Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Is An Organic Compound That Provides Energy To Drive
Uploaded by
AOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Is An Organic Compound That Provides Energy To Drive
Uploaded by
ACopyright:
Available Formats
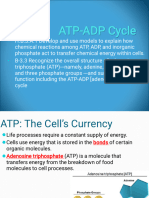
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive
many processes in living cells, e.g. muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and
chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the
"molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer.[2] When consumed
in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or
to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP so that the
human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day.[3] It is also
a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme.
From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate,
which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the
sugar ribose, and the triphosphate.
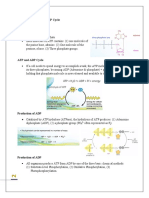
In terms of its structure, ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to
the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which in turn is attached at the 5' carbon atom of
the sugar to a triphosphate group. In its many reactions related to metabolism, the
adenine and sugar groups remain unchanged, but the triphosphate is converted to di-
and monophosphate, giving respectively the derivatives ADP and AMP. The three
phosphoryl groups are referred to as the alpha (α), beta (β), and, for the terminal
phosphate, gamma (γ).
ATP was discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann[39] and Jendrassik[40] and, independently,
by Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subba Rao of Harvard Medical School,[41] both teams
competing against each other to find an assay for phosphorus.
It was proposed to be the intermediary between energy-yielding and energy-requiring
reactions in cells by Fritz Albert Lipmann in 1941.[42]
It was first synthesized in the laboratory by Alexander Todd in 1948.[43]
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1997 was divided, one half jointly to Paul D.
Boyer and John E. Walker "for their elucidation of the enzymatic mechanism underlying
the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)" and the other half to Jens C. Skou "for
the first discovery of an ion-transporting enzyme, Na+, K+ -ATPase."[44]
Source: Wikipedia
You might also like
- ATP-ADP CycleDocument15 pagesATP-ADP CycleMay PaviaNo ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)Document1 pageAdenosine Triphosphate (ATP)Clemo 2No ratings yet
- Atp Group 5Document28 pagesAtp Group 5Dbez JonniNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Cycles - FermentationDocument13 pagesGen Bio Cycles - Fermentationyxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Atp Adp CycleDocument13 pagesAtp Adp Cycleelladomingo54No ratings yet
- Explain The Complete Reaction For The Hydrolysis of Adenosine Triphosphat1Document15 pagesExplain The Complete Reaction For The Hydrolysis of Adenosine Triphosphat1NURAIHAN BINTI HASHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument2 pagesEnergydR SHAMMIR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- ATP ADP CycleDocument20 pagesATP ADP CycleButz AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Atp CycleDocument4 pagesAtp CycleVignesh100% (1)
- Atp-Adp CycleDocument20 pagesAtp-Adp Cyclekim cchlNo ratings yet
- 19 AtpDocument34 pages19 AtpSheena BautistaNo ratings yet
- Karl Lohmann (1929) Discovered ATP in Muscle Cells. Fritz Lipmann and Herman Kalckar (1941) Were The First To Recognize The Role of ATP in Energy MetabolismDocument12 pagesKarl Lohmann (1929) Discovered ATP in Muscle Cells. Fritz Lipmann and Herman Kalckar (1941) Were The First To Recognize The Role of ATP in Energy Metabolismمحمد جانNo ratings yet
