Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grouting Corrosion Structural Behaviors: in Situ
Uploaded by
dela rosaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grouting Corrosion Structural Behaviors: in Situ
Uploaded by
dela rosaCopyright:
Available Formats
n bonded post-tensioning, tendons are permanently bonded to the surrounding concrete by the in
situ grouting of their encapsulating ducting (after tendon tensioning). This grouting is undertaken for
three main purposes: to protect the tendons against corrosion; to permanently "lock-in" the tendon
pre-tension, thereby removing the long-term reliance upon the end-anchorage systems; and to
improve certain structural behaviors of the final concrete structure.[9]
Bonded post-tensioning characteristically uses tendons each comprising bundles of elements (e.g.
strands or wires) placed inside a single tendon duct, with the exception of bars which are mostly
used unbundled. This bundling makes for more efficient tendon installation and grouting processes,
since each complete tendon requires only one set of end-anchorages and one grouting operation.
Ducting is fabricated from a durable and corrosion-resistant material such as plastic
(e.g. polyethylene) or galvanised steel, and can be either round or rectangular/oval in cross-section.
[2]:7
The tendon sizes used are highly dependent upon the application, ranging from building works
typically using between 2 and 6 strands per tendon, to specialized dam works using up to 91 strands
per tendon.
Fabrication of bonded tendons is generally undertaken on-site, commencing with the fitting of end-
anchorages to formwork, placing the tendon ducting to the required curvature profiles, and reeving
(or threading) the strands or wires through the ducting. Following concreting and tensioning, the
ducts are pressure-grouted and the tendon stressing-end
You might also like
- A Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsFrom EverandA Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsNo ratings yet
- تقرير كرار مسعود خشنDocument13 pagesتقرير كرار مسعود خشنكرار مسعود خشنNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Techel 3Document46 pagesTechel 3Sheryll de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Composite Steel and Concrete Structural Members: Composite Steel and Concrete Structures: Fundamental Behaviour (Second Edition)From EverandComposite Steel and Concrete Structural Members: Composite Steel and Concrete Structures: Fundamental Behaviour (Second Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Pre-Tensioned Concrete: Prestressed Concrete Is A Form ofDocument4 pagesPre-Tensioned Concrete: Prestressed Concrete Is A Form ofdwarika2006No ratings yet
- Introduction To: Prestressed ConcreteDocument26 pagesIntroduction To: Prestressed ConcreteTerityNo ratings yet
- Developments in External Post-Tensioning Systems: A Case Study On The Learnings From Multiple Structures Across OceaniaDocument10 pagesDevelopments in External Post-Tensioning Systems: A Case Study On The Learnings From Multiple Structures Across OceaniaAndrea GennaroNo ratings yet
- Elastic, Plastic and Yield Design of Reinforced StructuresFrom EverandElastic, Plastic and Yield Design of Reinforced StructuresNo ratings yet
- Pre Stress ConcreteDocument10 pagesPre Stress ConcreteSuraj WankhedeNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument15 pagesPrestressed ConcreteMariz Ellaine BaltazarNo ratings yet
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsFrom Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Post Tension StructuresDocument10 pagesPost Tension Structurestwinkle4545No ratings yet
- Corrosion and its Consequences for Reinforced Concrete StructuresFrom EverandCorrosion and its Consequences for Reinforced Concrete StructuresNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument15 pagesPrestressed ConcreteSheryll de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Bonded Vs UnbondedDocument10 pagesBonded Vs Unbondedarun0001100% (1)
- Research I Reinforcement Concrete II Prestressed Reinforced ConcreteDocument6 pagesResearch I Reinforcement Concrete II Prestressed Reinforced ConcreteHamez HabibiNo ratings yet
- Tendon SlideDocument32 pagesTendon SlideMuhammad Faiz bin Ahmad ShafiNo ratings yet
- TTM Slab Bonded and Unbonded SystemsDocument108 pagesTTM Slab Bonded and Unbonded SystemsMihai MarianNo ratings yet
- Post-Tensioning SystemsDocument5 pagesPost-Tensioning Systemsnewbebo877No ratings yet
- Dsi Usa What Is Post Tensioning UsDocument2 pagesDsi Usa What Is Post Tensioning UsBramodh JayanthiNo ratings yet
- Post Tensioned SlabsDocument11 pagesPost Tensioned SlabsTlvs MurthyNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument4 pagesPrestressed ConcreteNithun KumarNo ratings yet
- DMK Stay SystemDocument20 pagesDMK Stay SystemspqdragadosirelandNo ratings yet
- Building Technology 5: (Assignment No. 5)Document4 pagesBuilding Technology 5: (Assignment No. 5)Daryl AguilarNo ratings yet
- KGN BrochureDocument8 pagesKGN BrochureBijaya RaulaNo ratings yet
- Post TensioningDocument6 pagesPost TensioningmohdkhalidrazaNo ratings yet
- Strengthening Techniques of RC Columns Using Fibre Reinforced Polymeric MaterialsDocument8 pagesStrengthening Techniques of RC Columns Using Fibre Reinforced Polymeric MaterialsSirimantha KodituwakkuNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete STRUCTURES 1) Advantages of Prestressed ConcreteDocument2 pagesPrestressed Concrete STRUCTURES 1) Advantages of Prestressed ConcreteKannan CrNo ratings yet
- Materials and Jacketing TechniqueDocument5 pagesMaterials and Jacketing TechniqueHoussam Al MoussawiNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument32 pagesPrestressed ConcretejaffnaNo ratings yet
- Research Architectural: Tech VDocument6 pagesResearch Architectural: Tech VMark DanielNo ratings yet
- Rockfall BarrierDocument12 pagesRockfall BarrierĐorđe RadisavljevićNo ratings yet
- Lab Mannual PRC Final 1Document32 pagesLab Mannual PRC Final 1Khalil AhmedNo ratings yet
- On Pre Stressed ConcreteDocument6 pagesOn Pre Stressed ConcreteArjun Kisan Shende50% (2)
- Mones - Lets Analyze (P. 57)Document5 pagesMones - Lets Analyze (P. 57)Joshua MonesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Prestressed ConcreteDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Prestressed ConcreteDarlene Kate MonterdeNo ratings yet
- D-Product Watch Crigler Post Tension Revisit1Document4 pagesD-Product Watch Crigler Post Tension Revisit1khx2No ratings yet
- Pre Stressed ConcreteDocument5 pagesPre Stressed Concreteridzwan8789No ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument11 pagesPrestressed Concretesharan31No ratings yet
- FREYSSINET Prestress ManualDocument53 pagesFREYSSINET Prestress Manualras_deep100% (2)
- Prestressed Concrete: BT AR Joseph ReaDocument4 pagesPrestressed Concrete: BT AR Joseph ReaDaryl AguilarNo ratings yet
- Engineer TermsDocument8 pagesEngineer TermsBintang RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Post Tension IngDocument40 pagesPost Tension IngMmuthu KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Disney Theme Park in East AsiaDocument8 pagesDisney Theme Park in East Asiajerry elizagaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Prestressed ConcreteDocument1 pageIntroduction To Prestressed ConcreteJayson IsidroNo ratings yet
- Post Tensioning DefinedDocument2 pagesPost Tensioning DefinedkamnaralhanNo ratings yet
- MacroSyntheticFiberReinforced TunnelLinings PDFDocument13 pagesMacroSyntheticFiberReinforced TunnelLinings PDFDaniel ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Seminor On Prestressed ConcreteDocument43 pagesSeminor On Prestressed ConcreteNatarajan SaravananNo ratings yet
- Pre StressingDocument5 pagesPre StressingAakriti VermaNo ratings yet
- Advances in Flexible Pipe Design and Construction: A Seminar OnDocument20 pagesAdvances in Flexible Pipe Design and Construction: A Seminar OnChaithanya Kumar DanduNo ratings yet
- Husana, Thessaly Aubrey S. - Bt115 - Research No. 2aDocument19 pagesHusana, Thessaly Aubrey S. - Bt115 - Research No. 2aThessaly HusanaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Small Movement Exp Jts PDFDocument15 pagesLiterature Review Small Movement Exp Jts PDFRamesh P KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Post Tensioned ConcreteDocument3 pagesPost Tensioned ConcreteZekariyas AbushaNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete: Masood Khan B. Arch. 4 Year (DayDocument15 pagesPrestressed Concrete: Masood Khan B. Arch. 4 Year (Daymasood khanNo ratings yet
- Structural Behavior of Steel-Concrete Composite BeamDocument12 pagesStructural Behavior of Steel-Concrete Composite BeamJaime Morales BazalduaNo ratings yet
- 'Cables'in Lightweight and Membrane StructuresDocument8 pages'Cables'in Lightweight and Membrane StructuresSuvarna456100% (1)
- Obligations and Contracts 3.0Document139 pagesObligations and Contracts 3.0dela rosaNo ratings yet
- CIAP Document 102 PDFDocument77 pagesCIAP Document 102 PDFjeanvaljean999No ratings yet
- Plate No. I. Design of A One-Way SlabDocument11 pagesPlate No. I. Design of A One-Way Slabdela rosaNo ratings yet
- C.E. 324 - Ethics - 1.0Document103 pagesC.E. 324 - Ethics - 1.0dela rosaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 R.A 9184Document51 pages2.0 R.A 9184dela rosaNo ratings yet
- Nat. Bldg. CodeDocument34 pagesNat. Bldg. Codedela rosaNo ratings yet
- Dela Rosa Plate # 5Document8 pagesDela Rosa Plate # 5dela rosaNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of Soil Using Seashell and Coconut HuskDocument40 pagesStabilization of Soil Using Seashell and Coconut Huskdela rosaNo ratings yet
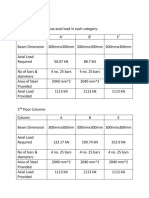
- Column Design SummaryDocument2 pagesColumn Design Summarydela rosaNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument1 pageContentsdela rosaNo ratings yet
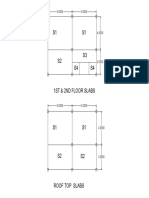
- Slab Layout PDFDocument1 pageSlab Layout PDFdela rosaNo ratings yet
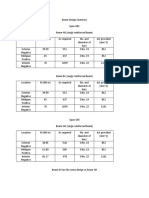
- Beam Design SummaryDocument2 pagesBeam Design Summarydela rosaNo ratings yet
- Slab Design SmmaryDocument2 pagesSlab Design Smmarydela rosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 1Document6 pagesChapter 3 1dela rosaNo ratings yet
- Pre Stressed 3Document1 pagePre Stressed 3dela rosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Results and DiscussionDocument1 pageChapter 4: Results and Discussiondela rosaNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of Clay Soil Using Seashells and Coconut HusksDocument14 pagesStabilization of Clay Soil Using Seashells and Coconut Husksdela rosaNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument59 pagesPrestressed ConcretescrNo ratings yet
- WEEK4ADocument1 pageWEEK4Adela rosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Review of Related Studies and LiteratureDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Review of Related Studies and Literaturedela rosaNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument59 pagesPrestressed ConcretescrNo ratings yet
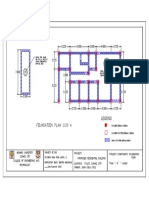
- Legend: COLUMN 250mm X 250mmDocument1 pageLegend: COLUMN 250mm X 250mmdela rosaNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument59 pagesPrestressed ConcretescrNo ratings yet
- WEEK3ADocument10 pagesWEEK3Adela rosaNo ratings yet
- Personal DataDocument1 pagePersonal Datadela rosaNo ratings yet
- WEEK3ADocument10 pagesWEEK3Adela rosaNo ratings yet
- Duty Time Record: Date Day/Month/Yea R Time Signature OF Supervisor Total Hours Remarks IN OUTDocument2 pagesDuty Time Record: Date Day/Month/Yea R Time Signature OF Supervisor Total Hours Remarks IN OUTdela rosaNo ratings yet
- Project: One Storey Residence Subject: Bills of Materials and Cost EstimateDocument6 pagesProject: One Storey Residence Subject: Bills of Materials and Cost Estimatedela rosaNo ratings yet
- WEEK3ADocument10 pagesWEEK3Adela rosaNo ratings yet
- Duty Time Record: Date Day/Month/Yea R Time Signature OF Supervisor Total Hours Remarks IN OUTDocument2 pagesDuty Time Record: Date Day/Month/Yea R Time Signature OF Supervisor Total Hours Remarks IN OUTdela rosaNo ratings yet