Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study SUBJECTIVE CUES
Uploaded by
AnnahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study SUBJECTIVE CUES
Uploaded by
AnnahCopyright:
Available Formats
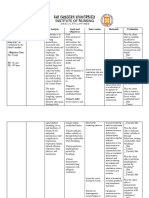
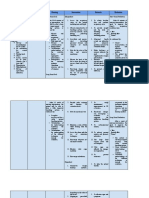
CUES NURSING OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
SUBJECTIVE CUES: Ineffective Short term goals: Independent: Short term
“permikogihangakm breathing At the end of 30 goals:
aam” as verbalized pattern minutes of thorough Allow client bed rest To conserve
by the patient. related to nursing care, the in between energy and Goals met.
shortness of patient will be able to. activities. to avoid After 15
oxygen overexertion minutes of
supply Demonstrate different Encourage slower thorough
OBJECTIVE CUES: kinds of relief respirations use of To assess nursing
Abnormal increase restlessness and pursed lip client in intervention,
of RR of 28cpm. feeling of breathless technique. taking the client was
control of the able to
Restlessness Appears restful situation and establish
Assist client on to reduce normal
Shortness of breath Establish normal semi-fowlers anxiety level. breathing
breathing pattern from position pattern from
23cpm to 20c.p.m To promote 28cpm to
expansion of 24cpm and
Long term goals: Monitor pulse lungs and demonstrated
After 8 hours of oximetry provide different kinds
thorough nursing comfort. of relief
intervention, the client restlessness
will able to: To and feeling of
verify/mainte breathless.
Maintain breathing Dependent: nance
pattern within the Provide oxygen improvement
normal range (12- therapy in oxygen
16cpm) saturation Long term
goals:
Goals met.
To maintain After nursing
an interventions,
acceptable the client was
level of able to
oxygen at maintain
tissue level. breathing
pattern within
the normal
range
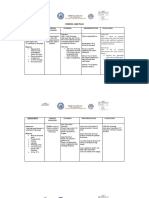
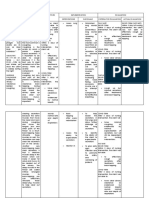
CUES NURSING OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
SUBJECTIVE CUES: Impaired Short term goals: Independent: Short term
Subjective cues: swallowing After15 minutes of Assist with To identify cause goals:
“maglisodkogtulonm related to thorough nursing diagnostic testing of swallowing
aam” as verbalized by abnormal intervention, the client of swallowing disorder Goals met.
the patient. function of will able to: activity. After 15
swallowing minutes of
mechanism Verbalize Encourage a rest thorough
understanding of period before nursing
OBJECTIVE: action of properly meals To minimize intervention,
intake of food and fatigue the client was
Coughing, choking, or water. able to
gagging before a Provide understand
swallow consistency of the action on
Lack of chewing Long term goals: food and fluid that For choking or how to intake
Delayed swallow After 8 hours of is most easily to aspiration can be properly the
thorough nursing swallowed. reduced food and
intervention, the client water
will able to: Dependent:
Able to demonstrate Long term
effective swallowing Refer to surgeon, goals:
without getting a gastroenterologist
problem. or neurologist Goals met.
Consider tube After nursing
feedings or For treat to interventions,
parenteral improved the client was
solutions, as swallowing able to
indicated demonstrate
For the client effective
who unable to wallowing
achieve without
adequate getting a
nutritional problem.
intake.
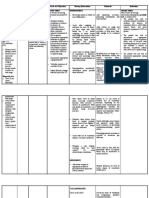
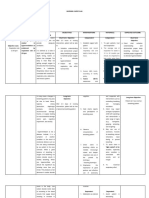
CUES NURSING OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
SUBJECTIVE CUES: Decreased Short term goals: Independent: Short
Heart palpitation cardiac After15 minutes of Administer fluids, To support termgoals:
Fatigue output thorough nursing diuretics, inotropic systemic and Goalsmet.Aft
Dyspnea;feeling related to intervention, the drugs, cardiac er15minuteso
breathless altered client will able to: antidysrhythmics, circulation and fthoroughnur
Anxiety heart rate steroids, determine singinterventi
or rhythm. Verbalize knowledge vasopressors and/or therapeutic, on,theclientw
OBJECTIVE: of the disease dilators, as indicated adverse, or toxic asableto
tachycardia process, individual amd evaluate effects of Verbalizekno
EKG [ECG] changes risk factors, and response. therapy. wledgeofnthe
( arrhythmia) treatment plan Provide adequate To promote diseaseproce
abnormal skin color including relaxation rest patient ss,individualri
alterations in blood techniques. relaxation skfactors,and
pressure readings Provide treatmentpla
cough Long term goals: psychological Honesty can be nincludingrel
After 8 hours of support. Maintain a reassuring when axationtechni
thorough nursing calm attitude, but so much activity ques.
