Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Section 1 Mechanics PDF
Section 1 Mechanics PDF
Uploaded by
Mecid AliyevOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 1 Mechanics PDF
Section 1 Mechanics PDF
Uploaded by
Mecid AliyevCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 1: Mechanics—Past papers
2005 June
Q1- (a) A student wants to use metal wire as part of a model bridge that she is building.
To test if a wire is suitable she hangs a mass of 0.5 kg from it and measures its
extension. Calculate the weight in newtons of the 0.5 kg mass.
......................................................................................................................................
............................................................. Weight = ........................... N (2)
(b) She continues to add masses to the end of the wire. The graph shows the results of
her experiment.
(i) Indicate on the graph the region associated with Hooke’s law. (1)
(ii) Explain your answer.
...............................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................(1)
(c) The student thinks the wire is too weak and decides to replace it with a thicker wire
of the same material and length. She tests it in the same way as before by hanging
masses from its end.
Show her possible results on the axes above. (2)
(Total 6 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer:
Q1 (a) 5N 4.9 using 9.8
W=mxg (1 mark) or w = 0.5 x 10 (1 mark)
2
(b) (i) indicates initial linear region
(ii) The region indicated is linear/ extension is proportional 1
to weight OWTTE 1
(c) (straight) line through origin of shallower slope than
Existing straight line (1 mark)
Straight line continues beyond weight associated with
Elastic limit for thinner wire (1 mark)
2
Total 6 marks
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q-9: On a day when there is no wind, a rock falls from a very high cliff. It does not hit
anything until it reaches the ground.
(a) Give the name and direction of each of the two forces, apart from upthrust, which act
on the rock as it falls.
1 ...................................................................................................................................
2 ...................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) One of the forces which acts on the rock changes significantly as the rock falls.
Name the force and explain what happens.
......................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................(2)
(c) The mass of the rock is 450 kg. At one point in its fall the unbalanced force on the
rock is 60 N.
Calculate the acceleration of the rock at this point and include its unit.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
................................................... Acceleration = .............................. (3)
(d) After some time, the falling rock reaches its terminal velocity.
(i) Describe the motion of the rock when it is at terminal velocity.
.............................................................................................................................. (1)
(ii) State the size of the unbalanced force on the rock as it falls at terminal velocity.
.............................................................................................................................. (1)
(Total 9 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
2005 Nov
Q3: A teacher suspends an object from a clamp. She places a small screen in front of
the object so that the students cannot see it. She then attaches a mass to the bottom of
the object. The mass applies a force to the object and the object extends.
(a) Different masses are attached to the bottom of the object.
The teacher measures the extension and the students calculate the value of the applied
force.
The table shows the results.
Plot the points on the grid. Draw the best straight line through the plotted points.
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(3)
(b) Use your graph to find the extension for a force of 8.0 N.
................................................................................................................................. (1)
(c) Explain why the extension for a force of 800 N is unlikely to be one hundred times
the value in (b).
......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................(1)
(d) The teacher tells her pupils that the object is one of three things:
a helical spring
a metal wire
an elastic band.
(i) Which one could it be?
............................................................................................................................(1)
(ii) Give two reasons for your choice.
1 .............................................................................................................................
2 .........................................................................................................................(2)
(Total 8 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q-9: (a) A cart becomes stuck in a river bed. A group of people gets it moving again.
Some of them push and some of them pull.
The diagram shows the horizontal forces which act on the cart.
(i) Complete the sentences.
The frictional force is force ...........
The pushing force is force .......... and the pulling force is force ........... (1)
(ii) Forces are vectors. How does the diagram show this?
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................ (1)
(iii) Force U is the unbalanced force which acts on the cart. Complete the equation
for force U in terms of X, Y and Z.
U = ......................................................................................................................... (1)
(b) A cart has a mass of 1500 kg. An unbalanced force of 1125 N acts on the cart in an
easterly direction.
Calculate the acceleration of the cart and state its unit and direction.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
Acceleration = ................................................... (4)
(Total 7 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
2007 June
Q-1: A model train travels between two stations. The velocity–time graph shows the train’s
motion.
(a) (i) State in which part of the journey A, B or C the train is decelerating.
.......................... (1)
(ii) Explain your answer.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(iii) What does the graph show about the deceleration?
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(b) (i) What feature of the graph represents the distance travelled between the two
stations?
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) A second train travels between the two stations at a constant velocity. It takes the
same time as the first train. On the axes above, draw a line showing the motion
of the second train. (3)
(Total 7 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
8. (a) State the principle of moments.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................. (2)
(b) The diagram shows a weighing device called a steelyard.
