Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microanatomy Practicals
Uploaded by
aferdita xhepaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microanatomy Practicals
Uploaded by
aferdita xhepaCopyright:
Available Formats
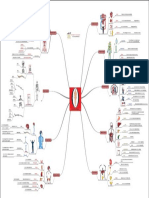
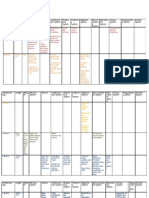
System Endocrine Lymphoid Gastrointestinal Respiratory Urinary Reproductive Circulatory Connective Tissue Muscle Nervous Integumental Epithelial
Organ Thyroid Adrenal Lymph nodes Thymus Spleen Tonsils Parotid Sublingual Submandibular Esophagus Stomach:Cardiac Stomach:Fundus Stomach:Body Stomach:Pylorus Duodenum Jejunum Ileum Colon Pancreas Liver Trachea Bronchus Bronchioles Lung Kidney Bowman's Capsule Ureter Bladder Testes Epididymis Prostate Ovaries Uterus Corpus Luteum Artery Vein Blood Loose Dense Reticular Elastic Adipose Cartilage:Hyaline Cartilage:Fibrous Cartilage:Elastic Compact Bone Spongy Bone Skeletal Cardiac Smooth Spinal Cord Peripheral Nerve Ganglion Epidermis Simple squamous Pseudo stratified ciliated Pseudo stratified with sterocilia Simple Columnar Transitional Stratified squamous keratinized Stratified Squamous non-keratinized
Image
Solid/hollow Solid Solid Solid Solid Solid Solid Solid Solid Solid Hollow Hollow Hollow Hollow Hollow Hollow Hollow Hollow Hollow Solid Solid Hollow Hollow Hollow Solid Solid n/a Hollow Hollow Solid Hard to tell Solid Solid Hollow n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
Description The parenchyma is made of Covered by a CT capsule that Covered by CT capsule that Covered by CT capsule that extends covered by CT capsule that extends Not covered by capsule but by the The parenchyma is made of secretory The parenchyma is made of secretory The parenchyma is made of It is a hollow organ of the digestive It is a hollow organ of the digestive It is a hollow organ of the It is a hollow organ of the digestive It is a hollow organ of the digestive It is a hollow organ of It is a hollow organ of the digestive It is a hollow organ of the It is a hollow organ of the digestive The parenchyma is made of The organ is covered by a CT It is a hollow organ. I can see 2 hollow It is a hollow organ. It is a hollow organ with a star The organ is a solid organ, the It is a solid organ covered by a dense CT It is a sac lined by simple squamous The organ has a star shaped lumen and The organ is a hollow organ as serveral The organ in the slide is a testis. The organ in the slide is the epididymis. The organ in the slide is the It is a solid parenchymal organ lined It is a hollow organ that appears to It is a structure that can be seen in the In the structure various layers of tissue In the structure various layers of tissue Blood components The tissue is characterised by The tissue is characterised by abundant The tissue is characterised by The tissue is characterised by abundant The tissue contains signet ring It is a connective tissue with large It is a connective tissue with large It is a connective tissue with large amount Osteons are clearly visible in the The tissue contains lamellae and Longitudinal section: The fibres are Longitudinal section: The tissue has Longitudinal section: The cells are The butterfly shaped structure in Due to the presense of myelinated Based on the morphology of the Clear division into different layers. Cells are tightly aposed and the Cells are tightly aposed and the ECM is Cells are tightly aposed and the Cells are tightly aposed and the Cells are tightly aposed and the Cells are tightly aposed and the Cells are tightly aposed and the ECM is not
cuboidal epithelial cells arranged extends septa inwards separating extends septa inwards to septa inwards to separate the organ septa inwards to separate the organ lining epithelium of the oral cavity epithelial cells arranged in units that are epithelial cells arranged in units that
secretory epithelial cells arranged system and it contains several tunicae: system and it contains several digestive system and it contains system and it contains several system and it contains several the digestive system system and it contains several tunicae: digestive system and it contains system and it contains several tunicae: secretory epithelial cells arranged capsule that extends septa organs attached to each other. On one It contains several tunicae: shaped lumen. parenchyma appears full of cavities capsule. In the parenchyma we can cells on its parietal side, lying on a several laminae can be seen - it is a tunicae can be seen. A layer of mucosa The outermost layer of It is a highly convoluted tube lined with prostate gland which is a solid by a germinal columnar lining have 3 layers, the middle one being ovary. It is a big structure that forms from and a central hollow lumen can be and a central hollow lumen can be ERYTHROCYTES: most abundant extracellular matrix extracellular matrix with a smaller number abundant extracellular matrix with a extracellular matrix which indicates that shaped cells with many whilte amount of intercellular matrix and amount of intercellular matrix and of intercellular matrix and scattered cells. slide with concentric lamellae and lacunae where osteocytes are very regular with an elongated and visible striations which indicates the elongated and fusiform and their the middle and the presence of the axonemes organised into bundles large spherical structures, we can The most superficial layer ECM is not abundant which not abundant which indicates that the ECM is not abundant which ECM is not abundant which ECM is not abundant which ECM is not abundant which abundant which indicates that the tissue is
in follicles (0.02-0.9 mm). It is the organ into lobules. The separate the organ into lobules. into lobules. The parenchyma is into lobules. We can distinguish 2 which is stratifies squamous tubuloacinar. It is surrounded by a CT are tubuloacinar. It is surrounded by a
in units that are tubuloacinar. It is Tunica Mucosa: lining epithelium is tunicae: several tunicae: tunicae: tunicae: and it contains several Tunica Mucosa: lining epithelium is several tunicae: Tunica Mucosa: lining epithelium is in units that are tubuloacinar. It is inwards to divide the organ into side it is the esophagus, on the other it Tunica Mucosa: lining epithelium It contains several tunicae: with squamous cells lining them. distinguish 2 different layers: a cortex and a basement membrane. Inside it there is hollow organ. The innermost layer is the and muscularis externa can be connective tissue is the serosa pseudostratified epithelium with organ surrounded by a epithelium. CT capsule - tunica a very thick muscular layer. remnant granulosa and theca cells after identified. Three main layers can be identified. Three main layers can be abundant, biconcave, no with a smaller number of cells of cells which indicates that the tissue is smaller number of cells which the tissue is connective tissue. The spaces. The cytoplasm and the scattered cells. The cells are scattered cells.It has dense The cells are rounded globular which a central canal in the middle located, however no osteocytes cylindric shape and contain very presence of stable sarcomeres. thicker middle portion contains the central canal indicate that the of nerve fibres the structure can be deduce that they are cell bodies (STRATUM CORNEUM) contains indicates that the tissue is epithelial tissue is epithelial tissue. The epithelial indicates that the tissue is indicates that the tissue is indicates that the tissue is epithelial indicates that the tissue is epithelial epithelial tissue. The cells are organised in many
