Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supplementary Notes For Cranial Cavity PDF
Supplementary Notes For Cranial Cavity PDF
Uploaded by
Camille Magdirila0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesOriginal Title
supplementary-notes-for-cranial-cavity.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesSupplementary Notes For Cranial Cavity PDF
Supplementary Notes For Cranial Cavity PDF
Uploaded by
Camille MagdirilaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
(supplementary notes)
Lecture: CRANIAL CAVITY IV.A ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
I. MAJOR CONTENTS FLOOR
a. Brain a. orbital plate of frontal bone
b. Intracranial parts of the cranial and spinal b. cribriform plate of the ethmoid
nerves - Transmits the Olfactory nerves (CN I)
c. Blood vessels, venous sinuses c. Crista galli
d. Meninges (dura, arachnoid, pia mater) - for the attachment of falx cerebri
e. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Houses the Frontal Lobes of the Cerebral
II. BONE STRUCTURES Hemispheres
a. Frontal
b. Parietal Boundaries:
c. Sphenoid o Anteriorly – frontal bone
d. Temporal
e. Occipital o Laterally – squamous part of the frontal
f. Ethmoid bone
o Midline – ethmoid bone
III. SUPERIOR PART OF CRANIUM (Calvaria)
- Its internal surface shows: o Posteriorly – posterior margin of lesser
a. Coronal sutures wing of the sphenoid
b. Sagittal sutures
- anterior margin of the chiasmatic sulcus
c. Lambdoid sutures
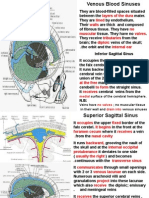
d. shallow sagittal groove (found in the midline) o Median part locates the groove for the
- lodges superior sagittal sinus optic chiasma
e. granular pits
- small pits found on both sides of the groove
- lodge the lateral lacunae and arachnoid IV.B MIDDLE CRANIAL FOSSA
granulations/pacchionian body
f. parietal foramen Supports the temporal lobes of the cerebral
- found at the sides of sagittal groove hemispheres
- transmits emissary vein Median part
g. narrow grooves - raised
- for the anterior and posterior div. of middle - formed by body of the sphenoid
meningeal vessels Anterior
- lesser wings of the sphenoid
IV. BASE OF THE SKULL - anterior clinoid process
- Its interior is divided into 3 cranial fossae: - anterior margin of the chiasmatic sulcus
a. Anterior Cranial Fossa Posterior
– frontal lobes - superior borders of the petrous parts of the
b. Middle Cranial Fossa temporal bones
– temporal lobes - Dorsum sellae
c. Posterior Cranial Fossa Lateral
– hindbrain - temporal bone (squamous part)
- greater wing of the sphenoid
- parietal bones
- petrous part of temporal bone
The floor of each lateral part of the middle Carotid canal
cranial fossa is formed by - opens into the side of Foramen lacerum
- greater wing of the sphenoid - transmits the Internal Carotid Artery (ICA)
- temporal bone – squamous and petrous and sympathetic nerves
parts
- Sella turcica TEGMEN TYMPANI
a. thin plate of bone
Superior Orbital Fissure b. forms the roof of mastoid antrum, tympanic
- Slit-like opening between the lesser and cavity and auditory tube
greater wings of sphenoid c. only major barrier separating infection in the
- Transmits: tympanic cavity from the temporal lobe
Oculomotor n.; Trochlear n.; lacrimal,
frontal and nasociliary branches of the SELLAE TURCICA
ophthalmic division of the Trigeminal a. Behind the Tuberculum Sella
n.; Abducens and Ophthalmic n b. Holds the pituitary gland
Optic Canal c. Bounded posteriorly by the Dorsum
- contains optic nerve, ophthalmic artery and Sellae
meninges
POSTERIOR CLINOID PROCESS
Foramen Rotundum a. Two tubercles at the superior angles of the
- Behind the medial end of the Superior dorsum sellae
Orbital Fissure b. Attachment for the Tentorium cerebelli