The weight of the shoulder balances the weight of the arm. The weight of the rider is
8.0 N and this balances the weight of the load when x = 0.12 m and y = 0.60 m.
Calculate the weight of the load in newtons.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
Weight of load = .................. N (2)
(Total 4 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
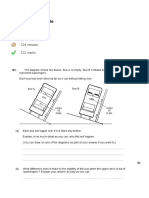
Q-12. (a) The diagram shows a lorry. It is travelling in a straight line and it is accelerating. The
total forward force on the lorry is F and the total backward force is B.
(i) Explain which is larger, force F or force B.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................(1)
(ii) State an equation which relates acceleration, mass and unbalanced force.
...............................................................................................................................(1)
(iii) An unbalanced force of 15 000 N acts on the lorry. The mass of the lorry is
12 500 kg. Calculate the lorry’s acceleration and give the unit.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Acceleration = .................................. (3)
(b) Another lorry is travelling at a steady speed. Explain how this lorry can be accelerating
even though its speed stays the same.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................(3)
(c) The thinking distance is the distance which a vehicle travels in the driver’s reaction
time. The braking distance is the distance which a vehicle travels when the brakes
are on.
(i) State one factor which increases the thinking distance.
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) State one factor which increases the braking distance.
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(Total 10 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
2007 Nov
(a) Complete the sentence.
Hooke’s law states that a force acting on a material produces an extension which is
............................................................. to the force. (1)
(b) A student attaches a load to the end of a spring.
(i) Name the type of force acting in the stretched spring.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) The student measured the length of the spring for different loads.
The table shows her data.
1. Deduce the load in newtons that would produce a length of 130 mm.
Load = ................................. N (1)
2. Estimate the maximum load in newtons at which the spring obeys Hooke’s
law.
Maximum load = .................................. N (1)
(c) A force–extension graph for a material is shown. Three regions A, B and C are
labelled.
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(i) In which region is Hooke’s law obeyed?
.......................... (1)
(ii) In which region is the material easiest to extend?
.......................... (1)
(iii) Explain your answer to (ii).
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(Total 7 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
a) (directly) proportional (1)
b)
(i) tension / weight / gravitational force(1)
(ii) 2.5 (N) (1)
(iii) 4.0 – 5.0 (1) (3)
c)
(i) A (1)
(ii) B (1)
(iii) large extension for small increase in force (1) (3)
Total 7 marks
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
12. A fishing boat is floating on the still water of a deep lake.
The fisherman drops a heavy anchor into the lake. The anchor falls through the water and
does not hit anything until it reaches the bottom.
(a) Three forces act on the anchor as it falls through the water.
(i) One of these forces is upthrust. State the name and direction of the other two
forces.
1 .............................................................................................................................
2 ............................................................................................................................. (2)
(ii) Which of the three forces changes significantly as the anchor falls?
...................................................
State how and why it changes.
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (2)
(b) The mass of the anchor is 12 kg. At one point in its fall the unbalanced force on the
anchor is 15 N.
Calculate the acceleration of the anchor at this point and give its unit.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
Acceleration = .......................................................... (3)
(c) After a short time the anchor reaches its terminal velocity.
(i) Describe the motion of the anchor when it is at its terminal velocity.
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (2)
(ii) State the size of the unbalanced force on the anchor as it falls at its terminal
velocity.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(Total 10 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answers
(a)
(i) weight down(wards) (1) ‘or’ (force of) gravity down(wards)
(water) resistance / drag / friction up(ward) (1) ‘or’
in opposite direction (to the movement / motion)
Notes - both force and direction for each either order
(ii) (water) resistance / drag / friction increases (1)
as speed/velocity increases (1) (depends on previous
so do not credit unless first mark gained) (4)
(b)
1.25 (2) ‘or’ F = ma (1) ‘or’ (a) = 15 ÷ 12 (1)
m/s2 or ms-2 (1) (3)
(c)
(i) down(wards) (1) at a steady speed (1)
‘or’ no acceleration / deceleration (2)
‘or’ constant velocity (2)
(ii) zero/0(N) (1) (3)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
2008 June
Q-1: (a) A child runs out in front of a car. The driver makes an emergency stop. The graph
shows the speed of the car from the time when the driver sees the child on the road.
(i) State the driver’s reaction time in seconds.
Time = ................................... s (1)
(ii) State the time in seconds for the brakes to stop the car.
Time = ................................... s (1)
(iii) Draw two more lines on the grid above to show how the speed might change if
the driver has been drinking alcohol and the road is slippery. (2)
(b) The condition of the tyres and the condition of the road surface are two factors which
affect the force of friction on a car.
(i) Name one other factor which affects the force of friction on a car.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) The diagram shows a car. The centre of gravity of the car is at the point
labelled X.
Add to the diagram an arrow showing the weight of the car. (1)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(Total 6 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q. No Correct Answer Acceptable Ans. Marks
1 (a)(i) 0.8 (seconds) 4/5 second 1
8/10 second (1)
1 (a)(ii) 3.2 (seconds) 3 1/5 1
allow ecf from (i)
4.0 – previous answer (1)
1 (a)(iii) one line two separate lines or 1
horizontal line beyond 0.8 one of these lines 1
less steep slope down (to the x axis) labelled 1 mark for each
dop correct (2)
1 (b)(i) air (resistance) Drag 1
mass of car Weight
speed (of the car) (force of) gravity
brakes Size
tyre pressure Shape
area of tyre velocity (of car)
streamlining REJECTED ANSWER
wind (resistance) (1)
temperature
1 (b)(ii) intentionally straight vertical arrow arrow from middle of 1
pointing downwards car
from, above, below or through point
X (1)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
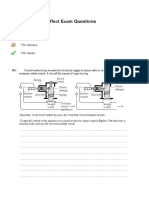
Q-9: (a) A boy jumps off a wall and lands on the ground without bending his knees. The graph
shows how the velocity of the boy varies with time as he lands.
(i) What property of a velocity-time graph can be used to determine acceleration?
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) Use the graph to calculate the boy’s deceleration and give its unit.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Deceleration = .......................................................... (3)
(iii) The mass of the boy is 70 kg. Calculate the resultant force in newtons acting on
the boy.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Force = ................................ N (3)
(b) Explain why the boy should bend his knees as he lands.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 10 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q. No. Correct Ans. Acceptable No. Rejected Marks
9 (a)(i) gradient slope area 1
-1
9 (a)(ii) 6.0 ÷ 0.25 = 24 N/kg or Nkg 3
2 -2
m/s or m/s/s or ms
ignore minus signs
9 (a)(iii) F=m×a ecf from (a)(ii) 70 x 10 3
= 70 × 24 nwn 700 x 24
= 1680 (N) score 0/3
9 (b) any three points comes to a stop damage to joints 1
same change in velocity over a longer
(in) more time distance effect of area of 1
-2
less acceleration or 24 ms is too contact and
deceleration ora high pressure
less force ora allow ‘slower 1
deceleration’ impact reduced
(3)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q11-C:
(c) The students also saw a material being stretched.
The graph shows the results.
(i) Name a material which would produce these results.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) Indicate on the graph the region associated with Hooke’s law. (1)
(iii) Explain your answer.
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(Total 12 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
ANSWER
Q. No Correct Ans. Acceptable Ans. Mark
11 (c)(i) metal metal spring 1
any metal metal wire
ignore ‘spring’
11 (c)(ii) linear region correctly marked 1
11 (c)(iii) dop elastic behaviour 1
proportionality between force(or
mass or load or weight) and
extension OWTTE
(Total 12 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
2008 Nov
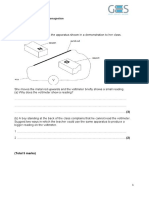
Q6: The diagram shows a barrier at a car park. The barrier arm is usually in the position
shown. An iron sphere is attached to the barrier arm at A. The weight of the barrier arm
acts at B. When there is a current in the coil the barrier arm pivots at P and end E moves
upwards.
(a) At which point, A, B, E or P, is the centre of gravity of the barrier arm?
Point ................ (1)
(b) Complete the sentence.
The coil acts as an ...................................................... (1)
(c) Why is the coil made of insulated wire?
......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... (1)
(d) What is the cause of the force on the barrier arm at A before the electricity is switched
on?
...................................................................................................................................... (1)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(e) When the electricity is switched on the total force which acts at A is 900 newtons.
This force can just start to pull the iron sphere down.
Use the distances shown on the diagram to calculate the weight in newtons of the
barrier arm.
Show your working.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
Weight of barrier arm = ....................... N (3)
(Total 7 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
6a- B (1)
6b-Electromagnet (1)
6c-to prevent shorting/a short circuit /to prevent current (accept electricity) from going directly
from one turn to the next
accept ‘… from one coil to the next’
do not credit any reference to
safety/electric
shock/heat
insulation
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q13: During a storm, a large rock falls from a high cliff into the sea.
The graph shows the velocity of the rock as it falls from the cliff until it reaches the bottom
of the sea. A, B and C are stages in its fall before it hits the sea.
(a) State the property of the graph that can be used to determine
(i) acceleration,
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) distance travelled.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(b) (i) Does the rock reach terminal velocity in air? (1)
...............................................................................................................................
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(ii) Explain your answer.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(c) A, B, C, D and E represent stages in the fall of the rock.
