Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eman Anwar Armstrong 28 March, 2020: Iodine Pale Yellow
Uploaded by
EMAN ANWAROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eman Anwar Armstrong 28 March, 2020: Iodine Pale Yellow
Uploaded by
EMAN ANWARCopyright:
Available Formats
Angels International College
Middle Years Programme
Chemistry-MYPIV
Name: Eman Anwar
Section: Armstrong
Date: 28th March, 2020
Unit: How do atoms bond?
Topic: Halogens
ATLs: Thinking skills, Communication skills
Learner Profile: Inquirers, Knowledgeable, Thinkers, Communicators
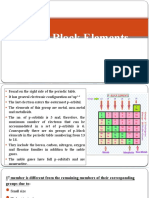
The Halogens (Group 7)
1. Link the halogens on the left with their colors on the right by drawing a line
between them.
iodine pale yellow
bromine green-yellow
fluorine dark orange
chlorine dark grey
2. Outline three properties of halogens.
MYPIV- 2019-20 Term II Page 1/1
Halogens exist in three physical states of matter (F and Cl as gas) (Br as liquid) (I and At as
solid)
Poisonous and toxic in their elemental states
Have low melting and boiling points
Halogens undergo displacement reactions with halide solutions
3. The following graph shows the electronegativity trend of group 7 down the group. State
what is meant by electronegativity and discuss electronegativity trend with respect to
increase in size of atoms as we move down the group.
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons towards itself.
The graph shows that as we move down, the group 7 elements’ ability to attract electrons
generally decreases. This is because down the group the atomic radius and size of atoms
increases, creating a shielding effect between the nucleus and valence shell. This decreases
the electrostatic force of attraction of the nucleus for the outermost shell, decreasing its
ability to attract electrons.
4. Complete the equations for reactions between the halogens and alkali metals to form
metal halides.
chlorine + sodium
Sodium chloride
Cl2 + 2Na 2NaCl
potassium bromide
Bromine + potassium
Br2 + 2K 2KBr
MYPIV- 2019-20 Term II Page 2/1
4. Complete the displacement reaction table.
Salt (aq) Potassium chloride Potassium Bromide Potassium iodide
Halogen
chlorine 2KCl + Br2 2KCl+ I2
bromine No reaction 2KBr+I2
iodine No reaction No reaction
5. Halogens are oxidizing agents. Discuss.
An oxidizing agent is defined as to being an electron accepter. Halogens have a high
tendency to accept electrons and are powerful oxidizing agents. For example in a
displacement reaction between chlorine and bromide with bromide having a negative
charge suggest that it has gained an electron to fully fill its outermost shell.
Cl2 + 2Br- = 2Cl- + Br2
In the above reaction initially we had chlorine and a bromide atom. The reaction is powered
by the ability of an atom to attract the extra valence electron that forms bromine atom to
bromide. Chlorine is more reactive than bromine and has higher electronegativity and so it
pulls in that electron from bromide making it an isolated bromine atom. . Then chlorine
becomes stable and forms chloride atom and bromine now needs one more valence
electron and so it reacts with another bromine atom to form a diatomic molecule. As
bromide lost an electron it was oxidized and chlorine acts as an oxidizing agent.
MYPIV- 2019-20 Term II Page 3/1
You might also like
- 1030 AnswersDocument2 pages1030 AnswersAJ Millard75% (8)
- Dehydrobromination of Meso-Stilbene DibromideDocument8 pagesDehydrobromination of Meso-Stilbene DibromideMo MlNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument1 pageCoursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionslizNo ratings yet
- MYP Chemistry AnswersDocument3 pagesMYP Chemistry AnswersDIEGO ALEJANDRO CASAS DELGADO-AlumnoNo ratings yet
- Endothermic and Exothermic Reaction Worksheet AnswersDocument5 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic Reaction Worksheet AnswersAyesha NoorNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab Act PrelimDocument20 pagesBiochem Lab Act PrelimcharlesNo ratings yet
- Group VIIDocument14 pagesGroup VIITimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 4 Group 17 Elements UpdatedDocument8 pages4 Group 17 Elements Updatedangie0812No ratings yet
- Halogen and Noble PDFDocument33 pagesHalogen and Noble PDFPrabhakar BandaruNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 - The P-Block ElementsDocument44 pagesRevision Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 - The P-Block ElementsDevashree NaikNo ratings yet
- Periodic 4.4Document31 pagesPeriodic 4.4Pushpa GaneshNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Handout Printable VersionDocument9 pagesGroup 7 Handout Printable VersionJohnclyde FerryNo ratings yet
- Dav School, Adambakkam Class-Xii Chemistry 7. The P-Block Elements (Class Notes)Document18 pagesDav School, Adambakkam Class-Xii Chemistry 7. The P-Block Elements (Class Notes)Maheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- HALOGENSDocument6 pagesHALOGENSokguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- 12 - Group 17Document48 pages12 - Group 17enderothNo ratings yet
- D BlockDocument29 pagesD BlockTara SinghNo ratings yet
- Halogen: © Boardworks LTD 2003Document20 pagesHalogen: © Boardworks LTD 2003Yolanda ArnNo ratings yet
- Ess Chem Unit 12 AnswersDocument2 pagesEss Chem Unit 12 AnswersSumathi GanasenNo ratings yet
- 72bd0be0-7231-11ee-a64d-dba66c595fb0Document29 pages72bd0be0-7231-11ee-a64d-dba66c595fb0carla.habib7579No ratings yet
- D-Block Elements: General Properties of Transition Elements Section - 1Document29 pagesD-Block Elements: General Properties of Transition Elements Section - 1VallabhNo ratings yet
- Group 7 The Halogens KLASS AnswersDocument4 pagesGroup 7 The Halogens KLASS AnswersKimberly Linderholm100% (1)
- Reactivity - MetalsDocument2 pagesReactivity - MetalsDroid4x BevinNo ratings yet
- HalogensDocument70 pagesHalogensKSINo ratings yet
- Group VII NotesDocument6 pagesGroup VII NotesA LEVEL TOPNo ratings yet
- The Halogens v1.0Document37 pagesThe Halogens v1.0asdfghjNo ratings yet
- P Block ElementsDocument24 pagesP Block Elementssanjusenthil8No ratings yet
- 4 Group 17 Elements UpdatedDocument8 pages4 Group 17 Elements UpdatedNorzilah MazaharNo ratings yet
- Group 7Document5 pagesGroup 7Wajid-ul-IslamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 5Document30 pagesChemistry Chapter 5Axad Ali ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Day - 1Document6 pagesDay - 1tnsqnrw000No ratings yet
- P-Block Elements (Halogens and Noble Gases) : ChemistryDocument23 pagesP-Block Elements (Halogens and Noble Gases) : ChemistrythinkiitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Chlorine PwptsDocument123 pagesChemistry of Chlorine PwptsGodfrey Muchai100% (1)
- P Block Elements - 105713Document8 pagesP Block Elements - 105713debasish124421No ratings yet
- P Block 17-18Document23 pagesP Block 17-18Aditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Group 7 HalogensDocument59 pagesGroup 7 HalogensHisham Jafar AliNo ratings yet
- Group I & II MetalsDocument60 pagesGroup I & II MetalsAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Periodic TableDocument27 pagesChapter 13 Periodic TableMatthew John RashadMehanyNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 P-Block ElementsDocument18 pagesUnit 9 P-Block ElementsfesinNo ratings yet
- AA IGCSE Unit 9Document10 pagesAA IGCSE Unit 9rickyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesChapter-8 ElectrolysisOhi AhmedNo ratings yet
- Group 17Document7 pagesGroup 17ahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Group 17 ElementsDocument3 pagesGroup 17 ElementsAmirah AmanNo ratings yet
- P Block Element (11th)Document14 pagesP Block Element (11th)Gudia kumariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry P-Block ElementDocument38 pagesChemistry P-Block ElementShivanjaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11 The P-Block ElementsDocument10 pagesChapter - 11 The P-Block ElementsManan TyagiNo ratings yet
- The P-Block ElementsDocument20 pagesThe P-Block ElementsNabiha KaleemNo ratings yet
- 12 P Block Revision Notes QuizrrDocument70 pages12 P Block Revision Notes QuizrrÃrjït ShûklãNo ratings yet
- The P-Block ElementsDocument6 pagesThe P-Block ElementsSteveMathewKuruvillaNo ratings yet
- 1 of 43 © Boardworks LTD 2009Document42 pages1 of 43 © Boardworks LTD 2009Justin HadinataNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 The Periodic Table of Elements 4.1 Periodic Table of ElementsDocument6 pagesBab 4 The Periodic Table of Elements 4.1 Periodic Table of ElementsChithiran CullenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Sport Swimming PresentationDocument18 pagesChemistry and Sport Swimming PresentationaniketbondeNo ratings yet
- 2 - Group 13Document11 pages2 - Group 13Mahin ChandwaniNo ratings yet
- 12 P Block Revision Notes QuizrrDocument69 pages12 P Block Revision Notes QuizrrMONEY ALLNo ratings yet
- Halogen and Noble GasesDocument33 pagesHalogen and Noble GasesYen ZaneNo ratings yet
- Oxidation & Reduction: 4 Examples of Redox ReactionDocument25 pagesOxidation & Reduction: 4 Examples of Redox ReactionlinieyNo ratings yet
- Elements of Group ViiDocument20 pagesElements of Group ViiNelima Stella mercyNo ratings yet
- Jahiem Nembhard Inorganic Lab 5Document6 pagesJahiem Nembhard Inorganic Lab 5Jahiem NembhardNo ratings yet
- Lectures 8,9,10-Gr13Document40 pagesLectures 8,9,10-Gr13Kumar KeshavNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens (Part 1)From EverandInorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens (Part 1)A. P. HagenNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry of Organic Halogen Compounds: International Series in Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandAnalytical Chemistry of Organic Halogen Compounds: International Series in Analytical ChemistryNo ratings yet
- A Doll's House Act1 AnalysisDocument3 pagesA Doll's House Act1 AnalysisEMAN ANWARNo ratings yet
- A Doll House DraftDocument1 pageA Doll House DraftEMAN ANWARNo ratings yet
- A Doll's House Character AnalysisDocument5 pagesA Doll's House Character AnalysisEMAN ANWARNo ratings yet
- Halogens-Recording Observations and Processing SkillsDocument3 pagesHalogens-Recording Observations and Processing SkillsEMAN ANWARNo ratings yet
- Comparitive Study of Commercial Antacids - 1Document12 pagesComparitive Study of Commercial Antacids - 1Hemant ChopraNo ratings yet
- Max e3-ENGDocument16 pagesMax e3-ENGDamVent DamVentNo ratings yet
- Sequencing of Separation TrainsDocument35 pagesSequencing of Separation TrainsMohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Chem 483 Manual ExperimentsDocument49 pagesChem 483 Manual ExperimentsJackie ApplewalkNo ratings yet
- iGCSE - Chem - Worksheet 20 - RatesDocument3 pagesiGCSE - Chem - Worksheet 20 - Rateskashif mohammedNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Heat: StructureDocument22 pagesUnit 2 Heat: StructureParminder singh parmarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24: Fiber Optics: True/FalseDocument6 pagesChapter 24: Fiber Optics: True/FalseChristopher Inoval Paril100% (1)
- Butadieno A04 431-1Document16 pagesButadieno A04 431-1Tasneem MNo ratings yet
- Context Clues: "Using Context Clues in The Sentences or Paragraph"Document4 pagesContext Clues: "Using Context Clues in The Sentences or Paragraph"Rizki fitriana dewiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties of Oxygen From 20-100KDocument2 pagesThermodynamic Properties of Oxygen From 20-100Kwesileh981No ratings yet
- Calorimeter Lab IntroductionDocument2 pagesCalorimeter Lab Introductionapi-348321624No ratings yet
- Tasco Q&aDocument386 pagesTasco Q&aMai PhamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument57 pagesFundamentals of Chemical ThermodynamicstNo ratings yet
- Steady 1D Heat ConductionDocument19 pagesSteady 1D Heat ConductionEn CsakNo ratings yet
- Patente Saponificacion Oleorresina de Marigold 3Document6 pagesPatente Saponificacion Oleorresina de Marigold 3Harry CortezNo ratings yet
- TechTip GC Liners 1Document4 pagesTechTip GC Liners 1bnechitaNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Prelim Take Home Exam December 25 2017Document2 pagesKinetics Prelim Take Home Exam December 25 2017Michelle Mendoza100% (1)
- Sebatian AromatikDocument100 pagesSebatian AromatikGanthimathi SugumaranNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Air CoolerDocument2 pagesIntroduction of Air CoolerHarshal Madgulkar (Harsh)100% (1)
- Ijertv2is80230 6Document13 pagesIjertv2is80230 6emad hayekNo ratings yet
- 17bec0026 Physics Da-1Document47 pages17bec0026 Physics Da-1gautamNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper With Solution 08 Jan 2020 Shift 1 Memory BasedDocument34 pagesJEE Main 2020 Question Paper With Solution 08 Jan 2020 Shift 1 Memory BasedmisostudyNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Hydrogen Uptake and Release From Heteroaromatic Compounds For Hydrogen StorageDocument9 pagesKinetics of Hydrogen Uptake and Release From Heteroaromatic Compounds For Hydrogen Storagesj singhNo ratings yet
- The Colloidal State: (I) Crystalloids (Ii) ColloidsDocument12 pagesThe Colloidal State: (I) Crystalloids (Ii) Colloidssrimant kumarNo ratings yet
- Vdoc - Pub Basic Corrosion Technology For Scientists and EngineersDocument178 pagesVdoc - Pub Basic Corrosion Technology For Scientists and EngineersAgeng LaksitoNo ratings yet
- FridgeDocument6 pagesFridgeshashlearnNo ratings yet
- Working With Non-Ideal Gases PDFDocument3 pagesWorking With Non-Ideal Gases PDFpolaris44No ratings yet