Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and Economics
Summary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and Economics
Uploaded by
Jean-Christ AdaïOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and Economics
Summary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and Economics
Uploaded by
Jean-Christ AdaïCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction to Accounting
and Economics
Topic 1: Introduction
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Summary of Lecture
The structure of the rest of this Topic is as follows:
• Words you must know
• An outline of the business environment
• What does an economist do?
• What does an accountant do?
• The structure of the course
• How you will be assessed
• Effective study skills
• Review of the topic
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 1
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Introduction
Welcome to the Accounting and Economics course,
the purpose of this topic is to introduce you to the
course. This lecture will cover:
- An outline of the business environment
- Differences between approaches adopted by economists
and accountants and the kind of problems they deal with
- The structure and content of the module and how you will
be assessed
- Suggestions for organising your study time to the
maximum effect.
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Words You Must Know
Economics: the study of how society decides when,
what and how to produce (Begg, 2009, p.2)
• Microeconomics – study of markets
• Macroeconomics – study of the economy as a whole
Accounting: the classification, recording and
interpretation of monetary transactions and other data
• Financial accounting – monetary transactions, for internal
and external use
• Management accounting – monetary transactions and other
data in support of management control and decision-making
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 2
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
An Outline of the Business
Environment
• This module is about individuals and businesses
that operate in a modern free market economy
• This implies an environment where there is an
efficient legal system that can be used to resolve
disputes and protect individuals and firms from
unlawful behaviour
• In this environment, businesses are free to make
and enforce contracts, subject to the norms of the
society
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
An Outline of the Business
Environment
What exactly do we mean by business? The
basic forms of business unit are as follows:
A Sole Trader:
• Simplest form of business unit
• An individual trading by him or herself
• Very few rules involved in setting up this kind of
business
• Tend to run very small businesses
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 3
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
An Outline of the Business
Environment
A Partnership:
• More complex business unit where two or
more individuals work together
• Partnership agreement
• Can be much bigger than a sole trader
• Often used by professionals such as
lawyers, accountants and doctors
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
An Outline of the Business
Environment
A Limited Company:
• Most complex form of business unit
• Legal entity distinct from the individuals
(shareholders) who own it
• A private limited company may be relatively small,
but a public limited company can be very large and
can raise money by selling shares to the public
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 4
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
An Outline of the Business
Environment
What is a large business?
• Difficult to precisely define the size of a
business
• Factors to consider:
- The annual sales of the business
- The number of people employed by the
business
- The value of the assets owned by the business
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
What does an Economist do?
• They study economics
• Economists deliberately simplify reality
• They use models of the real world that
focus on the essentials but leave out some
of the confusing detail
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 5
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
What does an Economist do?
• For example, an economist may want to study the market for
public transport e.g. a city’s bus network
• The economist chooses to look at one aspect of the bus
network – the relationship between the price of individual
tickets and the total revenue of the bus company
• May estimate an average price for tickets or to assume a
standard flat rate fare
• The economist goes out and collects some data and then
presents an analysis of the results
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
What does an Economist do?
• The analysis could look like this:
Bus Fare and Total Revenue of the Bus Company
Total
Revenue
Ticket Price
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 6
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
What does an Economist do?
• No numbers on either of the axes of the
graph, the economist is looking at causal
relationships without necessarily seeking to
quantify them
• The economist is looking at the essential
point that is that total revenue increases as
the price of tickets rises
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
What does an Economist do?
• The economist has just established a
relationship between two variables
• Other factors can then be brought into the
analysis, for example, changes in the
income of the bus passengers or the effects
of traffic congestion
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 7
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
What does an Accountant do?
• An accountant would look at the bus company in
an entirely different way
• Accountants prefer numbers to graphs – much
more detailed view
• For the bus company, a specified period would be
chosen – e.g. month of May of a specified year
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
What does an Accountant do?
