Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L14-CMOS Logic Devices
Uploaded by
Derek SunOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L14-CMOS Logic Devices
Uploaded by
Derek SunCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE 221 – Lecture14
CMOS Logic Devices
ECE 221 – Fall 2015
Implementation of Logic Gates
Principles of operation of logic gates
Transistor as a switch
MOS transistor, CMOS process
Reading assignment for this lecture
Mano, Chapter 10.7-10.8 (CMOS devices)
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 2
Device Physics - basics
Current = flow of electrical charges
Two types of charge carriers
Electrons
Holes Metal
Two types of semiconductors Oxide (SiO2)
n-type, rich in electrons Si-substrate
Semiconductor (Si)
p-type, rich in holes
MOS = metal, oxide, semiconductor structure
MOS transistor = voltage-controlled switch
When control (gate) voltage = high (1), transistor is ON, conducts
When control (gate) voltage = low (0), transistor is OFF
There are two types of MOS transistors
nMOS – conducting charges are electrons
pMOS – conducting charges are holes
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 3
The MOS Transistor
Polysilicon
Aluminum
nMOS
transistor
nMOS transistor
electrons in the channel conduct current when Gate is ON (1)
pMOS transistor
hoes in the channel conduct current when Gate is OFF (0)
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 4
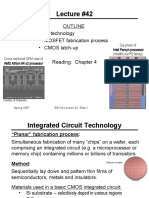
The CMOS Process
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gBAKXvsaEiw&feature=related
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wXVpQipeEh8&feature=related
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 5
Patterning of SiO2
Chemical or plasma
etch
Si-substrate
Hardened resist
SiO
2
(a) Silicon base material
Si-substrate
Photoresist
SiO
2 (d) After development and etching of resist,
chemical or plasma etch of SiO
Si-substrate 2
(b) After oxidation and deposition Hardened resist
of negative photoresist SiO
2
Si-substrate
UV-light
Patterned (e) After etching
optical mask
Exposed resist
SiO
2
Si-substrate Si-substrate
(f) Final result after removal of resist
(c) Stepper exposure
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 6
Transistor as a Switch
We need a switch to turn the gate ON or OFF
Switch implemented as MOS transistor
|VGS |
Non-zero resistance (R)
VGS V T nMOS
Ron
S D
pMOS
VT = threshold voltage, VGS = gate-to-source voltage
VGS must be greater than VT to turn the transistor ON
Two types of transistors/switches
nMOS – turns ON when gate voltage is logic 1, OFF when logic 0
pMOS – turns ON when gate voltage is logic 0, OFF when logic 1
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 7
CMOS Inverter
N Well VDD
VDD PMOS 2l
Contacts
PMOS
In Out
In Out
Metal 1
Polysilicon
NMOS
NMOS
GND
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 8
CMOS Inverter – Simplified Operation
V DD V DD
Vin = 0 V out V out
Vin = 1
Vin = 0, Vout = 1 Vin = 1, Vout = 0
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 9
CMOS Inverter - Operation
Vdd = power supply (~1.5V)
V DD V DD
Rp
V out V out
Vin = 0 Vin = 1 R n
Vin = 0, Vout = 1 Vin = 1, Vout = 0
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 10
CMOS NAND and NOR Gates
A
A
B
A B
Vout
A
Vout
B
A A B
NAND2 NOR2
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 11
Integrated Circuits
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 12
CMOS Process
CMOS = Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor
Fabrication technology, structure
Logic operation
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 13
Advanced Metallization
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 14
Advanced Metallization
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 15
CMOS Inverter Layout
GND In VD D
A A’
Out
(a) Layout
A A’
n
p-substrate Field
+ + Oxide
n p
(b) Cross-Section along A-A’
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 16
Perspectives
FinFET MOS transistor
ECE 221 - Fall 2016 17
You might also like
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Lec 7,8 Modern CMOS TechnologyDocument43 pagesLec 7,8 Modern CMOS TechnologyVikram MeenaNo ratings yet
- Digital Integrated Circuit (IC) Layout and DesignDocument23 pagesDigital Integrated Circuit (IC) Layout and DesignPoornima RajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Modern CMOS Technology - IDocument20 pagesChapter 2 Modern CMOS Technology - Ifadwa badiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Modern CMO PDFDocument20 pagesChapter 2 Modern CMO PDFheNo ratings yet
- Cmos Technology: Classification of Silicon TechnologyDocument10 pagesCmos Technology: Classification of Silicon TechnologyfirsamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: IC Fabrication: CMOS ProcessDocument42 pagesUnit 1: IC Fabrication: CMOS Processbadrinarayan2210298No ratings yet
- VLSI UNIT 1 Part - III PDFDocument35 pagesVLSI UNIT 1 Part - III PDFKARTHIKAYEN ANo ratings yet
- Chapter - 09 - CMOS DesignDocument41 pagesChapter - 09 - CMOS DesignAlex XanderNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of VLSI SystemsDocument34 pagesDesign and Implementation of VLSI SystemsLê Bá Phước LongNo ratings yet
- 3-CMOS Fab ProcessDocument5 pages3-CMOS Fab ProcessMarcus Jonathan SinsayNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design: Dept. of CSE Bangladesh UniversityDocument15 pagesVLSI Design: Dept. of CSE Bangladesh UniversityRasd sdaNo ratings yet
- Imel7002 L2Document106 pagesImel7002 L2就爱吃饭团No ratings yet
- MEL ZG621 VLSI DESIGN (Lect 2)Document40 pagesMEL ZG621 VLSI DESIGN (Lect 2)2023ht80200No ratings yet
- Lecture-13: Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)Document8 pagesLecture-13: Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)AKSHATHAVENKATESHNo ratings yet
- VLSI Unit 2 Technology - SDocument52 pagesVLSI Unit 2 Technology - SIndrajeet GautamNo ratings yet
- Transistors: Current (BJT) Voltage (FET)Document7 pagesTransistors: Current (BJT) Voltage (FET)Qin LingNo ratings yet
- Chap 9Document12 pagesChap 9GagneNo ratings yet
- Chip FabricationDocument34 pagesChip Fabricationrajatbarik_kiitNo ratings yet
- Chap02 (12 18 06) PDFDocument79 pagesChap02 (12 18 06) PDFHassan FarssiNo ratings yet
- Lec 03-04Document37 pagesLec 03-04Basem HeshamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document37 pagesChapter 2gopismiles1987No ratings yet
- Introduction To: Micro ElectronicsDocument25 pagesIntroduction To: Micro Electronicskuttan1113No ratings yet
- 1.VLSI IntroductionDocument41 pages1.VLSI Introductionductaingo0123No ratings yet
- Lecture 42Document18 pagesLecture 42Nathan KemboNo ratings yet
- Module 4 CMOS LogicDocument18 pagesModule 4 CMOS LogicJessie Tess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- VLSI Lec 01Document66 pagesVLSI Lec 01Maheen GulNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Integrated An Introduction To Integrated Circuits and CMOS TechnologyDocument34 pagesAn Introduction To Integrated An Introduction To Integrated Circuits and CMOS Technologymm16467No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 VLSI TechnologyDocument27 pagesLecture 3 VLSI TechnologyJ.V.'S CLASSNo ratings yet
