Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Mind Map
Uploaded by
marieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Mind Map
Uploaded by
marieCopyright:
Available Formats
tidal volumes-volume
of air displaced between hyperventilation-
respiratory volumes inhalation and exhalation breathing deeply and
rapidly
Copy of Basic Mind Map
how do vital capacity- greatest
residual air- portion (Student) Marie Wheeler | March 30, 2020
respiratory muscles amount of air that can importance of
of air contained in the increased co2 apnea,
cause volume leave the lungs co2 and o2 in apnead- cessation
lungs that cant leave leads to increas in hyperventilation and
changes that lead to modifying beathing of breathing
rate and depth rate and depth hypoventilation
airflow in lungs
why is it not hypoventilation-
when inhaling, possible tostop deep shallow
the volume expands breathing voluntarily breathing
due to the contraction
of diaphram protective
mechanisms of the
when o2 supply is respitory system
low, respiratory centers
unction: turns co2 will ignore messages
stucture and
o2 blood. plueral from cortex
function of lungs and
verings help protect
plueral coverings
lungs
hair and mucus
trap particles, dust
and bacteria
gas exchange in
lungs and tissues nonrespiratory air
movements
Respiratory
in the tissues, gas system
exchange occurs in alveoli so normal changes in sneezing, coghing,
oxygen enters the bloodsteam. respiratory system burping. These do not
in the lungs it delivers o2 from from young to old include gas exchange
lungs to bloodsteam weakend muscles
for breathing, thinning of
bones, decline in lung
physical factors capacity
that influence
respiratory rate bronchi- the
main brinchi within the
lungs provide a direct
path to the air sacs
age, gender, size, trachea- air going
weight through is moisturied and cathces
debris and things before they
go into the lungs
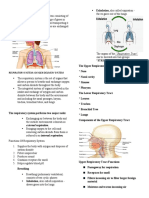
wheezing, chest Organs of the larynx- routes
tightness, shortness of respiratory system air and food into the
breath, coughing anf function proper channels and
mucus brain areas plays a role in
involved in control speech
of respiration
symtoms and probable Lungs- essemtial
Pharnyx- serves
structure of cauces of COPD and for normal human Nose- Air enters as passage way for
breathing through nose that consists
respiratory how is o2 and co2 lung cancer food and air
o2 enters the blood of nasal cavaties . Factor of
membrane transported in the due to the lungs and sense of smell is located in
mucosa
blood co2 is expelled out of
this membrane is
blood into lungs
very thin and consists
medulla oblongata, pons
of capilary wall and
alveolar wall
You might also like
- 2.1 Respiratory SystemDocument2 pages2.1 Respiratory Systemsmart guysNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - PhysiologyDocument4 pagesLesson Plan - PhysiologyBharathi 253No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for PneumoniaFARAH MAE MEDINANo ratings yet
- rusheDocument1 pagerusheCallie ParkNo ratings yet
- CAOLBOY Module 15 Activity Worksheet On Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesCAOLBOY Module 15 Activity Worksheet On Respiratory SystemAnton LeoncitoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PPT (Biology)Document8 pagesRespiratory System PPT (Biology)Maxxdlc 16No ratings yet
- Ncma 113Document4 pagesNcma 113Wonie booNo ratings yet
- Human Respiration HandoutDocument4 pagesHuman Respiration HandoutJulius GutierrezNo ratings yet
- External Respiration: Angiotensin-Converting EnzymeDocument4 pagesExternal Respiration: Angiotensin-Converting EnzymeEllä PabustanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPRoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaJhasmine MocnanganNo ratings yet
- O CO O CO O CO: Chapter 15: Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesO CO O CO O CO: Chapter 15: Respiratory SystemPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 978 1 349 09490 5 - 2 PDFDocument2 pages978 1 349 09490 5 - 2 PDFAbdullah Al NomanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 11 ANPH 111Document6 pagesWEEK 11 ANPH 111itsmearonsupanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 OxygenationDocument31 pagesChapter 20 OxygenationHannah Lat VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Airway ManagementDocument5 pagesAirway ManagementPriyanka KapuriaNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFsam KSSM 2019 DP DLP BIOLOGY FORM 4 PART 2-8Document1 page1 PDFsam KSSM 2019 DP DLP BIOLOGY FORM 4 PART 2-8deathangel88 GtNo ratings yet
- Iudmc ActivityDocument10 pagesIudmc ActivityJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaJojo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Careplan 1Document11 pagesCareplan 1ligaba1559No ratings yet
- Respiratory System OverviewDocument4 pagesRespiratory System Overviewbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- SPSF3 04 B2Document15 pagesSPSF3 04 B2Sin Ling WongNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Respiratory SystemAnnNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEMchartDocument1 pageRESPIRATORY SYSTEMchartninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemKent TutorNo ratings yet
- Animalphysio2nd 180428184330Document28 pagesAnimalphysio2nd 180428184330environmentalgyanNo ratings yet
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP For PneumoniaLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- Airway Clearance Nursing Interventions for Respiratory DistressDocument3 pagesAirway Clearance Nursing Interventions for Respiratory DistressMarc Jayson TobiasNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy and NebulizationDocument9 pagesOxygen Therapy and NebulizationArun Roa DanielNo ratings yet
- NCPPDocument11 pagesNCPPAngelo Miguel MuñozNo ratings yet
- Respiarotry SystemDocument4 pagesRespiarotry SystemrueNo ratings yet
- M7 RespiratoryDocument6 pagesM7 RespiratoryNel joy PaurilloNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Sample ChapterDocument6 pagesSample ChapterSupaporn MarknuiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care Planalexander abasNo ratings yet
- Ncma113 Lec Lab FinalDocument24 pagesNcma113 Lec Lab FinalJulla GalangNo ratings yet
- Dissection of The Amphibian Respiratory System and Mammalian Excretory SystemDocument6 pagesDissection of The Amphibian Respiratory System and Mammalian Excretory System门门No ratings yet
- 1a - Gonzalez, Jamaica Caryl N. (Respiratory)Document13 pages1a - Gonzalez, Jamaica Caryl N. (Respiratory)Jhamm GonzalezNo ratings yet
- OXYGENATIONDocument8 pagesOXYGENATIONJo Marchianne Pigar0% (1)
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument80 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- (BIOLOGY) Human Respiratory SystemDocument7 pages(BIOLOGY) Human Respiratory SystemHAJIRA RAMLANNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing SystemDocument10 pagesGas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing Systemka klklklNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument6 pagesRespirationAbu BeastNo ratings yet
- Summative Test ScienceDocument2 pagesSummative Test ScienceMheiabelle SagunNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDocument3 pagesAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Original PDF Medical Terminology A Living Language 7th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Medical Terminology A Living Language 7th Edition PDFmegan.soffel782100% (34)
- SN F3 Chapter 2Document40 pagesSN F3 Chapter 2Goh Hwei SiongNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceArabelle GONo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System I.: Subject: Subject TeacherDocument4 pagesThe Respiratory System I.: Subject: Subject TeacherHyacinth FarinasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System1Document5 pagesRespiratory System1Ombati StephenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment and Plan for Pneumonia PatientDocument9 pagesNursing Assessment and Plan for Pneumonia PatientKen IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 N LECTURE MidtermDocument42 pagesNCM 112 N LECTURE MidtermVivien IgnacioNo ratings yet
- NUR 213 Weekly Care Plane PneumoniaDocument10 pagesNUR 213 Weekly Care Plane PneumoniaSarah MoffattNo ratings yet
- 05 - SPSF3 03 B1Document16 pages05 - SPSF3 03 B1maza260399No ratings yet
- Ards Concept MapDocument1 pageArds Concept Mapchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Respiratory gymnastics (Translated): Purification - Health - Strength - EnergyFrom EverandRespiratory gymnastics (Translated): Purification - Health - Strength - EnergyNo ratings yet
- Specimen QP - Paper 3 OCR Biology (A) A-LevelDocument20 pagesSpecimen QP - Paper 3 OCR Biology (A) A-LevelAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- 〈90〉 Fetal Bovine Serum-Quality Attributes and Functionality TestsDocument4 pages〈90〉 Fetal Bovine Serum-Quality Attributes and Functionality Testsmehrdarou.qaNo ratings yet
- Carroll, S. B. - 2001 - Chance and Necessity. The Evolution of Morphological Complexity and Diversity PDFDocument8 pagesCarroll, S. B. - 2001 - Chance and Necessity. The Evolution of Morphological Complexity and Diversity PDFcontulmmivNo ratings yet
- B2.2 Movement in and Out of The CellDocument14 pagesB2.2 Movement in and Out of The Cellmenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- Tilenga ESIA Volume III - 28/02/19Document428 pagesTilenga ESIA Volume III - 28/02/19Total EP UgandaNo ratings yet
- Read Dis TooDocument6 pagesRead Dis TooNigga JohnNo ratings yet
- 3 The Apparatus Shown in The Diagram Below Was Used To Measure The Rate ofDocument3 pages3 The Apparatus Shown in The Diagram Below Was Used To Measure The Rate ofEricka AlvarezNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Microbial SpeciesDocument11 pagesThe Concept of Microbial SpeciesRin ChanNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis On The Use of Non Invasive Prenatal Testing For The Detection of Fetal Chromosomal Conditions in Singleton Pregnanciesprenatal Diagnosis - 2023 - HuiDocument15 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis On The Use of Non Invasive Prenatal Testing For The Detection of Fetal Chromosomal Conditions in Singleton Pregnanciesprenatal Diagnosis - 2023 - HuiYến ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Appn H Column Cleaning RegenerationDocument3 pagesAppn H Column Cleaning RegenerationducngoctrinhNo ratings yet
- Seeds & FruitDocument26 pagesSeeds & Fruitricabaloyo2002No ratings yet
- Part - 1 - Circulatory - System - 1.ppt Biology 2Document11 pagesPart - 1 - Circulatory - System - 1.ppt Biology 2RekaNo ratings yet
- New Hosts of Aeginetia PedunculataDocument3 pagesNew Hosts of Aeginetia PedunculataBikash Ranjan RayNo ratings yet
- AP Biology final exam revision guideDocument20 pagesAP Biology final exam revision guidealiNo ratings yet
- Pilot Study On Antardhuma Rasasindura A Forgotten AmbrosiaDocument8 pagesPilot Study On Antardhuma Rasasindura A Forgotten AmbrosiaKrasimir GeorgievNo ratings yet
- Basic Laboratory Equipment and Procedures in The Study of BacteriaDocument10 pagesBasic Laboratory Equipment and Procedures in The Study of BacteriaLloyd LozanoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Class 10Document35 pagesNervous System Class 10Just JaenNo ratings yet
- Epa 841 B 99 002 Hidrobiologia PDFDocument344 pagesEpa 841 B 99 002 Hidrobiologia PDFfredy perezNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas PutidaDocument8 pagesPseudomonas PutidaYazdhrik SilvaNo ratings yet
- SWSC2 - Learning Outcome 1Document9 pagesSWSC2 - Learning Outcome 1Marcela Coid100% (2)
- Food WebDocument8 pagesFood Webapi-4558008020% (2)
- Factors Affecting Drug ResponseDocument21 pagesFactors Affecting Drug ResponseChaseNo ratings yet
- EWMA Endorsements of Wound Centres Non Hospital Based ApplicationForm WordDocument17 pagesEWMA Endorsements of Wound Centres Non Hospital Based ApplicationForm WordCarlo BalzereitNo ratings yet
- 108 Most Suffix and Prefix CssprepforumDocument30 pages108 Most Suffix and Prefix CssprepforumZeeshan AhmadNo ratings yet
- PNLE - FON Practice Exam For Stress, Crisis, Crisis Intervention, Communication, Recording, Learning and DocumentationDocument21 pagesPNLE - FON Practice Exam For Stress, Crisis, Crisis Intervention, Communication, Recording, Learning and DocumentationAzurin JewelNo ratings yet
- Bakoume Et Al GRES2014Document14 pagesBakoume Et Al GRES2014Juan Gabriel Burgos GuerrónNo ratings yet
- Anuja - Chandrasekar - V2 (AD - V1)Document1 pageAnuja - Chandrasekar - V2 (AD - V1)khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Dance - Lars Chittka PDFDocument3 pagesDance - Lars Chittka PDFprabhudevmvNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Fetal DevelopmentDocument1 pageQuiz 2 Fetal DevelopmentDENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Trivial Pursuit - QuestionsDocument6 pagesTrivial Pursuit - Questionsapi-219485794No ratings yet