Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practical Manual 2020: Subject
Uploaded by
happy sadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical Manual 2020: Subject
Uploaded by
happy sadCopyright:
Available Formats
PRACTICAL MANUAL 2020
SUBJECT
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING II/ELECTROTECHNOLOGY II
(ELEN202) / (ETEC202) / (ETEM201)
SURNAME & STUDENT NUMBER
INITIALS 21712164
Qwabe SB
LECTURER’S NAME COURSE
Dr. G Sharma POWER ENG
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
EXPERIMENT NO: 1
AIM: - was to conduct the load test on a single phase transformer, finding its efficiency and voltage
regulation.
Apparatus Required:
Sr. No. Name of the apparatus Range Type Quantity
1 Ammeter (0-10A) MI 1
2 Ammeter (0-20A) MI 1
3 Voltmeter (0-150V) MI 1
45 Voltmeter (0-300V) MI 1
6 Wattmeter 150v/20A. UPF 1
7 Wattmeter 300V/10A. UPF 1
8 Lamp Bank 250 Watt 0.4
Circuit Diagram
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
Fig. 1 Load test on 1-Φ x, Mer
Observation
Conclusion:
The voltage regulation is defined as the change in the magnitude of receiving and
sending voltage of the transformer. The voltage regulation determines the ability of
the transformer to provide the constant voltage for variable loads.
A single-phase transformer is a type of power transformer that utilizes single-phase
alternating current, meaning the transformer relies on a voltage cycle that operates in
a unified time phase. They are often used to step-down long distance and localized
transmission currents into power levels more suitable for residential and
lightcommercial applications.
We can conclude that the primary and secondary current and wattmeter increases as
the number of bulbs in the circuits are switched on whilst the voltage remain the
same. This also increases the circuit efficiency whilst the regulation remains the
same.
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
Questions: -
1. Efficiency of a power transformer is near to the __B__
a) 100%
b) 98%
c) 50%
d) 25%
2. What is the correct formula of efficiency of a single phase transformer? __C__
a) Input/output
b) Output/losses
c) 1-(losses / (output + losses))
d) Cannot be determined
3. Voltage regulation of transformer is given by ____B____
a) E2-V2/V2
b) E2-V2/E2
c) V2-E2/E2
d) V2-E2/V2
5. Negative voltage regulation indicates ___A____
a) Capacitive loading only
b) Inductive loading only
c) Inductive or resistive loading
d) Cannot be determined
Calculation:
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
EXPERIMENT NO: 2
AIM: - To wire for a stair case arrangement using a two-way switch.
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
Apparatus Required: -
Sr. No. Components Quality/Range
1 Lamp 100V_100W 1
2 Lamp Holder 1
3 Two-way switch 2
4 Wires As required
Circuit Diagram: -
Fig. 2 Two way-switch of electrical wiring
Observation
SWITCH POSITION LAMP
CONDITION
S/W 1 S/W 2
ON ON OFF
ON OFF ON
OFF ON ON
OFF OFF OFF
Conclusion: -
In the above observation-table we can observe that as for the provided circuit the lamp only lights
when the switches are at the opposite states. In terms of improvement, designing was a little difficult
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
to kick start in the beginning. Maybe a few more demonstrations on how to wire and make
calculations helped to make these practical sessions more efficient. Overall, designing these circuits
was genuinely fun and gave us a taste of what real life circuiting is like.
Conducting this practical was not only an interesting and informational way to learn about electrical
circuiting, but also it allows us to understand how to apply the skills we learned in the practical
sessions to real life. We now understand how basic circuits are wired up in our houses, how current
flows through circuits, differences between series and parallel circuits, and even how basic household
appliances function.
Questions: -
1. How do you connect a two-way switch?
Answer: first you need a Lamp and two SPDT switches of which you connect the output from
the lamp to com of the first switch, then L1 of the first switch to L2 of the second switch and L2
of the first switch to L1 of the second switch and lastly connect the com of the second switch to
the Voltage Source.
2. What types of switches are used for staircase wiring?
Answer: Two two-way switches and intermediate switches
3. What is the use of staircase wiring?
Answer: Is to connect and control light bulb using two switches placed at different places,
regardless of the position.
4. What is the difference between one way and two-way light switch?
Answer: A one-way switch operates as a break switch. The two terminals connect when it is
switched on and the contact is broken when the switch is switched off. One way switch has
single throw whilst the two way switch has the double throw.
