Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Study Guide-Heredity (Atharva)
Science Study Guide-Heredity (Atharva)
Uploaded by
Atharva Satpute0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThis science study guide covers key concepts of heredity including:
1) Variation can be continuous with a wide range of values or discontinuous with only certain characteristics present. Species are groups that can reproduce to make offspring that can also reproduce.
2) Asexual reproduction does not require a mate while meiosis is used in sexual reproduction and forms gametes like eggs and sperm that are haploid.
3) DNA consists of a double helix with base pairs of adenine-thymine and cytosine-guanine that link the strands together through weak hydrogen bonds.
Original Description:
Original Title
Science Study Guide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis science study guide covers key concepts of heredity including:
1) Variation can be continuous with a wide range of values or discontinuous with only certain characteristics present. Species are groups that can reproduce to make offspring that can also reproduce.
2) Asexual reproduction does not require a mate while meiosis is used in sexual reproduction and forms gametes like eggs and sperm that are haploid.
3) DNA consists of a double helix with base pairs of adenine-thymine and cytosine-guanine that link the strands together through weak hydrogen bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesScience Study Guide-Heredity (Atharva)
Science Study Guide-Heredity (Atharva)
Uploaded by
Atharva SatputeThis science study guide covers key concepts of heredity including:
1) Variation can be continuous with a wide range of values or discontinuous with only certain characteristics present. Species are groups that can reproduce to make offspring that can also reproduce.
2) Asexual reproduction does not require a mate while meiosis is used in sexual reproduction and forms gametes like eggs and sperm that are haploid.
3) DNA consists of a double helix with base pairs of adenine-thymine and cytosine-guanine that link the strands together through weak hydrogen bonds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Science Study Guide-Heredity (Atharva)
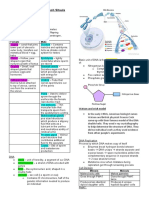
Variation- differentiating characteristics of an object
Continuous- wide range of values
Discontinuous- only a certain characteristic or not
Species- group of animals that can reproduce with each other to produce
offspring which can also reproduce
Asexual reproduction- reproduction that doesn’t require a mate
Mitosis- form of cloning itself, used in cell division
Meiosis- used for cell division, used in sexual reproduction
Gamete- egg and sperm cells (also called haploid, which means half)
Body Cells- Diploid, 23 chromosome pairs , 46 chromosome
Genome- all the DNA in each cell in an organism
DNA- Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
Gene- section of chromosomes that codes for your characteristics
23rd pair is special because it is called sex chromosome and it determines gender
xx- female
xy-male
DNA consists of these:
Adenine-Thymine
Cytosine-Guanine
DNA consists of a double helix, with 2 stands coiled and the strands are linked
through 2 specific base pairs.
A weak hydrogen bond joins the base pairs together.
The two strands in a DNA module are made of sugar and phosphate.
Allele- A form of a gene.
W have 2 alleles of every gene. If they are both the same, we call it homozygous
and if not then heterozygous.
Dominant- The stronger allele.
Recessive- The weaker allele.
Gene- Section of your chromosomes that codes for your characteristics.
Genotype- Different alleles that an organism has.
Phenotype-The characteristic an organism has.
Clone- a genetic copy of another single organism or group of cells
Genetic engineering- removing a gene from an organism and inserting it into
another organism.
