Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Sample Paper - 04 Summative Assessment - I Class Ix Mathematics
Uploaded by
Akash kohliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Sample Paper - 04 Summative Assessment - I Class Ix Mathematics
Uploaded by
Akash kohliCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE
Sample Paper - 04
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT – I
Class IX MATHEMATICS
Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90
General Instructions:
a) All questions are compulsory.
b) The question paper comprises of 31 questions divided into four sections A, B, C and D. You
are to attempt all the four sections.
c) Questions 1 to 4 in section A are one mark questions.
d) Questions 5 to 10 in section B are two marks questions.
e) Questions 11 to 20 in section C are three marks questions.
f) Questions 21 to 31 in section D are four marks questions.
g) There is no overall choice in the question paper. Use of calculators is not permitted.
Section - A
1. Is the number rational or irrational?
Ans. =
=9-7=2 which is rational.
2. Find the value of .
Ans.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 21
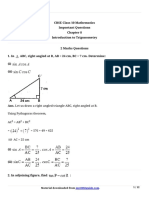
3. If ABC is an isosceles triangle and B = , find x.
Ans.
4.If the perimeter of a rhombus is 20cm and one of the diagonals is 8cm. Find the area
of the rhombus.
Ans. 24 sq cm
Section - B
5. Multiply by
Ans.
6. Using factor theorem, show that (x – y) is a factor of
Ans. Let
putting x = y in given polynomial p(x), we get
(x – y) is a factor of given polynomial p(x).
7. Find the remainder when is divided by
Ans. By remainder theorem,
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 21
8. In the figure, AB and AC are opposite rays and DAE = ADE. Prove that BAE =
CDE.
Ans. BAE + EAC = [Linear pair]....(i)
And EDA + EDC = [Linear pair]....(ii)
From eq. (i) and (ii), we have
BAE + EAC = EDA + EDC
BAE + EAC = DAE + EDC[Given DAE = ADE]
BAE = CDE
9. The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 10. Find the measure of each angle.
Ans. Let a triangle ABC and A : B : C = 3 : 5 : 10
Let the angles be A = B = and C =
A + B + C =
Angles are and
10. Find out the quadrant in which the following points lie:
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 21
(i) Point A = (ii) Point B =
(iii) Point C = (iv) Point D = (3, 4)
Ans. .(i) Point A lies in the fourth quadrant, since its abscissa is positive and ordinate is
negative.
(ii) Point A lies in the second quadrant, since its abscissa is negative and ordinate is positive.
(iii) Point A lies in the third quadrant, since both abscissa and ordinate arenegative.
(iv) Point A lies in the first quadrant, since both abscissa and ordinate are positive
Section - C
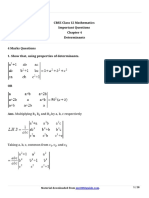
11. Simplify:
Ans.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 21
=
12. Express in the form , where p and q are integers and .
Ans. Letx=
Then, x=2.0151515..
Let y=0.151515.
Subtracting (ii) from (iii), we get
100y-y=15.1515..-0.151515...
99y=15
Now
13. Factories:
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 5 / 21
Ans.
14. Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of:
Ans. Let
If , then
15. State any 2 axioms given by Euclid. Give an example for each.
Ans. AXIOMS
1.Things which are equal to the same thing are equal to one another.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 6 / 21
2.If equals are added to equals , the wholes are equal.
16. In the given figure, if , and , find .
Ans. Through point , draw a line parallel to and parallel to .
Let and
Since, and is transversal
(co-interior angles are supplementary)
Similarly,
Since, is straight line,
17. In the given figure, . Find the measure of reflex .
Ans. Draw
Then,
Now, and is the transversal,
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 7 / 21
(co-int. angles)
Similarly,
Hence, reflex
18. In the following figure, it is given that and . Prove that
.
Ans. In and we have
And (vertically opposite angles)
(by angle sum property)
(1)
Now, (angles of a linear pair)
(using (1), and ....
(2))
Now, in and , we have
(given)
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 8 / 21
(from (2))
(given)
(by )
19. The following table gives measures (in degrees) of two acute angles of a right
triangle
x 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
y 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10
Plot the point and join them.
Ans.
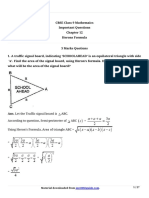
20. Manish has a vegetable garden in the shape of a rhombus. The length of each side of
the garden is 35m and its diagonal is 42m long. After growing the vegetables in it, he
wants to divide it in four equal parts. Find the area of each part.
