Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metabolic Alkalosis (Base Bicarbonate Excess) : Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors
Metabolic Alkalosis (Base Bicarbonate Excess) : Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors
Uploaded by
Allyssa Mackinnon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Metabolic Alkalosis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesMetabolic Alkalosis (Base Bicarbonate Excess) : Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors
Metabolic Alkalosis (Base Bicarbonate Excess) : Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors
Uploaded by
Allyssa MackinnonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
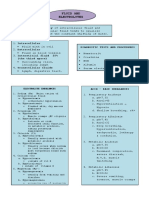
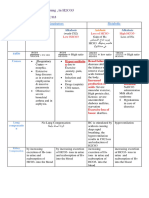
Metabolic Alkalosis
(Base Bicarbonate Excess)
Precipitating factors Predisposing factors
Volume depletion Long term diuretic therapy
(vomiting, NG suction) Medical conditions
Dehydration
Use of antacids
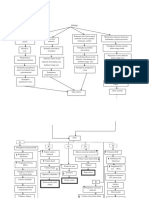
Metabolic Alkalosis
Extracellular potassium Loss of bicarbonate-poor,
Loss of gastric secretions chloride-rich extracellular fluid
concentration decreases
Hydrogen ion is excreted Potassium ions move out of Contraction of extracellular
the cells fluid volume
Bicarbonate ion is gained in
Hydrogen ions move into Bicarbonate mass is now
the extracellular space
the intracellular space dissolved in a smaller volume
of fluid
Bicarbonate mass is now
dissolved in a smaller volume
of fluid
Decrease in hydrogen ion
concentration
Increase in bicarbonate Rapid renal excretion of
bicarbonate
>pH 7.45
Decrease in HCO3
Decrease in the
stimulation of the
medullary chemoreceptors
A decrease respiratory rate
Carbon dioxide retention is
increased
Carbon dioxide retention is
increased
Signs and Symptoms
Tingling of the fingers and toes
Dizziness
Hypertonic muscles
Subsequent headache
Lethargy
Neuromuscular excitability
Sometimes with delirium, tetany, and
seizures.
Hypoventilation
Nausea and confusion
You might also like
- NBME 27 AnswersDocument198 pagesNBME 27 Answershaneen gf100% (4)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- Chapter 39 Pain Management in ChildrenDocument3 pagesChapter 39 Pain Management in ChildrenAllyssa Mackinnon0% (1)
- Chapter 39 Pain Management in ChildrenDocument3 pagesChapter 39 Pain Management in ChildrenAllyssa Mackinnon0% (1)
- Concept Map - F and EDocument1 pageConcept Map - F and EAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Diuretics - AMBOSS PDFDocument9 pagesDiuretics - AMBOSS PDFOpio Isaac100% (1)
- Chloride ImbalanceDocument5 pagesChloride ImbalanceTulauan FamilyNo ratings yet
- EDICTO Acute Metabolic Alkalosis (FINAL)Document1 pageEDICTO Acute Metabolic Alkalosis (FINAL)GLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Drugsaffecting GIsystemDocument12 pagesDrugsaffecting GIsystemJanine mae MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Web of Caution (Woc) EtiologiDocument3 pagesWeb of Caution (Woc) EtiologibondNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Care Acid Base ElectrolytesDocument7 pagesPerioperative Care Acid Base ElectrolytesIlyas HarunNo ratings yet
- Carbonic AcidDocument1 pageCarbonic Acidapi-327824216No ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide and Ocean AcidificationDocument1 pageCarbon Dioxide and Ocean AcidificationAvril Bolondi MedinaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument4 pagesAcid Base BalanceHenric CasimiroNo ratings yet
- Patho DiagramDocument1 pagePatho Diagrampaupaulala100% (2)
- Midterm Notes by F.L.F.Sanjuan, RMT, DtaDocument3 pagesMidterm Notes by F.L.F.Sanjuan, RMT, DtaIbtisam YusufNo ratings yet
- Guatemala DM Ro BWT CWT 2011Document127 pagesGuatemala DM Ro BWT CWT 2011Rolando PosseNo ratings yet
- Basic Environmental EngineeringDocument72 pagesBasic Environmental EngineeringAfewerkNo ratings yet
- CM All Compiled NotesDocument100 pagesCM All Compiled NotesKatrina Mae PatalinghugNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas InterpretationDocument28 pagesBlood Gas InterpretationgjdbfiuvaNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study 2Document3 pagesDrug-Study 2Macy MarquezNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate RevisitedDocument22 pagesSodium Bicarbonate RevisitedcrplzNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Module 2Document3 pagesDRUG STUDY Module 2Macy MarquezNo ratings yet
- BicarbonateDocument5 pagesBicarbonateRace MendezNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document13 pagesAssignment#1Mark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chesmistry 1A 3ADocument9 pagesInorganic Chesmistry 1A 3AJessica GutierrezNo ratings yet
- BIO 024 Session 1 7Document67 pagesBIO 024 Session 1 7Tracy DavidNo ratings yet
- Function of BicarbonateDocument3 pagesFunction of BicarbonateMalikkahNo ratings yet