At which of these stages does the rock have
(i) greatest acceleration, ............................. (1)
(ii) greatest deceleration, ............................. (1)
(iii) the greatest force acting on it due to air resistance? .............................. (1)
(d) Describe and explain the motion of the rock when it is in the sea at stage E. Use the
concepts of drag, weight, acceleration and velocity in your answer.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... (4)
(e) Explain how the graph shows that the height of the cliff is greater than the depth of
the sea.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................(2)
(Total 13 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
13 (a) (i) slope/gradient
13 (a) (ii) area (under graph)
13 (b) (i) no
13 (b) (ii)dop graph not horizontal or velocity not constant or (still) accelerating
13 (c) (i) A
13 (c) (ii) D
13 (c) (iii) C
13 (d) • constant velocity
• weight downwards/drag upwards
• equal
• no acceleration
13 (e) greater area under graph before sea
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
14. (a) Complete the sentence.
A scalar quantity has size but a vector quantity has both size and
................................................ (1)
(b) Identify the quantities in the table as either scalar (S) or vector (V). The first two have
been done for you.
Quantity Type
Speed S
Force v
Displacement
Density
Energy
Acceleration
(c) A student going to university pulls a large suitcase along the ground. The diagram
shows three forces acting on the suitcase.
Calculate the unbalanced force in newtons and state its direction.
Unbalanced force = .............................................. N
Direction ................................................................... (2)
(Total 5 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
14 (a) direction
14 (b) V
S
S
V
14 (c)0.4 N (1)
to the right (1)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
2009 June
Q8-The diagram shows the sizes of the two horizontal forces, X and Y, acting on a road
tanker.
(a) Force is a vector quantity.
What does this mean?
...................................................................................................................................... (1)
(b) The unbalanced force is sometimes called the resultant force.
Complete the equation for the unbalanced force on the road tanker.
Unbalanced force = ........................................................................................................ (1)
(c) A student writes this list of quantities.
acceleration density energy mass temperature volume
The student says they are all scalar quantities.
Do you agree with the student? Explain.
......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... (2)
(Total 4 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Number Acceptable Extra Reject Mark
Answers Information
8 (a) has either order unit 1
size/magnitud
e/(quantitativ
e) value/
quantity
/amount
and
direction
Question Number Acceptable Extra Information Mark
Answers
8 (b) (unbalanced force 1
=) X-Y
or in words
e.g. forward force
– backward force
forward force -
drag
Question Number Acceptable Extra Information Mark
Answers
8 (c) acceleration is a acceleration and 2
vector any one other
or from the list are
acceleration is not vectors/not scalars
a scalar scores 1
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q12-The velocity–time graph shows a journey made by a train.
(a) (i) State the equation which relates acceleration, change in velocity and time taken.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) Calculate the train’s acceleration between the start and point L and give the unit.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Acceleration = ......................................................... (3)
(b) Describe the motion of the train in the section MN.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................(2)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(c) A student uses the graph to calculate the distance travelled by the train.
She writes the equation shown in the box.
State the correct unit in this equation for D.
...................................................................................................................................... (1)
(Total 7 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Number Acceptable Extra Information Mark
Answers
12 (a)(i) acceleration = or any correctly transposed 1
change in version
velocity allow ‘speed’ instead of
time (taken) ‘velocity’
a = (v – u) /t
12 (a)(ii) correct pair of 45/30 = 1.5 45/0.5 = 90 1
readings from nwn nwn 1
the graph m/s/min m/s/h 1
e.g. 45 m/s
and 30
minutes
45/1800 =
0.025
nwn
2
m/s
Question Number Acceptable Ignore Mark
Answers
12 (b) 50 m/s scores 2 terminal velocity 2
marks 1
or
constant velocity
steady speed
uniform motion
or
not accelerating
scores only 1 mark
12 (c) km or kilometre 1
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q13-The diagram shows the forces which act on a coconut as it falls from a tall palm tree.
There is no wind.
(a) (i) Explain in terms of the forces involved why, at first, the coconut accelerates.
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) Name the friction force which acts on the coconut as it falls.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(iii) What happens to the friction force as the coconut accelerates?
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(iv) Name the term used for the downwards speed of the coconut when the friction
force equals the coconut’s weight.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(b) (i) State the equation which relates kinetic energy, mass and speed.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) The mass of the coconut is 0.80 kg. Just before it hits the ground its kinetic
energy is 32.4 J.
Calculate its speed just before it hits the ground and state the unit.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Speed = ............................................. (3)
(Total 8 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Number Acceptable Ignore Mark
Answers
13 (a)(i) weight/gravity is upthrust 1
greater than
friction/drag
ora
or
downward force
greater than
upward force
ora
13 (a)(ii) air resistance upthrust 1
air friction wind
drag
13 (a)(iii) increases 1
(gets) bigger
(gets) larger
builds up
Question Number Acceptable Answers Reject Mark
13 (a)(iv) terminal velocity 1
terminal speed
Question Number Acceptable Extra Information Mark
Answers
13 (b)(i) (kinetic energy) = or (KE) = ½ m v2 1
2
½ mass × speed or any correctly
transposed
version
2
13 (b)(ii) 32.4 = ½ × 0.80 × v = 81 or v = √81 1
2
v st 1
scores 1 mark 1
v = 9 nwn
m/s or
metres/second
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
2009 Nov
Q7: The diagram shows a tower crane on a building site.
(a) The crane is in equilibrium.
(i) What does the term equilibrium mean?
...................................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) Calculate the weight, in kN, of the load.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
Weight = .................................. kN (2)
(b) (i) Weight is a vector quantity.
Explain how you can tell this from the diagram.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) Give another example of a vector quantity.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(Total 5 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Acceptable Ans. Extra Information Mark
No.
7 (a)(i) (total) clockwise accept just ‘balanced’ 1
moment(s) accept ‘no unbalanced force’
= (total) anticlockwise
moment(s)
7 (a)(ii) 3.6 (kN) (2) credit either ‘12 x 2.7 = weight/load × 9’ 2
or ‘ = 12 x 2.7 ÷ 9’
or any transposed version which
will calculate to 3.6 with (1)
7 (b)(i) (size and) direction 1
shown
7 (b)(ii) acceleration or 1
momentum/velocity/displacement/impulse
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q12-Crash tests are used to measure the safety of new car designs. In one type of test, a car
accelerates along a straight and level track and then crashes into a barrier.
a)The velocity-time graph shows one set of results
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Use information from the graph to answer the questions.
(i) Calculate the acceleration of the car from the start to the barrier.
Show your working and give the unit.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Acceleration = ......................................... (3)
(ii) Calculate the distance in metres the car travels from the start to the barrier.
Show your working.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Distance = ..................................... m (3)
(iii) The car hits the barrier and a short time later it stops.
How long in seconds is this short time?
...............................................................................................................................
Time = ....................................... s (1)
(b) (i) State the equation which relates acceleration, mass and unbalanced force.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) When another car hits the barrier, it experiences an unbalanced force of 25 000 N
and decelerates at 20 m/s2.
Calculate the mass in kilograms of the car.
...............................................................................................................................
Mass = .................................... kg (2)
(Total 10 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Acceptable Ans. Extra information Marks
No.
12 (a)(i) 2 0 (2) m/s2 (1) or m s-2 or m/s/s 3
allow for (1) ‘28 ÷ 1.4’ or any
other correct indication that the
slope of the ascending line is
being used
12 (a)(ii) 19.6 (m) (3) or 3
clear indication that the distance
is given by the area under (the
main part of) the graph
(1)
a numerical statement which, if
correctly evaluated, leads to
19.6 e.g. ½ × 1.4 × 28 (1)
12 (a)(iii) (0).06 (s) 1
12 (b)(i) (unbalanced) force = mass × or F = ma 1
acceleration or any correctly
transposed version
12 (b)(ii) 1250 (kg) (2) or 25000 ÷ 20 (kg) (1) 2
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
2010 June
Q2: A child runs out in front of a truck. The driver makes an emergency stop.
The graph shows the speed of the truck from the time when the driver first sees the
child.
(a) (i) State the time, in seconds, for the driver to react.
Time = ................................... s (1)
(ii) Calculate the time, in seconds, for the brakes to stop the truck.
Time = ................................... s (1)
(b) The driver had been drinking alcohol. State the effect this may have had on:
(i) the time for the driver to react;
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) the time for the brakes to stop the truck.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(c) Give one feature of the road conditions which may increase the stopping distance of
a vehicle.
...................................................................................................................................... (1)
(d) The diagram shows a truck.
(i) The centre of gravity of the truck and its load is at the point labelled C.
Add to the diagram an arrow showing the total weight. (1)
(ii) State the name of a force which opposes the motion of the truck.
.............................................................................................................................. (1)
(Total 7 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Acceptable Answer Extra Info. Marks
No.
2(a)(i) 1.6 (s) 1
2(a)(ii) 4.4 (s) 1
2(b)(i) increase(d)/longer /more dna slower/slowed it 1
down
2(b)(ii) no effect/no change/stays the same/ 1
no difference/none/nothing
2(c) wet/slippery/icy/greasy/ loose dna poor condition of the 1
surface/muddy /snow/rain tyres
/smooth /gravel /oil or brakes
2(d)(i) Single straight arrow pointing judge by eye 1
downwards and on a vertical line ignore labels
through C
2(d) (ii) friction (between lorry and air)/air dna wind resistance 1
resistance/drag
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q13: In 1907, a tradition started of dropping a ball, made from wood and iron, into Times
Square in New York at midnight on New Year’s Eve.