Ans. Let be the garden
Draw
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 9 / 21
(by pythagoras theorem)
Area of
area of garden
Area of each part
Section - D
21. If , then find the value of:
(i)
(ii)
Ans.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 10 / 21
And
= =49-48
ab=1
Now, =
Now, =
22. Rationalize the denominators of the following: (i) (ii)
Ans. (i)
We need to multiply the numerator and denominator of by , to get
We need to apply the formula in the denominator to get
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 11 / 21
Therefore, we conclude that on rationalizing the denominator of , we get
(ii)
We need to multiply the numerator and denominator of by , to get
We need to apply the formula in the denominator to get
Therefore, we conclude that on rationalizing the denominator of , we get .
23. If the polynomials and leave the same
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 12 / 21
remainder when divided by then find the value of Also find the remainder
in each case.
Ans. Let and
Divisor = then remainder = and
According to the question,
24. If the polynomial az3 + 3z – 4 and z3 – 4z + a leave the same remainder when divided
by z – 3, find the value of a.
Ans. Let
When p(z) is divided by z – 3 the remainder is given by,
When q(z) is divided by z – 3 the remainder is given by,
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 13 / 21
According to questions, p(3) =q(3)
25. The volume of a cuboid is given by the expression . Find the possible
expressions for its dimensions.
Ans. The volume of cuboid is given by
26. Using remainder theorem factorise .
Ans.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 14 / 21
Coefficient of is 1
Constant =3
3 1 = 3
We can Put x= 3 and ( ) and check
Put= x=1
1 – 3 – 1 + 3 = 0
Remainder =0
27. In the figure, lines and intersect at . If and
, find and reflex .
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 15 / 21
Ans. Given:- ........ equation (i)
And
Now, putting the value of equation (ii) in equation (i),
Now,
(Angles at a common point on a line)
Reflex
Hence,
And reflex
28. In the following figure, lines and intersect at . If and
, find c.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 16 / 21
Ans. Given:-
And a : b = 2 : 3
Therefore,
.......... equation (i)
Now,
(therefore, )
= 2b + 3b =
= 5b =
Putting the value of b in equation (i)
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 17 / 21
Or,
Now, {Angles at a common point on a line}
29. In right triangle ABC, right angled at C, M is the mid-point of hypotenuse AB. C is
joined to M and produced to a point D such that DM = CM. Point D is joined to point B.
Show that:
(i) (ii) is a right angle
(iii) (iv)
Ans. In
BM = AM (M is midpoint)
DM = CM (given)
(opposite angles)
So,
Hence, DB = AC
So, (alternate angles are equal)
So, = right angle
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 18 / 21
(internal angels are complementary in
Case of tranversal of parallel lines)
DB = AC (proved earlier)
BC = BC (Commo side)
(proved earlier)
So,
So, AB = DC
SO, AM = BM = CM = DM
So,
30. Prove that difference of any two sides of a triangle is less than the third side.
Ans. To prove:
Construction: From cut . Join and
Proof:
(angles opposite to equal sides are equal)
In , ext. (ext. angle of a triangle is greater than its int. opp. Angle)
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 19 / 21
Similarly, in
Ext.
In
31. Show that ar (BPC) = ar (DPQ) if BC is produced to a point Q such that AD = CQ and
AQ intersect DC at P
Ans. Join AC
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 20 / 21
Hence, a pair of opposite side AD and CQ of the quadrilateral ADQC is equal and parallel.
