Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lebanese American University
Uploaded by
Eliot KhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lebanese American University
Uploaded by
Eliot KhCopyright:
Available Formats
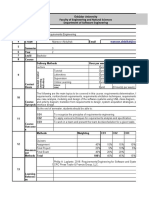
Lebanese American University INE 402
School of Engineering & Architecture Optimization Required
Department of Industrial & Mechanical Engineering MWF
3 Lecture Credits 10:00 AM 10:50 AM
1:00 PM 1:50 PM
Course syllabus Dr. Nabil Nehme Fall 18-19
Syllabus prepared by: Nabil Nehme Revised: August 2018
1. Course Description as in Academic Catalogue
This course covers queueing theory and models, linear programming, integer programming,
transportation/allocation, assignment, inventory, annealing, networks, dynamic programming, forecasting, and
simulation techniques.
Prerequisites: GNE333 Engineering Analysis I
2. Course Outcomes
Upon successful completion of this course, the student will:
1. Formulate mathematical linear programming problems found in practice and solve them using the
simplex algorithm and LINGO optimization software;
2. Manage analytically changes in the linear programming problem that affect optimality and feasibility;
3. Reason about concept of duality, the primal-dual relationship and their economic interpretation;
4. Formulate and solve the transportation and the assignment problem;
5. Formulate and solve the minimum cost network flow problem; the maximum flow/minimum cut
problem and the shortest path problem;
6. Formulate and solve dynamic programming problems;
7. Formulate and solve integer programming problems;
8. Formulate and solve nonlinear programming problems using the KKT conditions.
3. Relationship of Course to Student Outcomes
The course contributes to the delivery of the following student outcomes and performance indicators with
different degrees of emphasis placed on each outcome.
(a) ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering
a.1 Apply knowledge of linear algebra and probability and statistics as a tool for modeling systems and
processes
a.2 Apply engineering principles relevant to areas of Mathematical programming, Facilities and logistics,
Manufacturing and production systems, and Industrial management.
(c) ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as
economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability
c.4 Perform feasibility analysis and uses results to choose candidate solutions and evaluate quality of
solutions to select the best one
(e) ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems
e.1 Examines the scope of the problem and identifies problem variables and constraints
e.2 Uses basic mathematical, science, and engineering knowledge to formulate (select and apply) a
mathematical or computer model with appropriate scope and level of detail
e.3 Uses analytical or numerical methods to generate solutions
(k) ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice.
k.2 Use state of the art software and equipment needed in engineering practice
Program outcomes are achieved through structuring and focusing the course on the course learning
outcomes. The course learning outcomes are attained by the students when 70% or more of the
students (not counting withdrawals) pass the course
4. Contribution of course to meeting the professional component
Professional Component Credits
Mathematics and Basic Sciences 0
Engineering Topic 3
General Education 0
Optimization – INE 402 – Nehme
2/2
5. Course Outline
Relevant Chapters Course Content
3 Linear Programming
4 Simplex Method
6 Sensitivity Analysis and Duality
8 The Transportation and Assignment Problems
9 Network Flows
11 Integer Programming
12 Nonlinear Programming
6. Required tools / software / skills
Software: LINGO, TORA and any other related software.
7. Textbook[s]
Introduction to Operations Research by Hillier and Lieberman, McGraw Hill (9th Edition).
8. Grade Distribution
Exam I (Friday 5th October 2018) 25 %
Exam II (Friday 9th November 2018) 25 %
Final Exam (TBA) 40 %
Homework & Attendance 10 %
Note: Final is a comprehensive closed book exam
9. General Comments
All students must take exams as scheduled. Failure to take an exam or the final exam during the assigned class
period will result in a grade of zero. It is found according to University Rules and Regulations that a student is
eligible for a make up exam, the make up exam will be more difficult than the regular exam.
Preferred Communication: nabil.nehme01@lau.edu.lb
Office Hours: MWF: 3:00 PM - 4:00 PM
Room: ELRC 4106
10. General Rules and Regulations
A student can miss no more than 6 sessions of instruction. By the 7th session, the instructor may ask the
student to drop the course.
Cells phones, laptops and other gadgets are not allowed in class.
Students caught cheating on an exam receive a grade of Zero on the exam in the first cheating attempt
and a warning. Students caught cheating for the second time in the same course receive an F grade in the
course and a second warning. A grade of zero on an exam resulting from cheating must be counted in
the student’s course grade. The zero cannot be dropped in computing the final grade in case the instructor
has a policy of allowing students to drop their worst exam grade.
