Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Terrestrial Ecosystem
Uploaded by
Gie Marie Francisco Umali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
123 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Terrestrial ecosystem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
123 views2 pagesTerrestrial Ecosystem
Uploaded by
Gie Marie Francisco UmaliCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
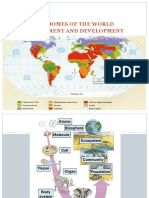
Terrestrial ecosystem
Is an ecosystem found only on lands.
A community of organisms and their environment that occurs on the land
masses of continents and islands.
Are distinguished from aquatic ecosystem by lower availability of water
and consequent importance of water limiting factor.
Are characterized by grater temperature fluctuations on both a diurnal
and seasonal basis than occur in aquatic ecosystem in similar climates.
The availability of light is greater in terrestrial ecosystem than in aquatic
ecosystem.
28.26% of Earth surface is occupied by terrestrial ecosystem.
Six primary terrestrial ecosystems exist:
1. TUNDRA: is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by low
temperatures and short growing seasons.
2. TAIGA: is also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome
characterized by coniferous forest consisting mostly of pines, spruces and
larches. Taiga is the largest biome apart from the oceans.
3. TEMPERATURE DECIDUOUS FOREST OR TEMPERATURE BROAD-LEAF
FOREST: are dominated by trees that lose their leaves each year. They are
found in areas with warm, moist summers and mild winters.
4. TROPICAL RAINFOREST: can be characterized in two words: hot and wet
5. GRASSLANDS: are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses;
however sedge and rush families can be also found. Grassland is fond in
most Eco regions of the Earth.
6. DESERT: is a barren area of land where little precipitation occurs and
consequently living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life
Aquatic Ecosystem
Is an ecosystem in a body form.
Communities of organisms that are dependent on each other and on their
environment live n aquatic ecosystem.
The two main types of aquatic ecosystem are marine ecosystems and
freshwater ecosystem.
TYPES
Marine
A marine ecosystem covers approximately 71% of the Earth’s surface and
contains approximately 97% of Earth’s water.
Marine ecosystem can be divided into many zones depending upon water
depth and shoreline features.
The oceanic zone is the vast open part of the ocean where animals such
whale, shark, and tuna live.
The benthic zone consists of substrates below water where many
invertebrates live.
The intertidal zone is the area between high and low tides.
Classes of organism n marine ecosystem include brown algae, din
flagellates, corals, cephalopods, echinoderms, and sharks.
Environmental problems concerning marine ecosystems include
unsustainable exploitation of marine resources example overfishing of
certain species, marine pollution, climate change, and building coastal
areas.
Freshwater
Freshwater ecosystem over 0.78% of Earth’s surface and inhabit 0.009% of
its total water.
There are three basics types of freshwater ecosystems:
1. LENTIC: slow moving water, including pools, ponds, and lakes.
2. LOTIC: faster moving water, for example streams and rivers.
3. WETLANDS: areas where soil is saturated or inundated for at last part of
the time.
Ponds
Ponds are small bodies of freshwater with shallow and still water, marsh,
and aquatic plants.
You might also like
- Curriculum Development (LET REVIEWER)Document3 pagesCurriculum Development (LET REVIEWER)Succeed Review92% (38)
- Quiz 3Document4 pagesQuiz 3Amelia BayonaNo ratings yet
- Professional Education ReviewerDocument16 pagesProfessional Education ReviewerDivine Habel96% (105)
- Professional Education ReviewerDocument16 pagesProfessional Education ReviewerDivine Habel96% (105)
- Professional Education ReviewerDocument16 pagesProfessional Education ReviewerDivine Habel96% (105)
- Types of Eco SystemDocument3 pagesTypes of Eco SystemGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- EcosystemsDocument2 pagesEcosystemsnasaiyumi5No ratings yet
- Types of EcosystemDocument4 pagesTypes of EcosystemSuganya AruchamyNo ratings yet
- Eco SystemDocument3 pagesEco SystemAnanya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Biomes and EcozonesDocument46 pagesBiomes and EcozonesCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Types of EcosystemDocument17 pagesTypes of EcosystemJayashwa Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Tema 11: La EcosferaDocument10 pagesTema 11: La EcosferaAinhoa Pérez GiménezNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument48 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSuperpower KhilafahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document37 pagesChapter 7daryl.pradoNo ratings yet
- Final Module EnviSciDocument55 pagesFinal Module EnviSciJeff Ray BarreraNo ratings yet
- Concept of An Ecosystem, Structure and FunctionDocument15 pagesConcept of An Ecosystem, Structure and Functionsahil shahNo ratings yet
- The Biosphere and Animal DistributionDocument65 pagesThe Biosphere and Animal DistributionWendanakNo ratings yet
- Different Types of EcosystemsDocument3 pagesDifferent Types of EcosystemsCherry BrutasNo ratings yet
- EVS PPT Group No. 8Document20 pagesEVS PPT Group No. 8Madhav kukrejaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept-1 (1) ScribdDocument22 pagesBasic Concept-1 (1) Scribdan nameless artistNo ratings yet
- Types of EcosystemsDocument6 pagesTypes of EcosystemsPranavNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Ecosystem and CommunitiesDocument18 pagesKinds of Ecosystem and CommunitiesBelmas CarbonellNo ratings yet
- Earth's Major BiomesDocument2 pagesEarth's Major BiomesSAAM_BLDNo ratings yet
- g 4 Ppt Wala Pang Ano YanDocument21 pagesg 4 Ppt Wala Pang Ano YanPyrrhus John BagamaspadNo ratings yet
- Unit V BiomesDocument14 pagesUnit V BiomesHyramae CuacoNo ratings yet
- 6-Types of EnvironmentDocument49 pages6-Types of EnvironmentFatimaNo ratings yet
- Hasnain RasheedDocument4 pagesHasnain RasheedKamran AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cynel賢人kenDocument34 pagesCynel賢人kenAnonymous wYyVjWTVibNo ratings yet
- Types Of Ecosystems In Depth GuideDocument2 pagesTypes Of Ecosystems In Depth GuideNikhil ThakurNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity & Ecology-1Document22 pagesBiodiversity & Ecology-1Rohit kumar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Types of BiomeDocument8 pagesTypes of Biomelizzie_mcgNo ratings yet
- inbound2273023591641698636Document20 pagesinbound2273023591641698636dalmandiana8No ratings yet
- Aquatic Ecosystem GuideDocument7 pagesAquatic Ecosystem GuideWira SentanuNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems and Types of EcosystemsDocument42 pagesEcosystems and Types of EcosystemsIbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- Handouts - Ecosystem and EvolutionDocument10 pagesHandouts - Ecosystem and EvolutionRinalyn AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument27 pagesIlovepdf MergedRinalyn AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Differents Ecosystem and Their Characteristics: Sofia Martínez, Saraí Macias y Paul NavarroDocument10 pagesDifferents Ecosystem and Their Characteristics: Sofia Martínez, Saraí Macias y Paul NavarrosofiaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Mr. Edward M. Marzan Jr. Biological Science TeacherDocument28 pagesPrepared By: Mr. Edward M. Marzan Jr. Biological Science TeacherAngela Gayle BautistaNo ratings yet
- P EcoDocument26 pagesP EcoCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Aquatic BiomeDocument2 pagesAquatic BiomekikaykiNo ratings yet
- Aquatic EcosystemsDocument14 pagesAquatic EcosystemsCris Ann Chatto IINo ratings yet
- The Aquatic BiomeDocument4 pagesThe Aquatic BiomeAngelie LapeNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Ecosystems: PolarDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of Ecosystems: PolarynaNo ratings yet
- Biomes of The WorldDocument12 pagesBiomes of The WorldOmaya Tariq100% (1)
- Gian Jyoti Institute of Management and Technology, Mohali Assignment No-1 Academic Session January-May 202Document4 pagesGian Jyoti Institute of Management and Technology, Mohali Assignment No-1 Academic Session January-May 202Isha aggarwalNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEM ScribdDocument23 pagesECOSYSTEM Scribdan nameless artistNo ratings yet
- Topic 2. Biome Definition and Characteristics PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 2. Biome Definition and Characteristics PDFMark Jether GasmenNo ratings yet
- PEE - Lesson 2 (MT)Document22 pagesPEE - Lesson 2 (MT)khlneNo ratings yet
- Module 3 RevisedDocument11 pagesModule 3 RevisedCj Nicole SURIAGANo ratings yet
- Ecosystem ExplainedDocument6 pagesEcosystem ExplainedGlorylourd Joana FulloNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Biomes and Energy FlowDocument12 pagesEcosystem and Biomes and Energy FlowKathleen Joy SarabosingNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life 2Document36 pagesEarth and Life 2Glyneth Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- HandOut (World Biomes)Document7 pagesHandOut (World Biomes)Jonel BarrugaNo ratings yet
- Lentic Which Are Characterized As HavingDocument8 pagesLentic Which Are Characterized As HavingPrecious ViterboNo ratings yet
- Biology Study Guide on BiomesDocument2 pagesBiology Study Guide on BiomeshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Land and Aquatic BiomesDocument35 pagesLand and Aquatic Biomesapi-234480965No ratings yet
- Biology Ss2Document5 pagesBiology Ss2TOSHO OSHOFFA IINo ratings yet
- Understanding Ecology Through Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument27 pagesUnderstanding Ecology Through Levels of Biological OrganizationLirofiatillahNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem InteractionsDocument65 pagesEcosystem InteractionsCeline Katrina Balulao100% (2)
- Ecosystem - Lesson 2Document7 pagesEcosystem - Lesson 2Jhon Lloyd Zarco BantigueNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Part 1Document13 pagesUnit 3 Part 1Pooja PatilNo ratings yet
- Marine Ecosystems Are Among The Largest of Earth'sDocument5 pagesMarine Ecosystems Are Among The Largest of Earth'skevinaveriaNo ratings yet
- Biomes of The World: Environmental, Ecology Bio-Diversity & Climate ChangeDocument21 pagesBiomes of The World: Environmental, Ecology Bio-Diversity & Climate ChangeMeenakshi SahuNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Fresh and Saltwater Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandEcosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Fresh and Saltwater Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Documents For TeachersDocument10 pagesDocuments For TeachersOdelle Rayos ReyesNo ratings yet
- LET Module 5Document6 pagesLET Module 5Jobert YayainNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Development Prof - EdDocument8 pagesChild and Adolescent Development Prof - EdTin SottoNo ratings yet
- PNU REVIEWERfdgdgDocument2 pagesPNU REVIEWERfdgdgGie Marie Francisco UmaliNo ratings yet
- Natural Science-General Educationnatural Science-General EducationDocument4 pagesNatural Science-General Educationnatural Science-General EducationIvan dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Kitchen fuels that caused big firesDocument5 pagesKitchen fuels that caused big firesGie Marie Francisco UmaliNo ratings yet
- LET Asian World HistoryDocument4 pagesLET Asian World HistoryMay-Ann S. CahiligNo ratings yet
- Educational TechnologyDocument6 pagesEducational TechnologyDo DongNo ratings yet
- EP GenEd Mix ReviewerDocument5 pagesEP GenEd Mix ReviewerGie Marie Francisco UmaliNo ratings yet
- 8.language and Literature ResearchDocument14 pages8.language and Literature ResearchDon Angelo De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 5 Theories and Proponents - 1Document6 pages5 Theories and Proponents - 1Unibelle Joy LachicaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Online LET Reviewer - General EducationDocument18 pages2017 Online LET Reviewer - General Educationreginald_adia_1No ratings yet
- Educational TechnologyDocument8 pagesEducational Technologyjonathan bacoNo ratings yet
- EP GenEd Phil History ReviewerDocument5 pagesEP GenEd Phil History ReviewerGie Marie Francisco UmaliNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument12 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentRodelNo ratings yet
- 032 Proponents and Their TheoriesDocument1 page032 Proponents and Their TheoriesDiana CalaguiNo ratings yet
- Folklore - Traditionally Derived and Orally Transmitted LiteratureDocument2 pagesFolklore - Traditionally Derived and Orally Transmitted LiteratureGie Marie Francisco UmaliNo ratings yet
- Philosophical FoundationsDocument2 pagesPhilosophical FoundationsVenusvenusNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Human LearningDocument5 pagesFacilitating Human LearningJayson YanguasNo ratings yet
- ISMsDocument1 pageISMsIzel NialaNo ratings yet
- Teaching ProfessionDocument10 pagesTeaching ProfessionPaulAliboghaNo ratings yet
- Review METgenedDocument7 pagesReview METgenedGie Marie Francisco UmaliNo ratings yet
- QUESTION and ANSWER With RATIONALIZATIONDocument11 pagesQUESTION and ANSWER With RATIONALIZATIONGie Marie Francisco UmaliNo ratings yet
- Prof EdDocument8 pagesProf EdLemuel KimNo ratings yet
- PROPONENT and TheoryDocument1 pagePROPONENT and TheoryAvelino Jr II PayotNo ratings yet
- Republic Acts FDocument7 pagesRepublic Acts FOnir JundisNo ratings yet
- Artificially Induced Rainfall TechniquesDocument99 pagesArtificially Induced Rainfall TechniquesSamantha Isabel AguimbagNo ratings yet
- Maths Holiday Homework: Efforts By:karuka Kalra Class: 10 - EDocument10 pagesMaths Holiday Homework: Efforts By:karuka Kalra Class: 10 - EKaruka KalraNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science For Grade 11Document8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science For Grade 11Michel Jay Arguelles EspulgarNo ratings yet
- One Ocean Chapter 3Document22 pagesOne Ocean Chapter 3بدريانشاNo ratings yet
- Pub 150 BKDocument247 pagesPub 150 BKmehdi moghimiNo ratings yet
- DamsDocument23 pagesDamsMeggy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Svalbard World Seed BankDocument7 pagesSvalbard World Seed BankjoseNo ratings yet
- LinesDocument3 pagesLines_shubham_tomar_No ratings yet
- Design Specification D6 - Site RegradingDocument11 pagesDesign Specification D6 - Site RegradingTairu HuangNo ratings yet
- From Roadkill To Road Ecology, A Review of The EcologicalDocument11 pagesFrom Roadkill To Road Ecology, A Review of The EcologicalRobinsonNo ratings yet
- Pollution OceanDocument36 pagesPollution Oceanlow manmanNo ratings yet
- ch19 Answerkey Hoefnagels2eDocument9 pagesch19 Answerkey Hoefnagels2eSteven LimantoroNo ratings yet
- Thuoret Et. Al. 2007Document24 pagesThuoret Et. Al. 2007Roger WaLtersNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology Exercise Rainfall AnalysisDocument16 pagesEngineering Hydrology Exercise Rainfall AnalysisgtNo ratings yet
- (문법 공략) 5.Our Earth Our Future Our Choice (01) - 천재 (이재영) 고1 영어 (20문제) (Q)Document8 pages(문법 공략) 5.Our Earth Our Future Our Choice (01) - 천재 (이재영) 고1 영어 (20문제) (Q)sominjakNo ratings yet
- Land and Sea Breezes Monsoon Cold and Warm Fronts ItczDocument40 pagesLand and Sea Breezes Monsoon Cold and Warm Fronts ItczJeric ValdezNo ratings yet
- Lanslide and It Classifications1Document72 pagesLanslide and It Classifications1Umesh joshiNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Psychrometric Chart No 1 Normal TDocument1 pageAshrae Psychrometric Chart No 1 Normal TFelipe ProcopioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document6 pagesChapter 10Ankur MishraNo ratings yet
- Real Time Integrated Reservoir operation-CSocrabyDocument71 pagesReal Time Integrated Reservoir operation-CSocrabyamitNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Ignou Pts5 KanpurDocument7 pagesSynopsis Ignou Pts5 KanpurAnjnaKandari100% (1)
- Ocean Atmosphere Circulation Cells Weather ClimateDocument47 pagesOcean Atmosphere Circulation Cells Weather ClimateNaga LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 WDocument5 pagesWorksheet 6 WLania WaengaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems Feel The Heat From Climate Change-Teacher-14Document7 pagesEcosystems Feel The Heat From Climate Change-Teacher-14Kaung Khant Win MyatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Horticultural Science 2nd Edition Arteca Solutions Manual DownloadDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Horticultural Science 2nd Edition Arteca Solutions Manual DownloadDavid Johansen100% (27)
- 4 3 7 Infiltration TrenchDocument14 pages4 3 7 Infiltration TrenchsomnathNo ratings yet
- Cleaning of Water BodiesDocument14 pagesCleaning of Water BodiesSaiTimmaraoNo ratings yet
- Rainfall and Runoff Analysis in Cavite 11 CheckedDocument12 pagesRainfall and Runoff Analysis in Cavite 11 Checkedb3aaastNo ratings yet
- Climate Srinagar - MeteoblueDocument6 pagesClimate Srinagar - MeteobluePrarthna RoyNo ratings yet