In
From (i) and (ii)
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 21 / 21
You might also like
- BandyHowtoBuildTradingSys PDFDocument113 pagesBandyHowtoBuildTradingSys PDFhaginile100% (1)
- Algebra 2 Readiness Practice TestDocument11 pagesAlgebra 2 Readiness Practice Testpidmap2No ratings yet
- Why Is Mathematics Important in Culinary ArtsDocument2 pagesWhy Is Mathematics Important in Culinary ArtsReiou Regie Manuel25% (4)
- HKUST COMP3211 Quiz1 SolutionDocument6 pagesHKUST COMP3211 Quiz1 SolutionTKFNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper - 03 Summative Assessment - I Class Ix MathematicsDocument19 pagesCBSE Sample Paper - 03 Summative Assessment - I Class Ix MathematicsAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 22Document22 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 22Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper - 01 Summative Assessment - I Class Ix MathematicsDocument19 pagesCBSE Sample Paper - 01 Summative Assessment - I Class Ix MathematicsAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample PaperDocument17 pagesCbse Sample PaperTesuNo ratings yet
- Math SampleDocument21 pagesMath SampleHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 23Document23 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 23Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 24Document24 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 24Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- Class X Maths Summative Assessment Sample PaperDocument4 pagesClass X Maths Summative Assessment Sample PaperjayNo ratings yet
- Cbse Mathematics Sa1 Solved 05Document4 pagesCbse Mathematics Sa1 Solved 05harshaNo ratings yet
- 9 Mathematics sp01Document29 pages9 Mathematics sp01Garima KaushikNo ratings yet
- 9 Mathematics sp01 PDFDocument29 pages9 Mathematics sp01 PDFpreethaNo ratings yet
- 12 Maths CBSE Sample Papers 2019Document16 pages12 Maths CBSE Sample Papers 2019Sanket SainiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper - 05 (Solved) Summative Assessment - I Class - X MathematicsDocument4 pagesCBSE Sample Paper - 05 (Solved) Summative Assessment - I Class - X MathematicsAkshay SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Sample Paper SolutionsDocument28 pagesCBSE Class 9 Maths Sample Paper SolutionsAyush SinghalNo ratings yet
- 12 Mathematics Ncert Ch04 Determinants 4.3Document7 pages12 Mathematics Ncert Ch04 Determinants 4.3Reetika MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Himanshu Math 2 PDFDocument12 pagesHimanshu Math 2 PDFhimanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- 9 Math Doe2017 SP 12Document12 pages9 Math Doe2017 SP 12Ayush SinghalNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics Sample Papers PDFDocument261 pages10 Mathematics Sample Papers PDFabhikhya aryaNo ratings yet
- For More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - IDocument4 pagesFor More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - Il8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Important Questions Determinants: R and R by A, B, C RespectivelyDocument28 pagesCBSE Class 12 Mathematics Important Questions Determinants: R and R by A, B, C RespectivelylucasNo ratings yet
- For More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - IDocument3 pagesFor More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - IGaganNo ratings yet
- CK VG QJK Q6 Yf NCVEmrd P2Document29 pagesCK VG QJK Q6 Yf NCVEmrd P2payalaanyaNo ratings yet
- Mycbseguide: Class 12 - Mathematics Term-2 Sample Paper - 01 Marks: 40 Time Allowed: 2 Hours InstructionsDocument10 pagesMycbseguide: Class 12 - Mathematics Term-2 Sample Paper - 01 Marks: 40 Time Allowed: 2 Hours Instructionsdhruv jainNo ratings yet
- Vim Maths QuestionsDocument313 pagesVim Maths Questionsrisk2br40No ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12Document12 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 12siddanshNo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument71 pagesTriangleArun KumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Math Sample Paper 1Document10 pagesCBSE Class 11 Math Sample Paper 1Sourav SamantNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Mathematics NCERT Exemplar Chapter 7 Integrals Short and Long Answer QuestionsDocument18 pagesCBSE Class 12 Mathematics NCERT Exemplar Chapter 7 Integrals Short and Long Answer QuestionsSweetha PrakashNo ratings yet
- 12 Mathematics Imp Ch11 4Document17 pages12 Mathematics Imp Ch11 4DeepakNo ratings yet
- Abc. According To Question, Semi-Perimeter of ABC Using Heron's Formula, Area of Triangle ABCDocument27 pagesAbc. According To Question, Semi-Perimeter of ABC Using Heron's Formula, Area of Triangle ABCSaipragati AravindNo ratings yet
- Nda 2020 Maths Sol 43Document62 pagesNda 2020 Maths Sol 43Keshab Chandra BihariNo ratings yet
- 11 Mathematics Ncert ch06 Linear Inequalities 6.1 PDFDocument13 pages11 Mathematics Ncert ch06 Linear Inequalities 6.1 PDFGaurangAdhiaNo ratings yet
- 2016 09 Mathematics Sample Paper Sa2 01Document5 pages2016 09 Mathematics Sample Paper Sa2 01Sàhíl VermaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 7 Coordinate GeometryDocument9 pagesCBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 7 Coordinate GeometryakshaypagariyaNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths Test Paper Ch7 Coordination GeometryDocument9 pages10 Maths Test Paper Ch7 Coordination GeometryPriyaprasad PandaNo ratings yet
- Cbse - Biz: MM 80 Full Syllabus Paper/Mock Test Time 3HDocument6 pagesCbse - Biz: MM 80 Full Syllabus Paper/Mock Test Time 3HShashank SinghviNo ratings yet
- see preparationDocument8 pagessee preparationAshokNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class - XII Mathematics Sample Paper-02: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 29Document29 pagesCBSE Class - XII Mathematics Sample Paper-02: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 29AR SHNo ratings yet
- Accepted. All The Answer and Necessary Solutions Should Be Placed On The Answer Sheet ProvidedDocument5 pagesAccepted. All The Answer and Necessary Solutions Should Be Placed On The Answer Sheet ProvidedMarvin L. BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 12Document12 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 12Vivek NegíNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II (2014-2015) Subject: Mathematics Class: VII Time: 2:30 Hrs. M.M. 70 General InstructionsDocument3 pagesSUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II (2014-2015) Subject: Mathematics Class: VII Time: 2:30 Hrs. M.M. 70 General Instructionsbal_thakreNo ratings yet
- 2022 Cavite Basic Education AssessmentDocument4 pages2022 Cavite Basic Education AssessmentKARIZZA ABOLENCIANo ratings yet
- Using Pythagoras Theorem, AC Ab + BC 576 + 49 625 AC 25 CMDocument12 pagesUsing Pythagoras Theorem, AC Ab + BC 576 + 49 625 AC 25 CMArunabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 20Document20 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 20Yashasvee SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Math 2Document10 pagesMath 2Mahal KoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: CBSE Sample Paper-04 (Solved) Summative Assessment - I Class - IXDocument4 pagesMathematics: CBSE Sample Paper-04 (Solved) Summative Assessment - I Class - IXLakshay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Applied Maths I Worksheet IDocument4 pagesApplied Maths I Worksheet Itesfayechala547No ratings yet
- 9 Mathematics sp02-1Document5 pages9 Mathematics sp02-1gagan.69801823No ratings yet
- CBSE Board Class X Mathematics Sample Paper 3Document5 pagesCBSE Board Class X Mathematics Sample Paper 3Mausam KumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education Exam ReviewREYLE ANNE VELARDENo ratings yet
- Mathematics Question of Class 11th Half Yearly PDFDocument5 pagesMathematics Question of Class 11th Half Yearly PDFAman HansdaNo ratings yet
- SDMDocument9 pagesSDMSoumya PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Mathematics 8Document6 pagesPre-Test Mathematics 8ROSE ANNE SIYANGNo ratings yet
- Archivetemp LCTG47-48Document9 pagesArchivetemp LCTG47-48Monhannah Calimbol Sumapal LimbutunganNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Mathematics (Unsolved)Document4 pagesSample Paper Mathematics (Unsolved)Ticker moviesNo ratings yet
- Exemplar Question BankDocument16 pagesExemplar Question BankKanika T. UmmatNo ratings yet
- 2016 09 SP Mathematics Sa1 Solved 05Document4 pages2016 09 SP Mathematics Sa1 Solved 05Syed BabaNo ratings yet
- Cds 1 2020 Maths Solution 16Document57 pagesCds 1 2020 Maths Solution 16ShubhamNo ratings yet
- SC Lici0202230095Document1 pageSC Lici0202230095Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- SQP Mathametics Class XDocument13 pagesSQP Mathametics Class XAnubhav SinhaNo ratings yet
- Class X Sample Question Paper 01 Maths SolutionsDocument17 pagesClass X Sample Question Paper 01 Maths SolutionsKushal SarkarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Paper - I (English Version) Partaandb: InstructionsDocument13 pagesMathematics - Paper - I (English Version) Partaandb: InstructionsAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Class X Math Study MaterialDocument105 pagesClass X Math Study MaterialmicrodotcdmNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Question Paper Final New Syllabus 2017 2018 10Document5 pagesClass 10 Question Paper Final New Syllabus 2017 2018 10Kushal Sarkar100% (1)
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 20Document20 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 20Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 24Document24 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 24Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- Math Test Spark School of Education 9988579475Document4 pagesMath Test Spark School of Education 9988579475Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- 9 Math SP Sa2 8Document23 pages9 Math SP Sa2 8PikunLenkaNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 23Document23 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 23Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- Spark School of Education: SAT IntroductionDocument10 pagesSpark School of Education: SAT IntroductionAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Shortcuts For Chapter 1Document1 