Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Latest Trends and Issues in Biology
Uploaded by
Love Grace Agus DavinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Latest Trends and Issues in Biology
Uploaded by
Love Grace Agus DavinCopyright:
Available Formats
MSEGS 210 - Advanced Topics in Biological Science
Latest Trends And Issues In Biology
Threats From Viruses
o Coronaviruses
What are VIRUSES?
A virus is a small parasite that cannot reproduce by itself. Once it infects a susceptible cell, however,
a virus can direct the cell machinery to produce more viruses. Most viruses have either RNA or DNA
as their genetic material.
What makes Virus infectious?
The entire infectious virus particle, called a virion, consists of the nucleic acid and an outer shell of
protein. The simplest viruses contain only enough RNA or DNA to encode four proteins. The most
complex can encode 100 – 200 proteins.
The nucleic acid of a virion is enclosed within a protein coat, or capsid, composed of multiple copies
of one protein or a few different proteins, each of which is encoded by a single viral gene. Because of
this structure, a virus is able to encode all the information for making a relatively large capsid in a
small number of genes.
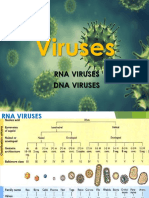
What is RNA VIRUS?
RNA Virus is a virus that has RNA (ribonucleic acid) as its genetic material. This nucleic acid is usually
single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but may be double stranded RNA (dsRNA).
What are CORONA VIRUSES (CoV)?
Coronaviruses are large family of viruses that cause illness ranging from the common cold to more
severe diseases such as MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV. (World Health Organization)
Coronaviruses are zoonotic. ( transmitted from animals to human)
Coronaviruses are enveloped, single stranded RNA viruses, which means that their genome consists
of a strand of RNA (rather than DNA) and that each viral particle is wrapped in a protein “envelope.”
Coronaviruses have the longest genomes of any RNA virus--- consisting of 30,000 letters or bases.
Mutation rates of RNA viruses are greater than DNA viruses, suggesting a more efficient adaptation
process for survival. The genome codes for at least four main structural proteins:
spike (S), membrane (M), envelope (E), nucleocapsid (N) proteins
and other accessory proteins which aid the replicative processes and facilitate entry into cells
CoVs mainly affect birds and mammals. Prior to 2019, there were only six CoVs that can infect human and
cause respiratory diseases: HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HKU1, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV. The last 2
are capable of causing severe respiratory syndrome in humans.
How the coronavirus infects?
Once inside the cytoplasm, the endosome opens to reveal the virus’ genetic material, a single stranded
RNA.
The virus hijacks the cells machinery to replicate the RNA and N proteins and uses the endoplasmic
reticulum to form its M protein outer layer, and the all important S protein.
After replication , the virus is carried by the golgi bodies out of the cell in a process known as exocytosis,
so that it can infect other cells.
The Wuhan Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV)
On the 31st of December 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) was alerted by Chinese authorities of a
series of pneumonia-like cases in the city of Wuhan, a city with the size of London with about 11 million people. It
was quickly identified that the first human infections likely originated from Huanan Seafood Market in Wuhan.
Two weeks later, a group of Chinese scientists, along with WHO announced that a new coronavirus (2019-
nCoV), identified through genomic sequencing, was the culprit of the pneumonia. Symptoms of infection included
fever, malaise, dry cough, shortness of breath and respiratory distress.
https://www.nature.com/articles/
Researchers have 2 main theories about the evolution of virus if the NCoV is a result of Natural
Evolution:
1. Evolved through natural selection in animals then jumped to humans.
2. Jumped from animals, and adapted in human-to-human phase enough to allow outbreaks
Presented by: Love Grace Davin
You might also like
- Corona VirusDocument8 pagesCorona VirusPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of CoronaDocument19 pagesBiochemistry of CoronaNikos FinnosNo ratings yet
- Scientific Journal Review Coronavirus Mutation (Science Summative by Chelsea)Document8 pagesScientific Journal Review Coronavirus Mutation (Science Summative by Chelsea)Jevon SolnaldoNo ratings yet
- Article Corona VirusDocument2 pagesArticle Corona VirusSarah MellaliNo ratings yet
- May Be Defined As: VirusesDocument21 pagesMay Be Defined As: VirusesZeresenayNo ratings yet
- Corona Virus: Q1: Coronavirus Life CycleDocument6 pagesCorona Virus: Q1: Coronavirus Life CycleTufail KhanNo ratings yet
- Where Did Viruses Come From?Document4 pagesWhere Did Viruses Come From?JamesNo ratings yet
- Asssiment Crona Virus 2Document18 pagesAsssiment Crona Virus 2mariaNo ratings yet
- Micro LectureDocument4 pagesMicro LectureJewel OlaezNo ratings yet
- COVIDDocument7 pagesCOVIDSky AgtarapNo ratings yet
- Middle East Respiratory Syndrome - Corona Virus (Mers-Cov) : A Deadly KillerDocument8 pagesMiddle East Respiratory Syndrome - Corona Virus (Mers-Cov) : A Deadly Killerdydy_7193No ratings yet
- Deoxyribo Virus and RibovirusDocument5 pagesDeoxyribo Virus and RibovirusAlyssa MercadoNo ratings yet
- Acellular PathogensDocument17 pagesAcellular Pathogensjeraldine marceraNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 - Where Did It Come FromDocument3 pagesCOVID-19 - Where Did It Come FromKryzler KayeNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure of Covid 19Document11 pagesCellular Structure of Covid 19atikamaryemNo ratings yet
- 16.science and Technology 3 Target - Prelims - 2020Document46 pages16.science and Technology 3 Target - Prelims - 2020naseerNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report About Viruses: From Group 4Document5 pagesNarrative Report About Viruses: From Group 4Jeoff Patrick TesoreroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Viruses - Wikipedia PDFDocument80 pagesIntroduction To Viruses - Wikipedia PDFSaad-ullah SultanNo ratings yet
- Negative Stranded RNA VirusesDocument47 pagesNegative Stranded RNA VirusesNovie Carla GayosaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 111Document31 pagesGeneral Biology 111Chioma AlexNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Class 11Document17 pagesBiology Project Class 11SK RulesNo ratings yet
- IPIntJComprAdvPharmacol 5-2-49 57Document9 pagesIPIntJComprAdvPharmacol 5-2-49 57jmakbar AkbarNo ratings yet
- MLT503 - L2 - General Properties of VirusesDocument51 pagesMLT503 - L2 - General Properties of VirusesMuhammad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Patrick Ch17Document49 pagesPatrick Ch17Caroline Lessa0% (1)
- Viral Infection of The Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesViral Infection of The Respiratory SystemAbdus SubhanNo ratings yet
- What Is Coronavirus? The Different Types of CoronavirusesDocument9 pagesWhat Is Coronavirus? The Different Types of Coronavirusesashley bendanaNo ratings yet
- Corona VirusDocument27 pagesCorona Viruspardhaja.vaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Structure of CoronavirusDocument6 pagesStructure of CoronavirusAlonsoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Infection: Origin, Transmission, and Characteristics of Human CoronavirusesDocument10 pagesCOVID-19 Infection: Origin, Transmission, and Characteristics of Human CoronavirusesVeronicaNo ratings yet
- COVID19 Research PaperDocument9 pagesCOVID19 Research PaperLove AmitNo ratings yet
- Animal VirologyDocument94 pagesAnimal Virologyabrilama90No ratings yet
- Overview On Pandemic Viral InfectionsDocument39 pagesOverview On Pandemic Viral Infectionsayushi shuklaNo ratings yet
- DraftDocument24 pagesDraftAHMED EMADNo ratings yet
- Virus Characteristic: in Oral CavityDocument23 pagesVirus Characteristic: in Oral CavityDiska Fitri AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus and HealthDocument3 pagesCoronavirus and HealthDilsha WejethungaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VirusesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To VirusesWhite RoseNo ratings yet
- Running Head: CORONA VIRUS 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: CORONA VIRUS 1BillyNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Tracing The SARS-coronavirusDocument4 pagesReview Article: Tracing The SARS-coronavirusIslam Ausraf RajibNo ratings yet
- Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses Against CoronavirusDocument17 pagesInnate and Adaptive Immune Responses Against CoronavirusHARDITA SALSABILA FORTUNA HARDITA SALSABILA FORTUNANo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument9 pagesVirologyAnisha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Approaches Against Coronaviruses Acute Respiratory SyndromeDocument21 pagesTherapeutic Approaches Against Coronaviruses Acute Respiratory Syndromenow youloseNo ratings yet
- VirusDocument4 pagesVirusmusamugabazi68No ratings yet
- Prof. Dalia M. Mohsen Lecture VirologyDocument24 pagesProf. Dalia M. Mohsen Lecture VirologyDalia M. MohsenNo ratings yet
- Viruses: Shafie Abdulkadir HassanDocument29 pagesViruses: Shafie Abdulkadir HassanShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- A Current Review On Covid-19Document6 pagesA Current Review On Covid-19Gunji Venkata LokeshNo ratings yet
- Updates On Rabies Virus Disease: Is Evolution Toward "Zombie Virus" A Tangible Threat?Document11 pagesUpdates On Rabies Virus Disease: Is Evolution Toward "Zombie Virus" A Tangible Threat?Moon5627No ratings yet
- May Be Defined As: VirusesDocument21 pagesMay Be Defined As: VirusesbetablockersNo ratings yet
- Influenza VirusDocument15 pagesInfluenza VirusadwNo ratings yet
- Covi 19Document17 pagesCovi 19santsj78No ratings yet
- Viruses Their ReplicationDocument39 pagesViruses Their ReplicationYsabella LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Pox Viruses: Structure and ReplicationDocument5 pagesPox Viruses: Structure and ReplicationIDRAAK HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Pox Viruses: Structure and ReplicationDocument5 pagesPox Viruses: Structure and ReplicationIdraak BhatNo ratings yet
- Assignment: ON Topic: Pox Viridae General Properties, Dna Replication & Cow Pox DiseaseDocument8 pagesAssignment: ON Topic: Pox Viridae General Properties, Dna Replication & Cow Pox DiseaseVinayak ChuraNo ratings yet
- Viruses Morphology and Ultrastructure. Viruses Cultivation in Chicken Embryo and Laboratory Animals Organism!Document21 pagesViruses Morphology and Ultrastructure. Viruses Cultivation in Chicken Embryo and Laboratory Animals Organism!Amirs AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 65 (Introduction To Viruses)Document16 pagesChapter 65 (Introduction To Viruses)leoNo ratings yet
- Virology Respiratory VirusesDocument6 pagesVirology Respiratory VirusesHisham ChomanyNo ratings yet
- Heinlein 2015Document15 pagesHeinlein 2015Arezki LehadNo ratings yet
- Basic Virology 3rd EditionDocument16 pagesBasic Virology 3rd EditionrouzbehnoroozyNo ratings yet
- MGY378 2014 Outline (1) - 88937Document4 pagesMGY378 2014 Outline (1) - 88937Christine QianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Acellular Life Dr. Muhammad RasoolDocument4 pagesChapter 5: Acellular Life Dr. Muhammad RasoolNau MaanNo ratings yet
- Open Elective III & IV Syllabus 2022 25012022Document25 pagesOpen Elective III & IV Syllabus 2022 25012022AlokNo ratings yet
- Genome Organization in ProkaryoteDocument21 pagesGenome Organization in ProkaryotegitaNo ratings yet
- Vertesi - The Use of Frequency V1Document654 pagesVertesi - The Use of Frequency V1Ekiskalibur NirvanaNo ratings yet
- Theory QuestionsDocument121 pagesTheory Questionsjanakansenthil2010No ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Viruses: 13.1 General StructuresDocument3 pagesChapter 13: Viruses: 13.1 General StructuresASPEN FERNANDONo ratings yet
- General Structure and Classification of Viruses 4Document50 pagesGeneral Structure and Classification of Viruses 4OROKE JOHN EJE100% (1)
- Viruses Their ReplicationDocument39 pagesViruses Their ReplicationYsabella LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam MD2140E - Virology, Mycology and ParasitologyDocument10 pagesFinal Exam MD2140E - Virology, Mycology and ParasitologyMah ShawdNo ratings yet
- Betaflexiviridae 2012Document22 pagesBetaflexiviridae 2012Leonardo Sulca GNo ratings yet
- Exam Quest Special 2023Document24 pagesExam Quest Special 2023Yalvant YadavNo ratings yet
- សំណួរត្រៀមDocument1,480 pagesសំណួរត្រៀមNobel PelNo ratings yet
- Local Media2180871509351945489Document2 pagesLocal Media2180871509351945489Jenie Munar RosarioNo ratings yet
- Prelims Micropara LecDocument14 pagesPrelims Micropara LecBSN1F- JACILDO, KUH KYLA C.No ratings yet
- PYC2605 Tutorial 201Document10 pagesPYC2605 Tutorial 201dikahunguNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VirologyDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Virologysumanth gowdaNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument91 pagesCombine PDFIbrahim SawaftaNo ratings yet
- Virus MorphologyDocument3 pagesVirus MorphologyAli AsgharNo ratings yet
- A Função Das MacromoléculasDocument76 pagesA Função Das MacromoléculasJoão EusébioNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - Virology PDFDocument20 pagesMicrobiology - Virology PDFLOUISE ANNE NAGALNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam in MicrobiologyDocument23 pagesSample Exam in MicrobiologyleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- Viral Classification: DNA VirusesDocument10 pagesViral Classification: DNA Virusess.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- Virology ModuleDocument165 pagesVirology ModuleAhmed KerAtyNo ratings yet
- 2006 - Forterre - The Origin of Viruses and Their Possible Roles in Major Evolutionary Transitions PDFDocument12 pages2006 - Forterre - The Origin of Viruses and Their Possible Roles in Major Evolutionary Transitions PDFJames Roi BerroyaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Virology NotesDocument13 pagesIntro To Virology NotesSpongebob Squarepants100% (1)
- Mcqs in MicrobiologyDocument19 pagesMcqs in MicrobiologyTawfeeq AuqbiNo ratings yet
- Wilson and Gisvold S Textbook of Organic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry - Chap9 - Antiviral - AgentsDocument26 pagesWilson and Gisvold S Textbook of Organic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry - Chap9 - Antiviral - AgentsEmily Larissa Saldanha PereiraNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (516)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)