Professional Documents
Culture Documents
sm1 049 PDF
sm1 049 PDF
Uploaded by
JanaínaMedeirosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
sm1 049 PDF
sm1 049 PDF
Uploaded by
JanaínaMedeirosCopyright:
Available Formats
PROBLEM 1.
49
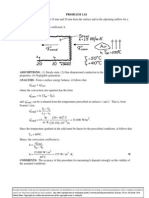
KNOWN: Boiling point and latent heat of liquid oxygen. Diameter and emissivity of container. Free
convection coefficient and temperature of surrounding air and walls.
FIND: Mass evaporation rate.
SCHEMATIC:
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state conditions, (2) Temperature of container outer surface equals
boiling point of oxygen.
ANALYSIS: (a) Applying mass and energy balances to a control surface about the container, it
follows that, at any instant,
dmst dEst &
= −m& out = − m
& evap = E in − E& out = q conv + q rad − q evap . (1a,b)
dt dt
With hf as the enthalpy of liquid oxygen and hg as the enthalpy of oxygen vapor, we have
Est = mst h f q evap = m
& out h g (2a,b)
Combining Equations (1a) and (2a,b), Equation (1b) becomes (with hfg = hg – hf)
& out h fg = q conv + q rad
m
& evap = ( q conv + q rad ) h fg = ⎡ h ( T∞ − Ts ) + εσ Tsur
m
⎣
4
− Ts4 ⎤ π D 2 h fg
⎦ ( (3) )
&
m =
⎡10 W m 2 ⋅ K ( 298 − 263) K + 0.2 × 5.67 × 10−8 W m 2 ⋅ K 4 2984 − 2634 K 4 ⎤ π ( 0.5 m )2
⎣ ⎦ ( )
evap
214 kJ kg
& evap = ( 350 + 35.2 ) W / m 2 0.785 m 2
m ( ) 214 kJ kg = 1.41 × 10−3 kg s . <
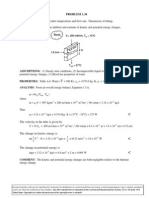
(b) Using Equation (3), the mass rate of vapor production can be determined for the range of
emissivity 0.2 to 0.94. The effect of increasing emissivity is to increase the heat rate into the container
and, hence, increase the vapor production rate.
1.9
Evaporation rate, mdot*1000 (kg/s)
1.8
1.7
1.6
1.5
1.4
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Surface emissivity, eps
COMMENTS: To reduce the loss of oxygen due to vapor production, insulation should be applied to
the outer surface of the container, in order to reduce qconv and qrad. Note from the calculations in part
(a), that heat transfer by convection is greater than by radiation exchange.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Pump Foundation DesignDocument18 pagesPump Foundation DesignSourav92% (12)
- Rotary Table (转盘)Document15 pagesRotary Table (转盘)Omar Fathy100% (1)
- Quiz 1 - Group 1Document5 pagesQuiz 1 - Group 1Kim OpenaNo ratings yet
- Lifting Plan V - 409 18ins Con ValDocument9 pagesLifting Plan V - 409 18ins Con ValAhmed Butt100% (1)
- BOSCH高压共轨原理诊断 PDFDocument99 pagesBOSCH高压共轨原理诊断 PDFwinter19980% (1)
- Rhourde El Baguel LPG Extraction Plant Feed Planning Rev 0 PDFDocument3 pagesRhourde El Baguel LPG Extraction Plant Feed Planning Rev 0 PDFZakari LOUNISNo ratings yet
- sm1 68Document1 pagesm1 68awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 56Document1 pagesm1 56awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 67Document1 pagesm1 67awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 64Document2 pagessm1 64awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 66Document1 pagesm1 66awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 61Document1 pagesm1 61awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 47Document1 pagesm1 47awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 50Document1 pagesm1 50awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 54Document1 pagesm1 54awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 46Document2 pagessm1 46awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 45Document2 pagessm1 45awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 44Document1 pagesm1 44awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 38Document1 pagesm1 38awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 39Document1 pagesm1 39awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 36Document1 pagesm1 36awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 35Document1 pagesm1 35awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 31Document1 pagesm1 31awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 30Document1 pagesm1 30awoods12835No ratings yet
- Guide To Steel Pipes For Vessels - Wide Flange Beams ExcelDocument195 pagesGuide To Steel Pipes For Vessels - Wide Flange Beams ExcelAlmario SagunNo ratings yet
- The Electrical Portal: Testing of DC MotorDocument2 pagesThe Electrical Portal: Testing of DC MotorGayathri Devi Yadav NakanaboyinaNo ratings yet
- Instant Electric Water Heater: Read This Manual Carefully Before Installation and UseDocument36 pagesInstant Electric Water Heater: Read This Manual Carefully Before Installation and UseAmin JamaludinNo ratings yet
- CNG A4-EngDocument8 pagesCNG A4-EngЭльмар ГафаровNo ratings yet
- Myers Triplex Water Pump D35 D50 D60 D65 Data SheetDocument2 pagesMyers Triplex Water Pump D35 D50 D60 D65 Data Sheetsergio100% (1)
- Astm A490M Heavy Hex Structural Bolts (Metric)Document7 pagesAstm A490M Heavy Hex Structural Bolts (Metric)cragmarNo ratings yet
- 2017-Kawasaki-Kx450f-7 Owners ManualDocument206 pages2017-Kawasaki-Kx450f-7 Owners ManualBong BongNo ratings yet
- Aeb04112 PDFDocument6 pagesAeb04112 PDFCesar G.0% (1)
- ASTM D 790-15e2Document12 pagesASTM D 790-15e2Indah FajarwatiNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation, & Maintenance Manual: Free Standing Jib CraneDocument20 pagesInstallation, Operation, & Maintenance Manual: Free Standing Jib CraneSam JohnNo ratings yet
- JLG m600jDocument2 pagesJLG m600jrawassatNo ratings yet
- Dodge Brass InsertsDocument40 pagesDodge Brass InsertsAce Industrial SuppliesNo ratings yet
- 3 Quantum Mechanics IntroDocument79 pages3 Quantum Mechanics IntroShan Yu XuanNo ratings yet
- Standard Specifications: Horizontal Wire Mesh Belt ConveyorDocument1 pageStandard Specifications: Horizontal Wire Mesh Belt Conveyorchuy215No ratings yet
- File 94catalogo SumitomoDocument28 pagesFile 94catalogo SumitomoJaime Arreola100% (1)
- TennsDocument8 pagesTennsconcretemadNo ratings yet
- Conventional Pumping Unit Specification BUKAKADocument2 pagesConventional Pumping Unit Specification BUKAKAachmad mahmudyNo ratings yet
- How A Refrigeration Compressor WorksDocument9 pagesHow A Refrigeration Compressor WorksYasir ButtNo ratings yet
- Portal FrameDocument7 pagesPortal FrameMuhammad Hasrul HasnanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Principles - Dynamics of Rotating SystemsDocument14 pagesMechanical Principles - Dynamics of Rotating SystemsSteven GoddardNo ratings yet
- SERVODocument7 pagesSERVONicole RodriguezNo ratings yet
- INSPECTION REPORT EQUIPMENT Vacum, W Truck 1 Rev.3Document4 pagesINSPECTION REPORT EQUIPMENT Vacum, W Truck 1 Rev.3tirtamas berkah makmur100% (1)
- Technical Data SheetDocument3 pagesTechnical Data SheetAhmad RobbyNo ratings yet