The LAU Student Code of Conduct (http://www.lau.edu.lb/about/governance-
policies/policies/student_code_of_conduct.pdf) will be strictly enforced. The following is a brief reminder
of some violations:
a. Unauthorized use of equipment or material on exams and projects.
b. Cheating, copying, collaborating with, or aiding another student in a manner not permitted by the
instructor.
c. Stealing or circulating an exam or an assignment.
d. Impersonating another student or an LAU official.
e. Outsourcing projects or assignments or submitting identical coursework.
f. Plagiarism and the inappropriate use of copyrighted material.
Any student who receives 3 warnings will be suspended.
You might also like
- Syllabus en 103Document5 pagesSyllabus en 103Ayman HadiNo ratings yet
- Python for Machine Learning: From Fundamentals to Real-World ApplicationsFrom EverandPython for Machine Learning: From Fundamentals to Real-World ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Flows, Wiley & Sons. Mathematical Programming, Thomson BooksDocument3 pagesFlows, Wiley & Sons. Mathematical Programming, Thomson BooksAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Ine544Document3 pagesSyllabus Ine544graceNo ratings yet
- Operations Research IDocument3 pagesOperations Research IKhaled TitiNo ratings yet
- Student Outcome - Performance Indicators Assessment MethodsDocument5 pagesStudent Outcome - Performance Indicators Assessment MethodsKim SanchezNo ratings yet
- Syllabus CSC 117 Java ProgrammingDocument7 pagesSyllabus CSC 117 Java Programmingabdulbaset alselwiNo ratings yet
- Elen2009 Cbo 2017Document5 pagesElen2009 Cbo 2017Mpumelelo JeffNo ratings yet
- Engg100 SoDocument6 pagesEngg100 SotchanlatifNo ratings yet
- EEN330 - Random Signals and Noise-Syllabus - Spring 22-23Document4 pagesEEN330 - Random Signals and Noise-Syllabus - Spring 22-23miss clairNo ratings yet
- CourseOutline W2021 ECE9039 9309 UpdatedDocument5 pagesCourseOutline W2021 ECE9039 9309 UpdatedNaumanNo ratings yet
- ME 171 SyllabusDocument7 pagesME 171 SyllabusLucas Penalva Costa SerraNo ratings yet
- EE049IU - Intro2EE SyllabusDocument3 pagesEE049IU - Intro2EE Syllabusansvn2 mathNo ratings yet
- Course Particulars: Dept. of Agricultural & Environmental Engineering, Federal University of Technology, Akure, NigeriaDocument5 pagesCourse Particulars: Dept. of Agricultural & Environmental Engineering, Federal University of Technology, Akure, NigeriaAbraham IsraelNo ratings yet
- Es310 Syl bb-1Document8 pagesEs310 Syl bb-1Ammar Abdulatef Ali Al-ShehariNo ratings yet
- Mat 121 Differential and Integral CalculusDocument105 pagesMat 121 Differential and Integral CalculusOnoja SamuelNo ratings yet
- American University of Science & Technology: Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer and Communications EngineeringDocument5 pagesAmerican University of Science & Technology: Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer and Communications EngineeringBernard MaacaronNo ratings yet
- CW 2022 4008Document8 pagesCW 2022 4008Ammar NasirNo ratings yet
- One Bundle Provides A 180 Day License To Microsoft Office 2010)Document7 pagesOne Bundle Provides A 180 Day License To Microsoft Office 2010)lifelongmaNo ratings yet
- CCN1016 Introduction To Internet Technology PDFDocument3 pagesCCN1016 Introduction To Internet Technology PDFdnlkabaNo ratings yet
- Network Planning To StudentsDocument132 pagesNetwork Planning To StudentsBasel wesamNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems SyllabusDocument5 pagesSignals and Systems SyllabusMewada HirenNo ratings yet
- B.E Syllabus For DLDocument4 pagesB.E Syllabus For DLMishra JiNo ratings yet
- 2020 Winter ECON 599 LECTURE B1Document7 pages2020 Winter ECON 599 LECTURE B1jgordon2No ratings yet
- 022-CPT 211 InteractivityDocument189 pages022-CPT 211 InteractivityEniola RudwanNo ratings yet
- Jiang OptimizationDocument2 pagesJiang OptimizationOugni ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Ceg4158 PDCDocument4 pagesCeg4158 PDCZichao ZhangNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Generation, Transmission, and Distribution Course OutlineDocument7 pagesElectric Power Generation, Transmission, and Distribution Course OutlineAhmad UsmanNo ratings yet
