Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Voltage Drop Calculation
Uploaded by
Paolo CastillonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Voltage Drop Calculation
Uploaded by
Paolo CastillonCopyright:
Available Formats
V OLTAGE D ROP C ALCULATION
Albert C. Velasco
This presentation uses a free template provided by FPPT.com
www.free-power-point-templates.com
Objectives
Given all the circuit parameters required, the listeners will be able to:
1. Calculate the voltage drop in each circuit ; and
2. Determine solutions on voltage drop problems;
In accordance with the Philippine Electrical Code 2017.
2 Voltage Drop Calculation
What to Expect
1. The Ohm’s Law and Power Formula
2. Voltage Drop Calculation
3. Examples
3 Voltage Drop Calculation
Voltage Drop (VD)
• amount of voltage loss that occurs through all parts of a
circuit due to impedance
• Wasted energy
• Reduction of voltage caused by energy lost at the medium
5 Voltage Drop Calculation
Effects of VD in Electrical Equipment
• Reduced efficiency
• Heating of apparatus
• Heating of conductors
• High current/ Overload
• Flickering of Lights
• Vibration of motors
6 Voltage Drop Calculation
The Ohm’s Law (Resistivity)
𝐿
𝑅= ρ
𝐴
where: R is the resistance in ohms
ρ is the resistivity constant of material
L is the length
ρ CU = 1.68 x 10-8 Ω-m A is the cross- sectional area
ρ AL = 2.65 x 10-8 Ω-m
7 Voltage Drop Calculation
The Ohm’s Law (Resistivity)
𝐿
𝑅α
𝐴
8 Voltage Drop Calculation
The Ohm’s Law
𝐸 𝐸
𝑅= 𝑅α
𝐼 𝐼
where: R is the resistance in ohms
E is the voltage, in volts, across the
resistance
I is the current that passes through the
resistance in amperes
9 Voltage Drop Calculation
Power Formula
𝐸*
𝑃=
𝑅
Normal, E = 230 V Abnormal voltage
E = 218.5 V
VD = 11.5 (%VD = 5%)
230* 218.5*
𝑃= = 5.29 kW 𝑃= = 4.77 kW
10 10
% Power Reduction = 9.83 %
10 Voltage Drop Calculation
Addressing Voltage Drop Problems
1. Reduce load
2. Break the circuit into several parts
3. Shorten circuit run
4. Increase wire size
5. Use higher efficient devices
6. Replace conductors with higher conductivity*
11 Voltage Drop Calculation
Voltage Drop Formula
General Formula
Common Types of Circuits
1. Single- Phase
VD=ILoad Zwire
2. Three- Phase
where:
𝑍 = √(𝑅 * + 𝑋 * )
12 Voltage Drop Calculation
Voltage Drop Formula
Single- Phase Circuits
𝐿 1
𝑉𝐷 = 2𝐼 𝑍 ( )( )
305 𝑁
where:
Z is the wire impedance, Ω
L is the total length of wire, m
N is the number of sets
13 Voltage Drop Calculation
Voltage Drop Formula
Three- Phase Circuits
𝐿 1
𝑉𝐷 = 𝐼 3𝑍 ( )( )
305 𝑁
where:
Z is the wire impedance, Ω
L is the total length of wire, m
N is the number of sets
Voltage drop in 3- phase system uses the Line to Neutral
14 Voltage Drop Calculation
2.15.1.2 Minimum Rating and Size (Feeders)
FPN No. 2: Conductors for feeders, as defined in Art. 1.1, sized to
prevent a voltage drop exceeding 3 percent at the farthest outlet of
power, heating, and lighting loads, or combination of such loads, and
where the maximum total voltage drop on both feeders and branch
circuits to the farthest outlet does not exceed 5 percent, will provide
reasonable efficiency of operation.
Philippine Electrical Code 2017, page 51
15 Voltage Drop Calculation
2.10.2.2 Minimum Ampacity and Size (Branch Circuit)
FPN No. 4: Conductors for branch circuit, as defined in Art. 1.1, sized
to prevent a voltage drop exceeding 3 percent at the farthest outlet of
power, heating, and lighting loads, or combination of such loads, and
where the maximum total voltage drop on both feeders and branch
circuits to the farthest outlet does not exceed 5 percent, will provide
reasonable efficiency of operation.
Philippine Electrical Code 2017, page 42
16 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 1
230 V, 1-Ø 𝑍 = √(𝑅 * + 𝑋 * )
𝑍 = √[ 0.78 * + 0.065 * ]
2-8mm2 THHN, 10m
32A 𝒁 = 𝟎. 𝟕𝟖𝟐𝟕 𝜴
MSE 𝐿 1
𝑉𝐷 = 2 𝐼𝑍 ( )( )
305 𝑁
2-2mm2 THHN, 20m 10 1
𝑉𝐷 = 2(32)(0.7827)( )( )
305 1
M 2 hp, 230V, 12A 𝑽𝑫 = 𝟏. 𝟔𝟒𝟐 𝐕
17 Voltage Drop Calculation
PEC 2017, page 942
8.0 mm2
X = 0.065 Ω
R = 0.78 Ω
18 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 1
230 V, 1-Ø
𝑉𝐷 = 1.642 V
2-8mm2 THHN, 10m 𝑉𝑀𝑆𝐸 = 230 − 1.642 = 𝟐𝟐𝟖. 𝟑𝟓𝟖 𝑽
32A
MSE (228.358 V) 𝑉𝐷
%𝑉𝐷 =
𝑉𝑆
2-2mm2 THHN, 20m 1.642
%𝑉𝐷 = 100 = 0.71% (𝑝𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑑)
230
M 2 hp, 230V, 12A
19 Voltage Drop Calculation
230 V, 1-Ø
2-8mm2 THHN
32A
MSE
2-2mm2 THHN
M 2 hp, 230V, 12A
PEC 2017, page 942
20 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 1
230 V, 1-Ø 𝑍 = √(𝑅 * + 𝑋 * )
𝑍 = √[ 3.1 * + 0.073 * ]
2-8mm2 THHN, 10m
32A 𝒁 = 𝟑. 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟖𝟔 𝜴
MSE (228.358 V) 𝐿 1
𝑉𝐷 = 2 𝑍 ( )( )
305 𝑁
2-2mm2 THHN, 20m 20 1
𝑉𝐷 = 2(12)(3.10086)( )( )
305 1
M 2 hp, 230V, 12A 𝑽𝑫 = 𝟒. 𝟖𝟖 v
21 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 1
230 V, 1-Ø
𝑉𝐷 = 4.88 v
𝑉𝑀𝑜𝑡𝑜𝑟 = 228.358 − 4.88 = 𝟐𝟐𝟑. 𝟒𝟕𝟖 𝑽
2-8mm2 THHN, 10m
32A
𝑉𝐷𝑇
MSE (228.358 V) %𝑉𝐷 =
𝑉𝑆
(230 − 223.478)
2-2mm2 THHN, 20m %𝑉𝐷 = 100
230
%𝑉𝐷 = 2.84% (passed)
M 2 hp, 230V, 12A
(223.478 V)
22 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 2
230 V, 3-Ø
3-38mm2 THHN, 25m
105A
MSE
3-8mm2 THHN, 20m
M 10 hp, 230V, 28A
PEC 2017, page 942
23 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 2
230 V, 3-Ø 𝑍 = √(𝑅 * + 𝑋 * )
𝑍 = √[ 0.16 * + 0.057 * ]
3-38mm2 THHN, 25m
105A 𝒁 = 𝟎. 𝟏𝟔𝟗𝟖𝟓 𝜴
MSE 𝐿 1
𝑉𝐷 = 𝐼 3 𝑍 ( )( )
305 𝑁
3-8mm2 THHN, 20m 25 1
𝑉𝐷 = 105( 3)(0.16985)( )( )
305 1
M 10 hp, 230V, 28A 𝑽𝑫 = 𝟐. 𝟓𝟑𝟐 v
24 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 2
230 V, 3-Ø
𝑉𝐷 = 2.532 v
3-38mm2 THHN, 25m 𝑉𝑀𝑆𝐸 = 230 − 2.532 = 𝟐𝟐𝟕. 𝟒𝟔𝟖 𝑽
105A
MSE (227.468 V) 𝑉𝐷
%𝑉𝐷 =
𝑉𝑆
3-8mm2 THHN, 20m 2.532
%𝑉𝐷 = 100 = 1.10% (𝑝𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑑)
230
M 10 hp, 230V, 28A
25 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 2
230 V, 3-Ø
3-38mm2 THHN, 25m
105A
MSE
3-8mm2 THHN, 20m
M 10 hp, 230V, 28A
PEC 2017, page 942
26 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 2
230 V, 3-Ø 𝑍 = √(𝑅 * + 𝑋 * )
𝑍 = √[ 0.78 * + 0.065 * ]
3-38mm2 THHN, 25m
105A 𝒁 = 𝟎. 𝟕𝟖𝟐𝟕 𝜴
MSE (227.468 V) 𝐿 1
𝑉𝐷 = 𝐼 3 𝑍 ( )( )
305 𝑁
3-8mm2 THHN, 20m 20 1
𝑉𝐷 = 28( 3)(0.7827) )( )
305 1
M 10 hp, 230V, 28A 𝑽𝑫 = 𝟐. 𝟒𝟖𝟗𝟏 v
27 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 2
230 V, 3-Ø
𝑉𝐷 = 2.4891 v
3-38mm2 THHN, 25m 𝑉𝑀𝑜𝑡𝑜𝑟 = 227.468 − 2.4891 = 𝟐𝟐𝟒. 𝟗𝟕𝟖𝟗 𝑽
105A
MSE (227.468 V) 𝑉𝐷
%𝑉𝐷 =
𝑉𝑆
3-8mm2 THHN, 20m (230 − 224.9789)
%𝑉𝐷 = 100
230
M 10 hp, 230V, 28A %𝑉𝐷 = 2.18% (𝑝𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑑)
(224.9789 V)
28 Voltage Drop Calculation
Example 3
29 Voltage Drop Calculation
Summary
1. Discussed the Ohm’s Law
2. Explain the relation of power formula
3. Solved some VD problems
30 Voltage Drop Calculation
References
1. Philippine Electrical Code 2017
2. https://en.wikipedia.org
3. https://electrical-engineering-portal.com
31 Voltage Drop Calculation
Assessment
1. Which of the following has greatest voltage drop?
a. 1- ⌀ circuit, 100 m run, 10 A, 22 mm2 TW wire, 25 mm dia. uPVC
b. 1- ⌀ circuit, 50 m run, 10 A, 22 mm2 TW wire, 25 mm dia. uPVC
c. 3- ⌀ circuit, 100 m run, 10 A, 22 mm2 TW wire, 25 mm dia. uPVC
d. 3- ⌀ circuit, 50 m run, 20 A, 22 mm2 TW wire, 25 mm dia. uPVC
32 Voltage Drop Calculation
Assessment
2. A voltage drop of 5% and below from ______ to ______ is considered
passed, as per PEC 2017.
a. Service point to main service equipment
b. Mains service equipment to the last outlet of the branch circuit
c. Panel board to the last outlet of the branch circuit
d. Service point to the last outlet of the branch circuit
33 Voltage Drop Calculation
End of Presentation
34 Voltage Drop Calculation
You might also like
- Meralco StandardsDocument28 pagesMeralco StandardsBenj Alvarez Capistrano100% (2)
- All The Words I Should Have Said - Rania NaimDocument167 pagesAll The Words I Should Have Said - Rania NaimNan Nan100% (2)
- Electrical Power System Design of High-Rise ResidentialDocument28 pagesElectrical Power System Design of High-Rise Residentialsjaveeds200383% (6)
- Symmetrical Components: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandSymmetrical Components: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Elec'ldesignanalysis Voltagedrop Shortcktcalcs PDFDocument120 pagesElec'ldesignanalysis Voltagedrop Shortcktcalcs PDFRaymond CoronaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Voltage Drop and Short Circuit Calculation PDFDocument12 pagesLecture 12 Voltage Drop and Short Circuit Calculation PDFGhunElardeNo ratings yet
- 35kv Xlpe Phelps Dodge PDFDocument2 pages35kv Xlpe Phelps Dodge PDFRodney LanagNo ratings yet
- CCTV PlanDocument1 pageCCTV PlanMyto MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Principles for Technicians: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandElectrical Engineering Principles for Technicians: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- PPA Application - 2700 Sloat BLVD (283 Units)Document8 pagesPPA Application - 2700 Sloat BLVD (283 Units)Sasha PerigoNo ratings yet
- Rubber Examination Gloves: Standard Specification ForDocument5 pagesRubber Examination Gloves: Standard Specification ForNguyễn Bảo TrâmNo ratings yet
- VOLTAGE DROP AND FAULT CURRENT CALCULATIONS - IIEE PresentationDocument210 pagesVOLTAGE DROP AND FAULT CURRENT CALCULATIONS - IIEE PresentationEarl Jenn Abella100% (1)
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- 3 Introduction To PECDocument24 pages3 Introduction To PECJay Sunga VillanNo ratings yet
- PEC Module1Document36 pagesPEC Module1John Israel CorpusNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectrical Design AnalysisJerome Virgo Catipay100% (2)
- What Should Be The Contents of My Electrical Plan - Based On PEC 2017 - Electrical Engineer ResourcesDocument15 pagesWhat Should Be The Contents of My Electrical Plan - Based On PEC 2017 - Electrical Engineer ResourcesJCuchapin100% (1)
- Module Introduction: This Module Will Contribute A Great Help To The StudentsDocument7 pagesModule Introduction: This Module Will Contribute A Great Help To The StudentsDanzel SepilloNo ratings yet
- Pec 2009 BookDocument60 pagesPec 2009 BookQueeny Verba83% (12)
- Short Circuit Calculations IIEE v5 - 1Document82 pagesShort Circuit Calculations IIEE v5 - 1kranthikoyyadaNo ratings yet
- EE405 Electrical System DesignDocument2 pagesEE405 Electrical System DesignHari KrishnanNo ratings yet
- IIEE Load Calculation and Voltage Drop PresentationDocument35 pagesIIEE Load Calculation and Voltage Drop PresentationJosamy Martinez100% (1)
- EE 158 - Electrical System Design (LECTURE 1)Document29 pagesEE 158 - Electrical System Design (LECTURE 1)Rovick Tarife0% (1)
- How To Become A Professional Electrical EngineerDocument27 pagesHow To Become A Professional Electrical Engineerrenante donidaNo ratings yet
- Riser Diagram 1 Single Line Diagram 2: General Notes and SpecificationDocument11 pagesRiser Diagram 1 Single Line Diagram 2: General Notes and SpecificationCarlo DoragosNo ratings yet
- Group3 Electrical System DesignDocument8 pagesGroup3 Electrical System DesignChristian AldeNo ratings yet
- Pec Provisions For Electrical System DesignDocument133 pagesPec Provisions For Electrical System DesignMira Alvarez100% (1)
- Pec Based Electrical Wiring Design Simulator For Commercial UnitsDocument50 pagesPec Based Electrical Wiring Design Simulator For Commercial Unitsnap_carino100% (1)
- Reviewer For RME-PEC ExamDocument61 pagesReviewer For RME-PEC ExamJeff CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Technical Presentation 2022 ANCPEC1Document112 pagesTechnical Presentation 2022 ANCPEC1elciNo ratings yet
- Basic Substation LectureDocument60 pagesBasic Substation LectureBer Salazar Jr67% (3)
- Short Circuit AnalysisDocument43 pagesShort Circuit AnalysisKouji Tomas0% (1)
- MR - Mentoring EE Educators Towards PEEEngr. Cirilo Calibjo Nov. 27 2015Document74 pagesMR - Mentoring EE Educators Towards PEEEngr. Cirilo Calibjo Nov. 27 2015ramelNo ratings yet
- Ee Laws Codes and Professional Ethics Bsee 201a Ella Mae D. Detablan Le2 PDFDocument26 pagesEe Laws Codes and Professional Ethics Bsee 201a Ella Mae D. Detablan Le2 PDFMark Lawrence BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Electrical System of The Pagamutan NG Dasmariñas Isbn 9781685642761Document217 pagesAssessment of Electrical System of The Pagamutan NG Dasmariñas Isbn 9781685642761YVES GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Philippine Electrical Code #5Document116 pagesPhilippine Electrical Code #5Jeffrey AlimarioNo ratings yet
- Refresher 1 2016 Philippine Electrical CodeDocument41 pagesRefresher 1 2016 Philippine Electrical CodeMylene100% (1)
- Practical TransformerDocument9 pagesPractical TransformerCJP TVNo ratings yet
- Pec Answers 1 To 100Document7 pagesPec Answers 1 To 100Kian Tecson100% (5)
- EE 104 Lecture 1 - Fundamental PrinciplesDocument31 pagesEE 104 Lecture 1 - Fundamental PrinciplesRogzJrBernzNo ratings yet
- WiringDocument23 pagesWiringNoel NantesNo ratings yet
- Basic Relaying IieeDocument59 pagesBasic Relaying Iieejanine colladoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design 101 40Document1 pageElectrical Design 101 40jungatbuntonNo ratings yet
- Electrical System Design - Lec2 PDFDocument39 pagesElectrical System Design - Lec2 PDFtowiwaNo ratings yet
- Sample Guide in TER PreparationDocument3 pagesSample Guide in TER PreparationLilet P. DalisayNo ratings yet