surrounded by a CT capsule. parenchyma is made of epithelial There is a subcapsular sinus, made of small cells that are different regions in the parenchyma: epithelium. They are groups of capsule that extends inwards to form CT capsule that extends inwards to surrounded by a CT capsule that squamous stratified non-keratinized Tunica Mucosa: lining epithelium is Tunica Mucosa: lining epithelium Tunica Mucosa: lining epithelium Tunica Mucosa: lining epithelium is tunicae: simple columnar with microvilli on the Tunica Mucosa: lining simple columnar with microvilli on the surrounded by a CT capsule that lobules surrounded by periportal is te Trachea. is ciliated pseudostratified Tunica Mucosa: lining epithelium This is typical of the lung, where medulla as well as hilum region. In the a space and in this space, there are mucosa which contains a layer of identified. The most superficial layer of and then we see a thick, very stereocilia on the apical surface. The fibromuscular capsule extending labuginea.It has 2 distinguishable The first layer consists of the lining ovulation. These cells transform into seen which suggests that it is a hollow seen which suggests that it is a hollow nucleus which indicates that the tissue is connective tissue. The cells are elongated indicated that the tissue is connective intensely stained fibres are organised in nucleus of the tissue is pushed to rounded globular which indicates arrangement of collagen fibers that indicates that they are chondrocytes in portion of the osteon which is the are present. This indicates the visible transverse striations. These Additionally darker lines can be seen in nucleus which is also consistent structure is the spinal cord. The identified as the peripheral nerve. of neurons. They contain stratified keratinised epithelium, tissue. The cells are organised in cells have a layered appearance but not epithelial tissue. The epithelial epithelial tissue. The cells are tissue. The cells are organised in tissue. The cells are organised in layers, i.e. the epithelial tissue is stratified. Cells
Inside the follicles, there is a cells, but we can distinguish 2 where afferent lymphatic vessels intensely stained and basophilis so red pulp and white pulp, which are rounded aggregates of lymphocytes septa dividing the organ into lobules. It form septa dividing the organ into extends inwards to form septa lying on a lamina propria of loose CT. simple columnar lying on a lamina is simple columnar lying on a is simple columnar lying on a simple columnar lying on a lamina Tunica Mucosa: lining apical surface (can't be resolved under epithelium is simple columnar apical surface (can't be resolved under extends inwards to form septa spaces (=CT). The classic lobules It contains several tunicae: columnar intercalated with is ciliated pseudostratified simple squamous epithelium lines medulla region, we can see pyramids whose capillaries lined by cells, lying in a transitional epithelial tissue with dome the mucosa is made of transitional evident capsule made of dense lining epithelium lies on a layer of into the organ. In fact, the stroma layers: a cortex and a medulla. In the epithelium surrounding the lumen is rounded foldings of endocrine cells: larger organ of the circulatory system. The organ of the circulatory system. The NEUTROPHILS: connective tissue. The cells are with irregular morphology i.e. they are tissue. The tissue in the slide contains parallel laminae and exhibit a wavy the periphery by lipid droplets they are chondrocytes. There is are arranged in ordery matter. The lacunae which is quite numerous in this Haversian canal. Between the presence of trabeculae as they represent the A and I lines of the places which represent intercalated with th cell shape. Extremities of lighter inner structure (butterfly( is The outermost layer of connective abundant cytoplasm and large about 15-30 layers - dead squamous only one layer, i.e. the epithelial all tissues originating at the basal lamina cells have a layered appearance organised in only one layer and many layers. The most superficial many layers, i.e. the epithelial are elongated, thin and flat - squamous epithelial
colloid released by the different regions in the parenchyma: drains the lymph into. The they are lymphocytes. We can interspersed and don't form distinct that are small basophilic intensely has branches of ducts of different sizes lobules. It has branches of ducts of dividing the organ into lobules. It Mucosa contains tubular mucous propria of loose CT. All cells in the lamina propria of loose CT. All lamina propria of loose CT. All propria of loose CT. All cells in the epithelium is simple a light microscope). The epithelium is with microvilli on the apical a light microscope) intercalated with dividing the organ into lobules. It have a distinct hexagonal shape. Tunica Mucosa: towards the lumen the mucous secreting Goblet cells columnar intercalated with the alveoli that are surrounded by apex is directed towards the hilum. In mesangeal matrix. Also, there are ducts shaped cells on the apical surface. The epithelium containing dome-shaped connective tissue - tunica connective tissue which constitutes the is made up of dense connective cortex, there are many follicles of columnar epithelium lying on CT paler granulosa cells, and smaller darker most central layer is the tunica intima most central layer is the tunical intima granulocytes so granules elongated with irregular fibroblasts. The cells are not abundant fibroblast and branched irregular pattern which allow then to stretch and removed during the H& E staining. also evidence of lacunae with cellare rounded globular which tissue. It is differentiated from the hyaline lamellae, osteons can be seen in don't require the Haversian stable sarcomeres (dark and pale discs connecting the individual cells. the cell are very thin. The the grey matter where the neurons tissue surrounging the entire nerve palely stained nucleus (due to cells (keratinocytes) still connected tissue is simple. Cells are reach the apical surface therefore the but not all tissues originating at all cells originating at the basal layer contains tissued that are tissue is stratified. Cells are cells. Nuclei are present in the most superficial
thyrocytes containing T3 and T4 a cortex and a medulla. The cortex parenchyma is made of small distinguish a cortex and a medulla. layers. In the white pulp, we see stained cells forming follicles. They so they are branched and lined by different sizes so they are branched has branches of ducts of different secreting glands (esophageal cardiac lining epithelium are mucous cells in the lining epithelium are cells in the lining epithelium are lining epithelium are mucous columnar with microvilli lying on a lamina propria of loose CT surface (can't be resolved under Goblet cells, lying on a lamina propria has branches of ducts of different Inside the lobule, the parenchymal lining epithelium is ciliated lying on a lamina propria of loose mucous secreting Goblet cells CT. Also, I can see cross sections between the pyramids, we can identify on both sides of this sac, along with a lamina propria is made up of loose cells on the apical surface. The next albuginea. The connective tissue lamina propria. The two layers make up tissue, elastic fibres and smooth different sizes and structures that contains simple tubular glands, theca cells. A clot of blood can be seen in containing a single layer of squamous containing a single layer of squamous in the cytoplasm, pale morphology i.e. they are and thick collagen fibres are present and fibres which are reticular fibes made then return to their original morphology. In the silver staining, the lipids will isogenic groups of cells. There is a indicates they are chondrocytes. cartilage by its many elastic fibers in lacunae with a system of system for the delivery of lines respectively). The nuclei are These help ensure simultaneous morphology of the cells and the are located. The outer layer is the is the epineurium. The smaller extended chromatin) as well as a by desmosomes which eventually elongated, thin and flat with epithelium is pseudostratifies. Cells are the basal lamina reach the apical lamina reach the apical surface, dome shaped and sometimes elongated, thin and flat - squamous layer, therefore the tissue is non-keratinised.
bound to thyroglobulin (inactive is composed of cells arranged in cells that are intensely stained In the cortex, the cells are tightly intensely stained small basophilic contain cryptae which are cuboidal epithelium (stratified, and lined by cuboidal epithelium sizes so they are branched and glands) in the final part. Mucosa also secreting cells and so they are not mucous secreting cells and so mucous secreting cells and so secreting cells and so they are not on the apical surface that contains simple tubular glands. a light microscope). The of loose CT. Mucosa exhibits infoldings sizes so they are branched and cells are cuboidal, and some of pseudostratified columnar intercalated CT. lying on a lamina propria of loose of star shaped bronchioles. (The columns whose staining is similar to that of blood vessel entering it. connective tissue with many elastic fibres. layer is made of connective tissue and projects into the organ dividing it the mucosa. The submucosa is not muscle cells. You can distinguish representing follicles at different and rich vascularization (spiral the middle which forms after ovulation. epithelial cells and a layer of loose epithelial cells and a layer of loose basophilic staining, nuclei fibroblasts. The cells are densely packed therefore we can of type III and type IV collagen. The The tissue is therefore elastic be dark. These indicates the cells highly basophilic homeogenic The chondrocytes are either singly addition to the collagen fibers. The Giesen cannaliculi spreading from them nutrients due to their smaller located in the periphery and have an contraction of all the cells. The muscle lack of striation (which means white matter containg the glial bundles of fibres are surrounded spherical intensely stained break and cells flake off. The next rounded nuclei bulging out, elongated with elongated nuclei located surface therefore the epithelium is therefore the epithelium is simple cover more than one cell in the epithelial cells. Nuclei are NOT
form). Inactive follicles have cords, and it has 3 layers: First and basophilic so they are packed, while in the medulla, they cells that are lymphocytes arranged in invaginations in the lining columnar, or stratified columnar for (stratified, columnar, or stratified lined by cuboidal epithelium contains a layer of smooth muscle cells intensely stained. Folding of they are not intensely stained. they are not intensely stained. intensely stained. Folding of (can't be resolved under Mucosa also contains 2 layers of epithelium is lying on a lamina forming crypts that contain simple lined by cuboidal epithelium them are binucleated, and they are with mucous secreting Goblet cells A layer of circularily arranged CT. As we move towards terminal differentiation between secondary the cortex region. I can tell that this is the This is the Bowman's capsule, and the These two layers together constitute the constitutes the lamina propria. This into lobes and lobules. In the present. The muscularis consists of two different zones: -peripheral zone stages of development, along with arteries might appear). This layer connective tissue. Between the first and connective tissue. Between the first - multilobed, intensely abundant which indicates that conclude that the tissue is dense fibres are organised in networks connective tissue which is seen are adipose tissues. On the other matrix with collagin fibers but not a or isogenous aggregates arranged stains elastic fiber black. which contain the osteocytes diameter and the possibility to elongated shape. Based on this we fibres are not regular, but instead there are no stable sarcomeres) cells. The central canal is lined by perineurium and endoneurium nucleolus which indicates the layer is STRATUM LUCIDUM - cells therefore the tissue is simple closer to the basement membrane, pseudostratifies. Cells are columnar. Both cell and the layer underneath. Some of them present in the most superficial
flattened cuboidal cells, while region just beneath the capsule is lymphocytes. We can distinguish are less dense. We can distinguish follicles that contain a central artery. epithelium. larger ducts), thus it is a compound columnar for larger ducts), thus it is a
(stratified, columnar, or stratified which is Muscularis Mucosa. mucosa creates gastrc pits which Folding of mucosa creates gastric Folding of mucosa creates gastrc mucosa creates gastrc pits which a light microscope). The smooth muscle cells which is propria of loose CT that tubular glands also containing goblet (stratified, columnar, or stratified arranged into lamina directed lying on a lamina propria of loose CT. smooth muscle cells between the bronchioles, the lining epithelium and tertiary is done on how much Kidney. structure inside it is the glomerulus. The mucosa which is intensely folded giving together with the epithelial tissue parenchyma, multiple layers of smooth muscle in the head where most of the glands are some interstitial glands. Towards the might have 2 distinguishable the second layer the internal elastic and the second layer there is no stained the tissue is loose connective connective tissue. If dense regular: rather than bundles therefore the primarily in the walls of arteries and hand, brown adipose tissues lot of elastic fibers. axially in their lacunae. However, it processes. In some places exchange metabolites with bone can conclude that the tissue is branch and fuse together. Based on this indicated that the tissue is smooth with ependymal cells, the surrounds each myelinated nerve cells are active in protein with advanced keratinisation. squamous epithelium. therefore the tissue is preudostratified elongated with elongated nuclei nucleus are elongates, and the are also multinucleated. The layer, therefore the tissue is
active ones have high cuboidal the Glomerulosa: the cells are a cortex and a medulla, and a some larger star shaped cells that The follicles might have germinal gland. The cells are serous secreting compound gland. It is a mixed gland, columnar for larger ducts), thus it Tunica Submucosa: loose CT contains glands open into at the bottom. pits which glands open into at the pits which glands open into at the glands open into at the bottom. epithelium is lying on a Muscularis Mucosa. contains simple tubular glands. cells among other cells. Mucosa also columnar for larger ducts), thus it is towards a central vein. Sinusoids Tunica Submucosa: loose CT and lamina propria and the becomes less pseudostratified, cartilage is found and how When I increase the magnification, I can see capillaries are lined on the outside by the organ the ability to stretch. No constitue the mucosa. The mucosa has seminiferous tubules are seen and the body of the organ, and of three located, -transitional zone around periphery, the follicles are very small, regions: a less stained one towards membrane can be seen. The middle internal elastic membrane. The middle EOSINOPHILS: nuclei - tissue. In the matrix collagen parallel collagen fibres present, fibroblasts tissue can be identified as reticular veins. contains multiple droplet of fat isn't dense connective tissue due to circumferential lamellae can be marros sinusoids by striated skeletal muscle tissue. characteristics we can conclude that the muscle. Cross section: The cells cytoplasm of which contains fibre. Each nerve fibre shows a synthesis. (In sympathetic STRATUM GRANULOSUM contains columnar. Long regular structures are located closer to the basement nucleus is located closer to the structure of the cells gives them keratinised.
cells. Around the follicles, there arranged in ovoid clusters. The hilum. In the cortex, we have are epithelio-reticular cells. In the centers. In the red pulp, we see many cells. They have a well-stained round since it has both serous and mucous is a compound gland. It is a elastic fibers and compound Lamina propria rich in tubular bottom. Lamina propria rich in bottom. Lamina propria rich in Lamina propria rich in tubular lamina propria of loose Tunica Submucosa: loose CT and Mucosa also contains 2 layers contains a layer of smooth muscle a compound gland. The cells are can be seen between the laminae mixed tubuloacinar glands. submucosa. and becomes ciliated columnar segmented is it) many nephrons in the cortex containing a podocytes but they can't be submucosa. The muscularis externa has many foldings which provides the which are surrounded by layers in the tail section. The whole the prostatic urethra -central zone and they are bigger towards the inside the lumen, and a more stained one layer - tunica media - contains smooth layer - tunica media - contains smooth bilobed, granules fibres can also be seen. are flat and squeezed between collagen connective tissue. Reticular CT is while not pushing the nucleus to its chondrocytes are surrounded by seen as well. (sometimes interconnected cannaliculi. Based Cross section: the fibres have a tissue is cardiac muscle. Cross section: vary in diameter and some of them intensely stained Nissl bodies. centrally placed axon (dark ganglion) The cell bodies have granules of keratin - the main present on the apical surface which can membrane, therefore the tissue is basal lamina. the ability to stretch which is
may be C cells that are second layer beneath is the lymphoid follicles, which when medulla, we see Hassal's corpuscle. sinuses, nucleus. secreting cells. The majority of the mixed gland, since it has both tubuloacinar glands. glands containing mucous tubular glands containing mucous tubular glands containing mucous glands containing mucous CT that contains simple blood vessels. of smooth muscle cells which is cells which is Muscularis Mucosa. serous secreting cells. They have a of cells. At the vertices of the Fibroelastic-Cartilagenous-muscular Tunica Submucosa: loose CT epithelium. Goblet cells also If the slide shows a terminal Bowman's capsule and a glomerulus inside. distinguished clearly using light two layers of smooth muscle - inner: organ with the ability to stretch. The intestitial connective tissue organ is covered by adventitia made up around the ejeculatory ducts. The of the cortex. In certain follicles, an towards the muscle layer they are muscle cells and elastic fibres. Between muscle cells and collagen fibres. The intensely stained - fibres. If dense irregular: sheets and wave typically located in lymphoid organs - the side. It has the appearance of a matrix. So it is a fibrous cartilage. present) The Volkman canal on the structure of the tissue we clear polygonal shape with the the cells vary in diameter and have have a visible eccentric nucleus (in staining) which is surrounded by a sereral processes joined to them product of keratinocytes. In the be resolved under the microscope, preudostratified columnar. Long related to their function in the
parafollicular cells that release Fasciculata: the cells are arranged activated form a pale Germinal cells are mucous secreting cells with serous and mucous secreting Muscularis Externa: 2 layers of muscle secreting cells at the neck, and secreting cells at the neck, and secreting cells at the neck, and secreting cells at the neck, and tubular glands. Mucosa Muscularis Externa: 2 layers of smooth Muscularis Mucosa. Peyer's Tunica Submucosa: loose CT and well-stained round nucleus. We can lobule, I can see the cross section layer: a C-shaped ring of hyaline and mixed tubuloacinar glands. become much fewer. bronchiole branching, we need to Around the nephrons, I can see ducts: microscopy. longitudinal and outer: circular. The muscle layer is very thick and has three forming the stroma of the organ of connective tissue. glands in the prostate are oocyte might appear in the follicle, but the functional and basal layer, the middle and external layer the last layer - tunica externa consists of acidophilic forms seen, nuclei are sparse. liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone sponges withinthe cell. containing blood vessels and can conclude that it is spongy nuclei located only in the peripheral irregular edges. This indicates that the the larger sections). This suggests myelin sheath (silver staning - therefore they are multipolar SPINOUS LAYER cells are pushed therefore they are not microvilli. Axoneme irregular structures are present on bladder and urethera.
Calcitonin. They are larger and in long parallel cords. The third layer center, and a darker Mantle flattened nuclei that are pushed to the
cells. The majority of the cells are cells, inner circular, outer longitudinal. different cell types. Mucosa also different cell types. Mucosa also different cell types. Mucosa also different cell types. Mucosa also also contains 2 layers of muscle cells, inner circular, outer Patches are also found in blood vessels. also detect centroacinar cells, of a vein, an artery, and a duct, all cartilage surrounded by fibroelastic Fibroelastic-Cartilagenous: plates A layer of circularily arranged write: Proximal convoluted ducts that have larger If visible: On one end I can see the outermost layer of connective tissue is the layers of muscle fibres which are which contains Leidig cells. The tubuloalveolar and contain it depends on the cut. This indicates respectively. external elastic membrane is seen. The connective tissue. The lumen of the BASOPHILS: granules marrow (but not the thymus!) nerves can be seen joining two bone. part. fibres branch and fuse together. that the morphology of the cells is dark, h&e- pale). External to the neurons. (In dorsal root ganglion) upward and flattened out. Finally in is present in the form of an intensely the apical surface which can be
paler. beneath is the Reticularis: the cells around it. Here B cells are bottom, and they are not intensely serous secreting cells which have In the first third, it is striated muscle, in contains 2 layer of perpendicularily contains 2 layer of contains 2 layer of contains 2 layer of perpendicularily smooth muscle cells longitudinal. mucosa, which are aggregates Muscularis Externa: 2 layers of smooth which are cells belonging to the surrounded by CT, forming the fibers, a layer of smooth muscle cells in of hyaline cartilage all around smooth muscle cells between the The organ is a solid organ, the diameter and irregular lumen than that of the proximal convoluted tubule, which has a adventitia. The organ is also surrounded oriented in dirrefent directions: two tubules and lined by germinal columnar secretory epithelial cells that this is the ovary. Primary, late No submucosa last layer - tunica externa consists of vessle is wide and has a collapsed very intensely stained - osteons. Based on this we can fusiform and that the tissue in the myelin space is a thin cytoplasmic The neurons are pseudounipolar STRATUM BASALE epidermal cells stained line on the apical membrane resolved under the microscope,
are arranged in anastomising cords. present meanwhile T cells are stained because mucous doesn't take well-stained round nuclei. The the second third, it is smooth and oriented smooth muscle cells perpendicularily oriented smooth perpendicularily oriented smooth oriented smooth muscle cells which is Muscularis Serosa: dense CT of lymphocytes (intensely muscle cells, inner circular, outer intercalated duct that are found in portal triad. This organ is the liver, the opening where there is no cartilage surrounded by CT. The smaller lamina propria and the parenchyma appears full of cavities Distal convoluted tubules. larger diameter and an ireegular lumen. by adipose tissue. The organ is a ureter outer layers of longitudinal muscles epithelium containing many as well as basal cells which are primary, secondary follicle with the 3 layers of muscularis externa: connective tissue. The lumen of the appearance (irregular shape). The wall basophilic, therefore conclude that the tissue is slide is smooth muscle tissue. rim representing the neurilemma. and don't contain synaptic are continuously replaced - mitotic therefore the structures are cilia. therefore they are not microvilli.
In the medulla, we can see located in the deep cortex. In the up the stain. The serous cells are mucous secreting cells are fewer striated, in the final third, it is smooth which is Muscularis Mucosa. muscle cells which is Muscularis muscle cells which is Muscularis which is Muscularis Mucosa. Mucosa. The submucosa exhibits folds (plicae), stained basophilic small cells). longitudinal. the lumen of the acinus. it is covered by Glisson's capsule. (Trachealis muscle). the bronchi the less there are submucosa. with squamous cells lining them. In the medulla, I can see long parallel arrays I can also see the distal convoluted and an inner layer of circular muscle Sertolli cells. The lining occasionally pseudostratified. antrum (theca interna and esterna). Submucosal (inner): parallel to the vessle is narrow and both internal and of the vessel is relatively thin. We can nuclei almost not visible compact bone tissue. Sometimes the nuclei of Schwann connections. The cell bodies are layer. Axoneme is not present as the
columnar cells arranged in irregular medulla, the cells are arranged fewer and have a well-stained round and they have flattened nuclei muscle cells. Tunica Submucosa: loose CT and Mucosa. Mucosa. Tunica Submucosa: loose CT and Tunica Submucosa: and the mucosa exhibits further folding They are a component of GALT Serosa: dense CT We can also distinguish aggregates The cells are hepatocytes, and the Adventitia: dense CT and elastic fibers cartilage plates and the more Tunica Submucosa: loose CT and This is typical of the lung, where of ducts, which are the loop of Henle and the tubule which has a round lumen and a constituting the detrusor muscle. On epithelium sits on a layer of Concretions can be detected in In the medulla, there is mostly loose long axis, Vascular (middle): external elastic layers are present conclude that it is a vein. LYMPHOCYTES: cells can be seen on the outer side surrounded by much smaller cells staining of the apical membrane
cords, and opening of several blood in chords. It also contains blood nucleus. that are pushed to the bottom, Adventitia: dense CT blood vessels. Tunica Submucosa: loose CT Tunica Submucosa: loose CT and blood vessels. loose CT contains to form villi. The folds contain or MALT. On the outer layer, Haustra can be of cells that are Islets of structures at the vertices are cross segmented they are, and this is mixed tubuloacinar glands. simple squamous epithelium lines collecting tubules that go all the way to the smaller diameter. I can also see the the outside the organ has a layer of connective tissue - lamina the lumen of the glands. CT, smooth muscle cells, and blood thickest, circular and spiral, therefore the vessel is an artery. agranulocytes, large of the myelin sheath. In a cross which are satellite cells. Based on is uniform and light. Therefore the
vessels.Adrenomedullar vein. vessels, and sinuses. and they are not intensely stained Muscularis Externa: 3 layers of and blood vessels. blood vessels. Muscularis Externa: 3 layers of compound tubular submucosa in them, while villi contain Tunica Submucosa: loose CT observed. Langerhans dispersed throughout sections of a branch of the portal how we can distinguish between The outermost layer is a CT layer the alveoli that are surrounded by papilla. Macula Densa in the Distal convoluted connective tissue which constitutes the propria. vessels and it is continuous with hilum Subserosal (outer): parallel to the round nucleus taking up section, the gaps in the myelin those characteristics we can structures are stereocilia.
because mucous doesn't take up muscle cells, inner oblique, Muscularis Externa: 3 layers of Muscularis Externa: 3 layers of muscle cells, inner oblique, glands (Brunner's the lamina propria and muscularis and blood vessels and Peyer's the slide. vein, hepatic artery, and a bile secondary and tertiary bronchi. seperating it from the lung CT. Also, I can see a terminal tubule, where there appears to be taller adventitia. Some adipose tissue may of organ. long axis almost the entire cell sheath represent the nodes of conclude that it is a ganglion.
the stain. The serous secreting intermediate circular, outer muscle cells, inner oblique, muscle cells, inner oblique, intermediate circular, outer glands) and blood mucosa. Patches. ductule. Adventitia: Dense CT with elastic parenchyma containing many bronchiole branching into 2 cells with nuclei that are more be present on the outside as well. The Serosa: peritoneum: mesothelium space Ranvier.
cells are more intensely stained, longitudinal. intermediate circular, outer intermediate circular, outer longitudinal. vessels. Muscularis Externa: 2 layers of fibers elastic fibers. respiratory bronchioles, whose wall prominent. The arteriole is also visible organ is the urinary bladder. laying on thin CT layer. MONOCYTES: kidney
and they are more abundant, and Serosa: dense CT longitudinal. longitudinal. Serosa: dense CT Muscularis Externa: 2 smooth muscle cells, inner is interrupted by alveolar ducts next to the capsule. That would let us conclude that this shaped, eccentric
thus they give the appearance of Serosa: dense CT Serosa: dense CT layers of smooth circular, outer longitudinal. reaching the alveolar sacs. is the uterus, and the 3 layers are nucleus, abundant
demilunes (an intensely stained muscle cells, inner Serosa: dense CT If visible, we need to write: The the Endometrium, Myometrium, and cytoplasm
crescent around the pale stained circular, outer The submucosa exhibits folds lining epithelium of the respiratory Perimetrium. PLATELETS: small, non-
Distinguishing features Folliclar arrangment of cells with Cortex and medulla arrangement. Subcapsular sinus. Cortex and Hassal's corpuscle Red pulp and white pulp. Follicles with No capsule, instead lining The ducts are striated: they have a The ducts are striated: they have a cells)ducts
The called Giannuzi's
are striated: they have Muscularis mucosa. Trachea should Lining epithelium all mucous Lining epithelium all mucous Lining epithelium all mucous Lining epithelium all mucous longitudinal.
Plicae and villi. (plicae),
Plicae and villi. Neither Brunner's glands Plicae
nor Peyer'sand
and thePeyer's
villi. mucosa
patches arepatches
found in the
Foldssubmucosa.
instead of Villi
villi, are
thatfinger-like
might lookand longer.
The presence of the islets of Cells are arranged in laminae Respiratory ciliated pseudo-stratified Plates of hyaline cartilage all Star shaped hollow organ in the bronchiole
Might is non-ciliated
be mistaken cuboidal.
as adipose Renal pyramids in the medulla with parallel Capsule with space inside, and a group Transitional epithelium, no submucosa, Transitional epithelium, no submucosa, Tunica albuginea, parenchyma - Pseudostratified epithelium with Concretions in the lumens. Primordial and primary follicles of Thick muscular layer. Glands shape A large paler structure in the ovary, with 3 layers, narrow lumen, internal and 3 layers, wide lumen, no internal nucleated,ofirregular
presence granules and Abundant ground substance and Adundant ground substance, some Fibres - dark staning (silver) Fibres - parallel, wavy, fibroblasts Signet ring highly basophilic homeogenic both isogenic groups and singly numerous of chondrocytes, elastic fibers osteons with lamellae, lacunae Lamellae and lacunae with Transverse striations, cylindric variable diameter, fibres branch and cells elongated and fusiform in Butterfly shape (grey matter) and Nerve fibres with dark centres - Cell bodies with abundant Non keratinised epithelium - most Cells aposed, one layer, thin and Cells aposed, not all reach surface - Cells aposed, not all reach Cells aposed, all cells reach the Cells dome-shaped, Aposed - epithelial, thin and flat - Aposed - epithelial, thin and flat - squamous,
colloid inside. No ducts. No ducts. Chords of cells. medulla. All cells lymphocytes. central artery. epithelium of oral cavity which is labyrinth appearance on their basal labyrinth appearance on their basal Demilunes.
a labyrinth appearance on their appear attached to it. secreting cells not like colon where secreting cells not like colon secreting cells not like colon Adventitia:glands
secreting cells not like colon where Brunner's dense in CTthe exhibits
seen further folding
in mucosa and to form like the gastric pits, but here the lining Langerhans help distinguish that directed towards a central vein. columnar epithelium. C- shaped around, segmentation of plates lung parenchyma, surrounded by Some larger
tissue, (Clara
however the cells) appear
cavities are ducts. Nephrons in the cortex with ducts of capillaries. Ducts all around. star shaped lumen, foldings of the many mucosal foldings, thick seminiferous tubules, stroma - stereocilia on the apical surface Stroma is more abundant than in different sizes. External columnar to in the mucosa. rounded folding of cells. Might contain a external elastic membranes, abundant elastic membrane, mostly collagen shape
their staning, shape of fibroblasts, some collagen fibres fibroblasts, thick collagen fibres organised in a network, not bundles, usually not visible due to staning, matrix, isogenic groups groups, orderly arrangement of and collagen fibers with osteocytes and cannaliculi, osteocytes but no osteons or fibres, nuclei in periphery, fuse, striations and intercalated discs longitudinal section, no striations. white matter on the outside, the axonemes, surrounded by myelin cytoplasm, palely stained nucleus superficial layer, then different layers flat cells with bulging rounded pseudostratified, can be resolved under surface - pseudostratified, no surface, elongated with nuclei multinucleated, cover more than squamous, layers - stratified, no layers - stratified, nuclei in most superficial layer -
Lymphoid follicles, some with stratified squamous. Contain surface. Special feature for salivary surface. Special feature for salivary basal surface. Special feature for cells are intercalated with mucous where cells are intercalated with where cells are intercalated with The submucosa
cells are intercalated with mucous submucosa. Villi are villi. The foldsVilli
submucosa. contain
shorter than epithelium is only intercalated with this is the pancreas not the parotid. The classic lobule (though tough to hyaline cartilage. Smooth muscle help distinguish between a layer of smooth muscle cells intercalated
lined but no squamous
by numerous Goblet cellscells,
are around. muscosa, two layers of smooth muscles in muscularis - 3 layers (long/circ/long) = connective tissue between them, the thyroid! cuboidal lining epithelium. blood clot in the middle. elastic fibres in tunica media, narrow and smooth muscle in tunica media, nucleus abundant ground substance therefore abundant ground substance collagen fibers, chondrocytes are Haversian canal, Volksman canal, Haversian canals polygonally shaped fibres in the seen in lingitudinal section In cross section - varying diameter presence of the central canal sheaths organised into bundles and intensely stained nucleolus, of epithelial tissues underneath nuclei microscope so not microvilli, axoneme axoneme - so not cilia, can be closer to basal lamina one calls in the layer below nuclei in most superficial layer - non-keratinised
Mantle and Germinal Center. cryptae. Lymphoid follicles. glands to distinguish it from the glands. It can also be distinguished salivary glands. It can also be secreting Goblet cells. Gastric pits. mucous secreting Goblet cells. mucous secreting Goblet cells. exhibits folds (plicae),
secreting Goblet cells. Gastric pits. leaf-like. submucosa in them, while villi
jejunum. mucous secreting Goblet cells rather Also, the lack of striated ducts help be distinguished in some slides) where there is no cartilage. secondary and tertiary bronchi. circulariyl arranged, and CT with found.
so we see many small nuclei muscularis, adventitia and adipose tissue detrusor muscle, adventitia + some parenchyma divided into lobes round lumen, thick wall wide irregularly shaped lumen, thin CT surrounded by matrix circumferential lamellae cross section - larger sections contain eccentric surrounded by perineurium and surrounded by satellite cells present so must be cilia resolved under microscope so not keratinised
pancreas. from the submandibular gland by distinguished from the sublingual Only contains mucous secreting Gastric pits. Gastric pits. Glands mostly mucous secreting. and the mucosa contain the lamina propria and than it all being mucous secreting like distinguish that this is not a salivary has a hexagonal shape with Respiratory epithelium. layer of many elastic fibers. around each cavity instead of the adipose tissue and lobules by CT, seminiferous wall nucleus epineurium. microvilli, therefore must be
having mostly mucous secreting cells, gland by having mostly serousd glands. Thick lamina propria and shallow Thick lamina propria and shallow Thin lamina propria and deep exhibits further folding muscularis mucosa. in the stomach. So we see pale gland. Also Pacini corpuscles might vessels and ducts at its vertices. smooth muscle cells between signet ring look with adipose tissue tubules - germinal epithelium stereocilia
and thus there are NO Giannuzi's secreting cells, and thus there Thin lamina propria and shallow gastric pits. gastric pits. gastric pits. to form villi. The folds stained cells between intensely stained be present. lamina propria and submucosa. where one cell has one nucleus and lamina propria
Demilunes. are Giannuzi's Demilunes. gastric pits. contain submucosa in cells. pushed to periphery.
Might contain Z line which is the them, while villi contain
line where there is abrupt transition the lamina propria and
between the squamous lining of muscularis mucosa.
esophagus and columnar lining of
stomach.
You might also like
- Chief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaDocument2 pagesChief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaL P100% (1)
- Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology BookDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and Physiology BookAnge Ouedraogo100% (1)
- Wall ChartDocument1 pageWall ChartLila Joy100% (3)
- Introduction To Autonomic Pharmacology: Part Ii Anatomy of Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Autonomic Pharmacology: Part Ii Anatomy of Peripheral Nervous SystemshreyansNo ratings yet
- Lymphatics and Lymph Circulation: Physiology and PathologyFrom EverandLymphatics and Lymph Circulation: Physiology and PathologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Mapa Conceptual Sistemas Cuerpo HumanoDocument1 pageMapa Conceptual Sistemas Cuerpo HumanoGisela_XL100% (1)
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Organelles of An Animal CellDocument2 pagesFunctions of The Organelles of An Animal Cellmburu. hNo ratings yet
- Vocab Fusionado MEDICALDocument78 pagesVocab Fusionado MEDICALLucio BladeNo ratings yet
- Body SystemDocument2 pagesBody SystemKD F2021No ratings yet
- WWW Careinsurance Com Blog Health Insurance Articles HealthDocument9 pagesWWW Careinsurance Com Blog Health Insurance Articles HealthDraku DakpaeNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Feedback Mechanism Cell Organ Tissue: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument1 pageHomeostasis and Feedback Mechanism Cell Organ Tissue: Anatomy & PhysiologyFaisa SalmaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy (An Orientation) : Dr. Tanveer Ahmed KhanDocument67 pagesHuman Anatomy (An Orientation) : Dr. Tanveer Ahmed KhanShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument1 pageCells and TissuesMohamad Syafie Bin SamsirNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 2 Organ Systems Overview Grp1 A28Document3 pagesWork Sheet 2 Organ Systems Overview Grp1 A28Japet Floyd AlipioNo ratings yet
- W1 L2 - FigureDocument1 pageW1 L2 - FigureRandomNo ratings yet
- How Do I Carry Out A Resonance Test?Document1 pageHow Do I Carry Out A Resonance Test?Inayattullah KhamkerNo ratings yet
- 22 Lecture PresentationDocument88 pages22 Lecture PresentationLeilaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument50 pagesUrinary SystemNunai SalipadaNo ratings yet
- ICC MedicalDocument43 pagesICC MedicalDaniel100% (1)
- Embryo Slide 7Document1 pageEmbryo Slide 7aaaNo ratings yet
- Reflex Areas Palms and FootDocument5 pagesReflex Areas Palms and Footdonald duckNo ratings yet
- Genetal JantanDocument39 pagesGenetal JantanBakas Afrandy WirawanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System With HighlightsDocument150 pagesReproductive System With HighlightsReinand Joseff ServanoNo ratings yet
- The Body1Document1 pageThe Body1Aya OsamaNo ratings yet
- Reflexology ChartDocument1 pageReflexology ChartEng. Sam100% (2)
- General Stem Cell Biology BrochureDocument32 pagesGeneral Stem Cell Biology BrochureSigma-AldrichNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System EditedDocument80 pagesEndocrine System EditedKyle Gwyneth BobierNo ratings yet
- Reflexology Association of Canada - Foot Chart: Plantar ViewDocument1 pageReflexology Association of Canada - Foot Chart: Plantar ViewprabhaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesFetal Growth and DevelopmentJas SlkNo ratings yet
- 1 - Male Reproductive SystemDocument10 pages1 - Male Reproductive SystemIbsa AbdulwabNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys - Position - Structure - Vasculature - TeachMeAnatomyDocument5 pagesThe Kidneys - Position - Structure - Vasculature - TeachMeAnatomystar shipNo ratings yet
- All Imp Diagrams Class 10Document15 pagesAll Imp Diagrams Class 10unknown starNo ratings yet
- Foot&Hand Map ReflexoDocument6 pagesFoot&Hand Map Reflexomusa_cristianNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument46 pagesReproductionDeshmukh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 7 - Autonomic Nervous Systemmichael3vo-1No ratings yet