The ball had a mass of 300 kg and was dropped from a great height.
(a) Calculate the weight, in newtons, of the ball.
......................................................................................................................................
Weight = ............................... N (2)
(b) The diagram shows a falling ball.
(i) Add a labelled arrow to the diagram to show the weight of the ball. (1)
(ii) Add another arrow to the diagram to show another force acting on the ball during
its fall through the air. (1)
(iii) State the name of this force.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(c) Eventually the ball reached terminal velocity when it was travelling at constant
speed.
Explain why the ball reached terminal velocity.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... (3)
(Total 8 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Acceptable Answer Extra Info. Marks
No.
13(a) W = mg (1) 2940 (N), 2943 (N) 1
= 300 x 10 = 3000 (N) (1) 1
13(b)(i) arrow vertically downwards by arrow starting from ball 1
eye (allow from an edge)
and ecf value from (a)
labelled 3000 (N) / weight/ W /
mg
13(b)(ii) arrow vertically upwards by eye within width of ball 1
ignore any label
13(b)(iii) air resistance/drag/air friction/ dna ‘friction’ 1
upthrust
13(c) upward force/air 1
resistance/drag
increased
idea of upward force = 1
downward
force/no net force/forces
balance/forces in equilibrium
no acceleration 1
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q16: The diagram shows a kite in the air and the size and direction of the forces which
act on it.
(a) Calculate the resultant upward force, in newtons, on the kite.
......................................................................................................................................
Resultant upward force = ..................................... N (1)
(b) Calculate the resultant sideways force, in newtons, on the kite and state its direction.
Resultant sideways force = ..................................... N
Direction ......................................... (2)
(c) The air temperature is 17 °C.
Temperature is a scalar quantity.
Explain what is meant by a scalar quantity.
......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... (2)
(d) State the word which is used to describe quantities, such as force and acceleration,
which are not scalar quantities.
...................................................................................................................................... (1)
(Total 6 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Acceptable Answer Extra Info. Marks
No.
16(a) 1.0 (N) 2
16(b) 1.5 (N) 2
right/arrow drawn to right i.e.
→/east
16(c) has size/magnitude/amount mark independently 1
has only size/magnitude
but no direction scores both marks 1
16(d) vector 1
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
2010 Nov.
Q5: A ticker timer is a device which makes dots on a paper tape.
A student fastens one end of the tape to a toy car and uses the ticker timer to record the
motion of the toy car.
Her investigation is shown below.
Part of the tape from the student’s investigation is shown in the following drawing.
(a) (i) The ticker timer produces dots at a steady rate of 50 dots per second.
Calculate how long, in seconds, it took the toy car to travel from A to B.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Time taken = ....................... s (2)
(ii) Distance A to B is 73 mm.
Calculate the average speed, in mm/s, of the car as it travelled this distance.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Average speed = ...................................................... mm/s (2)
(b) The diagram shows the toy car and the arrow shows where its weight acts.
Put an X on the diagram to show the position of the centre of gravity of the car.
The centre of the X should be at the centre of gravity.
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(1)
(Total 5 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Acceptable Answer Extra Info. Marks
No.
5(a)(i) 0.1 (s) or 1/10 (s) allow (1) for a time 2
interval of five
5(a)(ii) 730 mm/s allow ecf from part ai 2
allow (1) for clear
indication
that
(average) speed
= distance ÷ time
(taken)
5(b) centre of X at the start of the judge by eye 1
downwards arrow
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q8: A dockside crane is used to load containers onto a ship.
The jib is designed so that its weight is equally balanced on each side of the support.
The following diagram shows the other turning forces on the jib.
The jib is in equilibrium.
(a) (i) State the principle of moments for a system which is in equilibrium.
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) Use the principle of moments to calculate the weight, in kilonewtons, of the
concrete block.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Weight of the concrete block = .................................... kN (2)
(b) Another container weighs 26 000 N.
(i) State the equation which relates weight, mass and the gravitational field
strength, g.
............................................................................................................................... (1)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(ii) Calculate the mass of this container.
Show how you arrived at your answer and state the unit.
g = 10 N/kg
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Mass of container = ................................................. (3)
(Total 7 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Question Acceptable Answer Extra Info. Marks
No.