- PEC 2017 Short Circuit Calculation SampleDocument8 pagesPEC 2017 Short Circuit Calculation SamplemarvinNo ratings yet
- PEC OverviewDocument14 pagesPEC OverviewLauren OlivosNo ratings yet
- 11a. Electrical ComputationsDocument1 page11a. Electrical Computationsronald bayanNo ratings yet
- Rules On Governing RME, REE, and PEE Under RA 7920Document49 pagesRules On Governing RME, REE, and PEE Under RA 7920Arnulfo Lavares100% (1)
- Engr. Florencio D. BerenguelDocument79 pagesEngr. Florencio D. BerenguelJosamy MartinezNo ratings yet
- RME PEC Reviewer PDFDocument96 pagesRME PEC Reviewer PDFShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Fundamentals of Electrical Transmission and DistributionDocument29 pagesLecture 1 - Fundamentals of Electrical Transmission and DistributionJayson Bryan Mutuc100% (2)
- RMsE LectureDocument148 pagesRMsE Lectureuplbseles100% (10)
- Distribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electric Power CourseFrom EverandDistribution of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Distribution of Electric Power CourseNo ratings yet
- Local Media5941271462837301265Document65 pagesLocal Media5941271462837301265jason mr.perfect11No ratings yet
- Power System Analysis, Transformer Per UnitDocument31 pagesPower System Analysis, Transformer Per UnitSahib Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Voltage Drop and Short CircuitDocument39 pagesVoltage Drop and Short CircuitMinerva Abanto100% (1)
- Electrical AnalysisDocument4 pagesElectrical AnalysisjohnnycollideNo ratings yet
- Eda Bricolage PhilippinesDocument7 pagesEda Bricolage Philippinesven villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Load Loss and Positive Sequence Impedance TestDocument6 pagesTransformer Load Loss and Positive Sequence Impedance TestFabian Vazquez OrtegaNo ratings yet
- EXP 1-10 Manual HV LabbbbbbbbbbbbbbvbbbbbbbbDocument37 pagesEXP 1-10 Manual HV LabbbbbbbbbbbbbbvbbbbbbbbDEEPAK KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit CalculationsDocument44 pagesShort Circuit Calculationssasikumar100% (2)
- 10 - Notes - Transformers Part IDocument6 pages10 - Notes - Transformers Part IWillam MetzNo ratings yet
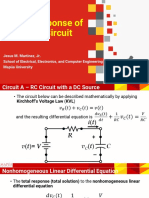
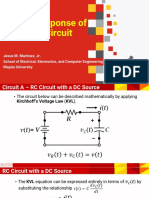
- Total Response of An RC CircuitDocument5 pagesTotal Response of An RC CircuitPaolo CastillonNo ratings yet
- Natural Response of An RC CircuitDocument6 pagesNatural Response of An RC CircuitPaolo CastillonNo ratings yet
- Forced Response of An RC CircuitDocument6 pagesForced Response of An RC CircuitPaolo CastillonNo ratings yet
- First-Order Switching CircuitDocument6 pagesFirst-Order Switching CircuitPaolo CastillonNo ratings yet
- Natural Response of An RC CircuitDocument6 pagesNatural Response of An RC CircuitPaolo CastillonNo ratings yet
- Total Response of An RC CircuitDocument5 pagesTotal Response of An RC CircuitPaolo CastillonNo ratings yet
- Forced Response of An RC CircuitDocument6 pagesForced Response of An RC CircuitPaolo CastillonNo ratings yet
- Arc Flash Analysis: Albert C. VelascoDocument28 pagesArc Flash Analysis: Albert C. VelascoPaolo CastillonNo ratings yet
- Learning Based Exposition-The Simple Present TenseDocument12 pagesLearning Based Exposition-The Simple Present Tenseyuri Berrocal YanceNo ratings yet
