Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MP 80865 PDF
Uploaded by
mineOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MP 80865 PDF
Uploaded by
mineCopyright:
Available Formats
Microprocessors and Microcontrollers – 11EC311
Architectural Model of 8086
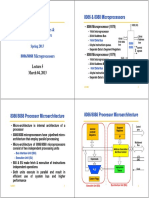
Microprocessor based System
Data Bus
CPU
General-
Serial
Purpose RAM ROM I/O Timer COM
Micro- Port
Port
processor
Address Bus
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 2
Microcontroller based System
CPU RAM ROM
A single chip
Serial
I/O Port COM
Timer
Port
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 3
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller
Microprocessor Microcontroller
CPU is stand-alone, RAM, ROM, CPU, RAM, ROM, I/O and timer
I/O, timer are separate are all on a single chip
Designer can decide on the Fixed amount of on-chip ROM,
amount of ROM, RAM and I/O RAM, I/O ports
ports.
Expensive Cheap
Used in Computers Used by Application Specific
Systems
General-purpose Single-purpose
Example : Intel’s x86, Motorola’s Example : Motorola’s 6811,
680x0 Intel’s 8051, Zilog’s Z8
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 4
Features of 8086 Microprocessor
●
16-bit Microprocessor
●
Data Bus – 16-bit
●
Address Bus – 20-bit
●
Supports Memory upto 1MB
●
16 Bit Registers
●
2.5 MIPS(Million of Instructions per second)
●
16 Logical Segments (Max 64KB Each)
●
Maximum and Minimum Modes of Operation
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 5
Memory Segmentation
●
Physical Address – 20 Bit (Wont fit in registers !!!)
●
Base Address / Segment Address – 16 Bit
●
Offset Address / Effective Address – 16 Bit
●
Code Segment
●
Data Segment
●
Extra Segment
●
Stack Segment
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 6
Physical Address Calculation
●
Physical Address = Base Address * 16d + Offset Address
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 7
Non-Overlapped vs Overlapped Segment
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 8
Advantages of Segmentation
●
It allows the memory capacity to be 1MB even though the
actual addresses to be handled by instructions are 16-bits
●
It allows use of separate memory areas for program, data
& stack, thus the protection of these is possible.
●
For large programs , it can use multiple segments for
program code, Data & Stack.
●
Program relocation can be very easily done.
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 9
Register Organization
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 10
Register Organization
●
Special Operation of General Registers
AX – Accumulator
–
– BX – Base Register
– CX – Count Register
– DX – Destination Register
●
Segment Registers hold Base Address of Segments
●
Indexed and Pointer Registers are for Storing Offsets for
particular segments
●
Flag Register Holds Status and Control Flags
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 11
Default Segment and Offset Registers
Segment Segment Offset Memory operation
Register Register
Code Segment CS IP Instruction fetch
Stack Segment SS SP,BP Stack operation
Data Segment DS BX/SI/DI General data access
Data Segment DS SI Source string data
access
Extra Segment ES DI Destination string
data access
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 12
Pipelining Model vs Non Pipelining Model
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 13
8086 Architecture
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 14
Components of Architecture
●
BIU – Bus Interface Unit (Fetch)
–Segment Registers – CS,DS,ES,SS
– Instruction Pointers – IP
– Adder
– 6 Byte Prefetch Queue
●
EU – Execution Unit (Execute)
– ALU
– General, Indexed and Pointer Registers
– Flags
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 15
Flag Register of 8086
6 Status Flags
3 Control Flags
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 16
Status Flags
●
Controlled by ALU after execute operation
●
Carry Flag
– 1 : Carry out of MSB
– 0 : No Carry out of MSB
●
Auxillary Carry Flag
– 1 : Carry out of Nibble
– 0 : No Carry out of Nibble
●
Parity Flag
– 1 : Odd Parity (Odd Number of 1's in lower byte)
– 0 : Even Parity
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 17
Status Flags
●
Zero Flag
– 1 : Result of Arithmetic or Logical Operation = 0
– 0 : Non-Zero Result
●
Sign Flag
– 1 : Result is Negative (MSB =1)
– 0 : Result is Positve
●
Overflow Flag
– 1 : Overflow Condition Occured
– 0 : No Overflow
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 18
Control Flags
●
Can be Controlled by user
●
Trap Flag
– 1 : Single Step Mode for Debugging
– 0 : Normal Mode
●
Direction Flag
– 1 : Address Decrement in String Operations
– 0 : Address Increment in String Operations
●
Interrupt Flag
– 1 : Interrupts Enabled
– 0 : Interrupts Disabled
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 19
References
●
https://www.sites.google.com/site/sripathroykoganti/my-forms
●
D.V.Hall “Microprocessor and Interfacing”, 2nd Edition Tata McGraw
Hill Publishing Company,2006.
●
A.K. Ray & K. M Bhurchandi, “Advanced Microprocessors &
peripherals”, Tata Mc Graw Hill Publishing Company 2002.
●
Rajkamal, “Microcontrollers - Architecture, Programming, Interfacing
& System Design”, 2 nd edition, Pearson Education.
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 20
Thank You
07/08/19 8086 Architectural Model - MPMC 21
You might also like
- Intel SWOT Analysis: Address Mobile Market & Reduce DependenceDocument8 pagesIntel SWOT Analysis: Address Mobile Market & Reduce DependenceSulaiman KashimNo ratings yet
- Short Notes IctDocument7 pagesShort Notes IctNoor Syafiq100% (2)
- Master System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15From EverandMaster System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15No ratings yet
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- 18CS44 MES Module3Document184 pages18CS44 MES Module3Madhu CkNo ratings yet
- GATE Questions-DBMS-Functional Dependencyas 1Document15 pagesGATE Questions-DBMS-Functional Dependencyas 1mine0% (1)
- Lab 1 - Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor EmulatorDocument10 pagesLab 1 - Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor EmulatorSaif Ullah100% (3)
- Dreamcast Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #9From EverandDreamcast Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #9No ratings yet
- ZX Spectrum 128 Service ManualDocument65 pagesZX Spectrum 128 Service Manuallugo76No ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8086Document47 pagesMicroprocessor 8086kaushik.sastra322395% (151)
- What Is A MicroprocessorDocument21 pagesWhat Is A MicroprocessorArghya SantraNo ratings yet
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3From EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Introduction To Microcontroller 8051aDocument105 pagesUnit 4 Introduction To Microcontroller 8051anitishNo ratings yet
- Microapps/ Part 2-Bus Width: PIC 8-BIT (PIC10F206) FeaturesDocument5 pagesMicroapps/ Part 2-Bus Width: PIC 8-BIT (PIC10F206) FeaturesAkinwumi OluwatosinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part1 PDFDocument49 pagesChapter 1 Part1 PDFtesfayebbNo ratings yet
- Iare Mpi Lecture Notes 0 PDFDocument158 pagesIare Mpi Lecture Notes 0 PDFPriya PreethiNo ratings yet
- MICRO-I Notes by Dr. Abhishek SharmaDocument27 pagesMICRO-I Notes by Dr. Abhishek SharmaAlfred SharmaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Software SystemDocument72 pagesMicroprocessor and Software SystemAkash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mpi Unit 1Document22 pagesMpi Unit 1sree ramyaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Microcontrollers, Embedded Control and The Motorola HC12 FamilyDocument15 pagesOverview of Microcontrollers, Embedded Control and The Motorola HC12 FamilyJuanNo ratings yet
- Tariq AbuMazen 1162419-Raed Samra1162596 Course ProjectDocument11 pagesTariq AbuMazen 1162419-Raed Samra1162596 Course ProjectRs sniperNo ratings yet
- MiP ArchitectureDocument45 pagesMiP ArchitectureKaushikperikaNo ratings yet
- Micro Controller Archtecture ProgrammingDocument94 pagesMicro Controller Archtecture ProgrammingyayavaramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Part 1Document21 pagesChapter 6 Part 1EYRICARLS ANNIENo ratings yet
- MicroC2 eCh13L02PICArchitectureDocument34 pagesMicroC2 eCh13L02PICArchitectureSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- Chapter - OneDocument53 pagesChapter - OneBereketab BeleteNo ratings yet
- Intel 8086Document4 pagesIntel 8086Shishir YalburgiNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Architecture (Coa) : EET 2211 4 Semester - Cse & Csit Overview of 8086 MicroprocessorDocument59 pagesComputer Organization and Architecture (Coa) : EET 2211 4 Semester - Cse & Csit Overview of 8086 MicroprocessorDibyanshu AmanNo ratings yet
- 8086 ArchitectureDocument8 pages8086 ArchitectureSwapnil PatilNo ratings yet
- PIC MicrocontrollerDocument18 pagesPIC Microcontrollerk2_chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- 01 Mik EngDocument34 pages01 Mik EngrbokisNo ratings yet
- 1.a Guest Lecture On Mechatronics Mp&Mc-2019-20 UpdatedDocument57 pages1.a Guest Lecture On Mechatronics Mp&Mc-2019-20 Updatedrajendra kulkarniNo ratings yet
- 5th Unit Micr - CNTL - 8051.ppsxDocument66 pages5th Unit Micr - CNTL - 8051.ppsxknowledge sharingNo ratings yet
- U3 8086 MicroprocessorDocument10 pagesU3 8086 MicroprocessorNishant Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- MICROCONTROLLER-8051 Features & ApplicationsDocument94 pagesMICROCONTROLLER-8051 Features & Applications12343567890No ratings yet
- UNIT IV-COntroller and AlgorithmsDocument47 pagesUNIT IV-COntroller and AlgorithmsKuppan Chetty RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 8086Document26 pagesIntroduction To 8086E.VigneshNo ratings yet
- Microcomputer and MicrocontrollerDocument95 pagesMicrocomputer and Microcontrollerknpatil89No ratings yet
- CH-6 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingDocument8 pagesCH-6 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingAnikhet MulkyNo ratings yet
- Archi & OrganizationDocument24 pagesArchi & OrganizationAditeeNo ratings yet
- 14mte02 Embedded Programming For Mechatronics Systems: Course OutcomesDocument104 pages14mte02 Embedded Programming For Mechatronics Systems: Course OutcomesHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- 8086 & 8088 Microprocessors: Spring 2013Document4 pages8086 & 8088 Microprocessors: Spring 2013Muhammad Fawad AbbasiNo ratings yet
- MPMC Digtal NotesDocument129 pagesMPMC Digtal NotesMr.K Sanath KumarNo ratings yet
- 4/18/2018 Microprocessors - CP 423L1Document47 pages4/18/2018 Microprocessors - CP 423L1Ragnar AlonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 The 8086 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument28 pagesChapter 2.1 The 8086 Microprocessor ArchitecturecudarunNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Lecture2Document6 pagesMicroprocessor Lecture2CS420100% (12)
- Ec8691 MPMC Question BankDocument31 pagesEc8691 MPMC Question Banksujithaa13No ratings yet
- Fall 2019/20 - Lecture Notes # 2: - Brief History of 80x86 Family of MicroprocessorsDocument16 pagesFall 2019/20 - Lecture Notes # 2: - Brief History of 80x86 Family of Microprocessorsrula mohammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter One and Two MicrocomputerDocument43 pagesChapter One and Two MicrocomputerBante TadeleNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller and MicroprocessorDocument16 pagesMicrocontroller and MicroprocessorShujaAmjadNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Systems ExplainedDocument10 pagesMicroprocessor Systems ExplainedDaisuke SSNo ratings yet
- EmbDocument358 pagesEmbsdot1209No ratings yet
- Esd Module-3 UpdatedDocument125 pagesEsd Module-3 Updatedsdot1209No ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Its ApplicationsDocument166 pagesMicroprocessor and Its ApplicationsDhivya Gokul100% (1)
- 3rd Unit FinalDocument80 pages3rd Unit FinalTARANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1:overview of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument34 pagesChapter 1:overview of 8085 Microprocessorzlight HagosNo ratings yet
- 6Document11 pages6itsaartihere001No ratings yet
- Ec6504 MPMC Unit 1Document249 pagesEc6504 MPMC Unit 1Anonymous IN80L4rRNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Unit-1 PART ADocument12 pagesMicroprocessor Unit-1 PART ASasi BhushanNo ratings yet
- Ece 8085 MicroprocessorDocument26 pagesEce 8085 Microprocessorgourav VermaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors II: Memory and Input/Output InterfacesDocument20 pagesMicroprocessors II: Memory and Input/Output Interfacesحاتم طلال علي جردوNo ratings yet
- PIC MicrocontrollerDocument27 pagesPIC Microcontrollermuthai100% (1)
- Introduction To 8086Document91 pagesIntroduction To 8086sayyanNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument42 pages8085 MicroprocessorSameerNo ratings yet
- Block Diagrams of Microcontrollers.: PD0-PD5 (Serial Port) PE0-PE7 (Eight ADC Inputs) PC0-PC7 PB0-PB7 PA3-PA6 PA0-PA2 PA7Document4 pagesBlock Diagrams of Microcontrollers.: PD0-PD5 (Serial Port) PE0-PE7 (Eight ADC Inputs) PC0-PC7 PB0-PB7 PA3-PA6 PA0-PA2 PA7novo orderNo ratings yet
- Greedy Method Session 8Document2 pagesGreedy Method Session 8Ponnapati LakshmimahithaNo ratings yet
- SESSION-11 Reading MaterialDocument8 pagesSESSION-11 Reading MaterialmineNo ratings yet
- SESSION-12 Reading MaterialDocument22 pagesSESSION-12 Reading MaterialmineNo ratings yet
- Sesion-4 Divide and Conquer TechniqueDocument32 pagesSesion-4 Divide and Conquer TechniquemineNo ratings yet
- SESSION-09 - Reading MeterialDocument5 pagesSESSION-09 - Reading MeterialmineNo ratings yet
- Session-7 Reading MeterialDocument7 pagesSession-7 Reading MeterialmineNo ratings yet
- Translation Look Aside BufferDocument17 pagesTranslation Look Aside BufferMeghanaNo ratings yet
- Sesion-4 Divide and Conquer TechniqueDocument32 pagesSesion-4 Divide and Conquer TechniquemineNo ratings yet
- Job Sequence With Deadlines ProblemDocument2 pagesJob Sequence With Deadlines ProblemmineNo ratings yet
- Quick Sort (A Best/good Case) : - It Occurs Only If Each Partition Divides The List Into Two Equal Size Sublists. - T (N) 2T (n/2) +CN O (Nlog N)Document5 pagesQuick Sort (A Best/good Case) : - It Occurs Only If Each Partition Divides The List Into Two Equal Size Sublists. - T (N) 2T (n/2) +CN O (Nlog N)mineNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Session 13 SegmentationDocument14 pagesOperating Systems Session 13 SegmentationmineNo ratings yet
- Session-6 - Reading MeterialDocument8 pagesSession-6 - Reading MeterialmineNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Session 10 Memory Virtualization: Address Spaces, Memory APIDocument25 pagesOperating Systems Session 10 Memory Virtualization: Address Spaces, Memory APImineNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Session 14 Free Space ManagementDocument23 pagesOperating Systems Session 14 Free Space ManagementmineNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Session 12 Address TranslationDocument16 pagesOperating Systems Session 12 Address TranslationmineNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument101 pagesComputer Organization and ArchitectureRam MNo ratings yet
- Session 19-20 ModifiedDocument34 pagesSession 19-20 ModifiedmineNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Session 15 PagingDocument15 pagesOperating Systems Session 15 PagingmineNo ratings yet
- Exercises B+TreeDocument9 pagesExercises B+Treekunal100% (1)
- HashingandIndexingas 2Document38 pagesHashingandIndexingas 2mineNo ratings yet
- The Abstraction The ProcessDocument12 pagesThe Abstraction The ProcessminniNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument101 pagesComputer Organization and ArchitectureRam MNo ratings yet
- Exercises B+TreeDocument9 pagesExercises B+Treekunal100% (1)
- Session 21-24 ModifiedDocument33 pagesSession 21-24 ModifiedmineNo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsDocument7 pagesPractice ProblemsmineNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument37 pagesComputer Organization and ArchitecturemineNo ratings yet
- MP 80863 PDFDocument21 pagesMP 80863 PDFmineNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument14 pagesChemistrymineNo ratings yet
- MicroProcessor SyllabusDocument8 pagesMicroProcessor Syllabustesfu zewduNo ratings yet
- Unit II 16 Bit Microprocessor Architecture 9Document37 pagesUnit II 16 Bit Microprocessor Architecture 9singhrps84100% (1)
- Embedded Systems Programming With The PIC16F877: Second Edition by Timothy D. GreenDocument196 pagesEmbedded Systems Programming With The PIC16F877: Second Edition by Timothy D. GreenRalph Anthony Constantino Planteras100% (1)
- Chapter 9: 8086/8088 Hardware SpecificationsDocument97 pagesChapter 9: 8086/8088 Hardware SpecificationsJohn ChalisseryNo ratings yet
- Elements of Embedded SystemsDocument40 pagesElements of Embedded SystemsAsante WilliamNo ratings yet
- Whcamacho - It150-8 - Ass 2.1Document2 pagesWhcamacho - It150-8 - Ass 2.1MICKAELA YEOGE BASCONo ratings yet
- Application of Digital Signal Processing ON TMS320C6713 DSKDocument21 pagesApplication of Digital Signal Processing ON TMS320C6713 DSKlakshamanaraoNo ratings yet
- Processors and Programmable Logic: Khaled Grati Grati - Khaled@Supcom - TN 2020-2021Document18 pagesProcessors and Programmable Logic: Khaled Grati Grati - Khaled@Supcom - TN 2020-2021ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit I Fundamentals of Computer Design and Ilp-1-14Document14 pagesUnit I Fundamentals of Computer Design and Ilp-1-14vamsidhar2008No ratings yet
- Computer Hardware and Software MCQ QuizDocument22 pagesComputer Hardware and Software MCQ QuizTareqNo ratings yet
- Dev Kit 8000Document5 pagesDev Kit 8000Shiva prasadNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument33 pagesMicroprocessor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMark kervin natividadNo ratings yet
- Aptitude TestDocument96 pagesAptitude TestSaikat MitraNo ratings yet
- 5.1 - Microcontroller and Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument35 pages5.1 - Microcontroller and Microprocessor ArchitectureMUHAMMAD HARIZ AZFAR AZAHARINo ratings yet
- Smart Cards: by Sravanthi KarumanchiDocument87 pagesSmart Cards: by Sravanthi KarumanchiSumaNo ratings yet
- Single Vs MulticoreDocument2 pagesSingle Vs MulticoreARTHEYA.R.S.No ratings yet
- Ucl 1.1Document73 pagesUcl 1.1Nick SofaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 SKEE3223 201520161 Rev3 - SOLUTION PDFDocument3 pagesTest 1 SKEE3223 201520161 Rev3 - SOLUTION PDFBAHARUDIN BURAHNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument16 pagesMicroprocessorReenaNo ratings yet
- 64 Bit Processors - 1Document15 pages64 Bit Processors - 1Asim NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Digit FastTrack May 2017Document101 pagesDigit FastTrack May 2017ArijitGhosh0% (1)
- 8086 Microprocesser InstructionsDocument22 pages8086 Microprocesser InstructionsSaddam HussainNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument19 pagesMicroprocessorParasNo ratings yet
- Change world, love job: TI Analog Eng InternDocument2 pagesChange world, love job: TI Analog Eng InternKunal KhareNo ratings yet
- Os (Unit 1)Document40 pagesOs (Unit 1)gopalhelpyouNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument28 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and ArchitectureAhmed Hassan MohammedNo ratings yet