5. What's the difference between single phase and three-phase?
Answer: Single phase requires a single wire to connect a circuit.
Three phase requires three wires to connect a circuit.
7
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
EXPERIMENT NO: 3
AIM: - To Study and performance of Go down Wiring.
Apparatus Required: -
Sr. No. Components Quality/Range
1 Lamp(120v_250) 4
2 Lamp Holder 4
3 Two-way switch 5
4 Wires As required
Circuit Diagram: -
Fig. 3 Go-down Wiring
Observation Table:
SWITCH POSITION LAMP CONDITION
S1 S2 S3 S4 B1 B2 B3 B4
On Off Off Off On off Off Off
Off On Off Off Off On Off Off
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
Off Off On off off Off On Off
Off Off Off On Off Off Off On
Conclusion:
Keeping switch 5 on all the time, is only when the lamps can switch on and keeping it
off will deny the light from coming on. Go-down wiring makes the feasibility for the
user to turn off the load when switching another, its circuit arrangement is in such a
way that, from common pole we can switch to both 1 & 2 poles, the 1st pole is
connected to load and 2nd to common pole of next and this sequence repeat. We can
switch OFF and Switch ON the bulb from both switches at the same time. in other
words, we can control (OFF or ON) the bulb from upper and lower switches.
In go-down wiring as the remaining switches are in position common to the 2nd pole
(c-2) then it is in contact with the common pole of next switch by this arrangement
we can connect infinite number of loads and switching one load OFF previous load
and ON next.
Switch S1 in the circuit is SPST (single pole single throw) and remaining are SPDT
(single pole double throw). In go-down wiring the number of loads can be connected
further to any extend.
QUESTIONS:
1. What is the importance of go-down wiring?
Answer: Go-down wiring circuit is needed in tunnel like structures, warehouses, long
passages, big go-downs having lots of rooms and different portions.
2. How does wiring save electricity?
Answer: The use of new wiring that reduces leakage current and losses in the wiring
conductor. The use of conductors that have less losses during electricity flow causes an
improved efficiency thus saving electricity.
3. Is black wire live or neutral?
Answer: Live
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
4. What is the role of two-way switch in go-down wiring?
Answer: It allow a previous load to be turned OFF when switched ON the next load in a
two-way switching.
5. Is neutral wire dangerous?
Answer: No
EXPERIMENT NO: 4
AIM: - To study the construction and operation of various types of lamp.
Apparatus Required:
Sr. No. Components Quality/Range
1. Incandescent Lamps.
2. Halogen Lamps
3. Compact Fluorescent Lamps (C.F.L.)
4. LED Lamps.
Applications:
1. Indoor lighting.
2. Outdoor lighting.
3. Flood lighting.
4. For vehicle head lights.
5. TV studios
CONCLUSION:
Lighting control systems reduce energy usage and cost by helping to provide light only
when and where it is needed. Lighting control systems typically incorporate the use of
time schedules, occupancy control, and photocell control (i.e. daylight harvesting).
Some systems also support demand response and will automatically dim or turn off
lights to take advantage of utility incentives. Lighting control systems are sometimes
10
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
incorporated into larger building automation systems. In response to daylighting
QUESTIONS:
1. What frequency do LED lights operate at?
Answer: 50 – 90 Hz
2. What are the benefits of using CFLs?
Answer:
a CFLs are up to four times more efficient than incandescent bulbs.
b While initially they cost more, CFLs are less expensive in the long run because they last much longer
than incandescent bulbs.
c You can do your part in reducing carbon emissions by changing over to CFLs.
