0% found this document useful (0 votes)
821 views13 pagesPiping Inspector Duties and Standards Guide
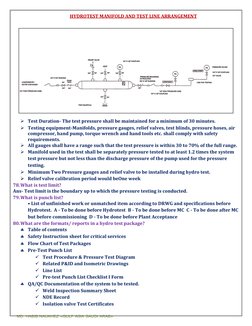
The document discusses the duties and responsibilities of a piping inspector which include ensuring work is done according to drawings, specifications, and standards. It also discusses piping inspection requirements at different stages of a project from material receiving to hydrotesting. The document also covers piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), isometric drawings, piping line designation, piping codes and standards such as ASME and ASTM, and non-conformance reporting for quality control.
Uploaded by
Raheel JibranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
821 views13 pagesPiping Inspector Duties and Standards Guide
The document discusses the duties and responsibilities of a piping inspector which include ensuring work is done according to drawings, specifications, and standards. It also discusses piping inspection requirements at different stages of a project from material receiving to hydrotesting. The document also covers piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), isometric drawings, piping line designation, piping codes and standards such as ASME and ASTM, and non-conformance reporting for quality control.
Uploaded by
Raheel JibranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Drawings and Materials
- Piping Supports and Testing