- AP-Lab Manual - UpdatedDocument110 pagesAP-Lab Manual - Updatedbaidnirvana8No ratings yet
- Operations Research IDocument2 pagesOperations Research IKhaled TitiNo ratings yet
- ITBIS105 Syllabus 1S2020 21tentativeDocument4 pagesITBIS105 Syllabus 1S2020 21tentativeaqeel aliNo ratings yet
- EE3017 Computer Communications - OBTLDocument9 pagesEE3017 Computer Communications - OBTLAaron TanNo ratings yet
- Independent University, Bangladesh Department of Computer Science & Engineering Course OutlineDocument4 pagesIndependent University, Bangladesh Department of Computer Science & Engineering Course OutlineZulker NienNo ratings yet
- BIA 652 Syllabus Spring 2017Document5 pagesBIA 652 Syllabus Spring 2017Henry MorenoNo ratings yet
- MENG331 Course Outline FALL 2022-2023Document3 pagesMENG331 Course Outline FALL 2022-2023Moboy11 hazardNo ratings yet
- MIT4700 Computer-Aided Design & ManufacturingDocument3 pagesMIT4700 Computer-Aided Design & ManufacturingAshley SmoakNo ratings yet
- CVEN9840 Structural Health Monitoring Fundamentals and PracticesDocument7 pagesCVEN9840 Structural Health Monitoring Fundamentals and PracticesGeEs AnggaNo ratings yet
- Applied Econometrics For ManagersDocument7 pagesApplied Econometrics For ManagersNikhil DixitNo ratings yet
- CVEN9415: Transport Systems Part 2: School of Civil and Environmental EngineeringDocument8 pagesCVEN9415: Transport Systems Part 2: School of Civil and Environmental EngineeringSumanNo ratings yet
- BIT C Elective Algorithms & Data StructuresDocument5 pagesBIT C Elective Algorithms & Data StructuresPuteri FaridahNo ratings yet
- Outline of Course of Study: Faculty of Engineering Secondary School Department of EngineeringDocument14 pagesOutline of Course of Study: Faculty of Engineering Secondary School Department of EngineeringJ SajatovicNo ratings yet
- Üsküdar University Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences Department of Software EngineeringDocument71 pagesÜsküdar University Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences Department of Software EngineeringSomeoneNo ratings yet
- Other: Sambita@cutm - Ac.inDocument3 pagesOther: Sambita@cutm - Ac.inDr-Harish Chandra Mohanta100% (1)
- ENG TECH 4MA3 Course Outline Fall 2020Document5 pagesENG TECH 4MA3 Course Outline Fall 2020Ryan TorresNo ratings yet
- EE4001 Software Engineering - OBTLDocument5 pagesEE4001 Software Engineering - OBTLAaron TanNo ratings yet
- CSC520 SyllabusDocument3 pagesCSC520 SyllabusLe Song LamNo ratings yet
- MFIN6002 - Spreadsheet Modelling in FinanceDocument4 pagesMFIN6002 - Spreadsheet Modelling in FinancejessieNo ratings yet
- Unit COMP5028 Object Oriented Analysis and DesignDocument5 pagesUnit COMP5028 Object Oriented Analysis and Designravikhatri1010No ratings yet
- Ece 4250Document3 pagesEce 4250asadnaNo ratings yet
- IAE Robotics Course DescriptionDocument6 pagesIAE Robotics Course Descriptionsatheesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Course Outline MEIE-4182 Fall-2011Document4 pagesCourse Outline MEIE-4182 Fall-2011عبدالعزيز مسلمNo ratings yet
- CSD363-Course DescriptionDocument3 pagesCSD363-Course Descriptionabhinav596singhNo ratings yet
- ELEN90055 Control Systems: Credit Points: Level: Commencement Date & LocationDocument3 pagesELEN90055 Control Systems: Credit Points: Level: Commencement Date & LocationtefsgNo ratings yet
- 2015 Winter Econ 599 Lecture b1Document5 pages2015 Winter Econ 599 Lecture b1jgordon2No ratings yet
- ME 430-001 - Introduction To Computer Aided DesignDocument6 pagesME 430-001 - Introduction To Computer Aided DesignSteve OkumuNo ratings yet
- ComE 223-Computer Fundamentals & Programming IIDocument2 pagesComE 223-Computer Fundamentals & Programming IIDinah Fe Tabaranza-OlitanNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusZaniNo ratings yet
- Course - Syllabus - COE 351 - Spring 2020 PDFDocument6 pagesCourse - Syllabus - COE 351 - Spring 2020 PDFsaudNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - 9718 PDFDocument3 pagesCourse Outline - 9718 PDFAnonymous fYHyRa2XNo ratings yet
- Busines PlanDocument21 pagesBusines PlanFatimah Binte AtiqNo ratings yet
- FDGDocument17 pagesFDGEliot KhNo ratings yet
- 2021 03 23 11 17 Guarda Multiwallet BackupDocument5 pages2021 03 23 11 17 Guarda Multiwallet BackupEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Accelerations, I.E. (Q, W, A), (Q, W, A), (Q, W, A), Find The Resultant Forces and Torques On The Manipulator Links and JointsDocument18 pagesAccelerations, I.E. (Q, W, A), (Q, W, A), (Q, W, A), Find The Resultant Forces and Torques On The Manipulator Links and JointsEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Accelerations, I.E. (Q, W, A), (Q, W, A), (Q, W, A), Find The Resultant Forces and Torques On The Manipulator Links and JointsDocument146 pagesAccelerations, I.E. (Q, W, A), (Q, W, A), (Q, W, A), Find The Resultant Forces and Torques On The Manipulator Links and JointsEliot KhNo ratings yet
- SFDGJBFDocument30 pagesSFDGJBFEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking: MGT 215 Lara Al ArabDocument23 pagesDesign Thinking: MGT 215 Lara Al ArabEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Module11 - Financial PlanDocument56 pagesModule11 - Financial PlanFarahana AzmiNo ratings yet
- Politecnico Di Milano: Department of Energy School of Industrial and Information EngineeringDocument2 pagesPolitecnico Di Milano: Department of Energy School of Industrial and Information EngineeringEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Project Control: Project Management Course Prepared by Dr. Pierrette Zouein 1Document28 pagesProject Control: Project Management Course Prepared by Dr. Pierrette Zouein 1Eliot KhNo ratings yet
- Engineers in Organizations: GNE 305 - SPRING 2018Document15 pagesEngineers in Organizations: GNE 305 - SPRING 2018Eliot KhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Detailed Planning - NetworkGeneration v3. PWPDocument74 pagesLecture 3 - Detailed Planning - NetworkGeneration v3. PWPEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Engineers and The Environment: Professional Ethics - Chapter 8 Spring 2018Document15 pagesEngineers and The Environment: Professional Ethics - Chapter 8 Spring 2018Eliot KhNo ratings yet
- Professional Ethics - Chapter 6Document17 pagesProfessional Ethics - Chapter 6Eliot KhNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring and Updating: Project Management Course Prepared by Dr. Pierrette Zouein 1Document55 pagesProject Monitoring and Updating: Project Management Course Prepared by Dr. Pierrette Zouein 1Eliot KhNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring and Updating: Project Management Course Prepared by Dr. Pierrette Zouein 1Document72 pagesProject Monitoring and Updating: Project Management Course Prepared by Dr. Pierrette Zouein 1Eliot KhNo ratings yet
- LPFCPDocument42 pagesLPFCPEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Optimization: 8. Linear ProgrammingDocument35 pagesNumerical Methods For Optimization: 8. Linear ProgrammingEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document2 pagesExercise 1Eliot KhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Detailed Planning - NetworkGeneration v3. PWPDocument74 pagesLecture 3 - Detailed Planning - NetworkGeneration v3. PWPEliot KhNo ratings yet
- DFHGDHDocument120 pagesDFHGDHEliot KhNo ratings yet
- FGDFGFDGDocument57 pagesFGDFGFDGEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Detailed Planning: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)Document26 pagesDetailed Planning: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)Eliot KhNo ratings yet
- RehgaergDocument2 pagesRehgaergEliot KhNo ratings yet
- AC Systems With Notes PDFDocument147 pagesAC Systems With Notes PDFEliot KhNo ratings yet
- FCHGCDocument13 pagesFCHGCEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Optimization Lecture 6: Maximum Flow ProblemsDocument30 pagesNumerical Methods For Optimization Lecture 6: Maximum Flow ProblemsEliot KhNo ratings yet
- NMO Lecture 7 PDFDocument34 pagesNMO Lecture 7 PDFEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Titolo Presentazione Sottotitolo: Electronic Power Conversion: ActodcDocument72 pagesTitolo Presentazione Sottotitolo: Electronic Power Conversion: ActodcEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Titolo Presentazione Sottotitolo: Electronic Power Conversion: DctoacDocument55 pagesTitolo Presentazione Sottotitolo: Electronic Power Conversion: DctoacEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Askari-Nasab Et Al - 2011 - 2011 - 03 - 05 - Hesam - SME - DenverDocument9 pagesAskari-Nasab Et Al - 2011 - 2011 - 03 - 05 - Hesam - SME - DenverJorge ValencaNo ratings yet
- Integer Programming Worksheet 4Document3 pagesInteger Programming Worksheet 4ESHAAN KULSHRESHTHANo ratings yet
- Sample Final Examination Questions IE406 - Introduction To Mathematical Programming Dr. RalphsDocument10 pagesSample Final Examination Questions IE406 - Introduction To Mathematical Programming Dr. RalphsLuis IvanNo ratings yet
- 1 A Simulation Based Model For The BerthDocument9 pages1 A Simulation Based Model For The Berthmonu_vitsNo ratings yet
- Scheduling Contractors' Farm-to-Farm Crop Harvesting OperationsDocument22 pagesScheduling Contractors' Farm-to-Farm Crop Harvesting Operationsec01No ratings yet
- Optimal Scheduling in A Yogurt Productio PDFDocument9 pagesOptimal Scheduling in A Yogurt Productio PDFAnali MaquezNo ratings yet
- Service Oriented Train Timetabling Mor KaspiDocument85 pagesService Oriented Train Timetabling Mor KaspiusuariodepruebasNo ratings yet
- Risk Management and Long-Term Production PDFDocument7 pagesRisk Management and Long-Term Production PDFPaulo Roberto Guimarães MelloNo ratings yet
- Operational Research Paper in BSC Prog Mathematical SciencesDocument20 pagesOperational Research Paper in BSC Prog Mathematical SciencesRAJEeNo ratings yet
- PSA2 - 18EE71 - Module 04 - Unit CommitmentDocument58 pagesPSA2 - 18EE71 - Module 04 - Unit CommitmentCheck This TechNo ratings yet
- Operations Research ProjectDocument21 pagesOperations Research ProjectDeepak KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Journal Review Manajemen OperasionalDocument16 pagesJournal Review Manajemen OperasionalimaNo ratings yet
- Mixed Integer Linear Programming: Combinatorial Problem Solving (CPS)Document68 pagesMixed Integer Linear Programming: Combinatorial Problem Solving (CPS)Anonymous 78iAn6No ratings yet
- Linear Programming: Formulation and Applications: Because Learning Changes EverythingDocument38 pagesLinear Programming: Formulation and Applications: Because Learning Changes EverythingNathan Roy OngcarrancejaNo ratings yet
- Quant Methods MCQDocument6 pagesQuant Methods MCQTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- Using Integer Programming For Airport Service Planning in Staff SchedulingDocument8 pagesUsing Integer Programming For Airport Service Planning in Staff SchedulingSurajNo ratings yet
- Classical Planning and Scheduling: Radek Ma R IkDocument83 pagesClassical Planning and Scheduling: Radek Ma R IkAzeddine BoughmarNo ratings yet
- 8 - Prescriptive AnalyticsDocument27 pages8 - Prescriptive AnalyticsGaurav BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Scheduling Unrelated Parallel Machines (Tem Instacias No Site)Document18 pagesScheduling Unrelated Parallel Machines (Tem Instacias No Site)Guilherme WeisNo ratings yet
- Chap06 Integer Linear ProgrammingDocument58 pagesChap06 Integer Linear ProgrammingbauemmvssNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Practical Management Science 6th by WinstonDocument14 pagesTest Bank For Practical Management Science 6th by Winstonaaronmillerdzjosgmtib100% (20)
- Operations Research: Integer ProgrammingDocument42 pagesOperations Research: Integer ProgrammingAndri IndriawanNo ratings yet
- What Is Operational ResearchDocument4 pagesWhat Is Operational ResearchShalini YadavNo ratings yet
- Case Problem 1 Textbook PublishingDocument2 pagesCase Problem 1 Textbook PublishingSomething ChicNo ratings yet
- Sven O Krumke Integer Programming Polyhedra and Algorithms Lecture NotesDocument188 pagesSven O Krumke Integer Programming Polyhedra and Algorithms Lecture NotesPride MwanemaNo ratings yet
- The Lagrangian Relaxation Method For Solving Integer Programming ProblemsDocument12 pagesThe Lagrangian Relaxation Method For Solving Integer Programming ProblemsbizNo ratings yet
- Suggested Solution To Written Exam Introduction To Linear and Integer Programming (DM515)Document18 pagesSuggested Solution To Written Exam Introduction To Linear and Integer Programming (DM515)Abdesselem BoulkrouneNo ratings yet
- Thesis Eric FinalDocument65 pagesThesis Eric Finalirene niyitangaNo ratings yet
- Advance Operations ResearchDocument255 pagesAdvance Operations Researchgoldy243usNo ratings yet