3. How does a tube light glow? Answer: They are energy efficient
4. Are LED lights dangerous?
Answer: Yes, because they emit less Carbon Dioxide
11
Revised by G Sharma (2020)
You might also like
- Electrical Machines 1 2 Lab ManualDocument47 pagesElectrical Machines 1 2 Lab ManualJom Ancheta BautistaNo ratings yet
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Lab Wiring 3Document10 pagesLab Wiring 3Nur Afiqah Mohamad NayanNo ratings yet
- Power System - Ii Lab Manual (EE-328) Vi Semester Electrical EngineeringDocument22 pagesPower System - Ii Lab Manual (EE-328) Vi Semester Electrical EngineeringRahul DuttaNo ratings yet
- GEC LAB EEE All Subjects Lab ManualDocument980 pagesGEC LAB EEE All Subjects Lab ManualnaveenNo ratings yet
- EE-328-F Power System Lab ManualDocument24 pagesEE-328-F Power System Lab ManualAbhilash GauravNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Hamza 106report8Document6 pagesMuhammad Hamza 106report8Muhammad Hamza 18-NTU-0106No ratings yet
- SRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203: Types of Wiring - Staircase Wiring, Fluorescent Wiring and Godown WiringDocument11 pagesSRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203: Types of Wiring - Staircase Wiring, Fluorescent Wiring and Godown WiringPrisha InaniNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 WorkshopDocument15 pagesExp 2 Workshopgautam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- BEEE (Experiment 7 and 8)Document5 pagesBEEE (Experiment 7 and 8)Surjosnath Guha ThakurtaNo ratings yet
- EMC 1 PracticalDocument27 pagesEMC 1 PracticalBlack EyeNo ratings yet
- 3.scott Connection of TransformersDocument3 pages3.scott Connection of Transformerschandrakanth100% (2)
- Summer Training Report InsightsDocument42 pagesSummer Training Report InsightsshubhamNo ratings yet
- BJT Security Alarm CircuitDocument4 pagesBJT Security Alarm CircuitsameeNo ratings yet
- 2.sumpner's Test On A Pair of Single Phase TransformersDocument5 pages2.sumpner's Test On A Pair of Single Phase Transformerschandrakanth100% (2)
- EE6503PE2018Document338 pagesEE6503PE2018LIFE of PSNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine and Power Lab New 1Document41 pagesElectrical Machine and Power Lab New 1Vinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Bee LabDocument5 pagesBee Labanitha paramasivamNo ratings yet
- Farhana Abdul Hamid 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1432 012021Document10 pagesFarhana Abdul Hamid 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1432 012021Roger PerezNo ratings yet
- Sumpners Test On A Pair Of 1-Φ Transformers: Experiment - 2Document4 pagesSumpners Test On A Pair Of 1-Φ Transformers: Experiment - 2joshua palizaNo ratings yet
- El-323Electricalmachines: Experiment # 09Document23 pagesEl-323Electricalmachines: Experiment # 09Lala's gamingNo ratings yet
- TEU Mombasa Lab Two: Transformers LabDocument7 pagesTEU Mombasa Lab Two: Transformers LabFaustin MailuNo ratings yet
- Power System-IDocument25 pagesPower System-IKaran Veer Singh ButtatNo ratings yet
- Buck Converter SimulationDocument5 pagesBuck Converter SimulationVishnuvardhanNo ratings yet
- 6 Single Phase AC Voltage Controller With R and RL LoadsDocument6 pages6 Single Phase AC Voltage Controller With R and RL LoadsSeminars BRECWNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Fa16-Bet-056 - Muneeb UllahDocument9 pagesLab 2 - Fa16-Bet-056 - Muneeb UllahPel Colour onNo ratings yet
- Report 8Document5 pagesReport 8Farhan Labib MahinNo ratings yet
- Socket See Pdl234 ManualDocument10 pagesSocket See Pdl234 ManualAnonymous ujdp7fCNo ratings yet
- Sectos Catalogue en 1YHA000354 REV D 12-2021Document24 pagesSectos Catalogue en 1YHA000354 REV D 12-2021ali rabieeNo ratings yet
- Sectos Catalogue en 1YHA000354 REV D 12-2021Document24 pagesSectos Catalogue en 1YHA000354 REV D 12-2021ali rabieeNo ratings yet
- Ee2304 Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument49 pagesEe2304 Power Electronics Lab ManualSree GaneshNo ratings yet
