Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Particle Size Distribution and Characteristics HW
Uploaded by
alaiali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThis document contains two questions regarding particle size distribution analysis. Question 1 provides size distribution data for two components, A and B, in a mixture and asks to calculate various particle size metrics for each component and the overall mixture. Question 2 provides number-based size distribution data for a dust sample and asks to convert it to a mass-based distribution, calculate specific surface area, and plot the cumulative size distribution curve to determine the D50 value. Sample calculations are required.
Original Description:
Original Title
kiki
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains two questions regarding particle size distribution analysis. Question 1 provides size distribution data for two components, A and B, in a mixture and asks to calculate various particle size metrics for each component and the overall mixture. Question 2 provides number-based size distribution data for a dust sample and asks to convert it to a mass-based distribution, calculate specific surface area, and plot the cumulative size distribution curve to determine the D50 value. Sample calculations are required.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesParticle Size Distribution and Characteristics HW
Uploaded by
alaialiThis document contains two questions regarding particle size distribution analysis. Question 1 provides size distribution data for two components, A and B, in a mixture and asks to calculate various particle size metrics for each component and the overall mixture. Question 2 provides number-based size distribution data for a dust sample and asks to convert it to a mass-based distribution, calculate specific surface area, and plot the cumulative size distribution curve to determine the D50 value. Sample calculations are required.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
HW No1
Q1. A random mixture consists of two components A and B in proportions
19 and 81 % by mass, respectively, the particles are spherical and A and B
have particle densities of 827 and 1120 kg/m 3, respectively. The cumulative
undersize mass distribution (FA, FB) of the two components are shown in
Table below.
Nominal Sieve FA FB
size, μm
2057 1
1676 0.77
1405 0.61 1.0
1204 0.35 0.83
1003 0.27 0.71
853 0.19 0.52
699 0.12 0.38
599 0.06 0.14
500 0.02 0.07
422 0 0
Find the followings:
1. AW, NW, DS, DV, DW for component A
2. Plot the particles size distribution curve (log-normal) for component B
(cumulative undersize)
3. Find the D80 of component B
4. The total number of particles for both components A and B in 1 kg
5. The number of particles in the size fraction 599/500 for component A
6. If samples of 1 g are withdrawn from the mixture find
a. The total number of particles in this 1 g of the mixture
b. Upper limit of variance of the mixture
c. Lower limit of variance of the mixture
Q2. The following table gives the size distribution of a dust as measured by
microscope. Convert these figures to obtain the distribution on a mass basis,
and calculate the specific surface (mass and volume), assuming spherical
particles of density 2650 kg/m3
Size range in microns Number of particles in the range
0-2 2000
2-4 600
4-8 140
8-12 40
12-16 15
16-20 5
20-24 2
Plot cumulative particle size distribution curve (log-normal) and find D50
You can use excel sheet for calculations, but you need to demonstrate
sample calculations
Deadline 08/10/2019 at 9:30 AM
You might also like
- Physics Unit 1 Paper 2 May June 2012Document22 pagesPhysics Unit 1 Paper 2 May June 2012John SmithNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneDocument20 pagesCSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneBill BobNo ratings yet
- CAPE Unit 1 Paper 2 2010 (PHYSICS)Document22 pagesCAPE Unit 1 Paper 2 2010 (PHYSICS)Christopher McCarthy100% (1)
- Thermal Radiation Heat Transfer 6th Howell Solution ManualDocument31 pagesThermal Radiation Heat Transfer 6th Howell Solution ManualAnn Rener100% (22)
- Physics Unit 2 Paper 2 May June 2015Document23 pagesPhysics Unit 2 Paper 2 May June 2015Joshua DavisNo ratings yet
- Mass Balancing McGillDocument20 pagesMass Balancing McGillMag Arias100% (4)
- Second Test With AnswersDocument10 pagesSecond Test With Answersmariaki_kolaNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering: Particle TechnologyDocument2 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering: Particle TechnologyKhan AaghaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet2Document3 pagesProblem Sheet2h59cpnc8tyNo ratings yet
- Workshop P3 - MetallurgyDocument4 pagesWorkshop P3 - Metallurgyabdul haji daudNo ratings yet
- Analytical and Numerical Analysis of Ovel Shaped Composite BeamDocument7 pagesAnalytical and Numerical Analysis of Ovel Shaped Composite BeamAnup M UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- CE50P-2/E01 Date: 05/06/20 CE-2 Numerical Differentiation and Integration Date: 24/07/20Document9 pagesCE50P-2/E01 Date: 05/06/20 CE-2 Numerical Differentiation and Integration Date: 24/07/20Vinz GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Unit 0 Test IDocument3 pagesUnit 0 Test Iserual.sergioNo ratings yet