- Lecture07 140310Document31 pagesLecture07 140310Ramya SNo ratings yet
- Dic Lec 02 Fabrication v01Document68 pagesDic Lec 02 Fabrication v01fatmaadelmoNo ratings yet
- Chapter III. MOS Transistor: .................. ..Slides 2-62Document79 pagesChapter III. MOS Transistor: .................. ..Slides 2-62Jorge RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Semiconductor Devices-Lecture39Document19 pagesPrinciples of Semiconductor Devices-Lecture39LIAKMANNo ratings yet
- Layout Lec 01 Fab v01Document53 pagesLayout Lec 01 Fab v01Ahmed MetwalyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Overview & Introduction of MOS Transistors Digital Systems, EE-208Document25 pagesLecture 1: Overview & Introduction of MOS Transistors Digital Systems, EE-208Kartikeya SinghNo ratings yet
- Ian Appelbaum: Electrical and Computer Engineering University of DelawareDocument39 pagesIan Appelbaum: Electrical and Computer Engineering University of DelawareLIAKMANNo ratings yet
- IC ManufacturingDocument54 pagesIC ManufacturingRajesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Source and Drain (S/D) Structure: WR R RDocument7 pagesSource and Drain (S/D) Structure: WR R RmabhatNo ratings yet
- New NotesDocument7 pagesNew NotesmabhatNo ratings yet
- Dasar Design CMOS TransistorDocument49 pagesDasar Design CMOS Transistormaqbulloh darojatiNo ratings yet
- C Cmos Basics - Ani PDFDocument17 pagesC Cmos Basics - Ani PDFAnindra NallapatiNo ratings yet
- VLSI System Design ECE3002 Winter 2018-19Document19 pagesVLSI System Design ECE3002 Winter 2018-19PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473No ratings yet
- UNIT - 1 INTRD To MOSDocument24 pagesUNIT - 1 INTRD To MOSgnitsiceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cmos Vlsi Design: Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic DesignDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Cmos Vlsi Design: Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Designavneet sandhuuuNo ratings yet
- DWF13 Amf Ent T0194 PDFDocument132 pagesDWF13 Amf Ent T0194 PDFsumitzz4737No ratings yet
- Brief Nwell CmosDocument26 pagesBrief Nwell Cmoswhosane_007No ratings yet
- Electronica-Virtual Automotive ToshibaDocument37 pagesElectronica-Virtual Automotive ToshibaJeremy ChiangNo ratings yet
- Ee6471 wk5Document56 pagesEe6471 wk5Murthy MvsNo ratings yet
- Our Labs BriefDocument7 pagesOur Labs BriefnemokoNo ratings yet
- W5 先進元件模組3newDocument40 pagesW5 先進元件模組3newcharlietu86No ratings yet
- Lecture2 - Si CMOS BasicsDocument36 pagesLecture2 - Si CMOS Basicseshwar_worldNo ratings yet
- Short-Channel Effect Immunity (CMOS Technology Boosters)Document33 pagesShort-Channel Effect Immunity (CMOS Technology Boosters)arjun raghavan.vNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of CMOS Integrated CircuitsDocument56 pagesFabrication of CMOS Integrated CircuitsVinay GoddemmeNo ratings yet
- CMOS and VLSI Design: Praveen MeduriDocument34 pagesCMOS and VLSI Design: Praveen MeduriPraveen MeduriNo ratings yet
- Bec010 Vlsi - NotesDocument109 pagesBec010 Vlsi - NotesFarukh ZafarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VLSI Fabrication Technologies: Emanuele BaravelliDocument38 pagesIntroduction To VLSI Fabrication Technologies: Emanuele BaravelliNelarapuMaheshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Modern CMO - 2Document27 pagesChapter 2 Modern CMO - 2heNo ratings yet
- FabricationDocument39 pagesFabricationfayazNo ratings yet
- Si PD Circuit eDocument4 pagesSi PD Circuit eMichael MitchellNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Upto 3unitDocument105 pagesVlsi Upto 3unitAsha PagidipalliNo ratings yet