pageFormulas and Shortcuts For Chapter 1Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement3Document1 pageSubject Verb Agreement3Akash kohliNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument2 pagesSubject Verb AgreementAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Sports EssayDocument3 pagesSports EssayAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Word List 1 AbateDocument2 pagesWord List 1 AbateAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Fee StructuresDocument2 pagesFee StructuresAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Feminism, gender equality, and empowering women in the workplaceDocument2 pagesFeminism, gender equality, and empowering women in the workplaceAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Test-1 Linear Equations in One Variable: 6. SolveDocument1 pageMathematics Test-1 Linear Equations in One Variable: 6. SolveAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Your ConvenienceDocument1 pageYour ConvenienceAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Definition of SentenceDocument1 pageDefinition of SentenceAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- OET Speaking by SparkDocument2 pagesOET Speaking by SparkAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- CrimeDocument2 pagesCrimeAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- 40 - IELTS Vocabulary Booster PDFDocument85 pages40 - IELTS Vocabulary Booster PDFjesse100% (2)
- LogarithmsDocument1 pageLogarithmsAkash kohliNo ratings yet
- Optionstar EZ Single Calls or Puts: #VALUE! ####### ####### ####### ####### ####### #######Document18 pagesOptionstar EZ Single Calls or Puts: #VALUE! ####### ####### ####### ####### ####### #######kirron005No ratings yet
- Physcis Hkcee PastpaperDocument34 pagesPhyscis Hkcee Pastpaperpetecostein2No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 3Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 3Aerdna Ela RuzNo ratings yet
- Math exam questions on history of numeration systemsDocument4 pagesMath exam questions on history of numeration systemsTrebor SwissNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution and Point EstimatesDocument9 pagesSampling Distribution and Point EstimatesShiinNo ratings yet
- MDM EverlynDocument15 pagesMDM EverlynSeth OderaNo ratings yet
- Free Keyboard Shortcuts (WIN) : Number PadDocument1 pageFree Keyboard Shortcuts (WIN) : Number PadLeonardo AguileraNo ratings yet
- IYPT Problemas 2020Document1 pageIYPT Problemas 2020Paul Kurono Palma GalvezNo ratings yet
- Iso 7902 1 2013 en PDFDocument11 pagesIso 7902 1 2013 en PDFAdamNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Books OnlineDocument14 pagesCambridge Books OnlineAnonymous fVtXn0JfgsNo ratings yet
- Flood Gate Opening System With AiDocument18 pagesFlood Gate Opening System With AiSapta AjieNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Linear Transformation: V T U T V U T U CT Cu TDocument28 pagesUnit 4: Linear Transformation: V T U T V U T U CT Cu TFITSUM SEIDNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04 - Primitive Data Types IDocument38 pagesLesson 04 - Primitive Data Types IShvan JaffNo ratings yet
- A Review of Software Fault Detection and Correction Process, Models and TechniquesDocument8 pagesA Review of Software Fault Detection and Correction Process, Models and TechniquesDr Muhamma Imran BabarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MalikDocument15 pagesChapter 1 MalikSujitha KanumarlapudiNo ratings yet
- Ilide - Info Aqwa Theory Manual PRDocument168 pagesIlide - Info Aqwa Theory Manual PRGabriel BaroniNo ratings yet
- STEM General Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 6 Graphical Analysis of MotionDocument28 pagesSTEM General Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 6 Graphical Analysis of MotionStevenNo ratings yet
- Generalised Hough TransformDocument14 pagesGeneralised Hough TransformMichelle HoltNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-7 PDFDocument1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-7 PDFahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- Closed Conduit FlowDocument5 pagesClosed Conduit FlowPatrick Joseph RoblesNo ratings yet
- A Project Report OnDocument44 pagesA Project Report OnVartika_07100% (1)
- ECE 274 - 2-bit Adder Carry RippleDocument5 pagesECE 274 - 2-bit Adder Carry Rippleprabhat athaNo ratings yet
- CL - 5 Maths Combined PDFDocument19 pagesCL - 5 Maths Combined PDFTechno Gaming OfficialNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North Mathematics Revision W/S - 2019-20 Fractions and Decimals ClassviiDocument3 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore North Mathematics Revision W/S - 2019-20 Fractions and Decimals ClassviiVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Computational Intelligence SystemsDocument15 pagesInternational Journal of Computational Intelligence SystemsbalajigandhirajanNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Hassan Saeed-284223-Lab 6Document13 pagesMuhammad Hassan Saeed-284223-Lab 6Hassan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Behind JNTUK - MOPUDocument10 pagesBehind JNTUK - MOPUfrAnkEnstEin liveNo ratings yet