Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vico, Niecolle P. BSMT 1C REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CONCEPT MAP 2 PDF
Uploaded by
Niecolle VicoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vico, Niecolle P. BSMT 1C REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CONCEPT MAP 2 PDF
Uploaded by
Niecolle VicoCopyright:
Available Formats
Vico, Niecolle P.
BSMT 1C
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CONCEPT MAP
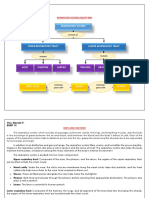
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
In males, includes In females, includes
TESTIS OVARIES
Contain cells that undergo Contain cells that undergo
SPERMATOGENESIS OOGENESIS
Gives rise to Gives rise to
SPERM CELLS EGG CELLS
Come together at
FERTILIZATION
Results in
ZYGOTE
Developmental stages include
PREEMBRYONIC EMBRYONIC FETAL BIRTH
Vico, Niecolle P.
BSMT 1C
PARTS AND FUNCTIONS
Humans are sexual, meaning that both a male and a female are needed to reproduce.
Each is equipped with specific organs capable of producing specific cells needed to
procreate.
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The female reproductive system is one of the most vital parts of the human reproductive
process. Although a man is needed to reproduce, it is the woman who incubates the
developing fetus and delivers the child into the world.
The major organs of the female reproductive system include:
Vagina: This muscular tube receives the penis during intercourse and through it a baby
leaves the uterus during childbirth.
Uterus: This organ holds and nourishes a developing fetus, if an egg was properly
fertilized.
Ovaries: The female gonads, the ovaries produce ova. When one matures, it is released
down into a fallopian tube.
Fallopian tubes: These small tubes transport ova from the ovaries to the uterus. This is
where an egg waits to be fertilized.
When properly fertilized with a man’s sperm — either through intercourse or artificial
insemination — a woman’s egg carries all of the necessary material to produce children.
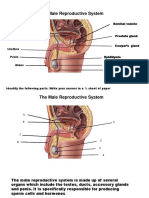
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
For men, the external reproductive organs include:
Penis: This tubular, muscular organ fills with blood during arousal, thus making sexual
intercourse possible.
Scrotum: This pouch-like sac hangs below the penis and encases the testes, or testicles.
Testicles: These two oval shaped organs produce sperm cells and testosterone.
While all men are born with all of their sexual organs, they don’t begin to function fully until
puberty. The average age of puberty for males is around 12. During this time, hormone
changes affect a boy’s gonads and create lasting changes that have typically been viewed
through history as “when a boy becomes a man.” This process has many effects, such as
growth in stature, muscular development, and hair growth on the genitals and face. In terms
of reproduction, puberty signals the time when a man has fully-functioning sexual organs and
is capable of fathering an offspring.