intervention, the admit concerns if and worry are
client will able to: questioned by the apparent to the Longtermgoal
client. patient. s:
Display Elevate legs when This limits Goalsmet.Aft
hemodynamic sitting(if heart venous stasis, ernursinginte
stability (e.g. blood failure present or improves venous rventions,the
pressure, cardiac extremities are return and clientwasable
output, renal edematous). Apply systemic to
perfusion/ urinary antiembolic hose or circulation, and Report/Demo
output, peripheral sequential reduces the risk nstratedecrea
pulses). compression of sedepisodeso
devices when thrombophlebitis fdyspnea,angi
Report/ indicated, being . na,anddysrhy
Demonstrate sure they are thmias
decreased episodes individually fitted
of dyspnea, angina, and appropriately To reduce
and dysrhythmias. applied. anxiety and
Encourage conserve energy
relaxation
techniques.
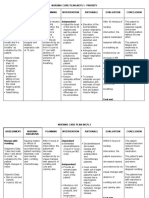
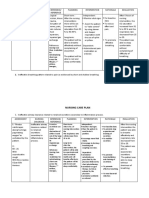
CUES NURSING OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
SUBJECTIVECUES: Impaired After 8 hours of Monitor vital signs It serves as a
Dyspnea gas nursing and cardiac baseline for data. All After8hoursof
Visual Disturbance exchange intervention, the rhythm. vital signs are nursinginterv
related to patient will be impacted by changes ention, the
OBJECTIVE: ventilation- able to maintain in oxygenation. patient was
Abnormal arterial perfusion optimal gas Elevate the head of able to
blood gases (ABGs)/ imbalance exchange and the bed and Elevation or upright maintain
arterial pH participate in position the client position facilitates optimal gas
Abnormal breathing treatment appropriately. respiratory function exchange as
pattern regimen (e.g. by gravity; however, evidenced by
Tachycardia breathing a patient in severe normal ABGs
excercises, Note the character distress will seek a and alert
effective and effectiveness position of comfort. responsive
coughing, use of of the coughing This affects the mentation or
oxygen) within mechanism. ability to clear no further
level of ability or airways of secretion. reduction in
situation. Assess level of mental status
consciousness and A decreases level of
mentation consciousness can be
changes. an indirect
measurement of
impaired
oxygenation, but it
Encourage also impairs one's
frequent position ability to protect
changes and deep- airway, potentially
breathing and further and adversely
coughing affecting
excercises. Use oxygenation.
incentive This promotes
spirometer, chest optimal chest
physiotherapy, expansion,
intermittent mobilization of
positive-pressure secretions, and
breathing, as oxygen diffusion.
indicated.
CUES NURSING OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
SUBJECTIVE: Impaired After 8 hours, the Monitor vital signs It serves as a After8hoursof
Exposure to oral mucous patient will be and cardiac baseline for data. All nursinginterv
pathogen membrane able to rhythm. vital signs are ention;
Oral pain or related to Verbalize impacted by changes Responses to
discomfort allergy understanding of in oxygenation. interventions
Difficulty in eating or causitive or risk Elevate the head of and actions
swallowing factor. the bed and Elevation or upright are
Identify specific position the client position facilitates performed.
OBJECTIVE: interventions to appropriately. respiratory function The patient
Geographic tongue promote healthy by gravity; however, was able to
Oral edema oral mucosa a patient in severe demonstrate
Difficulty speaking distress will seek a techniques to
Mucosal pallor Demonstrate Note the character position of comfort. restore
techniques to and effectiveness /maintain
restore/maintain of the coughing This affects the integrity of
integrity of oral mechanism. ability to clear oral mucosa.
mucosa airways of secretion.
