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- conceptmap-DIABETES MELLITUSDocument8 pagesconceptmap-DIABETES MELLITUSDonnabell DayudayNo ratings yet
- Week 7. Renal Pathology Continued.Document9 pagesWeek 7. Renal Pathology Continued.Amber LeJeuneNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Neuropathy: PathogenesisDocument19 pagesDiabetic Neuropathy: PathogenesismehboobNo ratings yet
- NCP: Chronic Renal FailureDocument14 pagesNCP: Chronic Renal FailureJavie77% (13)
- CKD - For Concept MappingDocument7 pagesCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- GoutDocument12 pagesGoutRana AtefNo ratings yet
- Parameter 1 2 3: Serum Bilirubin Serum Albumin Prothrombin Time Ascites Hepatic EncelopathyDocument3 pagesParameter 1 2 3: Serum Bilirubin Serum Albumin Prothrombin Time Ascites Hepatic EncelopathyFirst LastNo ratings yet
- Final CC EdemaDocument31 pagesFinal CC EdematabatchNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Lab 1 Nilai NormalDocument3 pagesPemeriksaan Lab 1 Nilai NormalSivasangkari AnbalaganNo ratings yet
- Secondary HypertensionDocument34 pagesSecondary HypertensionSumaiya AlhaliyahNo ratings yet
- Zalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingDocument16 pagesZalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Circulation Physiology SummaryDocument3 pagesCirculation Physiology SummaryNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Gantt ChartDocument3 pagesGantt ChartNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Preconceptional CareDocument1 pagePreconceptional CareNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax PDFDocument1 pagePneumothorax PDFNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Gantt ChartDocument3 pagesGantt ChartNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- QC Problem Set 1 and 3Document2 pagesQC Problem Set 1 and 3Nikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- FlowDocument1 pageFlowNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- National Service Training Program Literacy Training Service English Pre Test Batch 3Document4 pagesNational Service Training Program Literacy Training Service English Pre Test Batch 3Nikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Mima RopaDocument21 pagesMima RopaNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- InternshipDocument1 pageInternshipNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- SchedDocument2 pagesSchedNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lts Activity OutlineDocument9 pagesLts Activity OutlineNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Decision SupportDocument14 pagesClinical Decision SupportNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- National Service Training Program Literacy Training Service English Pre Test Batch 3Document4 pagesNational Service Training Program Literacy Training Service English Pre Test Batch 3Nikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Decision SupportDocument14 pagesClinical Decision SupportNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- ScribdDocument2 pagesScribdNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- TDDSDocument2 pagesTDDSNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Healthcare EconomicsDocument2 pagesHealthcare EconomicsNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Decision SupportDocument14 pagesClinical Decision SupportNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument1 pageEthicsNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- TDDSDocument2 pagesTDDSNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Examples of Drugs - AsDocument2 pagesExamples of Drugs - AsNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Signal Magnet 2 B Posts Electromagnetic Coil Writing Pen Noting An Event (Time & Stimulus Type) Noting Time in SecondsDocument2 pagesSignal Magnet 2 B Posts Electromagnetic Coil Writing Pen Noting An Event (Time & Stimulus Type) Noting Time in SecondsNikki VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Sinus ArrhythmiaDocument6 pagesSinus ArrhythmiaVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Cardio Q&aDocument147 pagesCardio Q&aHoney Lyn AlebioNo ratings yet
- ECG Made Easy - An Abnormal LookDocument46 pagesECG Made Easy - An Abnormal LookabdallahNo ratings yet
- Strong's EKG Chamber Enlargement - DraftDocument12 pagesStrong's EKG Chamber Enlargement - DraftMonica GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Lecture - 15 Inotropic DrugsDocument3 pagesPharmacology Lecture - 15 Inotropic DrugsChris Queiklin100% (1)
- Acute Kidney Injury Concept MapDocument1 pageAcute Kidney Injury Concept MapKEn PilapilNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument4 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeHaryaman JustisiaNo ratings yet
- Transposition of The Great Arteries PDFDocument6 pagesTransposition of The Great Arteries PDFSakuntalaPalanki100% (2)
- Hyperkalemia How To Recognize and How To ManageDocument26 pagesHyperkalemia How To Recognize and How To Managedhika2496No ratings yet
- Syncope: Global Cerebral Blood FlowDocument7 pagesSyncope: Global Cerebral Blood FlowChananNo ratings yet
- Evolut Pro Mini Product Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesEvolut Pro Mini Product Brochure PDFBalázs PalcsikNo ratings yet
- JV Electrophysiology of HeartDocument19 pagesJV Electrophysiology of HeartRiya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Angiography 50%Document17 pagesAngiography 50%Nova SipahutarNo ratings yet
- CARDIO Intensive CareDocument6 pagesCARDIO Intensive CareDianne Erika MeguinesNo ratings yet
- Informe DEMO Del Holter de Arritmia Contec TLC9803Document14 pagesInforme DEMO Del Holter de Arritmia Contec TLC9803Edward MoralesNo ratings yet
- Transcatheter Aortic Valve ImplantationDocument15 pagesTranscatheter Aortic Valve ImplantationJonathan BaileyNo ratings yet
- 25 Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument35 pages25 Cardiovascular DiseaseBramantyo NugrosNo ratings yet
- 118a - CardiomyopathyDocument10 pages118a - CardiomyopathyJoanna TaylanNo ratings yet
- ACLS DrugsDocument16 pagesACLS Drugstostc100% (2)
- Ecg NotesDocument35 pagesEcg NotesDanielle100% (1)
- Gaddam, Ikshwak: ResultDocument1 pageGaddam, Ikshwak: Resultpraveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Advances in Hemodiafiltration - Ed by Ayman KarkarDocument158 pagesAdvances in Hemodiafiltration - Ed by Ayman KarkarbeguenineNo ratings yet
- Echo Made Easy: System RequirementDocument16 pagesEcho Made Easy: System RequirementAkhi FaruqNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument22 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseMark MahumotNo ratings yet
- MCQ Internal Medicine PDFDocument448 pagesMCQ Internal Medicine PDFAyaa Yousef100% (5)
- The Association Between Emergency Department Crowding and Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Chest PainDocument10 pagesThe Association Between Emergency Department Crowding and Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Chest PainGrace Angelica Organo TolitoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests in CardiologyDocument38 pagesDiagnostic Tests in CardiologyDea Amelia YolandaNo ratings yet
- HPT, Prevention, Targets, and TreatmentDocument8 pagesHPT, Prevention, Targets, and TreatmentAdinda Raihana SitorusNo ratings yet
- CardiomegalyDocument31 pagesCardiomegalyDeepika LingamNo ratings yet
- Littmann Cardiac AuscultationDocument1 pageLittmann Cardiac AuscultationSri Wahyuni100% (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (23)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingFrom EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingNo ratings yet
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassFrom EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (26)