You might also like
- Fetal Development Nursing CareDocument20 pagesFetal Development Nursing CareiMaibelle BelleNo ratings yet
- Compilation Medsurg PrelimsDocument29 pagesCompilation Medsurg PrelimsEunice CuñadaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Female Reproductive System 01092010Document57 pagesPhysiology of Female Reproductive System 01092010Azry MustapaNo ratings yet
- Compare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument4 pagesCompare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsJung Somin100% (1)
- Score: Answer This Test in One Hour.: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesScore: Answer This Test in One Hour.: Multiple ChoiceMara LabanderoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Physiology (Female)Document23 pagesReproductive Physiology (Female)هدى قحطان جليل100% (1)
- Tarlac State University Nursing Quiz on Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesTarlac State University Nursing Quiz on Nervous SystemJobelle VergaraNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System FinalDocument5 pagesMale Reproductive System FinalJohn Dale Lulu CruzNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAriel CancinoNo ratings yet
- Hirchsprung Disease: A.K.A. Congenital AganglionicDocument29 pagesHirchsprung Disease: A.K.A. Congenital Aganglionicdesh_dacanayNo ratings yet
- Host Response To InfectionDocument36 pagesHost Response To InfectionFrancia Toledano100% (1)
- Male Reproductive System - PPTX NewDocument7 pagesMale Reproductive System - PPTX NewSarilyn SimonNo ratings yet
- MenstruationDocument6 pagesMenstruationOmhar CeresNo ratings yet
- Learning Module 1 - Reproductive Health FormsDocument3 pagesLearning Module 1 - Reproductive Health FormsReyna Mee AhiyasNo ratings yet
- Inversion of Uterus 170225210149Document54 pagesInversion of Uterus 170225210149anju kumawatNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and MaturationDocument21 pagesFertilization and MaturationRenz L. SalumbreNo ratings yet
- Human Fertilization Is The Union of A Human Egg and SpermDocument7 pagesHuman Fertilization Is The Union of A Human Egg and Spermoxidalaj100% (1)
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRalph CelesteNo ratings yet
- From Egg to Newborn - A Guide to Conception and PregnancyDocument63 pagesFrom Egg to Newborn - A Guide to Conception and PregnancyCristine Joy GuinoNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument10 pagesMenstrual CycleintanNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument25 pagesThe Reproductive SystemCoran St Nicholi Beckford INo ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerPointDocument22 pagesMeiosis PowerPointLary Bags100% (1)
- The Menstrual Cycle ExplainedDocument13 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle ExplainedBeanna Pinard100% (1)
- Prenatal Management (Part 5)Document36 pagesPrenatal Management (Part 5)Austine James Sabenicio PantiloNo ratings yet
- Intestinal and Commensal AmoebaDocument9 pagesIntestinal and Commensal AmoebaFuture TrekingNo ratings yet
- Roles of Hormones in Menstrual CycleDocument17 pagesRoles of Hormones in Menstrual CycleLeena Muniandy100% (1)
- Prenatal Management (Part 4)Document17 pagesPrenatal Management (Part 4)Austine James Sabenicio PantiloNo ratings yet
- Digestive System in HumanDocument20 pagesDigestive System in Humanapi-400692183No ratings yet
- 5 P - S of LaborDocument19 pages5 P - S of LaborPerrilyn PereyNo ratings yet
- FERTILIZATION & IMPLANTATION STAGESDocument20 pagesFERTILIZATION & IMPLANTATION STAGESMochammad Rizal Attamimi0% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocument89 pagesReproductive SystemIbrahim Mahmoud Ali100% (1)
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemJohn Paulo Morales50% (2)
- Menstrual Cycle: Anna Liza F. Rabo RN, ManDocument31 pagesMenstrual Cycle: Anna Liza F. Rabo RN, ManFhei Lya Dee TioNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Control of The Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesHormonal Control of The Reproductive SystemRamoj Reveche PalmaNo ratings yet
- Session #43 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document4 pagesSession #43 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19: Nutritional Needs of A NewbornDocument13 pagesChapter 19: Nutritional Needs of A NewbornAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument5 pagesNCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusKristine BartsNo ratings yet
- OogenesisDocument18 pagesOogenesisIsraa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4 GametogenesisDocument13 pagesLab Report 4 GametogenesisWnz NaiveNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pagesCoordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsSarah CruzNo ratings yet
- Placenta CirculationDocument11 pagesPlacenta CirculationJason Jimmy Lee PillayNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual Cycle: Name: Class: DateDocument3 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle: Name: Class: DateJustine Batis100% (2)
- Presented By-Ms. Nidhi Shukla M.Sc. Nursing 1 YearDocument43 pagesPresented By-Ms. Nidhi Shukla M.Sc. Nursing 1 YearFajar Islam SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Cilia and Flagella Structure and FunctionDocument10 pagesCilia and Flagella Structure and FunctionEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Patricia Benner's Stages of Clinical CompetenceDocument2 pagesPatricia Benner's Stages of Clinical CompetenceBea Trisha ArietaNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus-AnaDocument10 pagesCourse Syllabus-AnaMariamiraluz Khalidryan Sevilla-BurlasNo ratings yet
- Module 2 The Human Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument27 pagesModule 2 The Human Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyJhunna Talangan100% (1)
- Reproductive and Sexual Health NotesDocument9 pagesReproductive and Sexual Health NotesKayeNo ratings yet
- 5 - Care of The Mother and The FetusDocument36 pages5 - Care of The Mother and The FetusMa Nelia P Magsino100% (2)
- Biochem Introduction A PDFDocument107 pagesBiochem Introduction A PDFDaevy Toribio AmdosNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument15 pagesMale Reproductive SystemCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Bed Bath ExaMDocument2 pagesBed Bath ExaMKweng Kweng DoongNo ratings yet
- NCM QuizDocument7 pagesNCM QuizKyla Marie NabongNo ratings yet
- Expanded Newborn ScreeningDocument27 pagesExpanded Newborn ScreeningCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System OverviewDocument21 pagesReproductive System OverviewJacquelyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument11 pagesMenstrual CycleSteph QuisquinoNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta and AbortionDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta and Abortiondanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument30 pagesAssessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentWild Rose100% (2)
- Gametogenesis: Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis: Dr. Naveen Kumar MMMC ManipalDocument16 pagesGametogenesis: Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis: Dr. Naveen Kumar MMMC ManipalLim Yi QiNo ratings yet
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahNo ratings yet
- Ethics: M1 Lesson 1: Intro To Ethics - What Is Ethics?Document9 pagesEthics: M1 Lesson 1: Intro To Ethics - What Is Ethics?Niecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Rizal and Popular Nationalism: TopicDocument8 pagesRizal and Popular Nationalism: TopicNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Vico, Niecolle P. BSMT 1C URINARY SYSTEM CONCEPT MAP PDFDocument2 pagesVico, Niecolle P. BSMT 1C URINARY SYSTEM CONCEPT MAP PDFNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesLecture 12 Reproductive SystemNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Rizal and Popular Nationalism: TopicDocument8 pagesRizal and Popular Nationalism: TopicNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Vico, Niecolle P. BSMT 1C RESPIRATORY SYSTEM CONCEPT MAP PDFDocument2 pagesVico, Niecolle P. BSMT 1C RESPIRATORY SYSTEM CONCEPT MAP PDFNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- The Campaign FOR ReformsDocument37 pagesThe Campaign FOR ReformsNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Studies and Medical Imaging Understanding PathologyDocument6 pagesLaboratory Studies and Medical Imaging Understanding PathologyNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Practicum2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesPracticum2 ReviewerNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- CCIDocument2 pagesCCINiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Standard Precaution TermsDocument6 pagesLaboratory Standard Precaution TermsNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument2 pagesMicroNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Hematology TerminologiesDocument3 pagesHematology TerminologiesNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Studies and Medical Imaging Understanding PathologyDocument6 pagesLaboratory Studies and Medical Imaging Understanding PathologyNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 1 Clinical Chemistry 2 Clinical Chemistry 3Document1 pageClinical Chemistry 1 Clinical Chemistry 2 Clinical Chemistry 3Niecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Practicum2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesPracticum2 ReviewerNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- PracticumDocument5 pagesPracticumNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Centro Escolar University Urine and Stool Analysis ReportsDocument2 pagesCentro Escolar University Urine and Stool Analysis ReportsNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument2 pagesMicroNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Standard Precaution TermsDocument6 pagesLaboratory Standard Precaution TermsNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Isbb TermsDocument3 pagesIsbb TermsNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- CCIDocument2 pagesCCINiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Films that bring the issue of waste to lightDocument7 pagesFilms that bring the issue of waste to lightLaudianeSant'AnnaNo ratings yet
- 6BBL0325 2 TheoriesofAgeingRandomDamageDocument10 pages6BBL0325 2 TheoriesofAgeingRandomDamageVaidehi KatariaNo ratings yet
- Womens Basketball Spring Strength Training-2Document1 pageWomens Basketball Spring Strength Training-2api-548848665No ratings yet
- Sounds Like HealthyDocument22 pagesSounds Like Healthybucindonghae yoongiNo ratings yet
- SearchDocument216 pagesSearchTina LocklearNo ratings yet
- Measuring OutcomesDocument58 pagesMeasuring OutcomesEbony2514100% (1)
- Kejadian Plebitis Bulan April 2019Document326 pagesKejadian Plebitis Bulan April 2019Ridho YulfiahNo ratings yet
- The Hold Me Tight Workbook - Dr. Sue JohnsonDocument187 pagesThe Hold Me Tight Workbook - Dr. Sue JohnsonMoh100% (8)
- Myths and Facts About Guidance and CounsellingDocument4 pagesMyths and Facts About Guidance and CounsellingEfren Jonicel DomingoNo ratings yet
- Food Allergen Management Plan: Employees and TrainingDocument4 pagesFood Allergen Management Plan: Employees and TrainingKharisma NusantaraNo ratings yet
- Course Specification Mechanical Engineering FundamentalsDocument7 pagesCourse Specification Mechanical Engineering FundamentalsHassan Iftekhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Inverse Transcription 2Document4 pagesInverse Transcription 2Berenice CázaresNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement On Young MarriageDocument8 pagesThesis Statement On Young Marriagebser9zca100% (2)
- Kaplan-Meier Survival AnalysisDocument5 pagesKaplan-Meier Survival AnalysisDong DongNo ratings yet
- Calcium Oxide Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesCalcium Oxide Safety Data SheetGİZEM DEMİRNo ratings yet
- Lutz, Nutrition and Diet Therapy 6e ETBDocument15 pagesLutz, Nutrition and Diet Therapy 6e ETBShelly-ann Richards-FrancisNo ratings yet
- Isometrics Mass ManualDocument41 pagesIsometrics Mass Manualassssssssss100% (6)
- CPCWHS3001 - Learner Guide V1.0Document20 pagesCPCWHS3001 - Learner Guide V1.0sharma SoniaNo ratings yet
- Vital-Action LevelsDocument34 pagesVital-Action LevelsLuis GallegosNo ratings yet
- Quantum Academies Program OverviewDocument234 pagesQuantum Academies Program OverviewThomas Marti100% (1)
- Plagiarism Checker X Originality Report: Similarity Found: 24%Document5 pagesPlagiarism Checker X Originality Report: Similarity Found: 24%DonaldNo ratings yet
- Celebrating Our Newest LeadersDocument42 pagesCelebrating Our Newest LeadersBaptist Memorial Health CareNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Hipnoparenting Mengompol - May MinarniDocument7 pagesJurnal Hipnoparenting Mengompol - May MinarniBERGASPUSKESMASNo ratings yet
- MR No. Urine Test ResultsDocument1 pageMR No. Urine Test Results112345678900No ratings yet
- Maternal Child Nursing Care 6th Edition Perry Test BankDocument11 pagesMaternal Child Nursing Care 6th Edition Perry Test BankKristinGonzalezsczrm100% (14)
- Leyna Slivka-5Document1 pageLeyna Slivka-5api-490419585No ratings yet
- Nation Hal Turner: The Three-Legged StoolDocument54 pagesNation Hal Turner: The Three-Legged StoolBrian CharlesNo ratings yet
- BUS 5113 - Motivation TheoriesDocument5 pagesBUS 5113 - Motivation TheoriesEzekiel PatrickNo ratings yet
- Psychological TestDocument1 pagePsychological TestAniketShahNo ratings yet
- Personalizing Illenss and ModernityDocument29 pagesPersonalizing Illenss and ModernityChristos PapasNo ratings yet