- Practical Questions BookletDocument37 pagesPractical Questions BookletPrecious ChirangareNo ratings yet
- Er9000en 21204 1.00Document106 pagesEr9000en 21204 1.00Alexandru AnghelNo ratings yet
- Reptilian Astral WarsDocument4 pagesReptilian Astral WarsAlienraces1No ratings yet
- 5 OPERATIVE Dentistry-Fifth year-FIFTH lect-16-4-2020-FAILURE OF RESTORATIONDocument24 pages5 OPERATIVE Dentistry-Fifth year-FIFTH lect-16-4-2020-FAILURE OF RESTORATIONIna YaNo ratings yet
- Reference Manual - Model 6487 Picoammeter/Voltage SourceDocument338 pagesReference Manual - Model 6487 Picoammeter/Voltage SourceRanilson AngeloNo ratings yet
- CompanyDocument7 pagesCompanylotchanNo ratings yet
- Egs630-6 Komatsu GensetDocument2 pagesEgs630-6 Komatsu GensetimamfadiliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations Research 11E Ise 11Th Ise Edition Frederick S Hillier Full ChapterDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Operations Research 11E Ise 11Th Ise Edition Frederick S Hillier Full Chapterrobin.mccomb793No ratings yet
- Cablemaster RLC - ManualDocument8 pagesCablemaster RLC - ManualGlendinning Products, LLC.No ratings yet
- Constructionandmaintenanceof Riverembankments (Levees) - GuidelinesDocument7 pagesConstructionandmaintenanceof Riverembankments (Levees) - GuidelinesSushil DhunganaNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Rawat Inap PDFDocument2 pagesFishbone Rawat Inap PDFAbdul NasirNo ratings yet
- BrusselsDocument1 pageBrusselskmiqdNo ratings yet
- Inside The Social Network's (Datacenter) NetworkDocument49 pagesInside The Social Network's (Datacenter) NetworkVamsi Krishna PatchamatlaNo ratings yet
- Nurs 624 Reference List ApaDocument4 pagesNurs 624 Reference List Apaapi-698538548No ratings yet
- To FrameDocument5 pagesTo FrameMuhaimin RohizanNo ratings yet
- 1000-211-V8-0000-01003 Concrete Works (Trial Mix)Document38 pages1000-211-V8-0000-01003 Concrete Works (Trial Mix)hodigojiggfjlgkdgiohghfdiohghjfNo ratings yet
- Rumus Fizik 2021Document1 pageRumus Fizik 2021Azizi Abdullah100% (1)
- Performance Evaluation of TDL Channels For Downlink 5G MIMO SystemsDocument4 pagesPerformance Evaluation of TDL Channels For Downlink 5G MIMO SystemspruxmanNo ratings yet
- Stsgroup 1Document13 pagesStsgroup 1Wenalyn Grace Abella LlavanNo ratings yet
- Penurunan Waktu Tunggu Operasi Elektif Dengan Membuat Standar Prosedur Operasional Di Rumah Sakit Umum Karsa Husada BatuDocument8 pagesPenurunan Waktu Tunggu Operasi Elektif Dengan Membuat Standar Prosedur Operasional Di Rumah Sakit Umum Karsa Husada BaturirisNo ratings yet
- GAP Guidelines: Management Programs (Overview)Document27 pagesGAP Guidelines: Management Programs (Overview)LleiLlei100% (1)
- Competency Assessment FormDocument2 pagesCompetency Assessment FormLielet MatutinoNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer EquipmentDocument28 pagesHeat Transfer Equipmentdeepak.dce.meNo ratings yet
- Getachew Final EditedDocument76 pagesGetachew Final EditedDesalegn DgaNo ratings yet
- Friday 11 January 2019: Health and Social CareDocument24 pagesFriday 11 January 2019: Health and Social CareAnette RodriguezNo ratings yet
- DT Unit2Document11 pagesDT Unit2riyafsharma2013No ratings yet