0% found this document useful (0 votes)
370 views3 pagesGreen ICT: Strategies for Sustainability
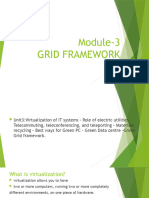
This course provides graduate students with an understanding of the role of information and communication technologies (ICT) and their impact on the global carbon footprint. Students will learn how to estimate the carbon footprint of an organization's ICT operations and ways to reduce it through procurement, operations, and business process changes. The course covers energy management in hardware, operating systems, and data centers, and teaches fundamentals of green computing including analyzing green computing frameworks and understanding green compliance issues. Learning outcomes include estimating and assessing ways to reduce organizational carbon footprints and acquiring skills to adopt green computing practices.
Uploaded by
dhanishCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
370 views3 pagesGreen ICT: Strategies for Sustainability
This course provides graduate students with an understanding of the role of information and communication technologies (ICT) and their impact on the global carbon footprint. Students will learn how to estimate the carbon footprint of an organization's ICT operations and ways to reduce it through procurement, operations, and business process changes. The course covers energy management in hardware, operating systems, and data centers, and teaches fundamentals of green computing including analyzing green computing frameworks and understanding green compliance issues. Learning outcomes include estimating and assessing ways to reduce organizational carbon footprints and acquiring skills to adopt green computing practices.
Uploaded by
dhanishCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd