Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Posture 2
Uploaded by
Surya Joy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesPostural control refers to maintaining stability and equilibrium of the body through static or dynamic control of posture, which is a complex function of the central nervous system. The goals of postural control are to control body orientation, maintain the center of mass over the base of support, and stabilize the head; this depends on intact sensory and motor systems.
Original Description:
Biomechanics
Posture
For all the medical students out there
Original Title
POSTURE-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPostural control refers to maintaining stability and equilibrium of the body through static or dynamic control of posture, which is a complex function of the central nervous system. The goals of postural control are to control body orientation, maintain the center of mass over the base of support, and stabilize the head; this depends on intact sensory and motor systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesPosture 2
Uploaded by
Surya JoyPostural control refers to maintaining stability and equilibrium of the body through static or dynamic control of posture, which is a complex function of the central nervous system. The goals of postural control are to control body orientation, maintain the center of mass over the base of support, and stabilize the head; this depends on intact sensory and motor systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
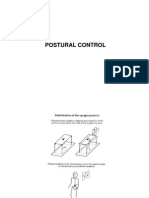
Postural Control
• Postural control refers to a person’s ability
to maintain stability of the body and body
segments in response to forces that
threaten to disturb the body’s equilibrium.
• It can be eitherstatic ordynamic .
• The control of posture is complex and is a
part of the body’s motor control system.
• The ability to maintain stability in the erect
standing posture is a skill that the central
nervous system learns, using information
from passive biomechanical elements,
sensory systems, and muscles.
• The CNS interprets and organizes inputs
from the various structures and systems
and selects responses on the basis of
past experience and the goal of the
response.
• Reactive(compensatory) responses occur
as reactions to external forces that displace
the body’s CoM.
• Proactive(anticipatory) responses occur in
anticipation of internally generated
destabilizing forces such as raising arms to
catch a ball or bending forward to tie shoes.
• The major goals of postural control in the
standing position are;
1. to control the body’s orientation in space,
2. maintain the body’s CoM over the BoS, and
3. stabilize the head with regard to the
vertical so that the eye gaze is
appropriately oriented.
• Postural control depends on the integrity
of
the CNS,
the visual system,
the vestibular system, and
the musculoskeletal system.
You might also like
- BeBalanced!: The innovative training program with Balance-pads & co.From EverandBeBalanced!: The innovative training program with Balance-pads & co.No ratings yet
- Mastering Posture A Comprehensive Guide to Optimal Body AlignmentFrom EverandMastering Posture A Comprehensive Guide to Optimal Body AlignmentNo ratings yet
- Impaired Balance CHP 8Document77 pagesImpaired Balance CHP 8Rimi TimiNo ratings yet
- POSTUREDocument46 pagesPOSTURENikks BoradeNo ratings yet
- Exercise For Impaired BalanceDocument43 pagesExercise For Impaired BalanceGildarts KunNo ratings yet
- Posture PDFDocument30 pagesPosture PDFSairelle Sordilla Obang100% (1)
- Biomechanics of Posture PDFDocument20 pagesBiomechanics of Posture PDFPhooi Yee Lau89% (9)
- postural control (서성우)Document4 pagespostural control (서성우)Faisal QureshiNo ratings yet
- Aarti - Introduction of Biomechanics PostureDocument64 pagesAarti - Introduction of Biomechanics PostureKalyani Savant0% (1)
- Posture Project 1 FinalDocument79 pagesPosture Project 1 FinalASHU KNo ratings yet
- Postural ControlDocument19 pagesPostural ControlcharbelhannaNo ratings yet