• Measures revenue for the month of May
and then matches this to costs for May
• Works out if the bus company made a profit
during May
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 8
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
The Structure of the Course
• The course or module is divided into 12 topics,
each comprising three activities. There will be:
- A lecture session designed to give you an outline of the
topic area (2 hours per topic)
- A private study session where you will be required to
complete activities on your own (4 hours per topic)
- A tutorial session where you can complete activities
supervised by your teacher, get feedback on your
personal work, and ask questions (2.5 hours per topic)
• The following chart gives an outline of the course
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
topic / Topic Subject Coverage
1. Introduction Economists and accountants, effective study skills
2. Supply & demand Supply, demand, elasticity
3. Market structures Perfect competition, imperfect competition
4. National income and output National income & output, growth, the business cycle, aggregate
demand, fiscal policy
5. Money Interest rates, inflation, monetary policy
6. The international dimension Global economy, exchange rates, balance of payments
7. Intro to accounting Transactions, accounting conventions, financial statements
8. Bookkeeping Basic requirements, double entry, trial balance
9. period-end adjustments Accruals & prepayments, inventories, depreciation, bad & doubtful
debts
10. Preparing financial From trial balance, income statement, balance sheet
statements
11. Interpreting financial Vertical, horizontal & ratio analysis
statements
12. Revision & review Economics, accounting, exam preparation
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 9
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
How You Will Be Assessed
• The purpose of assessment is to find out how much you have
learned
• The primary assessment is via a 2 hour examination
• Lecturers will assess your progress throughout the module in
order to provide further help as required
• If you work through this course properly and complete the
tasks given to you by your teacher, you will pass the course
• However, It is just as important that you concentrate on
learning something from the course, rather than just seeking
to pass an exam
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Effective Study Skills
• Organise yourself:
- Academic study is work and the most successful workers are
the most organised
- Productivity
- Prepare a study timetable for each week
- Your schedule should help you plan your commitments and
make sure you avoid working very hard at the last minute to
meet deadlines
- You should aim to work consistently during your time on the
course
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 10
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Effective Study Skills
• Set up a filing system:
- You have to take notes of lecture sessions and
of the books and articles that you read
- File these in a coherent way
- Use your notes to revise and deepen your
understanding
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Effective Study Skills
• Assessments/Private Study:
- Make sure you understand what is required of you
- Listen carefully to your teacher and read assessment
requirements/private study exercises carefully
- Do what you are asked to do and attempt to do everything
you are asked to do. Hand in work at the correct time
- Don’t try and negotiate with your teacher and don’t try
and make excuses!
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 11
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Effective Study Skills
• Examinations:
- Be well prepared
- Revise the main topic areas thoroughly
- Attempt practice papers: exam structure and
question type
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Effective Study Skills
- Highlight or underline key words in the questions and make sure
you cover these points in your answer
- Do the easiest questions first
- Clearly indicate which question or part of a question you are
answering
- Try and make your answer as easy to read as possible
- Use plenty of space on the paper. Take a new page for each
answer
- Write as neatly as possible
- Use your time wisely!
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 12
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Review of the topic
An outline of the main ideas that have been
covered during this module
• A list of words you should know
• A brief explanation of business topics
• An explanation of the different approaches adopted
by accountants and economists
• Advice about organising your study time in order to
maximise your chances for success on the course
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Questions for Students
1. What are you looking for from this
module?
2. Does this first topic suggest the
module will meet your requirements?
DISCUSS!
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 13
Topic 1 - Introduction Introduction to Accounting and Economics
Introduction Topic 1 - 1.‹#›
Topic 1
Any questions?
V2.0 © NCC Education Limited
V2.0 Visuals Handout – Page 14
You might also like
- Reservation Agreement FormDocument4 pagesReservation Agreement Formako si Elmoh75% (4)
- The Principles and Processes of Interactive Design PDFDocument209 pagesThe Principles and Processes of Interactive Design PDFArtur Renato Ortega100% (12)
- Tower Crane Market and OpportunitiesDocument65 pagesTower Crane Market and OpportunitiesSrini Parthasarathy100% (1)
- Modern Advanced Accounting in Canada Chapter 10 Solution ManualDocument54 pagesModern Advanced Accounting in Canada Chapter 10 Solution ManualJay-P100% (1)
- TAX320 Candidate Study GuideDocument585 pagesTAX320 Candidate Study GuideHafiz MusannefNo ratings yet
- OSD Topic 1Document33 pagesOSD Topic 1Kay TunNo ratings yet
- Cold Email Mastery Course - From Cold To Gold 2019Document116 pagesCold Email Mastery Course - From Cold To Gold 2019Andrei GrozaNo ratings yet
- PBO - Lecture 01 - Introduction To Business OperationsDocument10 pagesPBO - Lecture 01 - Introduction To Business OperationsDavid IyodoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting and Economics: © NCC Education Limited V1.0Document26 pagesIntroduction To Accounting and Economics: © NCC Education Limited V1.0Usman JavedNo ratings yet
- IAE Handout 7Document17 pagesIAE Handout 7Tran LouisNo ratings yet
- CP Topic 1Document15 pagesCP Topic 1Duha AbdullaNo ratings yet
- MBA4807 Module Overview 2024 FinalDocument20 pagesMBA4807 Module Overview 2024 FinalKatlego MonyaeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting and Economics: Topic 11: Analysis of Business PerformanceDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Accounting and Economics: Topic 11: Analysis of Business PerformanceUsman JavedNo ratings yet
- BITP Topic 1Document28 pagesBITP Topic 1Muhannad SultanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Lecture NotesAvneel KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.BEC 416 - E-BUSINESS STRATEGY LECTURE 1 - Ebusiness StrategyDocument27 pages1.BEC 416 - E-BUSINESS STRATEGY LECTURE 1 - Ebusiness StrategyLEM tvNo ratings yet
- TECH 4090 Class 1 PRSNTNDocument36 pagesTECH 4090 Class 1 PRSNTN沈悦双No ratings yet
- BITP Topic 2Document22 pagesBITP Topic 2Muhannad SultanNo ratings yet
- IAE Handout 11Document18 pagesIAE Handout 11Tran LouisNo ratings yet
- IAE Handout 8Document20 pagesIAE Handout 8Tran LouisNo ratings yet
- PBO - Lecture 06 - Goods and ServicesDocument11 pagesPBO - Lecture 06 - Goods and ServicesDavid IyodoNo ratings yet
- EoK MF Module 1Document32 pagesEoK MF Module 1khaled zayedNo ratings yet
- COBIT - Foundation V2.1 Support Presentation Du 1 Mai 2021Document136 pagesCOBIT - Foundation V2.1 Support Presentation Du 1 Mai 2021noahNo ratings yet
- MM2NM1 Course SynopsisDocument2 pagesMM2NM1 Course Synopsis刁逸达No ratings yet
- COBIT Foundation V1.1 (Master Slides)Document273 pagesCOBIT Foundation V1.1 (Master Slides)Fady Ealia100% (1)
- Principles of Marketing: Topic 2: Business and Marketing OrientationsDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: Topic 2: Business and Marketing OrientationsJean ChristNo ratings yet
- OSD Topic 1 PDFDocument8 pagesOSD Topic 1 PDFRoshan BcNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Template SY 2022-2023Document4 pagesSyllabus Template SY 2022-2023Angelo DefensorNo ratings yet
- Study Guide:: Financial Management Semester: Sept - Dec 2010Document9 pagesStudy Guide:: Financial Management Semester: Sept - Dec 2010Muhammad Nurakmal ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- INSTITUTE - University School of Business DEPARTMENT - Management M.B.ADocument14 pagesINSTITUTE - University School of Business DEPARTMENT - Management M.B.AAsrar ul haqNo ratings yet
- Poa Scheme of Work - September To December 2022 (Form 4)Document10 pagesPoa Scheme of Work - September To December 2022 (Form 4)pratibha jaggan martinNo ratings yet
- ch1 PDFDocument22 pagesch1 PDFTony MorganNo ratings yet
- Office Solutions Development: Topic 1: Application Software and Business ProcessesDocument24 pagesOffice Solutions Development: Topic 1: Application Software and Business ProcessesKi KiNo ratings yet
- SUSS - Developing The Business Case Workbook v3.1Document166 pagesSUSS - Developing The Business Case Workbook v3.1desmondNo ratings yet
- Web Results: Chapter 1 Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesWeb Results: Chapter 1 Introduction To Cost AccountingYassi CurtisNo ratings yet
- Form 1 4 Accounting Syllabus MinDocument35 pagesForm 1 4 Accounting Syllabus MinWayne nyax NyakuramwaNo ratings yet
- CF Teaching Note 01Document10 pagesCF Teaching Note 01Gabriel Afonso RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Peranggaran - Materi 2Document42 pagesPeranggaran - Materi 2citra kurniaNo ratings yet
- Computing Project: Topic 1Document45 pagesComputing Project: Topic 1Kay TunNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To Module - Accounting Concept - LectureDocument25 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To Module - Accounting Concept - Lecturehoang anhNo ratings yet
- Initial PagesDocument17 pagesInitial PagesAadityaNo ratings yet
- BCOM Syllabus Sem and 2Document28 pagesBCOM Syllabus Sem and 2anuprakash0812No ratings yet
- Syllabus BCOM 14102021Document15 pagesSyllabus BCOM 14102021Shreya MNo ratings yet
- Business Environment The Technology EnvironmentDocument33 pagesBusiness Environment The Technology EnvironmentAdruffNo ratings yet
- Aligning CMMI & ITIL: Where Am I and Which Way Do I Go?Document27 pagesAligning CMMI & ITIL: Where Am I and Which Way Do I Go?Wewe SlmNo ratings yet
- Kick Start Your Career in Investment Banking Programme With Job GuaranteeDocument21 pagesKick Start Your Career in Investment Banking Programme With Job Guaranteegaurav gargNo ratings yet
- Cbse Department of Skill Education Curriculum For Session 2021-2022Document11 pagesCbse Department of Skill Education Curriculum For Session 2021-2022Taniya SinghNo ratings yet
- Fnfe Iitd Brochure 1664463288773Document15 pagesFnfe Iitd Brochure 1664463288773Rutuja MahalleNo ratings yet
- Poa Scheme of Work - September To December 2020 (Form 4)Document8 pagesPoa Scheme of Work - September To December 2020 (Form 4)pratibha jaggan martinNo ratings yet
- ACCTG 208 Rev 2022 Acctg Govt Not For Profit OrgDocument8 pagesACCTG 208 Rev 2022 Acctg Govt Not For Profit OrgRoschelle MiguelNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Economics and Financial MarketsDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Economics and Financial MarketsluluNo ratings yet
- Post Graduate Certificate Program in Investment Banking in Collaboration With LGCADocument17 pagesPost Graduate Certificate Program in Investment Banking in Collaboration With LGCAsanket shikharNo ratings yet
- YE 2023 Awards: CSR Project Guidelines YE Audit Process Report Writing GuidelinesDocument71 pagesYE 2023 Awards: CSR Project Guidelines YE Audit Process Report Writing GuidelinesExtra AccountNo ratings yet
- Ems Study GuideDocument74 pagesEms Study GuideKesandra GovindasamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ADC605Document20 pagesChapter 1 ADC605jassmithaNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTANCY (Code No. 055) : RationaleDocument111 pagesACCOUNTANCY (Code No. 055) : RationalejodNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTANCY (Code No. 055) : RationaleDocument19 pagesACCOUNTANCY (Code No. 055) : RationaleGangeshNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTANCY (Code No. 055) : RationaleDocument18 pagesACCOUNTANCY (Code No. 055) : RationaleAryaman SinghalNo ratings yet
- Business Environment: The Types of EnvironmentDocument28 pagesBusiness Environment: The Types of EnvironmentAdruffNo ratings yet
- Me 1Document45 pagesMe 1Khushi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bba 1 SemmoduleDocument33 pagesBba 1 Semmoduleinf12309No ratings yet
- COBIT's Value For Small and Medium Enterprises: Greet VoldersDocument84 pagesCOBIT's Value For Small and Medium Enterprises: Greet VoldersHai Vo Nguyen DangNo ratings yet
- Course Title:: Financial Reporting and AnalysisDocument8 pagesCourse Title:: Financial Reporting and Analysisswaroop darojiNo ratings yet
- EoK MF M2Document41 pagesEoK MF M2khaled zayedNo ratings yet
- Summary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and EconomicsDocument25 pagesSummary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and EconomicsJean-Christ AdaïNo ratings yet
- Summary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and EconomicsDocument17 pagesSummary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and EconomicsJean-Christ AdaïNo ratings yet
- Summary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and EconomicsDocument20 pagesSummary of Lecture: Introduction To Accounting and EconomicsJean-Christ AdaïNo ratings yet
- Jean-Christ Adai - 00186013 - SCS - B PDFDocument3 pagesJean-Christ Adai - 00186013 - SCS - B PDFJean-Christ AdaïNo ratings yet
- Legal M7Document9 pagesLegal M7clarisse juanNo ratings yet
- Treasury BillsDocument3 pagesTreasury BillsvijaydhNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Human Resources ManagementDocument5 pagesLiterature Review Human Resources Managementauhavmpif100% (1)
- 2 H310520221049546353-GroupOfPDFS 1Document19 pages2 H310520221049546353-GroupOfPDFS 1SupalNo ratings yet
- Orlin PetkovDocument2 pagesOrlin PetkovOrlin PetkovNo ratings yet
- HF 3 - Maintenance RSDocument2 pagesHF 3 - Maintenance RSJohn MelvinNo ratings yet
- Cambridge CPP BrochureDocument2 pagesCambridge CPP BrochureAshutosh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Aak's Memorandum On Mitigating The Negative Impacts of Covid-19 On Kenya's Construction Industry PDFDocument7 pagesAak's Memorandum On Mitigating The Negative Impacts of Covid-19 On Kenya's Construction Industry PDFDanielNo ratings yet
- Organic Skin Care Products Business Plan by SlidesgoDocument60 pagesOrganic Skin Care Products Business Plan by SlidesgoSrinath NalluriNo ratings yet
- Con WorldDocument10 pagesCon WorldMaica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: "Miss Sumita Dutta Roy" "Debyani Saha" "Changes of Packaging"Document16 pagesAcknowledgement: "Miss Sumita Dutta Roy" "Debyani Saha" "Changes of Packaging"Ryan XinghaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 001/3/2021: Semester 1 and 2Document49 pagesTutorial Letter 001/3/2021: Semester 1 and 2Lerato MnguniNo ratings yet
- 50 Reasons Why Some Businesses Fail While Others SucceedDocument2 pages50 Reasons Why Some Businesses Fail While Others SucceedAlex EvanNo ratings yet
- GS What Lies Beneath PresentationDocument112 pagesGS What Lies Beneath PresentationBob MoncrieffNo ratings yet
- (ENTP Assignment3-HMT Watches Case Study) 30 March 2020Document4 pages(ENTP Assignment3-HMT Watches Case Study) 30 March 2020Manita DhandaNo ratings yet
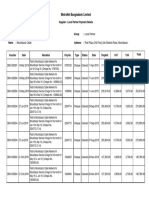
- Moulvibazar StatementDocument5 pagesMoulvibazar StatementTanisha IslamNo ratings yet
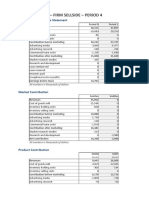
- Financial Report - Firm Sellside - Period 4: Company Profit & Loss StatementDocument73 pagesFinancial Report - Firm Sellside - Period 4: Company Profit & Loss StatementNancy suri100% (1)
- The Law Pertaining To Private Personal and Commercial RelationsDocument8 pagesThe Law Pertaining To Private Personal and Commercial RelationsBoenYatorNo ratings yet
- Pundro University of Science and TechnologyDocument4 pagesPundro University of Science and TechnologyTanvir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Oracle Finance BasicsDocument132 pagesOracle Finance BasicsRajeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic - Develop BCG Matrix On Unilever ProductsDocument15 pagesTopic - Develop BCG Matrix On Unilever Productsraj vardhan agarwalNo ratings yet
- 002016-2017 S2S TRAINING PROPOSAL SLAC On THE DEVT OF SCHOOL MRFDocument7 pages002016-2017 S2S TRAINING PROPOSAL SLAC On THE DEVT OF SCHOOL MRFBenjamin MartinezNo ratings yet
- Personal BondDocument1 pagePersonal BondFarisNo ratings yet
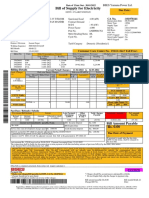
- Bill of Supply For Electricity: Due DateDocument1 pageBill of Supply For Electricity: Due DateSaurav BansalNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2 LOG2603 (Group) Session 2 2021 - 2022 (COMPLETED)Document3 pagesAssessment 2 LOG2603 (Group) Session 2 2021 - 2022 (COMPLETED)Muhammad Zarif IshakNo ratings yet