Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classification of Skin Presenting Disorders Bener
Uploaded by
cat momsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classification of Skin Presenting Disorders Bener
Uploaded by
cat momsCopyright:
Available Formats
Classification of Skin Presenting Disorders
Inflammatory Diseases Based on Abnormal Humoral Reactivity and Other Inflammatory Diseases
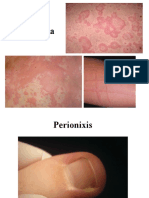
1. Urticaria and Angioedema
- Urticaria : skin lesion consisting of a wheal-and-flare reaction in which localized
intracutaneous edema (wheal) is surrounded by an area of redness (erythema) that is
typically pruritic.
- Circumscribed, raised, erythematous, highly pruritic, evanescent areas of edema that
involve the superficial portion of the dermis
- Arise suddenly, can last 24 to 48 hours
- They can be as small as millimeter or 6 to 8 inches in diameter (giant urticaria).
- Angioedema : can be caused by the same pathogenic mechanisms as urticaria, but the
pathology is in the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue and swelling is the major
manifestation.
- The overlying skin may be erythematous or normal
- Commonly affects the face or a portion of an extremity, lips, cheeks, and periorbital areas,
but also may affect tongue, pharynx, or larynx.
- Last several days
- Less pruritus, but pain or burning may be present
2. Erythema Multiforme
- Acute self-limited, usually mild, frequent reccurent
- Related to an acute infection : Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
- Face & extrimities
3. Epidermal Necrolysis ( Steven-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis)
- Rare, life-threatening, mainly drug induced
- Widespread and extensive necrosis of keratinocytes
- Confluent pupuric, erythematous macules ,flaccid blisters, detachment of the epidermis,
associated with mucous membrane
- the trunk and upper limbs
4. Cutaneous Reaction to Drugs
- Drug-induced
- They range from common nuisance rashes to rare life-threatening diseases
- Exanthematous, urticarial, pustular, bullous, erythema multiforme-like eruptions
5. Pityriasis Rosea
- Pityriasis : scale, rosea : pink
- Most often begins as a single 2 to 4 cm thin oval plaque with a fine collarette of scale
located inside the periphery of the plaque (“herald patch”). Similar-appearing, but smaller,
lesions then appear several days to weeks later and are typically distributed along the lines
of cleavage on the trunk (in a “Christmas tree” pattern)
- Usually asymptomatic, but sometimes with pruritus and mild flu-like symptoms
- Occurs most commonly in teenagers and young adults
Shindy Octavia W | B3 | 130110120010
6. Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figure Erythemas
- No single cause, uncommon disorder
- Annular expanding erythematous rings, which enlarge rapidly, fade, and then disappear, as
new lesions appear
- Can be superficial or deep lesion
7. Granuloma Annulare
- Relatively common disorder, children and young adults
- A localized ring of beaded papules on the extrimities is typical; generalized, subcutaneous,
perforating
Disorders of Epidermal Differentiation and Keratinization
1. Irritant Contact Dermatitis
2. The Ichthyoses
- A heterogenous group of skin diseases, generalized scaling, and often, areas of thickened
skin
- Most types are inherited, usually present at birth, however, some forms are acquired
- Scale may vary in size, color, and body site
- May be accompanied by erythema, abnormalities in other parts of skin, and adnexal
structures
- May be associated with systemic findings, such as failure to thrive, increased susceptibility
to infection, atopic dermatitis, neurosensory deafness, neurologic and other disease
3. Inherited Keratodermas of Palms and Soles
- Chronic thickening of palms and soles may be found alone (simple), in combination with skin
lesions elsewhere (complex), or in association with complex syndrome (syndromic),
including ectodermal dysplasia where hair, teeth, and nails may be affected
4. Acantholytic Disorders of the Skin
- Darier-White Disease : genetic disorder; warty papules and plaques in seborrheic areas,
specific nail changes, palmo-plantar pits, and papules on the dorsum of the hands and feet
- Acrokeratosis Verruciforms : rare, multiple small flat papules on the dorsum of the hands
and feet
- Grover Disease : pruritic, polymorphic, cutaneous papulovesicular eruption on the trunk,
occurs in adults after long-term sun damage
- Hailey-Hailey Disease : also called familial benign chronic pemphigus, late-onset blistering
dermatosis, painful erosions and fissures (rhagades) in the flexures
5. Porokeratosis
- Chronic progressive disorder of keratinization
- Hyperkeratotic papules or plaques surrounded by a thread-like elevated border that
expands centrifugally
Shindy Octavia W | B3 | 130110120010
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- HemaLec MLS3D Module1.1Document9 pagesHemaLec MLS3D Module1.1Carmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- 05 Szasz and TorreyDocument14 pages05 Szasz and Torreyscribd4kmhNo ratings yet
- Memo and MinutesDocument3 pagesMemo and MinutesJennifer BeguinwaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of COVID-19Document3 pagesSymptoms of COVID-19Xx XxNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Bone TumorsDocument6 pagesGeneral Principles of Bone TumorsRonald TejoprayitnoNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter To The EditorDocument2 pagesCover Letter To The EditorMohamed GhaliNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument5 pagesHematologyIvy Jan OcateNo ratings yet
- ADN3-1 Digestive HP - 200 - Yang, Myung SookDocument37 pagesADN3-1 Digestive HP - 200 - Yang, Myung SookNorPhea - នភាNo ratings yet
- GLIOBLASTOMADocument20 pagesGLIOBLASTOMACece RereNo ratings yet
- CACCN Study Guide, Final Questions, Answers Oct 2010Document63 pagesCACCN Study Guide, Final Questions, Answers Oct 2010Chris Zantira100% (2)
- Case Report: Giant Condyloma Acuminatum of Vulva in An HIV-Infected WomanDocument4 pagesCase Report: Giant Condyloma Acuminatum of Vulva in An HIV-Infected WomanPutri Intan SolehahNo ratings yet
- Recapitulare TestDocument38 pagesRecapitulare TestDana ChitoiNo ratings yet
- APHERESIS Is A Term of Greek Derivation That Means "To Separate or ToDocument4 pagesAPHERESIS Is A Term of Greek Derivation That Means "To Separate or ToMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- L3 - Bronchial AsthmaDocument37 pagesL3 - Bronchial Asthmazaini nieNo ratings yet
- XIJU5502Document3 pagesXIJU5502Praveen ReddyNo ratings yet
- BFS Case DiscxnDocument23 pagesBFS Case DiscxnLennon Ponta-oyNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) During Pregnancy - Clinical Findings, Etiology, and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument23 pagesDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) During Pregnancy - Clinical Findings, Etiology, and Diagnosis - UpToDateCristinaCaprosNo ratings yet
- Corona Ebook PDFDocument18 pagesCorona Ebook PDFManish Mishra100% (1)
- Fosbac Plus T (F+T) : in Broiler ProductionDocument25 pagesFosbac Plus T (F+T) : in Broiler Productionthanh ba matNo ratings yet
- 4 Protein NotesDocument4 pages4 Protein NotesChitogeNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Corticospinal and Corticobulbar Tracts in The Human NewbornDocument6 pagesFunctions of The Corticospinal and Corticobulbar Tracts in The Human NewbornMas ArikNo ratings yet
- Variations of HIV Testing PDFDocument20 pagesVariations of HIV Testing PDFDeekuNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal: Bleeding in Infants and ChildrenDocument16 pagesGastrointestinal: Bleeding in Infants and ChildrenAdelia AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Contaminants From Food and Food HandlingDocument26 pagesContaminants From Food and Food HandlingLien Mar GastadorNo ratings yet
- NMC High Risk ObjectivesDocument4 pagesNMC High Risk ObjectivesAwudu RuhainatNo ratings yet
- Clinical Microscopy Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument5 pagesClinical Microscopy Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersGlazel TulaganNo ratings yet
- 5 Naila Choudhury - Med Student - Essay Prize 2022Document11 pages5 Naila Choudhury - Med Student - Essay Prize 2022ANDRE AURELLIONo ratings yet
- Polycythemi A: Presented By: Palaran, Nina Mae CDocument16 pagesPolycythemi A: Presented By: Palaran, Nina Mae CJichutreasureNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Midwifery & Gynaecology Nursing Papers QPDocument14 pages3.1 Midwifery & Gynaecology Nursing Papers QPTapobrata Sarkar100% (1)
- Acute Pancreatitis 2023Document25 pagesAcute Pancreatitis 2023raphael chidiebereNo ratings yet