- Atp and Biological Energy PDFDocument7 pagesAtp and Biological Energy PDFAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Atp and Coupled ReactionDocument3 pagesAtp and Coupled ReactionBhea Mariel CaipangNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio G6 3Document16 pagesGen Bio G6 3chuuu 89No ratings yet
- WordDocument6 pagesWordJonel SorianoNo ratings yet
- AtpDocument10 pagesAtpSheba HernandezNo ratings yet
- Atp EssayDocument3 pagesAtp EssayValeria PunzoNo ratings yet
- A Level RespirationDocument19 pagesA Level RespirationBWAMBALE HARISONNo ratings yet
- Adenosine TriphosphateDocument2 pagesAdenosine TriphosphateThanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q2 Wk2 QADocument32 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q2 Wk2 QAEdreyan Adong Cortez LimbagaNo ratings yet
- Reactions That Produce and Consume ATPDocument7 pagesReactions That Produce and Consume ATPsittinginthecorner1No ratings yet
- Atp-Adp Cycle: Presentation By: Miranda, Morales, Morando, NietesDocument7 pagesAtp-Adp Cycle: Presentation By: Miranda, Morales, Morando, NietesYOSEF AZRIEL CONCEPCION MORALESNo ratings yet
- Q2Week-1 ATP ADP-CouplingDocument13 pagesQ2Week-1 ATP ADP-Couplingjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- Atp and Biological EnergyDocument7 pagesAtp and Biological EnergyFaiza AzzamtaNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument10 pagesGenbiojerrylinbermudezNo ratings yet
- Atp STR FinDocument16 pagesAtp STR FinNimsha KamalaNo ratings yet
- ATP ADP SlidesDocument14 pagesATP ADP SlidesNorsaifah AbduljalalNo ratings yet
- Atp: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: - Aditya Sunil Nair - Class XI D - Roll No: 22Document10 pagesAtp: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: - Aditya Sunil Nair - Class XI D - Roll No: 22Aditya Sunil NairNo ratings yet
- ATP PPTDocument13 pagesATP PPTMA. HAZEL TEOLOGONo ratings yet
- Energy CouplingDocument3 pagesEnergy CouplingHannah VillocenoNo ratings yet
- ATPDocument3 pagesATPshekinah656No ratings yet
- ATP: Adenosine TriphosphateDocument3 pagesATP: Adenosine TriphosphateClaire ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Adenosine TriphosphateDocument4 pagesAdenosine TriphosphateFizzah AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Atp-Adp CycleDocument4 pagesAtp-Adp Cyclejeff garingaraoNo ratings yet
- Role of ATP in Energy Coupling and TransferDocument1 pageRole of ATP in Energy Coupling and TransferOmbrog JustinNo ratings yet
- (Wasla Bashir) (26) (Z 1802) (Assignment 3)Document8 pages(Wasla Bashir) (26) (Z 1802) (Assignment 3)Rafia NaeemNo ratings yet
- ATP-ADP Cycle PowerpointDocument18 pagesATP-ADP Cycle PowerpointJohn Iderf LagardeNo ratings yet
- ATP: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: ATP Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesATP: Universal Currency of Cellular Energy: ATP Structure and FunctionCielo PepitoNo ratings yet
- NOTES 1 ATP and ADP CycleDocument4 pagesNOTES 1 ATP and ADP CycleJillian Reyes SantosNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Week 1 - Module 1Document11 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Week 1 - Module 1Regine Ann ViloriaNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationDocument19 pagesA2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationKajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationDocument20 pagesA2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationArnel100% (1)
- ATP - ADP Cycle: Module 1 - Energy TransformationDocument10 pagesATP - ADP Cycle: Module 1 - Energy TransformationNoreen AlipioNo ratings yet
- Atp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesDocument5 pagesAtp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesJohn Carlo G. NolascoNo ratings yet
- Namrata - Atp Intro Energy Currency Btech MLB 104 UseDocument32 pagesNamrata - Atp Intro Energy Currency Btech MLB 104 Usemaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Mitochondria ATPDocument5 pagesAerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Mitochondria ATPjatsugbNo ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE 1 NotesDocument4 pagesSTUDY GUIDE 1 NotesBae SeujiNo ratings yet