Assess level of A decreases level of
consciousness and consciousness can be
mentation an indirect
changes. measurement of
impaired
oxygenation, but it
Encourage also impairs one's
frequent position ability to protect
changes and deep- airway, potentially
breathing and further and adversely
coughing affecting
excercises. Use oxygenation.
incentive
spirometer, chest The patient
physiotherapy, maintains optimal
intermittent gas exchange as
positive-pressure evidenced by normal
breathing, as ABGs and alert
indicated. responsive
mentation or no
further reduction in
mental status
You might also like
- NCP Copd FinalDocument3 pagesNCP Copd FinalGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Plueral Effusion NCPDocument7 pagesPlueral Effusion NCPJill Rae Lloren ConsolacionNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Expected Outcome Evaluation Subjective: Independent: Short Term Goal: Goals MetDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Expected Outcome Evaluation Subjective: Independent: Short Term Goal: Goals Metapi-3828211No ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pageNursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternnikkilyceeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKim SungaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMargareth GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesAbie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesNursing Care PlanRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation of a Client with Increased Airway SecretionsDocument3 pagesAssessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation of a Client with Increased Airway SecretionsNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Lumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsDocument4 pagesLumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsPatricia Ortega100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJanmae JivNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Record for Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNursing Process Record for Ineffective Breathing PatternTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPKrishcel Canlapan InsoNo ratings yet
- Vii. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Expected Outcome Evaluation Subjective: Independent: Short Term GoalDocument1 pageVii. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Plan of Care Expected Outcome Evaluation Subjective: Independent: Short Term Goalapi-3828211No ratings yet
- Group 3 - End-of-Life Care Case StudyDocument6 pagesGroup 3 - End-of-Life Care Case StudyLheane Marley LopenaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKyle OxfordNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives: Nursing Intervention Rationale: EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives: Nursing Intervention Rationale: EvaluationMaria Eliza AgustinoNo ratings yet
- ncpDocument3 pagesncpDana LabusonNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Document6 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Karissa GuerreroNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP AsthmaDocument8 pagesNCP Asthmaqweyo yhuNo ratings yet
- Vi. Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesVi. Nursing Care PlanJopaii TanakaNo ratings yet
- Vii. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Prioritization SignificanceDocument7 pagesVii. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Prioritization SignificanceMarichu Bajado0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanShania Erika EnajeNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternJose Marlon CandelariaNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument2 pagesNCP FormatFrancesca MalbogNo ratings yet
- NCP 6thBDocument1 pageNCP 6thBLester Lopez Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Ineffective BreathingDocument3 pagesAssessing and Managing Ineffective BreathingEdem LeeNo ratings yet
- Managing Pain and Constipation Through Targeted Nursing InterventionsDocument4 pagesManaging Pain and Constipation Through Targeted Nursing InterventionsCiara ManguiatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for DyspneaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for DyspneaBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Final Thyroid Storm NCPDocument6 pagesFinal Thyroid Storm NCPoguitekim1No ratings yet
- Actaul Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActaul Drug Studyjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- NCP GeriaDocument6 pagesNCP Geriagrazelantonette.calubNo ratings yet
- Goal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionDocument4 pagesGoal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceKenj Pereña100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- NCP For OxygenationDocument6 pagesNCP For OxygenationChriz LechNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationDocument4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationVanessa Charlotte LagunayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans:Guidelines For Individualizing Client Care Across The Lifespan, 7 Edition DoengesDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plans:Guidelines For Individualizing Client Care Across The Lifespan, 7 Edition DoengesNica PinedaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Client: N. D. Age: 39 Gender: Male Medical Diagnosis: Community Acquired Pneumonia, Moderate Risk, PTBDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan Client: N. D. Age: 39 Gender: Male Medical Diagnosis: Community Acquired Pneumonia, Moderate Risk, PTBGertrude Araneta JavierNo ratings yet
- Viray, Messiah Jezreel: NCP #3 For RHDDocument3 pagesViray, Messiah Jezreel: NCP #3 For RHDJezzy VeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of DyspneaDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern As Evidenced by Use of Accessory Muscles and Episodes of DyspneaNiel MinatozakiNo ratings yet
- Managing COPD ExacerbationDocument17 pagesManaging COPD ExacerbationSean Menard Flores100% (1)
- AssessmentDocument1 pageAssessmentFat NrqzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- Nursing Care Plans for Common IllnessesDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans for Common Illnessesjeng214No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceRodel Yacas67% (3)
- NCP MiniparDocument9 pagesNCP MiniparKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Nursing Care Plan SampleDocument2 pagesModule 4 Nursing Care Plan SamplejanNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBjannica_villarealNo ratings yet
- Pedia Clinical Enrichment NCPDocument5 pagesPedia Clinical Enrichment NCPIsabelle Hazel BenemileNo ratings yet
- A Beginner’s Guide to Acupuncture: Discover the Power of Acupuncture and How its Benefit to Your LifeFrom EverandA Beginner’s Guide to Acupuncture: Discover the Power of Acupuncture and How its Benefit to Your LifeRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Sleep Better Live Better: A Guide to Healthy Sleep Habits and Restorative SleepFrom EverandSleep Better Live Better: A Guide to Healthy Sleep Habits and Restorative SleepNo ratings yet
- GG business model optimized for busy professionalsDocument6 pagesGG business model optimized for busy professionalsAnnahNo ratings yet
- How to Play Dota 2 Like Me: Salman's 3 RulesDocument5 pagesHow to Play Dota 2 Like Me: Salman's 3 RulesAnnahNo ratings yet
- MY THOUGHTS ABOUT "A Beautiful Mind": Daro, Farhannah T. Bsn-3Document1 pageMY THOUGHTS ABOUT "A Beautiful Mind": Daro, Farhannah T. Bsn-3AnnahNo ratings yet
- A.) Culture and Its Role in Moral BehaviourDocument6 pagesA.) Culture and Its Role in Moral BehaviourAnnahNo ratings yet
- Transform BoundaryDocument1 pageTransform BoundaryAnnahNo ratings yet
- Dessert Business Plan1 PDFDocument155 pagesDessert Business Plan1 PDFAnnahNo ratings yet
- MY THOUGHTS ABOUT "A Beautiful Mind": Daro, Farhannah T. Bsn-3Document1 pageMY THOUGHTS ABOUT "A Beautiful Mind": Daro, Farhannah T. Bsn-3AnnahNo ratings yet
- Iud FinalDocument3 pagesIud FinalAnnahNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Results Summary for Nursing ImplicationsDocument3 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic Results Summary for Nursing ImplicationsAnnahNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACTDocument1 pageABSTRACTAnnahNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Biochemical Roles: Biochemistry 3070Document38 pagesVitamins: Biochemical Roles: Biochemistry 3070AnnahNo ratings yet
- Internet CafeDocument13 pagesInternet Cafeapi-375964680% (5)
- Arthropods and infectious diseasesDocument4 pagesArthropods and infectious diseasesAnnahNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections of the Lower Respiratory Tract and SkinDocument2 pagesFungal Infections of the Lower Respiratory Tract and SkinAnnahNo ratings yet
- Business Plan For Margaret BakeryDocument4 pagesBusiness Plan For Margaret BakeryLouiejay SalvoNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Arlyn M. FabroaDocument8 pagesPrepared By:: Arlyn M. FabroaEmmanuel Recodo100% (1)
- Dessert Business Plan1 PDFDocument155 pagesDessert Business Plan1 PDFAnnahNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Results Summary for Nursing ImplicationsDocument3 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic Results Summary for Nursing ImplicationsAnnahNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Arlyn M. FabroaDocument8 pagesPrepared By:: Arlyn M. FabroaEmmanuel Recodo100% (1)