You might also like
- Lesson 3 - Personal Power Lab - AtharvaDocument3 pagesLesson 3 - Personal Power Lab - AtharvaAtharva Satpute50% (4)
- Science Selection Exam NotesDocument58 pagesScience Selection Exam Notesibrahim.chauhdary7No ratings yet
- Genetics DefinitionsDocument1 pageGenetics DefinitionsvaughanNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument2 pagesBio NotesEmily Tsang-xNo ratings yet
- Holmesan123 GeneticsDocument2 pagesHolmesan123 GeneticsdanishNo ratings yet
- NOTESSSSSDocument8 pagesNOTESSSSSBauGarpNo ratings yet
- Genetics Vocabulary: A A, PB, or HIS4Document4 pagesGenetics Vocabulary: A A, PB, or HIS4Andrey_gpNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument2 pagesDefinitions - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Revision Yr10Document10 pagesGenetics Revision Yr10Rachel QuahNo ratings yet
- Bio Term DefinitionDocument2 pagesBio Term DefinitionElle HoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Terms and DefinitionsDocument4 pagesGenetic Terms and DefinitionsRICKSON KAWINANo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 VocabDocument1 pageChapter 13 VocababNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Term 3Document17 pagesScience Notes Term 3Ollie StocksNo ratings yet
- Mama Papa CytogeneticsDocument16 pagesMama Papa CytogeneticsKaneki KenNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument4 pagesInheritanceThimani WijepalaNo ratings yet
- Science Exam Preparations - Joel TDocument12 pagesScience Exam Preparations - Joel TvaughanNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument2 pagesMITOSISCUIZON, GEORDETTE DIVINENo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument2 pagesDefinitions - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEG VeezNo ratings yet
- HSB - Study NotesDocument1 pageHSB - Study NotesRayad AliNo ratings yet
- Key Points (2 Copies)Document1 pageKey Points (2 Copies)Zendrix PauloNo ratings yet
- Biology: What Is Living Organisms?Document13 pagesBiology: What Is Living Organisms?Rohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- X Bio Masterkey Definition 22 - 236Document44 pagesX Bio Masterkey Definition 22 - 236Varenayam editzNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and GametogenesisDocument24 pagesCell Division and Gametogenesisaqsa shafiqueNo ratings yet
- Genetics Year 10 NSW 2022Document10 pagesGenetics Year 10 NSW 2022Rachel QuahNo ratings yet
- 3.0 DNA Is The Inherited Material Responsible For VariationDocument62 pages3.0 DNA Is The Inherited Material Responsible For VariationNick YamNo ratings yet
- Inheritance: Genetic InformationDocument15 pagesInheritance: Genetic InformationJorifNo ratings yet
- 4 - Chromosomes and Their AbnormalitiesDocument146 pages4 - Chromosomes and Their AbnormalitiesJustina VillageNo ratings yet
- Biological Foundation of Human Development 01062022 123018pm 03102022 082939am 11032023 023436pmDocument40 pagesBiological Foundation of Human Development 01062022 123018pm 03102022 082939am 11032023 023436pmaisha ashrafNo ratings yet
- Genetics Vocabulary - Tanisha MDocument5 pagesGenetics Vocabulary - Tanisha Malgu46368No ratings yet
- Science Study Notes (Genes and Chromosomes, Genotype and Phenotype)Document2 pagesScience Study Notes (Genes and Chromosomes, Genotype and Phenotype)Reinne Louise RegalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HredirtyDocument15 pagesUnit 2 HredirtyMarga AbabaNo ratings yet
- Biology 10 2 DNA Genes and ChromosomesDocument26 pagesBiology 10 2 DNA Genes and ChromosomesAvegail YsidoroNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Mendel: Meiosis: The Process of Producing Haploid Sex CellsDocument32 pagesMeiosis and Mendel: Meiosis: The Process of Producing Haploid Sex CellsshiyiNo ratings yet
- Lapuz - GeneticsDocument3 pagesLapuz - GeneticsEllyza LapuzNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes NotesDocument10 pagesChromosomes Notesapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Dna GenesDocument23 pagesDna GenesKevin KibirNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer For Summative 4th QuarterDocument5 pagesScience Reviewer For Summative 4th QuartermcassandraabelisssNo ratings yet
- The Structure of DNA: Thymine, T Adenine, A Guanine, G Cytosine, CDocument5 pagesThe Structure of DNA: Thymine, T Adenine, A Guanine, G Cytosine, Cshalinta tyagiNo ratings yet
- Science Notes 2022 GEDocument12 pagesScience Notes 2022 GESukritNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Bio NotesDocument14 pagesChapter 18 Bio Notesgeezariana790No ratings yet
- Cellular Reproduction and GeneticsDocument31 pagesCellular Reproduction and GeneticsMary Grace LemonNo ratings yet
- 3 Genetics: 3.1 GenesDocument22 pages3 Genetics: 3.1 Genesapi-285490927100% (1)
- The Cell: Basic Unit of Plant & Animal LifeDocument11 pagesThe Cell: Basic Unit of Plant & Animal Lifepotionyesterday100% (2)
- BSC1005L Notes SheetDocument4 pagesBSC1005L Notes Sheet9ch4g2qpc6No ratings yet
- Science Review Q2 TestDocument3 pagesScience Review Q2 TestkccerenioNo ratings yet
- Genetics, DNA & Evolution - : Topic NotesDocument10 pagesGenetics, DNA & Evolution - : Topic NotesAljanna LameraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal Science - 1Document14 pagesIntroduction To Animal Science - 1Jesus Gomez Cortizzo100% (1)
- Inheritance NotesDocument3 pagesInheritance NotesTashwaar TamimNo ratings yet
- Cytomls - Prelims ReviewerDocument7 pagesCytomls - Prelims ReviewerJohn Oliver AsiaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis CH 5.3 7thDocument24 pagesMeiosis CH 5.3 7ththegedusNo ratings yet
- Module of GeneticsDocument29 pagesModule of GeneticsbiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - Genetics NotesDocument8 pagesUNIT 3 - Genetics NotesJB - 10SS 731765 Harold M Brathwaite SSNo ratings yet
- 1A - Genetics Notes (MAIN)Document54 pages1A - Genetics Notes (MAIN)KRISH MEDIRATTANo ratings yet
- Cytomls - Prelims ReviewerDocument10 pagesCytomls - Prelims ReviewerxoxoNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument54 pagesGeneticsBrian James BurtonNo ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 Study Notes P2Document14 pagesLIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 Study Notes P2thatohatsihlohonolofatsoNo ratings yet
- Biologia Tema 2Document4 pagesBiologia Tema 2María GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - 5 BIOLOGY GENETICS - MITOSISDocument11 pagesKami Export - 5 BIOLOGY GENETICS - MITOSISgefegNo ratings yet
- Structure-of-Chromosomes-Cell-Cycle-and-Cell-DivisionDocument5 pagesStructure-of-Chromosomes-Cell-Cycle-and-Cell-DivisionKamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Precision and AccuracyDocument6 pagesPrecision and AccuracyAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Delegate Guide 2020 PDFDocument13 pagesDelegate Guide 2020 PDFAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- CSEC Jan 2012 p2Document6 pagesCSEC Jan 2012 p2Atharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Physics Work Set 13th Dec 2021Document3 pagesPhysics Work Set 13th Dec 2021Atharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Homework - Fun Home (Sexuality Question)Document2 pagesHomework - Fun Home (Sexuality Question)Atharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table 1Document65 pagesPeriodic Table 1Atharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument19 pagesPeriodic TableAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Edited Stoichiometry WorkbookDocument43 pagesEdited Stoichiometry WorkbookAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 SyllabusDocument2 pagesTopic 2 SyllabusAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- An African Thunderstorm Analysis All LevelsDocument3 pagesAn African Thunderstorm Analysis All LevelsAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Astonishment - Poem AnalysisDocument2 pagesAstonishment - Poem AnalysisAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Periodicity (6 Hours) : Assessment Statement Obj Teacher's NotesDocument2 pagesTopic 3: Periodicity (6 Hours) : Assessment Statement Obj Teacher's NotesAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Total Periodic PresentationDocument33 pagesTotal Periodic PresentationAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Solids and LiquidsDocument27 pagesStates of Matter Solids and LiquidsAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 3Document63 pagesAtomic Structure 3Atharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Birdshooting Season Analysis All LevelsDocument4 pagesBirdshooting Season Analysis All LevelsAtharva Satpute100% (1)
- Ol Higue 1st LevelDocument2 pagesOl Higue 1st LevelAtharva Satpute100% (1)
- To Kill A Mockingbird EssayDocument2 pagesTo Kill A Mockingbird EssayAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Once Upon A Time Analysis All LevelsDocument4 pagesOnce Upon A Time Analysis All LevelsAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- To Kill A Mockingbird Chapters 1-11 3rd LevelDocument2 pagesTo Kill A Mockingbird Chapters 1-11 3rd LevelAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- To Kill A Mockingbird Essay, 1 DraftDocument2 pagesTo Kill A Mockingbird Essay, 1 DraftAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- TKAM CSEC TEST InstructionsDocument1 pageTKAM CSEC TEST InstructionsAtharva Satpute100% (1)
- Emma, 3 Level Reading: By: AtharvaDocument2 pagesEmma, 3 Level Reading: By: AtharvaAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- The U-Tube Manometer: By: Atharva and LillianDocument4 pagesThe U-Tube Manometer: By: Atharva and LillianAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Business Cognate School Based AssessmentDocument10 pagesBusiness Cognate School Based AssessmentAtharva Satpute100% (1)