Professional Documents
Culture Documents
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1
Uploaded by
Kaung Myat SanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1
Uploaded by
Kaung Myat SanCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:______________________________( ) Class:_________ Date:___________
TEST
Chapter 1: Kinetic Particle Theory
25
Multiple-Choice Questions (10 marks)
1. A liquid has a definite __________.
A shape and volume only B mass and volume only
C mass and shape only D mass, shape and volume ( B )
2. Which of the following statements about the kinetic particle theory is not true?
A The particles of a gas move faster than those of a liquid.
B The particles of a solid have more kinetic energy than those of a gas.
C The particles that make up matter are always moving.
D The forces of attraction between the particles of a solid are very strong. ( B )
3. The particles of a gas __________.
A vibrate about fixed positions
B are packed close together in a disorderly arrangement
C are far apart and move in all directions
D are stationary in an orderly arrangement ( C )
4. Gases can be compressed because __________.
A their particles are smaller than those of liquids or solids
B there is plenty of space between their particles
C they have low boiling points
D their particles are more elastic than those of liquids or solids ( B )
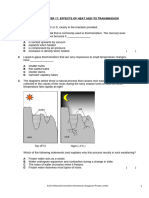
5. Which letter (A, B, C or D) represents the process of condensation?
Liquid
A D
B C
Solid Gas
( D )
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1
6. An inflated balloon is placed in a refrigerator. Which statement describes the movement of
the gas particles in the balloon?
A The particles move more slowly and become closer together.
B The particles move more slowly and become further apart.
C The particles move faster and become closer together.
D The particles move faster and become further apart. ( A )
7. A substance Y has a melting point of –7ºC and a boiling point of 63ºC. At which
temperature is Y a liquid?
A B C D
__________________________________________________
–50 –25 0 25 50 75 100 125 150
Temperature/C
( B )
8. What happens when water evaporates?
A Particles of the water vapour lose energy to their surroundings.
B Particles of the water vapour are spaced further apart.
C The speed of the particles of the water increases.
D The temperature of the remaining water rises. ( B )
9. A substance is a liquid at room temperature and pressure. Which property is true of the
melting and boiling points of the substance?
Melting point Boiling point
A Below room temperature Below room temperature
B Above room temperature Above room temperature
C Above room temperature Below room temperature
D Below room temperature Above room temperature
( D )
2 © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
10. The graph below shows part of the cooling curve of a substance. Which row correctly
identifies P, Q and R?
Temperature/°C
Q
R
Time/min
P Q R
A Gas Gas and liquid Liquid
B Liquid Liquid and gas Gas
C Gas Liquid Solid
D Solid Liquid Gas
( A )
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 3
Structured Questions (15 marks)
11. The list below shows the different processes.
Boiling Evaporation Melting
Condensation Freezing
Select from the list above the word that best describes the following observations.
(a) Bubbles of ethanol vapour forming in liquid
ethanol that is being heated Boiling [1]
(b) Puddles of water on the road slowly drying Evaporation [1]
(c) Layers of ice forming in lakes during winter Freezing [1]
(d) Water droplets forming on a cold glass surface Condensation [1]
(e) A lighted candle becoming shorter gradually Melting [1]
12. A solid compound X was heated steadily for 20 minutes. The graph below shows the
change in temperature of X with time.
Temperature/C
100
80
60
40
20
0 Time/min
(a) At what temperature did X melt? 40°C [1]
(b) What is the boiling point of X? 90°C [1]
(c) What is the highest temperature at which X can exist as
a solid? 40°C [1]
4 © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
(d) What is/are the physical state(s) of X
(i) at 26C? solid [1]
(ii) at 40C? solid and liquid [1]
(iii) at 100°C? gas [1]
13. Use your knowledge of the kinetic particle theory to explain the following statements.
(a) Ice loses its shape when it melts. [2]
Particles of ice gain heat energy from the surroundings and break away from their
____________________________________________________________________
_closely packed orderly arrangement. [1] When the ice has melted to become a
liquid, particles are no longer in fixed positions but are free to move about and
____________________________________________________________________
_slide over each other. [1]
____________________________________________________________________
_
____________________________________________________________________
_
(b) A solid generally has a higher density than its liquid and gaseous states. [2]
Particles are more closely packed together. [1] There are more particles in a given
____________________________________________________________________
_volume. [1]
____________________________________________________________________
_
____________________________________________________________________
_
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 5
Table of Specifications
Question no. Type of Syllabus learning Assessment No. of marks
question outcome objective*
1 2.1(a) K/C 1
2 2.1(a) K/C 1
3 2.1(a) K/C 1
4 2.1(a) K/C 1
5 Multiple- 2.1(a) K/C 1
6 choice 2.1(a) K/C 1
7 2.1(a) K/C, A 1
8 2.1(a) K/C 1
9 2.1(a) K/C 1
10 2.1(a) K/C 1
11 2.1(a) K/C, A 5
12 Structured 2.1(a) K/C, A 6
13 2.1(a) K/C, A 4
* K/C: Knowledge/Comprehension
A: Application
6 © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
You might also like
- © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document5 pages© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 DPPs-75-76Document2 pagesCBSE Class 9 DPPs-75-76Mehul MayankNo ratings yet
- DPP Class Ix MatterDocument2 pagesDPP Class Ix MatterMehul Mayank100% (1)
- (CHEM CS) 2021 Mock Paper 1 - AnswersDocument8 pages(CHEM CS) 2021 Mock Paper 1 - Answerslohbernard168No ratings yet
- 9th Chapter 1Document10 pages9th Chapter 1EdumaaNo ratings yet
- NSEJSMatterELP 1finalDocument4 pagesNSEJSMatterELP 1finalBitan DasNo ratings yet
- CF Ph-1 Practice Paper CMM-3Document3 pagesCF Ph-1 Practice Paper CMM-3Divyansh Jain KingNo ratings yet
- Matter SolvedDocument2 pagesMatter SolvedimbhoomiguptaNo ratings yet
- Phase Test 1Document2 pagesPhase Test 1pankaj16xissNo ratings yet
- Chap.2Test 6 PDFDocument1 pageChap.2Test 6 PDFShair MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Matt 1 1Document2 pagesMatt 1 1Moinack Saha VII E 19No ratings yet
- 2019feqtr1g 12 Stem Chem2Document6 pages2019feqtr1g 12 Stem Chem2Elcid BocacaoNo ratings yet
- 2018 Paper 1 Specimen PaperDocument8 pages2018 Paper 1 Specimen PaperCode Breaker 03: Youki Tenpouin (The Legend)No ratings yet
- Worksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9Document3 pagesWorksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9Random AccNo ratings yet
- 444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 9-9Document1 page444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 9-9whatisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question BanakDocument14 pagesChemistry Question BanakBikash DasNo ratings yet
- MCQ Cbse 9 Chapter-1 ScienceDocument5 pagesMCQ Cbse 9 Chapter-1 ScienceAgam VermaNo ratings yet
- CH - 1Document4 pagesCH - 1Phantom GamingNo ratings yet
- IX - Chemistry KAT Worksheet - IDocument4 pagesIX - Chemistry KAT Worksheet - IGajula Anjaneyulu AnjaneyuluNo ratings yet
- Particles of MatterDocument9 pagesParticles of MatterFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- October BookletDocument54 pagesOctober BookletnivineNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Practice SheetsDocument34 pagesUnit 1 Practice SheetssamamansorNo ratings yet
- #MOCK JEE Main Practice Test 6 Expansion, Calorimetry, KTG & ThermodynamicsDocument5 pages#MOCK JEE Main Practice Test 6 Expansion, Calorimetry, KTG & Thermodynamicsayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- KPT 1rfDocument3 pagesKPT 1rfzannateen nayeemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Paper SA1 Class 9 CBSEDocument2 pagesChemistry Practice Paper SA1 Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Chemistry Class Ix Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument6 pagesChemistry Class Ix Matter in Our SurroundingstnmscharanNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Test-2 Class IX WTDocument2 pagesPhase 1 Test-2 Class IX WTpankaj16xissNo ratings yet
- KS3 TestDocument6 pagesKS3 TestVytheeshwaran Vedagiri80% (5)
- Ib Chemistry 1ed TR CB AnsDocument155 pagesIb Chemistry 1ed TR CB AnsPassent ElewaNo ratings yet
- OL Physics Book 2 (MCQ Theory) 2008 Till 2021Document386 pagesOL Physics Book 2 (MCQ Theory) 2008 Till 2021ABDULLAH'S SWEET VIDEOSNo ratings yet
- First Assessment Test Chemistry Form 4 NAME: .. CLASS: SECTION A: Answer All The Questions in This SectionDocument7 pagesFirst Assessment Test Chemistry Form 4 NAME: .. CLASS: SECTION A: Answer All The Questions in This SectionZainab AriffinNo ratings yet
- PM Test C10 (Student)Document7 pagesPM Test C10 (Student)damonchooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Water: Section A: Choose The Best Answer and Write The Letter Next To It in The Answer BoxDocument2 pagesChapter 4: Water: Section A: Choose The Best Answer and Write The Letter Next To It in The Answer BoxFaizanAusNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Theory: Answers To Textbook ExercisesDocument3 pagesKinetic Particle Theory: Answers To Textbook ExercisesariiNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Secunderabad: For The Questions (6) To (10), Find Out The Option From (A), (B), (C), (D)Document5 pagesDelhi Public School Secunderabad: For The Questions (6) To (10), Find Out The Option From (A), (B), (C), (D)Vedant SinghalNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 17Document18 pagesTest Chapter 17damonchooNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings - Daily Home Assignment 03 - (Neev 2024)Document3 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings - Daily Home Assignment 03 - (Neev 2024)Wooh gamerZNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter - WorksheettDocument10 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter - Worksheettssohxq100% (4)
- CHEMISTRYQuestionDocument18 pagesCHEMISTRYQuestionGandhimathi mathiNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings - Practice SheetDocument3 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings - Practice Sheetsifivar867No ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar - Science - Class 9 PDFDocument173 pagesNCERT Exemplar - Science - Class 9 PDFsiddharthNo ratings yet
- NCERT Science ExemplarDocument86 pagesNCERT Science ExemplarRishik Madan Jai100% (1)
- Chapter Wise Test CombinedDocument26 pagesChapter Wise Test CombinedMetre SNo ratings yet
- 2 SolutionsDocument2 pages2 SolutionsArchanaa PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- IX-Deeksha (Liquid State)Document5 pagesIX-Deeksha (Liquid State)N. HarshaNo ratings yet
- Peq1 1Document3 pagesPeq1 1Baiye RandolfNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DPP-01Document1 pageChemistry DPP-01OFFICIAL Tamojeet ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Phase Changes - QuizizzDocument7 pagesPhase Changes - QuizizzMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science 1Document5 pagesClass 9 Science 1chandralok_kumarNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Neev 2024)Document2 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Neev 2024)Vansh GargNo ratings yet
- Chem 9th MB Chapter No 05Document2 pagesChem 9th MB Chapter No 05Safeer AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2022 Assessment Science 8Document4 pages2022 Assessment Science 8Crecencia BasongitNo ratings yet
- CH 19 Surface ChemistryDocument4 pagesCH 19 Surface Chemistryshivanijain4443No ratings yet
- States of Matter QuizDocument5 pagesStates of Matter QuizMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Science 7-Diagnostic TestDocument6 pagesScience 7-Diagnostic TestRussell AyadNo ratings yet
- Liquid SolutionDocument16 pagesLiquid SolutionMohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CDD FinalDocument4 pagesChemistry CDD Finalsurya pratapNo ratings yet
- VIII-Chemistry - PWS-3Document6 pagesVIII-Chemistry - PWS-3AINo ratings yet
- © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document1 page© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document7 pages© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document7 pages© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedDocument1 page© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document4 pagesWorksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Name: - Class: - DateDocument7 pagesWorksheet: Name: - Class: - DateKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - DateDocument6 pagesName: - Class: - DateKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- DCS C01 Quiz TeacherDocument2 pagesDCS C01 Quiz TeacherKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedDocument7 pagesWorksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedDocument12 pages© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - DateDocument5 pagesName: - Class: - DateKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganiDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganiKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Axial Piston Pumps: Series Pvplus - Design Series 47 Variable DisplacementDocument72 pagesAxial Piston Pumps: Series Pvplus - Design Series 47 Variable DisplacementJhonata CavalcanteNo ratings yet
- Tenatative List of Rexroth Make Hydraulic Items To Be Procured (As Provided by Various Shops)Document62 pagesTenatative List of Rexroth Make Hydraulic Items To Be Procured (As Provided by Various Shops)vsvinaykumarNo ratings yet
- Process Modeling & Simulation (CH-401) : Practical WorkbookDocument67 pagesProcess Modeling & Simulation (CH-401) : Practical WorkbookIffatNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices For City Gas Distribution (CGD)Document19 pagesSafety Practices For City Gas Distribution (CGD)tulasiraoNo ratings yet
- Co 2 Flow Meters Vs RegulatorsDocument2 pagesCo 2 Flow Meters Vs RegulatorswentropremNo ratings yet
- A-512B B&G Lead-Free Circuit Setter Plus BrochureDocument2 pagesA-512B B&G Lead-Free Circuit Setter Plus Brochurekeith dietrichNo ratings yet
- C C C CDocument10 pagesC C C CMaarij RaheemNo ratings yet
- R 0.1889 Kpa M T PDocument10 pagesR 0.1889 Kpa M T PAriel Carlos De LeonNo ratings yet
- The Science of Spray PaintDocument1 pageThe Science of Spray PaintChristine SabioNo ratings yet
- API Piping Plans join crane 约翰克兰机械密封冲洗方案Document34 pagesAPI Piping Plans join crane 约翰克兰机械密封冲洗方案DelfinshNo ratings yet
- Simbologia ValvulasDocument43 pagesSimbologia Valvulasdanillomodesto100% (1)
- Modelling Plasma Arcs For Electrical SimulationsDocument4 pagesModelling Plasma Arcs For Electrical Simulationsadmatama221100% (1)
- Chapter 13 - Gas Bearing Formation InterpretationDocument22 pagesChapter 13 - Gas Bearing Formation Interpretation1234abcd100% (1)
- Experiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice Meterf20221047No ratings yet
- Power Requirement (Agitator and High-Torque Stirrer)Document8 pagesPower Requirement (Agitator and High-Torque Stirrer)DozdiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Hydraulic Course PDFDocument85 pagesAdvanced Hydraulic Course PDFGerman Toledo100% (1)
- Advantages and Limitations of Valve TypesDocument6 pagesAdvantages and Limitations of Valve TypesHaridas PaulNo ratings yet
- Low Pressure Effusion of GasesDocument10 pagesLow Pressure Effusion of Gasesglen-576661No ratings yet
- LMF-GP LX15-8 - 10 - 13Document2 pagesLMF-GP LX15-8 - 10 - 13MAZEN0% (1)
- CNG ProjectDocument66 pagesCNG ProjectDaniel RicciNo ratings yet
- Steam Bench: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesSteam Bench: Objectiveحسين عمريNo ratings yet
- Thermophysical Properties of Fluids. II. Methane, Ethane, Propane, Lsobutane and N-ButaneDocument222 pagesThermophysical Properties of Fluids. II. Methane, Ethane, Propane, Lsobutane and N-ButaneCan YıldırımNo ratings yet
- Effect of Chevron Angle and Surface Roughness On Thermal Performance of Single Phase Water Flow in A Plate Heat ExchangerDocument9 pagesEffect of Chevron Angle and Surface Roughness On Thermal Performance of Single Phase Water Flow in A Plate Heat ExchangerAkash AhmedNo ratings yet
- Vertical Spiral Rib Tubeless Steam BoilersDocument6 pagesVertical Spiral Rib Tubeless Steam BoilersbenNo ratings yet
- Co2 Recovery - IffcoDocument21 pagesCo2 Recovery - IffcoAbizer JamaliNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 3Document53 pagesPertemuan 3Arif Pradana WIbowoNo ratings yet
- Mu01 8Document1 pageMu01 8manju.aalawakaNo ratings yet
- GA90-500 GR110-200 Brochure PDFDocument22 pagesGA90-500 GR110-200 Brochure PDFmageedNo ratings yet
- Application of Modified K-Ȧ Model To Predicting Cavitating Flow in Centrifugal PumpDocument9 pagesApplication of Modified K-Ȧ Model To Predicting Cavitating Flow in Centrifugal PumpiOScar UltronNo ratings yet
- Discharge CoefficientDocument11 pagesDischarge Coefficientsisai12u2420% (2)