- Internet CafeDocument13 pagesInternet Cafeapi-375964680% (5)
- Acyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyDocument3 pagesAcyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyAnnahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Effective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Effective Airway ClearanceAnnahNo ratings yet
- Dessert Business Plan1 PDFDocument155 pagesDessert Business Plan1 PDFAnnahNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Results Summary for Nursing ImplicationsDocument3 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic Results Summary for Nursing ImplicationsAnnahNo ratings yet
- Basketball InjuriesDocument3 pagesBasketball InjuriesAnnahNo ratings yet
- 101 ConclusionDocument2 pages101 ConclusionAnnahNo ratings yet
- Internet CafeDocument13 pagesInternet Cafeapi-375964680% (5)
- Significance of Nursing Informatics Research Studies by Amany AbdrboDocument8 pagesSignificance of Nursing Informatics Research Studies by Amany AbdrboAnnahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanAnnahNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Case Write Up 1Document14 pagesInternal Medicine Case Write Up 1Roshandiep GillNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exercise Effective CoughDocument52 pagesBreathing Exercise Effective CoughDesy Suryani Pais100% (1)
- Cbest Essay PromptsDocument4 pagesCbest Essay Promptstuevptvhd100% (2)
- Tobacco Smoking in YouthDocument6 pagesTobacco Smoking in YouthNipunNo ratings yet
- LPUN College of Nursing Guide for Nursing ProcessDocument6 pagesLPUN College of Nursing Guide for Nursing ProcessCaryl EteNo ratings yet
- BAIAE in Pregnancy.Document6 pagesBAIAE in Pregnancy.Mark Arthur MartinezNo ratings yet
- FINAL CAHS RLE and CP Health Declaration Revised 1Document2 pagesFINAL CAHS RLE and CP Health Declaration Revised 1Laila EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Disease Deep Dive Kathryn CrimDocument7 pagesDisease Deep Dive Kathryn Crimapi-579320483No ratings yet
- ABC Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesABC Lecture NotesLady Shayne YapNo ratings yet
- Cardiology 1Document60 pagesCardiology 1ChibuNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Case ProgressionDocument2 pagesCase Progressionczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe AssesmentDocument4 pagesHead To Toe AssesmentYemaya84100% (1)
- NP3Document12 pagesNP3Lyca BerinNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Disease of Lung and Physiotherapy ManagementDocument76 pagesObstructive Disease of Lung and Physiotherapy Managementphysio43100% (1)
- Respiratory Case StudiesDocument6 pagesRespiratory Case Studiesadom09No ratings yet
- Case History For 2nd Year StudentsDocument4 pagesCase History For 2nd Year StudentsAkshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet - Sodium Fluoride MSDSDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet - Sodium Fluoride MSDSGodIsTruthNo ratings yet
- WHISNANT 2016 Slides PDFDocument203 pagesWHISNANT 2016 Slides PDFlocoproanimal100% (5)
- Fluid Management PubmedDocument8 pagesFluid Management PubmedResti DwiuNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Long Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesHealth Assessment Long Answer QuestionsSraddha Patel50% (2)
- Chapter 24 Management of Patients With Chronic Pulmonary DisordersDocument3 pagesChapter 24 Management of Patients With Chronic Pulmonary DisordersPeej Reyes100% (1)
- RENR Test Prep 2017Document12 pagesRENR Test Prep 2017Tk100% (3)
- Respiratory Disorders GuideDocument66 pagesRespiratory Disorders GuidewinarsohNo ratings yet
- Management of Life-Threatening Asthma (@ eDocument10 pagesManagement of Life-Threatening Asthma (@ eLex X PabloNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Study: Pulmonology Physician: Pulmonologist Function: Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesRespiratory System: Study: Pulmonology Physician: Pulmonologist Function: Exchange of GasesSakshi BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Complications Druing HemodialysisDocument30 pagesComplications Druing HemodialysisMD Hajj83% (6)
- Evaluation of Dyspneic PatientDocument15 pagesEvaluation of Dyspneic Patientcamila perillaNo ratings yet
- Low TSH, low T4, low T3 in the ICU setting is likely centralhypothyroidism. A high TSH would help confirm the diagnosis as centralhypothyroidismDocument126 pagesLow TSH, low T4, low T3 in the ICU setting is likely centralhypothyroidism. A high TSH would help confirm the diagnosis as centralhypothyroidismmaimoona suleman0% (1)
- Child's Military Tuberculosis CaseDocument31 pagesChild's Military Tuberculosis CaseRifka WindiputriNo ratings yet