- Animalia Kingdom: CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesAnimalia Kingdom: CharacteristicsIldefonso MuñozNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Lecture PresentationDocument90 pagesCH 01 Lecture PresentationNie TofuNo ratings yet
- YNSAengl Trainingcomplete PDFDocument77 pagesYNSAengl Trainingcomplete PDFfaikhaaNo ratings yet
- 18 03 2017YNSAengl - HandoutcompleteDocument77 pages18 03 2017YNSAengl - HandoutcompleteGanga Singh100% (1)
- 7 MM FrogDocument28 pages7 MM FrogNiki Reroll04No ratings yet
- The Human Body: An Orientation: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument79 pagesThe Human Body: An Orientation: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical Collegeenewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- Web Launch 2020Document1 pageWeb Launch 2020api-534316253No ratings yet
- Aparatos y sistemas-APPARATUS AND SYSTEMSDocument10 pagesAparatos y sistemas-APPARATUS AND SYSTEMSAzucena OrtizNo ratings yet
- The Human BodyDocument1 pageThe Human BodyMaria TaratielNo ratings yet
- Interpreting PDX Dot BlotsDocument2 pagesInterpreting PDX Dot BlotsSpy CameraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 Reproductive System PDFDocument172 pagesCHAPTER 16 Reproductive System PDFAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument118 pagesThe Endocrine Systemtran anhkhoaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy TermsDocument1 pageAnatomy TermsStephanie MolinaNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Cairan - DR Harijadi PDFDocument50 pagesFisiologi Cairan - DR Harijadi PDFChristian SiagianNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 Reproductive SystemDocument172 pagesCHAPTER 16 Reproductive SystemCindy BelmesNo ratings yet
- LP1 - TerminologyDocument17 pagesLP1 - Terminologystephcruz0726No ratings yet
- Guyton Physiology Trang 784 796Document13 pagesGuyton Physiology Trang 784 796Bùi Nguyễn Yến VyNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument42 pagesNervous TissueKatherineVoNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Plant Tissues Animal TissuesDocument1 pageTissues: Plant Tissues Animal TissuesRAM MISHRANo ratings yet
- Examples of TissuesDocument2 pagesExamples of Tissuessoumya dishriNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For Nurses PDFDocument22 pagesUrinary System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For Nurses PDFKhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Responses To Exercise-1Document48 pagesHormonal Responses To Exercise-1CHANGEZ KHAN SARDARNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument4 pagesAcute Renal FailureKim GarciaNo ratings yet
- Group D Case Study Cushing SyndromeDocument6 pagesGroup D Case Study Cushing SyndromeMari IllustriousNo ratings yet
- Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kelancaran Pengeluaran ASI Pada Ibu Menyusui Di Puskesmas Rumbai Bukit PekanbaruDocument11 pagesFaktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kelancaran Pengeluaran ASI Pada Ibu Menyusui Di Puskesmas Rumbai Bukit PekanbaruFitri AndaliaNo ratings yet
- Human Body in Health and Disease 7th Edition Thibodeau Test BankDocument22 pagesHuman Body in Health and Disease 7th Edition Thibodeau Test Banklaeliacaixpoyf100% (32)
- NEUROTRANSMITTERDocument28 pagesNEUROTRANSMITTERiqiqiqiqiq100% (1)
- Science and Health: Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesScience and Health: Digestive SystemAnonymous yIlaBBQQ100% (1)
- Skrining HK Pada GAKIDocument33 pagesSkrining HK Pada GAKIdiyahNo ratings yet
- Oxford Stroke ClassificationDocument1 pageOxford Stroke ClassificationSyimah UmarNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document9 pagesModule 5CamilleCalmaLenonNo ratings yet
- Iycf AsiaDocument68 pagesIycf AsiaYahye CMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - The Theory of Essence, Qi, Blood and Body FluidsDocument10 pagesChapter 3 - The Theory of Essence, Qi, Blood and Body FluidsAudrygodwynNo ratings yet
- Booklet Mecup 2019Document4 pagesBooklet Mecup 2019Andika Ajie PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Smua ElpDocument19 pagesSmua ElpAzri Asyraf AsariNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of KidneyDocument13 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of KidneyEmira EzunaNo ratings yet
- Baroreceptor Reflex (Costanzo 3rd Ed)Document2 pagesBaroreceptor Reflex (Costanzo 3rd Ed)Gita FebrianyNo ratings yet
- Point Selection 1Document1 pagePoint Selection 1Alex ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Pleura: LungsDocument7 pagesPleura: LungsbarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Bio 10th - Excretion - Extensive TestDocument1 pageBio 10th - Excretion - Extensive TestDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Body An OrientationDocument59 pages1.1 The Human Body An OrientationDon KeyNo ratings yet
- GI System AssessmentDocument60 pagesGI System AssessmentAmyNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Anfisman2Document30 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Anfisman2Aswin Gumelar R.No ratings yet
- Pancreas Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument34 pagesPancreas Anatomy and PhysiologySourabh MishraNo ratings yet
- Pharm-Immuno 9-11 Cell Mediated Immunity: Dr. Saber HusseinDocument48 pagesPharm-Immuno 9-11 Cell Mediated Immunity: Dr. Saber Husseinmmoney1No ratings yet
- Atelectasis: CausesDocument4 pagesAtelectasis: Causesaznknight323No ratings yet
- Respiratory TransesDocument4 pagesRespiratory TransesAriane Shane BidoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of STEMI and NSTEMI Patients in The Emergency DepartmentDocument4 pagesComparison of STEMI and NSTEMI Patients in The Emergency DepartmentazizhaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System 1. List The Functions of The KidneysDocument6 pagesUrinary System 1. List The Functions of The KidneysheerNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept Mapmild_tea100% (1)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (516)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationFrom EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (37)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)