0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views2 pagesBevel Gearing Design Parameters Guide
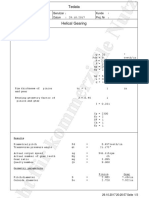
This document provides the results of a bevel gear design analysis. It calculates geometry parameters, forces, stresses, and safety factors for a pinion gear with 17 teeth and an output gear with 62 teeth. The analysis determines that the expected bending and contact stresses are below the allowable stress limits for through-hardened steel.
Uploaded by
willy rojas zeballosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views2 pagesBevel Gearing Design Parameters Guide
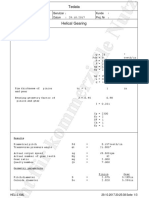
This document provides the results of a bevel gear design analysis. It calculates geometry parameters, forces, stresses, and safety factors for a pinion gear with 17 teeth and an output gear with 62 teeth. The analysis determines that the expected bending and contact stresses are below the allowable stress limits for through-hardened steel.
Uploaded by
willy rojas zeballosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd