Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrochemistry: Date: 05/06/2020 Assignment No-2 Q.1
Uploaded by
Seerat Ghai0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThis document contains 5 questions regarding electrochemistry concepts. Question 1 asks why conductivity decreases with dilution of a solution. Question 2 asks how to determine the molar conductivity of water. Question 3 provides data to calculate the degree of dissociation and dissociation constant for methanoic acid. Question 4 provides data to calculate the dissociation constant for acetic acid. Question 5 asks to calculate the molar conductivity for CaCl2 and MgSO4 using given ion conductivity data.
Original Description:
Original Title
0506201343364281.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 5 questions regarding electrochemistry concepts. Question 1 asks why conductivity decreases with dilution of a solution. Question 2 asks how to determine the molar conductivity of water. Question 3 provides data to calculate the degree of dissociation and dissociation constant for methanoic acid. Question 4 provides data to calculate the dissociation constant for acetic acid. Question 5 asks to calculate the molar conductivity for CaCl2 and MgSO4 using given ion conductivity data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageElectrochemistry: Date: 05/06/2020 Assignment No-2 Q.1
Uploaded by
Seerat GhaiThis document contains 5 questions regarding electrochemistry concepts. Question 1 asks why conductivity decreases with dilution of a solution. Question 2 asks how to determine the molar conductivity of water. Question 3 provides data to calculate the degree of dissociation and dissociation constant for methanoic acid. Question 4 provides data to calculate the dissociation constant for acetic acid. Question 5 asks to calculate the molar conductivity for CaCl2 and MgSO4 using given ion conductivity data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
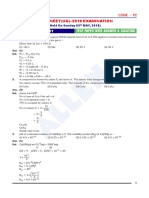
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Date : 05/06/2020
Assignment No- 2
Q.1 Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Q,2 Suggest a way to determine the m value of water.
Q 3 The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L–1 methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm2 mol–1. Calculate its degree of
dissociation and dissociation constant. Given (H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol–1 and (HCOO–) = 54.6 S cm2
mol–1.
Q.4 The conductivity of 0.001028 mol L–1 acetic acid is 4.95 × 10–5 S cm–1. Calculate its dissociation
constant if m for acetic acid is 390.5 S cm2 mol–1.
Q.5 Calculate m for CaCl2 and MgSO4 from the data given in Table 3.4
Ion 0/(S cm2mol–1) Ion 0/(S cm2 mol–1)
Ca2+ 119.0 Cl- 76.3
Mg2+ 106.0 SO42− 160.0
You might also like
- Endohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideFrom EverandEndohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problems 2ND YearDocument9 pagesNumerical Problems 2ND Yeardhanushdhanup178No ratings yet
- Redox Titration Questions - Docx 1Document6 pagesRedox Titration Questions - Docx 1petersonramsey254No ratings yet
- Titration Calculations: Revision Summary: Number 59 WWW - Curriculumpress.co - UkDocument3 pagesTitration Calculations: Revision Summary: Number 59 WWW - Curriculumpress.co - UksandalailaNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY Worksheet With AnswersDocument5 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY Worksheet With AnswersG.D. Pranav.LaskhminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Softening 2Document5 pagesSoftening 2Xherine Bico CordialNo ratings yet
- Revision - Electrochemistry (Cbse 2023)Document2 pagesRevision - Electrochemistry (Cbse 2023)Sahana BanuNo ratings yet
- 6 Redox (2) (S)Document18 pages6 Redox (2) (S)Mr TanNo ratings yet
- 010 2059 Prahasti Rombel 01 Tugas Ke 04Document14 pages010 2059 Prahasti Rombel 01 Tugas Ke 04prahasticynthiaNo ratings yet
- Redox Tutorial AnswersDocument14 pagesRedox Tutorial AnswersJonathan NgNo ratings yet
- ch03 SM Chemistry2eDocument36 pagesch03 SM Chemistry2eLLL0% (1)
- CH 17Document55 pagesCH 17Aljebre Mohmed67% (3)
- Electrochemistry ProblemsDocument14 pagesElectrochemistry ProblemsExporting WarriorNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob (Resource Page) : Redox Reactions Occur When There Is A Change in Oxidation NumberDocument4 pagesPrepared by Dr. Tony Jacob (Resource Page) : Redox Reactions Occur When There Is A Change in Oxidation NumberUday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Class 12 ChemistryDocument10 pagesClass 12 ChemistryDHRUV goswamiNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry - Iodine Clock Reaction Lab ReportDocument4 pagesAP Chemistry - Iodine Clock Reaction Lab ReportJustin MorrowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Important QuestionsSukh sainiNo ratings yet
- 2012 Redox Tutorial-TutorDocument11 pages2012 Redox Tutorial-TutorKarunya NarayanamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Leo PalNo ratings yet
- Solution: Part 1Document4 pagesSolution: Part 1Aljebre MohmedNo ratings yet
- Universiti Sains Malaysia: EBS 336/3 - Analytical ChemistryDocument15 pagesUniversiti Sains Malaysia: EBS 336/3 - Analytical ChemistryKrystel Monica ManaloNo ratings yet
- Solubility Question 2Document14 pagesSolubility Question 2Unidentified PersonNo ratings yet
- Redox TitrationsDocument12 pagesRedox TitrationsStefani Ann Cabalza100% (1)
- Leaching Principles and KineticsDocument2 pagesLeaching Principles and KineticsThembi MatebulaNo ratings yet
- Honors Chemistry WKSHT Solution Stoichiometry With Some ANSWERSDocument5 pagesHonors Chemistry WKSHT Solution Stoichiometry With Some ANSWERSIan CacciatoreNo ratings yet
- กัญกร อโนทิพย์Document14 pagesกัญกร อโนทิพย์Kanyakorn AnothipNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Title: Volumetric Analysis ObjectiveDocument9 pagesExperiment 2: Title: Volumetric Analysis ObjectiveU2004839 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument43 pagesReviewerTiffany LiuNo ratings yet
- 2012 Aipmt Mains Exam Paper With SolutionDocument30 pages2012 Aipmt Mains Exam Paper With SolutionAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- Tugas Latihan TitrasiDocument9 pagesTugas Latihan TitrasithomasdarmaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 AnsDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 Ansharsh jetaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PracticalsDocument24 pagesChemistry PracticalsnknikhilkouravNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases Practice Problems MCDocument24 pagesAcids Bases Practice Problems MCalbertvdatu278No ratings yet
- Determination of The Solubility Product and Enthalpy of Dissolution of Sparingly Soluble Salts by ConductometryDocument4 pagesDetermination of The Solubility Product and Enthalpy of Dissolution of Sparingly Soluble Salts by Conductometrykasun1237459No ratings yet
- 21CH12 Cie 1Document2 pages21CH12 Cie 1akashNo ratings yet
- Group No. (4) Exp. No. (11) Date:-17/12/2008 Exp Name: - Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesGroup No. (4) Exp. No. (11) Date:-17/12/2008 Exp Name: - Chemical Kineticsشركة العاصمة لخدمات التنظيفNo ratings yet
- 6 4Document1 page6 4Dominic FungNo ratings yet
- Ultrasensitive Fluorescence Detection of Peroxymonosulfate Based On A Sulfate Radical-Mediated Aromatic Hydroxylation - SuppDocument15 pagesUltrasensitive Fluorescence Detection of Peroxymonosulfate Based On A Sulfate Radical-Mediated Aromatic Hydroxylation - SuppSantosh Srinivas NNo ratings yet
- Topic 5-PRETREATMENT-2021Document25 pagesTopic 5-PRETREATMENT-2021Bilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Music 2Document18 pagesMusic 2JonathanNgNo ratings yet
- s6 Unit 11. SolubilityDocument44 pagess6 Unit 11. Solubilityyvesmfitumukiza04No ratings yet
- College of Arts and Sciences CHM 331-02: Homework Set 2 (10 PTS) Due Date: Wednesday, September 13, in ClassDocument1 pageCollege of Arts and Sciences CHM 331-02: Homework Set 2 (10 PTS) Due Date: Wednesday, September 13, in ClassNajmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper With Answer SolutionDocument11 pagesChemistry Paper With Answer SolutionNahasNo ratings yet
- Hem Actsheet: Redox Equilibria IV - Redox TitrationsDocument3 pagesHem Actsheet: Redox Equilibria IV - Redox TitrationsAya ZhNo ratings yet
- 142A Practiceexam3 W20KEYDocument3 pages142A Practiceexam3 W20KEYAlana Yudha-WrightNo ratings yet
- Honors Chemistry WKSHT Solution Stoichiometry With Some ANSWERSDocument5 pagesHonors Chemistry WKSHT Solution Stoichiometry With Some ANSWERSAlbert LinNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - 555Document12 pagesLab 4 - 555ZawanahNo ratings yet
- Kcet 2014 Chemistryr1 PDFDocument14 pagesKcet 2014 Chemistryr1 PDFAnweshaBose80% (20)
- Pages From @bohring Bot ? EXERCISE JEE Main Redox Reaction CombinedDocument11 pagesPages From @bohring Bot ? EXERCISE JEE Main Redox Reaction CombinedYuvarajNo ratings yet
- Redox TitrationDocument14 pagesRedox Titrationnorsiah100% (2)
- 03 QualityDocument22 pages03 QualityMKPashaPasha67% (3)
- Exercise 4Document32 pagesExercise 4Mas IzyanNo ratings yet
- JVHDocument5 pagesJVHrahulNo ratings yet
- Assignment ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesAssignment ElectrochemistryanshNo ratings yet
- Chem 213 Chemical Analysis Final June 9, 2003Document10 pagesChem 213 Chemical Analysis Final June 9, 2003ramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Ap ChemDocument4 pagesAp ChemEthan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Model Answers For Inorg Quiz 2010Document2 pagesModel Answers For Inorg Quiz 2010Sunil kumar KumawatNo ratings yet