Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mensuration 8
Mensuration 8
Uploaded by
Akash Sahu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views18 pagesmesuration math
Original Title
mensuration-8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmesuration math
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views18 pagesMensuration 8
Mensuration 8
Uploaded by
Akash Sahumesuration math
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
WHAT WE WILL LEARN ?
AREA OF QUADRILATERALS AND
POLYGONS
SURFACE AREA OF SOLIDS
VOLUME OF SOLIDS
FOR
THE AMOUNT OF SPACE INSIDE THE BOUNDARY OF TWO PERIMETER
ADD UP
DIMENSIONAL SHAPE LENGTH
OF ALL SIDS
THE DISTANCE AROUND THE OUTSIDE OF TWO DIMENSIONAL SHAPE
`
SQUARE
Square (regular quadrilateral): all four sides are of equal length (equilateral), and
all four angles are right angles. An equivalent condition is that opposite sides are
parallel (a square is a parallelogram), that the diagonals perpendicularly bisect
each other, and are of equal length. A quadrilateral is a square if and only if it is
both a rhombus and a rectangle (four equal sides and four equal angles).
Rectangle: all four angles are right angles. An equivalent condition is that the
diagonals bisect each other and are equal in length. Rectangles include squares
and oblongs. Informally: "a box or oblong" (including a square).
TRIANGLE
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic
shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted triangle ABC.
PARALLELOGRAM
Parallelogram: a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. Equivalent conditions
are that opposite sides are of equal length; that opposite angles are equal; or that
the diagonals bisect each other. Parallelograms include rhombi (including those
rectangles we call squares) and rhomboids (including those rectangles we call
oblongs). In other words, parallelograms include all rhombi and all rhomboids, and
thus also include all rectangles.
TRAPEZIUM
In Euclidean geometry, a convex quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides
is referred to as a trapezoid . The parallel sides are called the bases of the trapezoid
and the other two sides are called the legs or the lateral sides (if they are not
parallel; otherwise there are two pairs of bases). A scalene trapezoid is a trapezoid
with no sides of equal measure, in contrast to the special cases below.
RHOMBUS
Rhombus or rhomb: all four sides are of equal length. An equivalent condition is
that the diagonals perpendicularly bisect each other. Informally: "a pushed-over
square" (but strictly including a square, too).
A Cube has 6 square faces.
The length of each square face is equal.
LENGTH
LENGTH
LENGTH
Volume of CUBE = LENGTH X LENGTH X LENGTH
= l X l X l
= l³
CUBOID
A cuboid also has 6 faces but NOT all the
faces are equal
Height
Breadth
Length
Volume of CUBOID = LENGTH X BREADTH X HEIGHT
= X l X
b h
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Parts of Circles, Area, CircumferenceDocument5 pagesParts of Circles, Area, Circumferencepaola varillasNo ratings yet
- Emami Product MixDocument17 pagesEmami Product MixAkash SahuNo ratings yet
- India Banking Fraud Survey: Edition IIDocument36 pagesIndia Banking Fraud Survey: Edition IIAkash SahuNo ratings yet
- Beauty and Personal Care Industry Set For Exponential Growth, Retail News, ET RetailDocument8 pagesBeauty and Personal Care Industry Set For Exponential Growth, Retail News, ET RetailAkash SahuNo ratings yet
- Amity University, Chhattisgarh: Climate ChangeDocument21 pagesAmity University, Chhattisgarh: Climate ChangeAkash SahuNo ratings yet
- Math Olympiad Problems Collection v2 PDFDocument144 pagesMath Olympiad Problems Collection v2 PDFSaba TavdgiridzeNo ratings yet