- BiologicalReview29 4 ATP PresentationDocument21 pagesBiologicalReview29 4 ATP Presentationsmithsashay74No ratings yet
- Quarter 2 / Semester 1, Week 1: Print Material/sDocument6 pagesQuarter 2 / Semester 1, Week 1: Print Material/sMonica SolomonNo ratings yet
- U-5 Energy Transformation PDFDocument41 pagesU-5 Energy Transformation PDFHawi kelbessaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: Fructose Glucose GalactoseDocument3 pagesGlycolysis: Fructose Glucose GalactoseCy Santiago GarridoNo ratings yet
- Atp AdpDocument1 pageAtp AdpHanna Evidente BakalNo ratings yet
- A Cell Performs Three Main Kinds of Work ReviewerDocument1 pageA Cell Performs Three Main Kinds of Work ReviewerShylyn Kris BuensucesoNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation - Atp-Adp CycleDocument33 pagesEnergy Transformation - Atp-Adp CyclePrincess EscandalloNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisJoshua MeraNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Document3 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Maria Bettina DizonNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument111 pagesEnergy TransformationDanielNo ratings yet
- Amoeba SistersDocument1 pageAmoeba SistersrebekaNo ratings yet
- Cls M Specifications 1Document15 pagesCls M Specifications 1kishor150688No ratings yet
- Noise ControlDocument1 pageNoise ControlANo ratings yet
- Noise PollutionDocument1 pageNoise PollutionANo ratings yet
- Silica FumeDocument1 pageSilica FumeANo ratings yet
- Rhe OlogyDocument1 pageRhe OlogyANo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument1 pageAcousticsANo ratings yet
- Light PollutionDocument1 pageLight PollutionANo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Metabolism (/məˈtæbəlɪzəm/, from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, "change") is the set of lifeDocument1 pageMetabolism: Metabolism (/məˈtæbəlɪzəm/, from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, "change") is the set of lifeANo ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument1 pageAcousticsANo ratings yet
- Noise PollutionDocument1 pageNoise PollutionANo ratings yet
- Light PollutionDocument1 pageLight PollutionANo ratings yet
- Superabsorbent Polymer: Superabsorbent Polymer (SAP) (Also Called Slush Powder) Can Absorb and Retain Extremely LargeDocument1 pageSuperabsorbent Polymer: Superabsorbent Polymer (SAP) (Also Called Slush Powder) Can Absorb and Retain Extremely LargeANo ratings yet
- Noise ControlDocument1 pageNoise ControlANo ratings yet
- Organelle: Bound and Non-Membrane Bound OrganellesDocument1 pageOrganelle: Bound and Non-Membrane Bound OrganellesANo ratings yet
- Active AbsorptionDocument1 pageActive AbsorptionANo ratings yet
- Types of DeformationDocument2 pagesTypes of DeformationANo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Metabolism (/məˈtæbəlɪzəm/, from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, "change") is the set of lifeDocument1 pageMetabolism: Metabolism (/məˈtæbəlɪzəm/, from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, "change") is the set of lifeANo ratings yet
- Organelle: Bound and Non-Membrane Bound OrganellesDocument1 pageOrganelle: Bound and Non-Membrane Bound OrganellesANo ratings yet
- Lipid: Source: WikipediaDocument1 pageLipid: Source: WikipediaANo ratings yet
- Maintenance RespirationDocument1 pageMaintenance RespirationANo ratings yet
- Active AbsorptionDocument1 pageActive AbsorptionANo ratings yet
- Ultimate Tensile StrengthDocument1 pageUltimate Tensile StrengthANo ratings yet
- PolystyreneDocument1 pagePolystyreneANo ratings yet
- Ductile MaterialsDocument1 pageDuctile MaterialsANo ratings yet
- DeformationDocument1 pageDeformationANo ratings yet
- ThermoplasticDocument1 pageThermoplasticANo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument1 pagePolymerANo ratings yet
- Dispersed MediaDocument1 pageDispersed MediaANo ratings yet
- PolyurethaneDocument1 pagePolyurethaneANo ratings yet
- FoamDocument1 pageFoamANo ratings yet