- EEC 249 PracticalDocument66 pagesEEC 249 Practicalsanialiu2711No ratings yet
- Lab File Basics of Electronics & Electrical Engg. (For PTU B.Tech. 1st Year)Document49 pagesLab File Basics of Electronics & Electrical Engg. (For PTU B.Tech. 1st Year)Cutie33% (3)
- Adaptive Lighting System For Automobiles: A Project Report OnDocument13 pagesAdaptive Lighting System For Automobiles: A Project Report Onashishgusain1991No ratings yet
- Tesca 33517Document1 pageTesca 33517claudia espinozaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Document41 pagesLab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Ilavarasan TamizhNo ratings yet
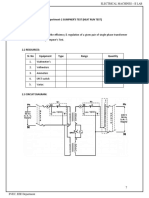
- EDC Lab No.9 (BJT ApplicationsTransistor Switches-Security Alarm)Document4 pagesEDC Lab No.9 (BJT ApplicationsTransistor Switches-Security Alarm)Umair WaqasNo ratings yet
- Aim of The Experiment: Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument20 pagesAim of The Experiment: Linear Variable Differential TransformerAryan BatraNo ratings yet
- Plugin-LM ECE EMEC ManualDocument0 pagesPlugin-LM ECE EMEC Manualnainesh goteNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of Two Single Phase Transformers: Experiment No: 05Document18 pagesParallel Operation of Two Single Phase Transformers: Experiment No: 05Bhanoth MohanNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document11 pagesPs 1pandabk00No ratings yet
- DC Exp 8 Student ManualDocument8 pagesDC Exp 8 Student ManualAsifur R. HimelNo ratings yet
- Electrical MeasurementsDocument47 pagesElectrical MeasurementsManikantaNo ratings yet
- Python Programming 2nd EditionDocument106 pagesPython Programming 2nd Editionshivanand_shettennav100% (1)
- Exp-8 Staircase WiringDocument3 pagesExp-8 Staircase WiringUjjwal GargNo ratings yet
- Ex 5001 Electromagnetic Field Theory Nov 2018Document41 pagesEx 5001 Electromagnetic Field Theory Nov 2018Syed Khurshid AlamNo ratings yet
- EE6611-Power Electronics and Drives LaboratoryDocument104 pagesEE6611-Power Electronics and Drives Laboratoryarshia tabassumNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document3 pagesExp 3Harshit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Verify 2-way & 3-way lamp controlDocument3 pagesVerify 2-way & 3-way lamp controlsakshi rainaNo ratings yet
- My Notes - UnderstandingsDocument14 pagesMy Notes - UnderstandingsLubaba Bashar MomiNo ratings yet
- Ism LabDocument67 pagesIsm LabpadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Buck Converter AnalysisDocument15 pagesBuck Converter AnalysisOmar JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument41 pagesPe Lab ManualGopalakrishna Murthy C RNo ratings yet
- Ef50287299d8cd2 EkDocument6 pagesEf50287299d8cd2 EkTedNo ratings yet
- Surge Protection System 280311Document21 pagesSurge Protection System 280311izzat ismailNo ratings yet
- 21 - ENG - 102715 Practical 03Document6 pages21 - ENG - 102715 Practical 03Waruna NirmanNo ratings yet
- Design of Front-End Push-Pull Sine Wave Inverter: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceDocument8 pagesDesign of Front-End Push-Pull Sine Wave Inverter: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental SciencePABLO MAURONo ratings yet
- PW3Document2 pagesPW3LOKKESHNo ratings yet
- Design A Single Phase Inverter With A LCL Filter: AbstractDocument4 pagesDesign A Single Phase Inverter With A LCL Filter: AbstractPham Viet QuanNo ratings yet
- Fuculty of Engineering Department: Instrumentoin and Control IDocument15 pagesFuculty of Engineering Department: Instrumentoin and Control Ihappy sadNo ratings yet
- Assignm RentDocument14 pagesAssignm Renthappy sadNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Distribution: Week 1-2Document30 pagesElectrical Power Distribution: Week 1-2vish5936100% (1)
- Leadershippptpresentation 130912004539 Phpapp02Document11 pagesLeadershippptpresentation 130912004539 Phpapp02Irna MegawatyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Distribution: Week 1-2Document30 pagesElectrical Power Distribution: Week 1-2vish5936100% (1)
- Monarch User ManualDocument90 pagesMonarch User ManualMoh Aya100% (1)
- Climate Master Installation ManualsDocument52 pagesClimate Master Installation ManualsBulent InanNo ratings yet
- s7300 PDFDocument238 pagess7300 PDFLong HuynhNo ratings yet
- Manual WI-rooms Vaccine Room PO enDocument36 pagesManual WI-rooms Vaccine Room PO enmohammed alnaasNo ratings yet
- Mascott DCI 2003 EN PDFDocument262 pagesMascott DCI 2003 EN PDFviper33_4uNo ratings yet
- Ansi-Rvia Egs-1-2022Document36 pagesAnsi-Rvia Egs-1-2022damaso taracenaNo ratings yet
- Esb 135 1Document0 pagesEsb 135 1edwinramonNo ratings yet
- CMD 2019 Power Modules Low ResDocument44 pagesCMD 2019 Power Modules Low ResDerek OngNo ratings yet
- EET 4 Calculation of The Cross-Sectional Areas of Circuit Live Conductors and CablesDocument4 pagesEET 4 Calculation of The Cross-Sectional Areas of Circuit Live Conductors and CablesLinus AbokiNo ratings yet
- User Manual (SZGH-SD Series) V2.0-UDocument66 pagesUser Manual (SZGH-SD Series) V2.0-UDmytroKrNo ratings yet
- Miller Pro 500BW Sprayer Manual PDFDocument96 pagesMiller Pro 500BW Sprayer Manual PDFHoward MischNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Tia Technology India Pvt. LTDDocument83 pagesUser Manual: Tia Technology India Pvt. LTDRobin PNo ratings yet
- List of International Standards: API Standards Block (25 Nos.)Document4 pagesList of International Standards: API Standards Block (25 Nos.)Siva baalan100% (1)
- ABB - Cable Management Systems - 2007 PDFDocument28 pagesABB - Cable Management Systems - 2007 PDFVilius BukysNo ratings yet
- P499VBS 401CDocument8 pagesP499VBS 401CHassan AshrafNo ratings yet
- NEMA SG 11-2008 Guide For Handling and Maintenance of Alternating Current Outdoor High-Voltage Circuit Breakers PDFDocument24 pagesNEMA SG 11-2008 Guide For Handling and Maintenance of Alternating Current Outdoor High-Voltage Circuit Breakers PDFElenoNo ratings yet
- UniSec SG6 Switch DisconnectorDocument56 pagesUniSec SG6 Switch DisconnectorD Ace Gol DNo ratings yet
- Yhau-Cg Direct Fired Absorption Chiller-Heater: Pre-Start UpDocument8 pagesYhau-Cg Direct Fired Absorption Chiller-Heater: Pre-Start UpUmar MajeedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3a - Sizing Basic Circuits - Rev2013Document34 pagesLecture 3a - Sizing Basic Circuits - Rev2013Carter SiyNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm Nfpa PDFDocument12 pagesFire Alarm Nfpa PDFMohamed EssamNo ratings yet
- R220LC 9SDocument293 pagesR220LC 9SJoseph Emmanuel ParedesNo ratings yet
- 800-21815 Rev. A-PRO3000 VEDocument207 pages800-21815 Rev. A-PRO3000 VELAM QUANG TUYENNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Eléctrico Caterpillar 3406E PDFDocument2 pagesDiagrama Eléctrico Caterpillar 3406E PDFDavid.Quijano100% (3)
- 5E-FE Engine and Engine RebuildDocument205 pages5E-FE Engine and Engine Rebuildjferrell4380100% (10)
- © 2004 Hunter Fan Company 41810-01 08/20/2004: 41810-01 - Rev 8-20-04 V 3.pmd 8/21/04, 4:45 PM 1Document12 pages© 2004 Hunter Fan Company 41810-01 08/20/2004: 41810-01 - Rev 8-20-04 V 3.pmd 8/21/04, 4:45 PM 1gr1mr343prNo ratings yet
- SG2 Smart PLC User ManualDocument267 pagesSG2 Smart PLC User ManualPedriosinho changomanNo ratings yet
- Meaure and Monitor WSH PerformanceDocument16 pagesMeaure and Monitor WSH PerformanceKhidir PritoNo ratings yet
- 230 Volt Standardisation-The Next Steps: 10%. 6% Around Nominal Voltage or A Power Input of 15%Document5 pages230 Volt Standardisation-The Next Steps: 10%. 6% Around Nominal Voltage or A Power Input of 15%Yong Shen LimNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification For Fire Alarm System of ARPFDocument28 pagesTechnical Specification For Fire Alarm System of ARPFAnbarasu PonnuchamyNo ratings yet
- Division 14 - Elevator Design Standards 1 GeneralDocument28 pagesDivision 14 - Elevator Design Standards 1 GeneralAnsara Pasir TumbohNo ratings yet