- EMF (Khaled Elbeltagy - 201605178)Document6 pagesEMF (Khaled Elbeltagy - 201605178)alaa AlsabehNo ratings yet
- Prob.1: CEE 4630 Future Transportation Technologies & SystemsDocument9 pagesProb.1: CEE 4630 Future Transportation Technologies & SystemsEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Two-Stream Mixing Process Heat CalculationDocument35 pagesTwo-Stream Mixing Process Heat CalculationJacintoOrozcoSamuelNo ratings yet
- The Atomic Theory of Matter: Chemistry 1: WorksheetsDocument1 pageThe Atomic Theory of Matter: Chemistry 1: WorksheetsMehul SunejaNo ratings yet
- TEM Diffraction - Take Home AnswerDocument36 pagesTEM Diffraction - Take Home AnswerRajasekarakumar VadapooNo ratings yet
- NJC Physics Prelim Exam ReviewDocument21 pagesNJC Physics Prelim Exam ReviewAnonymous t4uG4pFdNo ratings yet
- Vlookup 2010Document3 pagesVlookup 2010rajithasreenivasNo ratings yet
- An Example Report by Cecil Dybowski (Dybowski@udel - Edu) : List All Names of People Involved, Along With Email AddressesDocument8 pagesAn Example Report by Cecil Dybowski (Dybowski@udel - Edu) : List All Names of People Involved, Along With Email AddressesAmr OkashaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Density Calculations and Their Impact on Material PropertiesDocument33 pagesTheoretical Density Calculations and Their Impact on Material PropertiesRicardo Rincon VegaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 (2006) SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment 3 (2006) Solutionsapi-383542133% (3)
- Phase Diagram Analysis of the Al-Cu Binary SystemDocument6 pagesPhase Diagram Analysis of the Al-Cu Binary Systemnilanga123No ratings yet
- General 250 1586564070Document12 pagesGeneral 250 1586564070Abitekaniza HassanNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - Sem 2 AY1718Document6 pagesFinal Exam - Sem 2 AY1718Dhadkan D KCNo ratings yet
- Escuela Superior Politécnica Del Litoral: AGOSTO 2021Document7 pagesEscuela Superior Politécnica Del Litoral: AGOSTO 2021HomeroOjedaNo ratings yet
- Regression and CorrelationDocument2 pagesRegression and CorrelationKhurram ShahzadaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Hooke's Law Yr 10Document4 pagesWorksheet Hooke's Law Yr 10wembley1629No ratings yet
- Experiment No 03-Submission FormDocument6 pagesExperiment No 03-Submission FormArjita AhmedNo ratings yet
- U.C.E. Mock Examinations Mathematics 456/1 Paper 1 Time: 2hrs 30minsDocument5 pagesU.C.E. Mock Examinations Mathematics 456/1 Paper 1 Time: 2hrs 30minsAthiyo MartinNo ratings yet
- 2023.1 Title ANH - PH 20201367Document4 pages2023.1 Title ANH - PH 20201367Hồng Anh PhạmNo ratings yet
- As Book 1 2008 Till 2020Document441 pagesAs Book 1 2008 Till 2020Samreen ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Charge-to-Mass Ratio of An Electron: Phys211LDocument7 pagesCharge-to-Mass Ratio of An Electron: Phys211LElias HannaNo ratings yet
- Reporte SedimentscionDocument13 pagesReporte SedimentscionANDREA CAMARGONo ratings yet
- Lab 03Document6 pagesLab 03Rakeen Ashraf ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Me62o June2021Document3 pagesMe62o June2021Rambo 420No ratings yet
- Structural Question/P.1 - Hong Kong Advanced Level Exam 1984 Physics Question on Steel Wire PropertiesDocument8 pagesStructural Question/P.1 - Hong Kong Advanced Level Exam 1984 Physics Question on Steel Wire PropertiescheongjiajunNo ratings yet
- Question Paper CodeDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Codekarthikeyankv.mech DscetNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 PropertiesDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 1 PropertiesAli MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Coulomb's LawDocument9 pagesExp 1 Coulomb's Lawadriana dahlia100% (2)
- Biology 2023 U2 P2Document19 pagesBiology 2023 U2 P2johnathanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Modelling Class1 Exercise Sheet 2022Document4 pagesMolecular Modelling Class1 Exercise Sheet 2022Ngoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- HS2019 Solution07Document7 pagesHS2019 Solution07KAMAL HAASANNo ratings yet
- Modelling Interstellar Extinction in Three DimensionsDocument8 pagesModelling Interstellar Extinction in Three DimensionsDr-Arindam ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Tifr Dec2011 Question PaperDocument15 pagesTifr Dec2011 Question Papertvsagar830% (1)
- CSEC Physics June 2005 P3Document7 pagesCSEC Physics June 2005 P3aidan kamrajNo ratings yet
- 3.032 Problem Set 5 Solutions: (Note That This Date Is Later Than in Your Syllabus Due To New Due Date of Lab 2.)Document3 pages3.032 Problem Set 5 Solutions: (Note That This Date Is Later Than in Your Syllabus Due To New Due Date of Lab 2.)SAMNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 CHMT 4006-4008 2019Document4 pagesTutorial 2 CHMT 4006-4008 2019Da Saint0% (1)
- Free Vibration of A Single Degree of Freedom SystemDocument6 pagesFree Vibration of A Single Degree of Freedom SystemStephanieNo ratings yet
- Topic4 - Moment Distribution Stiffness Factor ModificationDocument24 pagesTopic4 - Moment Distribution Stiffness Factor ModificationMary Joanne Capacio AniñonNo ratings yet
- LTTechNote1 TelescopeThroughputDocument13 pagesLTTechNote1 TelescopeThroughputJaduqueNo ratings yet
- Physics of Gamma Rays in Nuclear MeasurementsDocument29 pagesPhysics of Gamma Rays in Nuclear MeasurementsDadadad dadadadadadNo ratings yet
- Memo For The Particulates Section of Test On The 12thDocument5 pagesMemo For The Particulates Section of Test On The 12thRicardoNo ratings yet
- Theory 2 Solutions Truss ExampleDocument10 pagesTheory 2 Solutions Truss ExampleHilton D. CalawenNo ratings yet
- IPhO 2013 Experiment 2 SolutionDocument12 pagesIPhO 2013 Experiment 2 SolutionmpecthNo ratings yet
- Printable Ink Lenses, Diffusers, and 2D Gratings: Supporting InformationDocument6 pagesPrintable Ink Lenses, Diffusers, and 2D Gratings: Supporting InformationMainul HossainNo ratings yet
- Granulometric analysis and Atterberg limits of two soil samplesDocument3 pagesGranulometric analysis and Atterberg limits of two soil samplesRaven ReyNo ratings yet
- Tarea #3: Difusión en Estado Estacionario y Pseudoestacionario Sin Reacción QuímicaDocument8 pagesTarea #3: Difusión en Estado Estacionario y Pseudoestacionario Sin Reacción QuímicaDiego Fidel Gonzalez ContrerasNo ratings yet
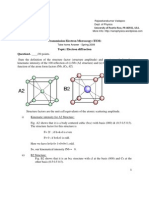
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- 26 JJJDocument86 pages26 JJJalaialiNo ratings yet
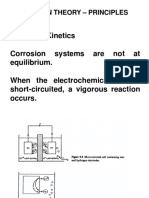
- It Is The Prevention of Corrosion By: Anodic ProtectionDocument53 pagesIt Is The Prevention of Corrosion By: Anodic ProtectionalaialiNo ratings yet
- Corrosion PreventionDocument38 pagesCorrosion PreventionmujahaddadNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document40 pagesLec 4alaialiNo ratings yet
- Lectures 10-11 PDFDocument59 pagesLectures 10-11 PDFalaialiNo ratings yet
- Size Reduction Techniques and Industrial ApplicationsDocument86 pagesSize Reduction Techniques and Industrial ApplicationsalaialiNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Corrosion RatesDocument37 pagesFactors Affecting Corrosion RatesalaialiNo ratings yet
- LectDocument74 pagesLectalaialiNo ratings yet
- Properties of Particulate SolidsDocument69 pagesProperties of Particulate SolidsalaialiNo ratings yet
- Uniform, or General Attack. Galvanic, or Two-Metal Corrosion. Crevice Corrosion. PittingDocument49 pagesUniform, or General Attack. Galvanic, or Two-Metal Corrosion. Crevice Corrosion. PittingalaialiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Properties of Particulate Solids2 PDFDocument19 pages2 - Properties of Particulate Solids2 PDFalaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Report Writing PDFDocument16 pagesTopic 4 Report Writing PDFalaialiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Properties of Particulate Solids2 PDFDocument19 pages2 - Properties of Particulate Solids2 PDFalaialiNo ratings yet
- FeeerrDocument36 pagesFeeerralaialiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Flow Through Packed BedsDocument24 pages5 - Flow Through Packed BedsاشرفاللساميNo ratings yet
- Topic Six Memos Letters and EmailsDocument35 pagesTopic Six Memos Letters and EmailsalaialiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Properties of Particulate Solids2 PDFDocument19 pages2 - Properties of Particulate Solids2 PDFalaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 What Are EssayDocument24 pagesTopic 3 What Are EssayalaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Oral Presentation Part 1Document19 pagesTopic 8 Oral Presentation Part 1alaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Oral Presentation Part 2Document23 pagesTopic 8 Oral Presentation Part 2alaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 ListeningDocument37 pagesTopic 9 ListeningalaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Essentila Academic Writing InformationDocument23 pagesTopic 2 Essentila Academic Writing InformationalaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 CV and Cover Letter PDFDocument35 pagesTopic 5 CV and Cover Letter PDFalaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 ListeningDocument37 pagesTopic 9 ListeningalaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document28 pagesTopic 1alaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 CV and Cover Letter PDFDocument35 pagesTopic 5 CV and Cover Letter PDFalaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Report Writing PDFDocument16 pagesTopic 4 Report Writing PDFalaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Oral Presentation Part 1Document19 pagesTopic 8 Oral Presentation Part 1alaialiNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Oral Presentation Part 2Document23 pagesTopic 8 Oral Presentation Part 2alaialiNo ratings yet