8(a)(i) (total) clockwise moment(s) = allow ‘turning effect’ for ‘moment’ 1
(total) anticlockwise moment(s) dna sum of clockwise = sum of
anticlockwise
allow ‘force × distance’ is the same on
both sides of the fulcrum/turning
point/line
allow moment same on both sides
dna ‘turning force’ for ‘moment’
8(a)(ii) 18 (kN) allow (1) for clear indication that 2
weight (of concrete block) x 8
= 24 x 6
8(b)(i) weight = mass × g or any correctly transposed 1
W = mg version
8(b)(ii) 2600 (2) allow (1) for clear indication that 3
kg (1) mass = any weight ÷ 10
2.6 tonnes /t (3) e.g. 2400 (1)
2400 kg (2)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Q9: The photograph shows two people pushing a car.
They have to push the car with a large force before it just starts to move.
(a) Name the type of force that opposes motion.
...................................................................................................................................... (1)
(b) When the car is moving the unbalanced force acting on the car is 150 N.
(i) State the equation which relates unbalanced force, mass and acceleration.
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(ii) What does the term unbalanced force mean?
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... (1)
(iii) The mass of the car is 1200 kg.
Calculate the acceleration of the car and state its unit.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
Acceleration .............................................. (2)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
(c) The velocity-time graph shows how the car moves from rest during ten seconds.
Explain whether the graph supports your answer in (b)(iii).
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................... (2)
(Total 7 marks)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
Answer
Question Acceptable Answer Extra Info. Marks
No.
9(a) friction allow drag/air resistance 1
9(b)(i) F = ma or any transposed version 1
words or symbols
9(b)(ii) reference to net/resultant force ignore ‘not balanced’ and ‘total’ 1
or difference in the forces acting
or push force – friction
9(b)(iii) a = 150/1200 = 0.125 allow 1/8 1
2
m/s 1
ignore N/kg
9(c) slope = acceleration or use of any v/t from graph 1
slope shown to be about 0.125
or use v = at (1) and compare
with v value from graph (1) 1
ecf from (b)(iii)
Khalid Mazhar Qureshi www.edexcel-cie.com
You might also like
- Waves Practice Test SACE Stage 1Document14 pagesWaves Practice Test SACE Stage 1ShubhamNo ratings yet
- As Physics Unit 1 Strctured QuestionsDocument14 pagesAs Physics Unit 1 Strctured QuestionsZeenia IfNo ratings yet
- Physics Yr 11 Revision QsDocument14 pagesPhysics Yr 11 Revision QsPunitha PanchaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy & PowerDocument16 pagesWork, Energy & PowerSam LankaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy & Power-AQADocument16 pagesWork, Energy & Power-AQAmzzha3No ratings yet
- Paper-2 Set A (Source)Document9 pagesPaper-2 Set A (Source)Dewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Exam Questions AS: Minutes MarksDocument75 pagesMechanics Exam Questions AS: Minutes MarksSheikh SamirNo ratings yet
- 2.3 WavesDocument23 pages2.3 Wavesrabin bajagainNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws EQ MSDocument24 pagesNewtons Laws EQ MSnchauhan212No ratings yet
- Year-7-Science-revision 2Document17 pagesYear-7-Science-revision 2Cally ChewNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector DiagramDocument2 pagesPages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector Diagramlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Section 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedDocument43 pagesSection 6 Magnetism Electromagnetism - UnlockedgesNo ratings yet
- Form 4 - 35. Electromagnetic Induction 2QDocument10 pagesForm 4 - 35. Electromagnetic Induction 2QlisemaNo ratings yet
- P3 07 MomentsDocument76 pagesP3 07 MomentsOmar AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument6 pagesCircular MotionCaesha ColemanNo ratings yet
- P3 10 Motor EffectDocument58 pagesP3 10 Motor EffectHiruni FernandoNo ratings yet
- Physics QuestionsDocument32 pagesPhysics QuestionsAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- 2 Moments Hydraulics CM Self Study QuestionsDocument48 pages2 Moments Hydraulics CM Self Study QuestionsRiyan PurewalNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Resolving & MomentsDocument21 pages2.1 Resolving & MomentsCraazyNo ratings yet
- P2 Forces and Motion QuestionsDocument72 pagesP2 Forces and Motion QuestionsSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Class-X Physics Home Work-1B (Theory) : Chapter: Physical Quantity, Kinematics, DynamicsDocument18 pagesClass-X Physics Home Work-1B (Theory) : Chapter: Physical Quantity, Kinematics, DynamicsNuha TasniahNo ratings yet
