0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views2 pagesOverview of Animal Cell Structure
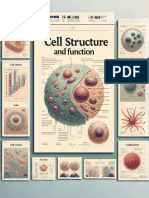
Animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts found in plant cells. The cell membrane protects the interior of the cell by selectively allowing substances to enter or exit. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that break down worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria. The endoplasmic reticulum is a network involved in protein and lipid synthesis, while the nucleus controls protein synthesis and contains DNA. The Golgi apparatus processes and packages macromolecules like proteins and lipids. Vesicles form during secretion, uptake, and transport within the cytoplasm. Ribosomes produce protein needed for cell functions. Mitochondria act as the cell's powerhouses by breaking down nutrients to create energy molecules.
Uploaded by
jerkCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views2 pagesOverview of Animal Cell Structure
Animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts found in plant cells. The cell membrane protects the interior of the cell by selectively allowing substances to enter or exit. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that break down worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria. The endoplasmic reticulum is a network involved in protein and lipid synthesis, while the nucleus controls protein synthesis and contains DNA. The Golgi apparatus processes and packages macromolecules like proteins and lipids. Vesicles form during secretion, uptake, and transport within the cytoplasm. Ribosomes produce protein needed for cell functions. Mitochondria act as the cell's powerhouses by breaking down nutrients to create energy molecules.
Uploaded by
jerkCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd