Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fail Safe Safe Life and Damage Tolerance
Fail Safe Safe Life and Damage Tolerance
Uploaded by
hemarajuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fail Safe Safe Life and Damage Tolerance
Fail Safe Safe Life and Damage Tolerance
Uploaded by
hemarajuCopyright:
Available Formats
FAIL-SAFE, SAFE-LIFE AND DAMAGE TOLERANCE
DESIGN PHYLOSOPHIES
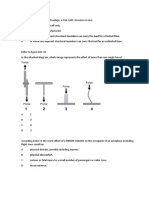
1- FAIL-SAFE
This type of design philosophy considers “the effects of failures and combinations of failures in
defining a safe design”1; this means that the principal idea of this philosophy is to see how a failure
or failures could cause a negative effect in the safety of the design. The fail-safe design concept
has two different meanings, one for structures and another one for the systems. Fail-Safe for a
structure refers to the residual strength after the sustaining of damage, while the Fail-Safe concept
for a system refers to the functional implications when a failure occurs and the possibilities that a
failure occurs.
The Fail-Safe for structures is governed by 14 CFR 25.571 and the methods of compliance are
outlined in the AC 25.571-1C. The Fail-Safe for systems is specified in the 14 CFR 25.1309 2.
2- SAFE-LIFE
This design philosophy refers to the period of operation of the component or system; it means
that the component or system is designed to not fail in a certain period of time, the desire with
this philosophy is to extend as long as possible the service life time of the component or system.
The design under this philosophy requires a testing and an analysis to estimate the service life
time of a component, but due to the inability of predict the specific service time of a component is
necessary to include a good safety factor to ensure that a catastrophic failure will not occur in any
case.
3- DAMAGE TOLERANCE
This design philosophy is focus in the fact that a very important component can resist a failure due
to some preexistent damage without risking the safe operation of the other components or
systems and until the damage can be repaired. This philosophy is focus in two points 3 with the
assumption that already exist a crack in the structure. The first point is the possibility to establish
the fracture load for a specific crack size. The second point is to predict the period of time for a
new crack to grow to the same size and can cause a fracture in the structure. At this point is very
important to implement a very good maintenance program that allows detecting all the damages
before they can reduce the strength of the structure before the acceptable limit.
1
From the web page: http://aviationglossary.com/aviation-safety-terms/fail-safe-design-concept/ ,
consulted the 9 of August at 9:00 pm.
2
From the web page: http://aviationglossary.com/aviation-safety-terms/fail-safe-design-concept/ ,
consulted the 9 of August at 9:00 pm
3
From the PDF document: DAMAGE TOLERANCE OF AERO STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS, TATA consultancy
services.
You might also like
- Composite Damage Tolerance and Maintenance Safety Issues - FAADocument33 pagesComposite Damage Tolerance and Maintenance Safety Issues - FAAAnonymous 1rLNlqUNo ratings yet
- 4281 - 03 Stiffened Shear WebDocument26 pages4281 - 03 Stiffened Shear WebAndrew GilbrideNo ratings yet
- 10.5 Certification of Aircraft, Parts and AppliancesDocument56 pages10.5 Certification of Aircraft, Parts and Appliancesmohan reddyNo ratings yet
- DTA Guidelines For Repairs and AlterationsDocument55 pagesDTA Guidelines For Repairs and Alterationsskullmac100% (1)
- Final Aircraft StructureDocument5 pagesFinal Aircraft StructureAmirul Haqim Mohd Jora100% (1)
- FAA and USAF Damage ToleranceDocument20 pagesFAA and USAF Damage ToleranceDenis LimNo ratings yet
- Airframes Revision NotesDocument16 pagesAirframes Revision NotesAntonio Valente50% (2)
- Aircraft Reliability and Maintenance Cost NadeemDocument4 pagesAircraft Reliability and Maintenance Cost NadeemSyedNadeemAhmed100% (1)
- Aircraft Design EmpennageDocument56 pagesAircraft Design EmpennageTeklemichael GhirmayNo ratings yet
- Damage ToleranceDocument59 pagesDamage Tolerancetv009334100% (8)
- Aircraft Dynamic and Static Loads Design CriteriaDocument98 pagesAircraft Dynamic and Static Loads Design CriteriaJawad KhawarNo ratings yet
- A Comparison Between Safe Life Damage Tolerance AnDocument13 pagesA Comparison Between Safe Life Damage Tolerance AnIqbal MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design ProjectDocument37 pagesAircraft Design ProjectAdrian ArasuNo ratings yet
- Aero 2017 CatalogDocument68 pagesAero 2017 CatalogFatih AkgülNo ratings yet
- Aircraft & Engine Maintenance Part 1-Day 1Document49 pagesAircraft & Engine Maintenance Part 1-Day 1AnthonyNColucciNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Maintenance Repair by Ralph D Bent James L Mckinley 0070048126Document5 pagesAircraft Maintenance Repair by Ralph D Bent James L Mckinley 0070048126m sai ravi tejaNo ratings yet
- Mass & Balance Exam 2Document16 pagesMass & Balance Exam 2momanbhNo ratings yet
- Hittite Vocabulary BookDocument272 pagesHittite Vocabulary BookCodyBeatonNo ratings yet
- Section3 Flight TestDocument30 pagesSection3 Flight TestOmri AmayaNo ratings yet
- Project Landing Gear - ReportDocument81 pagesProject Landing Gear - ReportAbdul Hafiz100% (2)
- AWHWAES Basic Instruments BookDocument210 pagesAWHWAES Basic Instruments Bookmolengene882100% (2)
- Airframe and Aircraft Components PDFDocument168 pagesAirframe and Aircraft Components PDFPravin HandeNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Flutter BannerDocument11 pagesAerodynamic Flutter BannerRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Flight Control by Pallet PDFDocument332 pagesAutomatic Flight Control by Pallet PDFAlexánder JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Prathama Solarconnect Energy Private Limited: Short Circuit Study ReportDocument18 pagesPrathama Solarconnect Energy Private Limited: Short Circuit Study Reportramesh cuppuNo ratings yet
- Module 11A.1.1 L2 2016-08-12Document136 pagesModule 11A.1.1 L2 2016-08-12Abdul Aziz Khan100% (1)
- Sharp Crested WeirDocument7 pagesSharp Crested WeirAizuddinNo ratings yet
- Tu Delft Aircraft Performance Syllabus Dec 2016Document9 pagesTu Delft Aircraft Performance Syllabus Dec 2016chhetribharat08No ratings yet
- CAIP Vol II PropellersDocument32 pagesCAIP Vol II PropellersSHM 555No ratings yet
- Propeller 2Document194 pagesPropeller 2Umar Ubaidullah100% (2)
- Nastran DST Group TN 1700Document69 pagesNastran DST Group TN 1700Minh LeNo ratings yet
- Fastener FlexibilityDocument3 pagesFastener FlexibilitySonell ShroffNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Strucutural Integrity 2016Document20 pagesAircraft Strucutural Integrity 2016lynx437100% (1)
- Fatigue and Damage Tolerance Analysis of Aircraft Structural Components - 0517Document15 pagesFatigue and Damage Tolerance Analysis of Aircraft Structural Components - 0517DP SinghNo ratings yet
- FAA AMT Powerplant Vol 1Document337 pagesFAA AMT Powerplant Vol 1Abdul rahman bin Ahmad YusoffNo ratings yet
- Understanding Aircraft Structures (PDFDrive)Document224 pagesUnderstanding Aircraft Structures (PDFDrive)Dayananda100% (1)
- Fault Tree Analyses As A Tool For Flight Control System Architezture DesignDocument6 pagesFault Tree Analyses As A Tool For Flight Control System Architezture DesignMustafa AkınNo ratings yet
- Unmanned Aircraft SystemsFrom EverandUnmanned Aircraft SystemsElla AtkinsNo ratings yet
- Continued Airworthiness of Composite Repairs To Primary Structures For Military AircraftDocument10 pagesContinued Airworthiness of Composite Repairs To Primary Structures For Military AircraftLuis Javier SantillanNo ratings yet
- Revised BOIS FORM Revised 2022Document1 pageRevised BOIS FORM Revised 2022Paul Bryan Aquino91% (11)
- FAA Safety PresentationsDocument208 pagesFAA Safety Presentationsf_mashayekhiNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Systems and InstrumentsDocument132 pagesAircraft Systems and InstrumentsJoao Russi100% (1)
- Aircraft Maintenance Management: Course by Nur Rachmat, Dipl. IngDocument30 pagesAircraft Maintenance Management: Course by Nur Rachmat, Dipl. IngAditya PramuditaNo ratings yet
- Reliability Program GuidlinesDocument8 pagesReliability Program GuidlinesAayush BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- 2018 Book InitialAirworthinessDocument434 pages2018 Book InitialAirworthinessTAN WEI HAN0% (1)
- Lesson 3 FAIL SAFE, DAMAGE TOLERANCEDocument2 pagesLesson 3 FAIL SAFE, DAMAGE TOLERANCEjeevan basnyatNo ratings yet
- CH 06 - Aircraft SystemsDocument40 pagesCH 06 - Aircraft SystemsFahmi Prayogi100% (1)
- M3u@watchtv - Best 453Document6 pagesM3u@watchtv - Best 453alexandreavila2015No ratings yet
- Weight Control of AircraftDocument50 pagesWeight Control of AircraftSteve MahoneyNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of LED Bulbs FactoryDocument2 pagesFeasibility Study of LED Bulbs FactoryAmjad AtiqueNo ratings yet
- Gte QuestionsDocument46 pagesGte QuestionsMatt SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Gama 13 Monument Certification and Structural SubstantiationDocument64 pagesGama 13 Monument Certification and Structural SubstantiationЖаркоСмиљанићNo ratings yet
- Summary of Semimonocoque and Monocoque DesignDocument5 pagesSummary of Semimonocoque and Monocoque Designperkasagagah42100% (2)
- Flight MechanicsDocument536 pagesFlight MechanicsArpit Dodia100% (2)
- Airframe and Systems, ElectricsDocument430 pagesAirframe and Systems, ElectricsdkskmuiaeemkgftsmrNo ratings yet
- Principles of Helicopter Flight by W J Wagtendonk 5 Star ReviewDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Helicopter Flight by W J Wagtendonk 5 Star Reviewdark_horse99990% (1)
- Airframe Electrical FAA QuestionsDocument5 pagesAirframe Electrical FAA QuestionsJAYACHANDRANNo ratings yet
- Faa Ac29-2cDocument1,258 pagesFaa Ac29-2crobbertmdNo ratings yet
- Jinas Resume For AmeDocument2 pagesJinas Resume For AmeVipul ShindeNo ratings yet
- Caip Part IDocument728 pagesCaip Part IEncik FekryNo ratings yet
- Steady Aircraft Flight and PerformanceFrom EverandSteady Aircraft Flight and PerformanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Current Aeronautical Fatigue Problems: Proceedings of a Symposium Held in Rome, 23–25 April 1963From EverandCurrent Aeronautical Fatigue Problems: Proceedings of a Symposium Held in Rome, 23–25 April 1963No ratings yet
- Fail-Safe Designs 1Document4 pagesFail-Safe Designs 1Karthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- 2018380186MDBILASHMEHEDIfatigue Life ModelDocument14 pages2018380186MDBILASHMEHEDIfatigue Life Modelbilash mehediNo ratings yet
- Annexure-C Drawings PDFDocument6 pagesAnnexure-C Drawings PDFManish PandeyNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting To Soil FormationDocument17 pagesFactors Affecting To Soil FormationMary Rose Bobis VicenteNo ratings yet
- One Way ANOVA Using SPSSDocument23 pagesOne Way ANOVA Using SPSSAngela SantosNo ratings yet
- PROJECT REPORT Personal Selling PDFDocument19 pagesPROJECT REPORT Personal Selling PDFHimaja GharaiNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Frequency DistributionDocument11 pages4.3 Frequency DistributionCedric Dela CostaNo ratings yet
- Canvas Garments Pvt. Ltd. - Accord T&C VI Report PDFDocument10 pagesCanvas Garments Pvt. Ltd. - Accord T&C VI Report PDFz018125No ratings yet
- De Thi Hoc Ki 2 Tieng Anh 7 Global Success de So 2 1679998444Document3 pagesDe Thi Hoc Ki 2 Tieng Anh 7 Global Success de So 2 1679998444Phan TrangNo ratings yet
- PCART PART 18 Transportation-of-Dangerous-Goods-by-AirDocument36 pagesPCART PART 18 Transportation-of-Dangerous-Goods-by-AirRyan W MasonNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument9 pagesExampleJamesNo ratings yet
- Induction MatrixDocument47 pagesInduction MatrixSanjana KalanniNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rates 8Document1 pageAnalysis of Rates 8Aman ThakurNo ratings yet
- RX 1839 PDFDocument3 pagesRX 1839 PDFРоман Сойнов100% (1)
- Trigonometri: Jadi, π radian = 180° Jadi, 1° = 0,02 radian Jadi, 1° radian = 57,296° atau 57,3°Document8 pagesTrigonometri: Jadi, π radian = 180° Jadi, 1° = 0,02 radian Jadi, 1° radian = 57,296° atau 57,3°dhikaNo ratings yet
- Altercasting Theory Long ExplainationDocument12 pagesAltercasting Theory Long ExplainationDorepe IconNo ratings yet
- (Doi 10.1016 - b978-012374473-9.00026-6) Houde, E.D. - Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences - Fish LarvaeDocument11 pages(Doi 10.1016 - b978-012374473-9.00026-6) Houde, E.D. - Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences - Fish LarvaeAnkeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Front Page and AppendicesDocument16 pagesFront Page and AppendicesHandsome DevilNo ratings yet
- Second Order Differential Equations - Dynamics - 2020Document13 pagesSecond Order Differential Equations - Dynamics - 2020rory mcelhinneyNo ratings yet
- Tmpa 8859 Service Manual: ContentDocument14 pagesTmpa 8859 Service Manual: ContentNeto Garcia100% (1)
- Theory European Journal of SocialDocument19 pagesTheory European Journal of SocialChristian HdezNo ratings yet
- 02 - G29 Powertrain-ChassisDocument62 pages02 - G29 Powertrain-ChassisNguyễn Hoàng LongNo ratings yet
- Manual de Usuario de Banco de Baterías de LitioDocument99 pagesManual de Usuario de Banco de Baterías de Litiojose luisNo ratings yet
- A CNN-Based Fusion Method For Super-Resolution of Sentinel-2 DataDocument5 pagesA CNN-Based Fusion Method For Super-Resolution of Sentinel-2 DataOne piece videoNo ratings yet
- Romantic Love EssayDocument6 pagesRomantic Love Essayb72hvt2d100% (2)
- The Compound Light MicroscopeDocument2 pagesThe Compound Light MicroscopeIsabela MartinezNo ratings yet