- Session Plan High PressingDocument7 pagesSession Plan High Pressinghadi syahmiNo ratings yet
- Psych Assessment 1Document13 pagesPsych Assessment 1Ronald Jacob PicorroNo ratings yet
- Ultrafiltration Skid: Operating ParametersDocument2 pagesUltrafiltration Skid: Operating ParameterssaptaNo ratings yet
- Japan and IndiaDocument2 pagesJapan and IndiaLimeylen IsNoobNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Rheological Basics For Modeling of Extrusion Process of Wood Polymer CompositesDocument16 pagesPolymers: Rheological Basics For Modeling of Extrusion Process of Wood Polymer CompositesMuhammad IlyasNo ratings yet
- Harald Jers. The Impact of Location On The Singing Voice.Document16 pagesHarald Jers. The Impact of Location On The Singing Voice.Юрий СемёновNo ratings yet
- 32-4-3 Social ScienceDocument11 pages32-4-3 Social ScienceshreyasNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument57 pagesMorphologyMervat ElgindyNo ratings yet
- The Creative Edge - Discover - D - Matthew AshimolowoDocument141 pagesThe Creative Edge - Discover - D - Matthew AshimolowoJulien Khalil100% (1)
- RT GEN 16 002 - MR - ReddyDocument31 pagesRT GEN 16 002 - MR - Reddynishant singhNo ratings yet
- 2581 DBDDF 575Document9 pages2581 DBDDF 575fatimaNo ratings yet
- 2023 GPT4All Technical ReportDocument3 pages2023 GPT4All Technical ReportLeonel rugamaNo ratings yet
- Fault Code 471 Engine Oil Level - Data Valid But Below Normal Operational Range - Least Severe LevelDocument4 pagesFault Code 471 Engine Oil Level - Data Valid But Below Normal Operational Range - Least Severe LevelAhmedmahNo ratings yet
- 13 DPWH: Central OfficeDocument1 page13 DPWH: Central OfficeJohn Wilmiths TubbanNo ratings yet
- C1557 Tension y Modulo Compuestos FibraDocument10 pagesC1557 Tension y Modulo Compuestos FibraSandra LocarnoNo ratings yet
- Air Washer Test RigDocument2 pagesAir Washer Test Rigtinkusk24No ratings yet
- FSW M 1x2 Mini Optical Switch Data Sheet 520401Document5 pagesFSW M 1x2 Mini Optical Switch Data Sheet 520401GLsun MallNo ratings yet
- MTTRDocument3 pagesMTTRbkmineroNo ratings yet
- Reading B1 - Matching Worksheet 3 Passage 1Document8 pagesReading B1 - Matching Worksheet 3 Passage 1Dung NgọcNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Registration of VaccineDocument60 pagesGuideline For Registration of VaccineMatiyas ZewdeNo ratings yet
- Mastering The Art of ApproachingDocument2 pagesMastering The Art of ApproachingElvin MitraNo ratings yet
- Languagecert Expert C1 Level 2 International Esol (Speaking) Practice Paper 3Document7 pagesLanguagecert Expert C1 Level 2 International Esol (Speaking) Practice Paper 3maria muela bravoNo ratings yet
- Assignments No. 678Document22 pagesAssignments No. 678Christine Yvette UyNo ratings yet
- First Quarter ENGLISH (Week 6)Document9 pagesFirst Quarter ENGLISH (Week 6)Evan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- Microstructure and Enhanced Dielectric Properties of Yttrium AndzirconiumDocument5 pagesMicrostructure and Enhanced Dielectric Properties of Yttrium AndzirconiumrechemNo ratings yet
- 442 1262 1 SPDocument7 pages442 1262 1 SPAbdul MuchlisNo ratings yet
- BS144 Coal Tar Creosote For Wood PreservationDocument26 pagesBS144 Coal Tar Creosote For Wood PreservationKelvinNo ratings yet
- Importance of Sustainable Development GoalsDocument2 pagesImportance of Sustainable Development GoalsDyas FerNo ratings yet
- Lilha Education Centre BST RevisionDocument39 pagesLilha Education Centre BST RevisionAlan walkerNo ratings yet
- Pipe ViseDocument12 pagesPipe ViseShaik SultanNo ratings yet