- Basic Water ChemistryDocument4 pagesBasic Water ChemistryZAHID HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- 7 Acidbase-ImbalanceDocument5 pages7 Acidbase-ImbalanceMarie Louise Nicole TuvillaNo ratings yet
- AcidDocument6 pagesAcidfisiruadama88No ratings yet
- Unit7-3-WWT-Biological Treatment PDFDocument85 pagesUnit7-3-WWT-Biological Treatment PDFnickNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Hypercalcemia Part 2Document2 pagesConcept Map Hypercalcemia Part 2Queenie Rose ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Municipal and Domestic Wastewater TreatmentDocument37 pagesMunicipal and Domestic Wastewater TreatmentBerlian SitorusNo ratings yet
- مراجعة ال abg - 240111 - 221447Document3 pagesمراجعة ال abg - 240111 - 221447peternady202No ratings yet
- Acid Base StatusDocument28 pagesAcid Base Statustoto loloNo ratings yet
- ENG15B00342Y Newton Woleru Course Code: Cve503Document4 pagesENG15B00342Y Newton Woleru Course Code: Cve503Able ManNo ratings yet
- Medication ReviewDocument2 pagesMedication ReviewJn CaducoyNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Bland: 1 Running Header: Acid-Base BalanceDocument4 pagesJonathan Bland: 1 Running Header: Acid-Base BalancejonNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesPathophysiologyJerica Mae VenoyaNo ratings yet
- Raw Water & Waste Water: Utilities Unit - Area SpecificDocument6 pagesRaw Water & Waste Water: Utilities Unit - Area SpecificYasir ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Kelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enDocument16 pagesKelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enAgustinusNo ratings yet
- Nutri Diet 6Document6 pagesNutri Diet 6jellybeandumpppNo ratings yet
- Kelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enDocument14 pagesKelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enhilan sasewaNo ratings yet
- Dietary RequirementsDocument7 pagesDietary RequirementsdadaksaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Laboratorium Pada Gangguan Asam BasaDocument62 pagesPemeriksaan Laboratorium Pada Gangguan Asam BasaOkta Besti ArdikaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Acidosis - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders - Merck Manuals Professional EditionDocument2 pagesMetabolic Acidosis - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders - Merck Manuals Professional Editionmaulidanabilah5No ratings yet
- Raw Water: 19.998 m3/h 4.00 KG N/HDocument2 pagesRaw Water: 19.998 m3/h 4.00 KG N/HPratikNo ratings yet
- Analisis Gas Darah Dan Pem Lab Neonatus PDFDocument64 pagesAnalisis Gas Darah Dan Pem Lab Neonatus PDFvina zulfianiNo ratings yet
- Esrd Diagram PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesEsrd Diagram PathophysiologySTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument6 pagesAcid BaseYlooner QuitsNo ratings yet
- Alkalosis Acidosis ChartDocument1 pageAlkalosis Acidosis ChartrobingailNo ratings yet
- AGE PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAGE Pathophysiologyjosephcanlas67% (3)
- Group 1ADocument4 pagesGroup 1AAna Eunice Mahilum LintagNo ratings yet
- Biological Self-Healing ConcreteDocument21 pagesBiological Self-Healing ConcreteqnaqsNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Process Disinfection PDFDocument6 pagesWater Treatment Process Disinfection PDFAriff JasniNo ratings yet
- Detection of Functional Groups-OrganicDocument10 pagesDetection of Functional Groups-OrganicfaithNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Sodium Bicarbonate and Lactulose)Document5 pagesDRUG STUDY (Sodium Bicarbonate and Lactulose)Vraxx GrayNo ratings yet
- Topic: Using The Earth's Resources: Water WaterDocument8 pagesTopic: Using The Earth's Resources: Water WaterBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia Concept MapDocument3 pagesHypercalcemia Concept MapAlvin Dagumbal100% (1)
- Concept Map HypovolemiaDocument3 pagesConcept Map HypovolemiaAllyssa Mackinnon67% (3)
- vt59.2708 21181224998 - 1701189390091407 - 7293683638689607120 - n.pdf3ND Surgical Group Research Paper - PDFDocument189 pagesvt59.2708 21181224998 - 1701189390091407 - 7293683638689607120 - n.pdf3ND Surgical Group Research Paper - PDFAllyssa MackinnonNo ratings yet
- Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument20 pagesXavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan Bachelor of Science in NursingAllyssa MackinnonNo ratings yet
- Cushingoid Appearance. Due To The Overproduction of Cortisol by The Adrenal CortexDocument5 pagesCushingoid Appearance. Due To The Overproduction of Cortisol by The Adrenal CortexAllyssa MackinnonNo ratings yet
- Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan College of Nursing: Case Analysis On Concept of Preoperative CareDocument12 pagesXavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan College of Nursing: Case Analysis On Concept of Preoperative CareAllyssa MackinnonNo ratings yet
- Rle Journal MackinnonDocument4 pagesRle Journal MackinnonAllyssa MackinnonNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Alkalosis (Base Bicarbonate Excess) I. Brief DescriptionDocument3 pagesMetabolic Alkalosis (Base Bicarbonate Excess) I. Brief DescriptionAllyssa MackinnonNo ratings yet
- Lec Cerae - Mackinnon NDDocument2 pagesLec Cerae - Mackinnon NDAllyssa MackinnonNo ratings yet
- Surgical Gowning and GlovingDocument15 pagesSurgical Gowning and GlovingAllyssa MackinnonNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument8 pagesAcute Respiratory FailureCayunk NorlianaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Respiratory PhysiologyDocument10 pagesDevelopmental Respiratory PhysiologySakina Paramita SulistijoNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Oxygen TherapyDocument20 pagesBasic Principles of Oxygen TherapyAdikurniawan100% (1)
- American Journal of Emergency Medicine: MD, MD, MD, MDDocument11 pagesAmerican Journal of Emergency Medicine: MD, MD, MD, MDSyed Shahrul Naz Syed100% (1)
- Causes: Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory AlkalosisDocument4 pagesCauses: Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory AlkalosisKristie Stiles100% (1)
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument12 pagesBirth Asphyxiaannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Pulse Oximetry - UpToDate PDFDocument26 pagesPulse Oximetry - UpToDate PDFLOIDA ESTHER DIAZ MONTESNo ratings yet
- Lfurbot,+aabp 1994 v28 002 AnaesthesiaInCattleDocument7 pagesLfurbot,+aabp 1994 v28 002 AnaesthesiaInCattleAngelette CaoyongNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in OxygenationDocument8 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in OxygenationRed StohlNo ratings yet
- Lo Tropmed 1Document49 pagesLo Tropmed 1belleNo ratings yet
- Measures of Oxygenation and Mechanisms of Hypoxemia - UpToDateDocument11 pagesMeasures of Oxygenation and Mechanisms of Hypoxemia - UpToDateraniakusmantoNo ratings yet
- Aicu Worksheet 1.Document4 pagesAicu Worksheet 1.Cyril SolimanNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gases - UpToDateDocument13 pagesArterial Blood Gases - UpToDatedevi efrinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 Acute Lung Injury, Pulmonary Edema and Multi Organ System FailureDocument10 pagesChapter 27 Acute Lung Injury, Pulmonary Edema and Multi Organ System FailureShanin SalapuddinNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument65 pagesArterial Blood Gas InterpretationDaniel AryanNo ratings yet
- The Role of Training in The Development of Adaptive Mechanisms in FreediversDocument14 pagesThe Role of Training in The Development of Adaptive Mechanisms in Freediversalena292007No ratings yet
- ESICM Guidelines On Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Definition, Phenotyping and Respiratory Support StrategiesDocument33 pagesESICM Guidelines On Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Definition, Phenotyping and Respiratory Support StrategiesAbenamar VelardeNo ratings yet
- Intensive Care of The Neonatal FoalDocument32 pagesIntensive Care of The Neonatal FoalAristoteles Esteban Cine VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Neonatal AnaesthesiaDocument30 pagesNeonatal Anaesthesiavenkatesh chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Respiratory Muscle Function StrengthDocument8 pagesAssessment of Respiratory Muscle Function StrengthsstavrosNo ratings yet
- Download textbook The Sages Manual Of Pediatric Minimally Invasive Surgery 1St Edition Danielle S Walsh ebook all chapter pdfDocument53 pagesDownload textbook The Sages Manual Of Pediatric Minimally Invasive Surgery 1St Edition Danielle S Walsh ebook all chapter pdfmarylee.lites749No ratings yet
- Chapter 24 Management of Patients With Chronic Pulmonary DisordersDocument3 pagesChapter 24 Management of Patients With Chronic Pulmonary DisordersPeej Reyes100% (1)
- PulmCrit - Mastering The Dark Arts of BiPAP & HFNCDocument13 pagesPulmCrit - Mastering The Dark Arts of BiPAP & HFNCTusar KoleNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Hypoxia and AsphyxiaDocument24 pagesIntrauterine Hypoxia and Asphyxiazerish0208No ratings yet
- Personal Notes Excpetional StuffDocument352 pagesPersonal Notes Excpetional StuffYagyeshNo ratings yet
- CHPT 70 Respiratory Part 2Document56 pagesCHPT 70 Respiratory Part 2helen brockNo ratings yet
- Emergency Neurological Life Support: Airway, Ventilation, and SedationDocument17 pagesEmergency Neurological Life Support: Airway, Ventilation, and SedationLezard DomiNo ratings yet
- NP3 RatioDocument17 pagesNP3 RatioArnie Jude CaridoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure, Hypoxia and HypercapneaDocument4 pagesRespiratory Failure, Hypoxia and HypercapneaLinda NguyenNo ratings yet