- Math4-Q3M4-Relating Triangles To Quadrilaterals and Relating One Quadrilateral To Another Quadrilateral-Roque AnDocument27 pagesMath4-Q3M4-Relating Triangles To Quadrilaterals and Relating One Quadrilateral To Another Quadrilateral-Roque AnHans Derick ValdezNo ratings yet
- Standard 1 Learner Development - Math Lesson - 2d Shapes - QuadrilateralsDocument10 pagesStandard 1 Learner Development - Math Lesson - 2d Shapes - Quadrilateralsapi-367135087No ratings yet
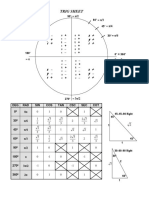
- Trig Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesTrig Sheet PDFSherbimInternetNo ratings yet
- Find The Six Circular Functions of The Below. 1. 8Document4 pagesFind The Six Circular Functions of The Below. 1. 8Sir LogNo ratings yet
- Class - V Mathematics Full Marks:190 Time: 3 HrsDocument13 pagesClass - V Mathematics Full Marks:190 Time: 3 HrsSUBHANo ratings yet
- Year 9 Revision 1st Term FinalDocument25 pagesYear 9 Revision 1st Term FinalMehmet Derin OzserNo ratings yet
- Numeracy Test Grade 10 Part 1 2Document6 pagesNumeracy Test Grade 10 Part 1 2Lea CardinezNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Questions and Answers - Basics of Section of SolidsDocument22 pagesEngineering Drawing Questions and Answers - Basics of Section of SolidsMANIKANDAN KNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore North: 1 - GraphDocument4 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore North: 1 - GraphVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- 15ME105L Engg Graphics Exercise Questions 7 - Aug - 17Document16 pages15ME105L Engg Graphics Exercise Questions 7 - Aug - 17Rɩsʜʌv SɩŋʛʜNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 Triangles N PolygonDocument40 pagesCHAPTER 11 Triangles N PolygonKeng KengjungNo ratings yet
- Perimeter Lesson Plan Ed216Document1 pagePerimeter Lesson Plan Ed216hernans3781No ratings yet
- School of Saint Joseph The Worker: Learning Module Mathematics Grade 7Document7 pagesSchool of Saint Joseph The Worker: Learning Module Mathematics Grade 7Rondex PabloNo ratings yet
- Intermediate GeometryDocument16 pagesIntermediate GeometryD.SREEPRANAD 7a2020No ratings yet
- Oxford University Press 2Document1 pageOxford University Press 25B24 Li Hei Yu HaybeNo ratings yet
- GRE Test Prep - Quantitative Comparison II - Worksheet - Test PaperDocument6 pagesGRE Test Prep - Quantitative Comparison II - Worksheet - Test PaperManjeet BhatiaNo ratings yet
- 8-2 Notes GeometryDocument2 pages8-2 Notes GeometryNoah BlautNo ratings yet
- Relationships in Space: Geometry and Trigonometry in 2D and 3DDocument28 pagesRelationships in Space: Geometry and Trigonometry in 2D and 3D이유태No ratings yet
- Arc Lengths and Areas of Sectors (Answers)Document4 pagesArc Lengths and Areas of Sectors (Answers)Joel OkohNo ratings yet
- IMO Training 2008 Yufei ZhaoDocument1 pageIMO Training 2008 Yufei ZhaojohnsonNo ratings yet
- Ex 12 8 FSC Part1 Ver3Document10 pagesEx 12 8 FSC Part1 Ver3Younman9635No ratings yet
- 2024 Term 1 GR 12Document25 pages2024 Term 1 GR 12Onalenna LegodiNo ratings yet
- Definition of A Triangle: Derivation of Hero's FormulaDocument5 pagesDefinition of A Triangle: Derivation of Hero's FormulaJhumel BongancisoNo ratings yet
- CAT GEOMETRY - (2017, 2018 and 2019)Document5 pagesCAT GEOMETRY - (2017, 2018 and 2019)Jack FullerNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry (Nda)Document2 pagesCoordinate Geometry (Nda)AarushNo ratings yet
- Geometry First 9 Weeks Test Review 1 2011Document6 pagesGeometry First 9 Weeks Test Review 1 2011esvraka1No ratings yet
- Class 6 MathsDocument4 pagesClass 6 Mathsesivaks2000No ratings yet
- Part 66 MathsDocument62 pagesPart 66 MathsmikeNo ratings yet