- Transmits the Maxillary division of the
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) Cavernous sinus
a. Directly related to the side of the body of the
Foramen Ovale Sphenoid
- Posterolateral to Foramen rotundum
- Transmits the following:
IV.C POSTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
Sensory and Motor roots of the
Mandibular division of the Trigeminal Very deep
nerve (CN V) Lodges parts of the Hindbrain
Lesser Petrosal nerve a. Cerebellum
b. Pons
Emissary veins c. Medulla oblongata
Accessory meningeal vein/artery
Boundaries:
Foramen spinosum - Anteriorly – superior border of the petrous
- Posterolateral to Foramen ovale part of temporal bone, basilar part of
- Transmits the Middle Meningeal Artery occipital bone , dorsum sellae
- Posteriorly - squamous part of occipital
Foramen lacerum bone
- Large - Lateral – parietal bone
- Triangular/irregular - Floor – occipital bone and temporal bone
- Between apex of petrous part of Temporal
bone and Sphenoid
- transmits very small blood vessels from the
cranial cavity to the neck
Foramen magnum
– central part of the floor
- Spinal cord
- meninges
- ascending spinal parts of accessory
nerve
- Two (2) vertebral arteries
- anterior and posterior spinal arteries
Hypoglossal Canal
- Anterolateral boundary of the F. magnum
- Transmits
Hypoglossal nerve
emissary veins
meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal
artery
Jugular foramen
- Between petrous part of the Temporal bone
and condylar part of the Occipital bone
- Transmits the following:
a) Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
b) Vagus nerve (CN X)
c) Accessory nerves (CN XI)
Sigmoid sinus leaves the skull and becomes the
Internal jugular vein
Internal Acoustic Meatus
- Petrous part of the Temporal bone
- Transmits the following:
Vestibulocochlear or Auditory nerve (CN VIII)
Facial nerve (CN VII)
Internal auditory artery
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Ballenger's Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery - 16th EdDocument1,631 pagesBallenger's Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery - 16th Edvioletachka100% (6)
- Middle Fossa TrianglesDocument1 pageMiddle Fossa TrianglesZeptalanNo ratings yet
- MAXILLADocument21 pagesMAXILLACamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Blood Erythropoiesis: Ibutnadi Iduyan Ilagan Jarin LopezDocument15 pagesBlood Erythropoiesis: Ibutnadi Iduyan Ilagan Jarin LopezCamille Magdirila100% (1)
- Skeletal Muscle Sarcomere FinalDocument32 pagesSkeletal Muscle Sarcomere FinalCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Inferior Nasal Conchaa PDFDocument18 pagesInferior Nasal Conchaa PDFCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physio PDFDocument41 pagesMuscle Physio PDFCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Frontal Bone: External and Internal SurfaceDocument18 pagesFrontal Bone: External and Internal SurfaceCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Safari 6 Aug 2020 at 857 AM PDFDocument1 pageSafari 6 Aug 2020 at 857 AM PDFCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- T. Domingo Dental Clinic: Brgy. 7A Giron St. Laoag Polyclinic, Ilocos Norte (0921) 4922 560/ (0927) 7161380Document1 pageT. Domingo Dental Clinic: Brgy. 7A Giron St. Laoag Polyclinic, Ilocos Norte (0921) 4922 560/ (0927) 7161380Camille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Course Code: DDM 3101 Course Title: Dental MaterialsDocument4 pagesCourse Outline: Course Code: DDM 3101 Course Title: Dental MaterialsCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Blood Suppply of Lower LimbDocument8 pagesBlood Suppply of Lower LimbCamille Magdirila100% (2)