- Full Mock - 1 Paper-2Document16 pagesFull Mock - 1 Paper-2Dewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Resistivity QDocument28 pagesResistivity QJellyfishNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Fields and Further Mechanics - Complete BookDocument92 pagesUnit 4 Fields and Further Mechanics - Complete BookVimeshMunohurNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion New-1-1Document7 pagesProjectile Motion New-1-1Drish ShahNo ratings yet
- Electromotive Force & Internal Resistance QPDocument10 pagesElectromotive Force & Internal Resistance QPcrochetbyellaa4No ratings yet
- Newtons Laws EQ MSDocument31 pagesNewtons Laws EQ MSJamieNo ratings yet
- Mo MoDocument11 pagesMo Mowidov0% (1)
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Electricity)Document25 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Electricity)lelon810% (1)
- Mechanics Questions NO MOMENTUM and Answers in One FileDocument92 pagesMechanics Questions NO MOMENTUM and Answers in One FileFin Brickman100% (1)
- Waves Path Phase N SpeedDocument14 pagesWaves Path Phase N SpeedkamrunnisaNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Magnetism) PDFDocument5 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Magnetism) PDFKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Paper 3Document17 pagesPaper 3Ahmad OmarNo ratings yet
- Practice Test - Forces and Motion - Triple Science Year 10Document9 pagesPractice Test - Forces and Motion - Triple Science Year 10Gd Acceler8No ratings yet
- Oscillation (A2) Name Roll No. Class Date 1. Figures1and 2Document4 pagesOscillation (A2) Name Roll No. Class Date 1. Figures1and 2fassekingNo ratings yet
- A2 Force and MomentumDocument41 pagesA2 Force and MomentumDhan Bahadhur Mr.Dhan Bahadur BoharaNo ratings yet
- Absorption of X-Rays QPDocument5 pagesAbsorption of X-Rays QPtharindu_rulsNo ratings yet
- 6BI02 01 Que 20120521Document2 pages6BI02 01 Que 20120521Ruwan BandaraNo ratings yet
- ST 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Introductory Electronics) PDFDocument10 pagesST 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Introductory Electronics) PDFSaleem ShahidNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Final Raw Source & MsDocument20 pagesPaper 2 Final Raw Source & MsDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- KS3 Forces 3Document36 pagesKS3 Forces 3Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Force Questions: GCE Physics 1.3.2 ForcesDocument19 pagesForce Questions: GCE Physics 1.3.2 ForcesJjrlNo ratings yet
- Waves EQ MSDocument63 pagesWaves EQ MSEng-Mohamed Ahmed AbdiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Worksheet: Addu High School Hithadhoo/Addu RKSHDocument5 pagesMagnetic Field Worksheet: Addu High School Hithadhoo/Addu RKSHDhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument44 pagesWork, Energy and Powercaramelrobin17No ratings yet
- A2 TPM-7 QP (2020) PDFDocument9 pagesA2 TPM-7 QP (2020) PDFANo ratings yet
- Physics Mechanics) QuestionsDocument40 pagesPhysics Mechanics) QuestionsN4y33mNo ratings yet
- Moments, Levers and Gears 3 QPDocument19 pagesMoments, Levers and Gears 3 QPdeepheat_008No ratings yet
- Revision Questions PDFDocument9 pagesRevision Questions PDFmwagweNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Materials PDFDocument98 pages1.4 Materials PDFIdrus FitriNo ratings yet
- Further MechanicsDocument39 pagesFurther MechanicsLio EditzNo ratings yet
- Electrical Current Distribution N PotentialDocument6 pagesElectrical Current Distribution N PotentialkamrunnisaNo ratings yet
- Paper-2 Set A (Final)Document16 pagesPaper-2 Set A (Final)Dewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Energy) PDFDocument7 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Energy) PDFMuhammad ObaidullahNo ratings yet
- Q1. (A) Define The Density of A MaterialDocument15 pagesQ1. (A) Define The Density of A MaterialKen OtooNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticeDocument27 pagesIGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticealfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- Intro To Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesIntro To Organic Chemistryyvg95No ratings yet
- Chem Structure BondingDocument7 pagesChem Structure BondingJake blakeNo ratings yet
- Basic Trading and Profit and Loss Account and Balance SheetDocument2 pagesBasic Trading and Profit and Loss Account and Balance SheetJake blake100% (1)
- WorksheetDocument1 pageWorksheetJake blakeNo ratings yet
- Correcting Errors: Errors Not Affecting Trial BalanceDocument2 pagesCorrecting Errors: Errors Not Affecting Trial BalanceJake blakeNo ratings yet
- Questi On Numbe R MarksDocument6 pagesQuesti On Numbe R MarksJake blakeNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument3 pagesDepreciationJake blakeNo ratings yet
- Correcting Errors - Booklet+lectureDocument22 pagesCorrecting Errors - Booklet+lectureJake blakeNo ratings yet
- "Control Accounts": IGCSE Accounting Manarat AhmedDocument2 pages"Control Accounts": IGCSE Accounting Manarat AhmedJake blakeNo ratings yet
- Bad DebtsDocument5 pagesBad DebtsJake blakeNo ratings yet