- Petrous Apex FinalDocument53 pagesPetrous Apex Finalpravinxyz100% (1)
- Skull Base Course BrochureDocument3 pagesSkull Base Course BrochureEslam KandilNo ratings yet
- Role of X-Rays in OtolaryngolgoyDocument25 pagesRole of X-Rays in OtolaryngolgoyDr. T. Balasubramanian67% (3)
- Radiographic Classification of Temporal Bone Fractures: Clinical Predictability Using A New SystemDocument5 pagesRadiographic Classification of Temporal Bone Fractures: Clinical Predictability Using A New SystemTaufik ShidkiNo ratings yet
- Norma Basalis: Inferior Aspect of SkullDocument33 pagesNorma Basalis: Inferior Aspect of Skullkavya0% (1)
- The Far-Lateral Approach and Its Transcondylar, Supracondylar, and Paracondylar ExtensionsDocument15 pagesThe Far-Lateral Approach and Its Transcondylar, Supracondylar, and Paracondylar Extensionsbodeadumitru9261No ratings yet
- Epidural Hematoma Case ReportDocument48 pagesEpidural Hematoma Case ReportJansept Bruce Guinto67% (6)
- Aa AnatomyDocument109 pagesAa AnatomyshailendraNo ratings yet
- Canal Wall UP Mastoidecto MY: By: Dr. Aditya Tiwari, Resident, Dept. of ENTDocument90 pagesCanal Wall UP Mastoidecto MY: By: Dr. Aditya Tiwari, Resident, Dept. of ENTAdi SitaruNo ratings yet
- Venous SinusesDocument15 pagesVenous SinusesJennifer RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Temporal Os Mastoid & PetrosumDocument34 pagesTemporal Os Mastoid & PetrosumAyuning SinchittaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Midterm 2Document92 pagesAnatomy Midterm 2Cassandra DavisNo ratings yet
- Mastoidectomy VS Tympanoplasty - A Conceptual Renaissance. Preamble To An Original Method of Mastoidectom PDFDocument5 pagesMastoidectomy VS Tympanoplasty - A Conceptual Renaissance. Preamble To An Original Method of Mastoidectom PDFPutu Reza Sandhya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Tentorial IncisuraDocument23 pagesTentorial Incisurabodeadumitru9261100% (1)
- Ear Anatomy: OtolaryngologyDocument18 pagesEar Anatomy: OtolaryngologysafitriNo ratings yet
- Dural Venous Sinuses PDFDocument3 pagesDural Venous Sinuses PDFSuprit SnNo ratings yet
- Craneo Sobotta PDFDocument111 pagesCraneo Sobotta PDFMaria Teresa AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- FormatDocument3 pagesFormatJo Hn Vengz0% (1)
- Pap 0106Document31 pagesPap 0106Bogdan PraščevićNo ratings yet
- Projectile InjuryDocument6 pagesProjectile InjuryNimmal KesavanNo ratings yet
- Textbook Aiims Mamc Pgi S Comprehensive Textbook of Diagnostic Radiology 1St Edition Niranjan Khandelwal Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Aiims Mamc Pgi S Comprehensive Textbook of Diagnostic Radiology 1St Edition Niranjan Khandelwal Ebook All Chapter PDFbarry.smith728100% (20)
- Temporal Bone Dissection - Basic Surgery of The Temporal BoneDocument26 pagesTemporal Bone Dissection - Basic Surgery of The Temporal BoneIvana MatejováNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Temporal Bone and Surgical ImplicationsDocument378 pagesAnatomy of Temporal Bone and Surgical ImplicationsEric Grossi Morato100% (1)
- The Foramen Magnum: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DDocument39 pagesThe Foramen Magnum: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.Dbodeadumitru9261100% (1)
- CheatSheet - ForamenDocument1 pageCheatSheet - ForamenHermenegildo GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Dural Opening/Removal For Combined Petrosal Approach: Technical NoteDocument5 pagesDural Opening/Removal For Combined Petrosal Approach: Technical NoteWilson Quispe AlanocaNo ratings yet
- Temporal Bone and EarDocument76 pagesTemporal Bone and EarGuo YageNo ratings yet
- 02.external Views of The SkullDocument25 pages02.external Views of The SkulltanzilanasibzadaNo ratings yet