- What Is Postural ControlDocument11 pagesWhat Is Postural ControlIrina BachvarovaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics Poture AnalysisDocument84 pagesBiomechanics Poture AnalysisMuqeet76No ratings yet
- Posture ClassDocument56 pagesPosture Classnarainder kumarNo ratings yet
- PostureDocument24 pagesPostureBhargavNo ratings yet
- Kine Assignment by Arsh NazDocument10 pagesKine Assignment by Arsh NazArsh NazNo ratings yet
- PostureDocument20 pagesPostureAnita Gajari100% (2)
- PostureDocument20 pagesPostureBalram Jha100% (1)
- POSTUROLOGIE PPSXDocument187 pagesPOSTUROLOGIE PPSXmihael26100% (9)
- Posture AnalysisDocument45 pagesPosture AnalysisPriyanka Choursiya100% (1)
- BALANCEnwDocument68 pagesBALANCEnwSwathy AshokNo ratings yet
- PostureDocument2 pagesPostureJohanna AlexaNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument41 pagesEquilibriumGiorgi PopiashviliNo ratings yet
- Lec 04.postureDocument207 pagesLec 04.posturepashaNo ratings yet
- BalanceDocument27 pagesBalancetehreem tariqNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 2 Lesson 2Document14 pagesPathfit 2 Lesson 2Steffany Anne PobladorNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Posture - 3rd Sem PDFDocument112 pagesAnalysis of Posture - 3rd Sem PDFShibila ShirinNo ratings yet
- Applying Mechanics To The Human BodyDocument2 pagesApplying Mechanics To The Human BodyAdvis VijayNo ratings yet
- Development of Postural Control and BalanceDocument11 pagesDevelopment of Postural Control and BalanceBautista Marjorie R.No ratings yet
- Motor Control Motor LearningDocument56 pagesMotor Control Motor LearningJune EpeNo ratings yet
- Postural Orientation and Equilibrium: What Do We Need To Know About Neural Control of Balance To Prevent Falls?Document5 pagesPostural Orientation and Equilibrium: What Do We Need To Know About Neural Control of Balance To Prevent Falls?Paula MateusNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Postuure 2020 1,2,3Document116 pagesTherapeutic Postuure 2020 1,2,3Mustafa Mabrouk100% (2)
- Lesson 2 Physical Fitness Pathfit IDocument32 pagesLesson 2 Physical Fitness Pathfit IJohnne Erika LarosaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Body Mechanics and R.O.M ExerciseDocument6 pagesGroup 1 Body Mechanics and R.O.M ExerciseCeline Rose AlvorNo ratings yet
- Major 4 - ActivitiesDocument10 pagesMajor 4 - ActivitiesJasper Diñoso JacosalemNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Body MovementsDocument11 pagesBiomechanics and Body MovementsRyza BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Posture and Factor Affecting Posture in Physical TherapyDocument28 pagesPosture and Factor Affecting Posture in Physical TherapyAnand Vaghasiya100% (2)
- Balance Assessment and TreatmentDocument55 pagesBalance Assessment and TreatmentMhmd Iraky100% (1)
- Horak 2006 Postural Orientation and Equil PDFDocument5 pagesHorak 2006 Postural Orientation and Equil PDFPhooi Yee LauNo ratings yet
- PostureDocument46 pagesPostureFarrukh Shahzad100% (1)
- MODULE 1 - THXDocument13 pagesMODULE 1 - THXZgama AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Pathfit-2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesPathfit-2 ReviewerPASCUA, ROWENA V.No ratings yet
- Horak 2006 Postural Orientation and EquilDocument5 pagesHorak 2006 Postural Orientation and EquilthisisanubisNo ratings yet
- Pe MidtermDocument8 pagesPe MidtermJham L. PatraNo ratings yet
- Mobility Activity Positioning Massage PainDocument20 pagesMobility Activity Positioning Massage Pain황춘히No ratings yet
- Posture: Deswaty Furqonita, Ssi, MbiomedDocument30 pagesPosture: Deswaty Furqonita, Ssi, MbiomedYusuf HidayatNo ratings yet
- 2022 Neurorehabilitation PrintDocument16 pages2022 Neurorehabilitation Print蘇永泓No ratings yet
- College of Education Physical Activity Towards Health and Fitness 1Document11 pagesCollege of Education Physical Activity Towards Health and Fitness 1Marcelo SakitingNo ratings yet
- Mobility and ImmobilityDocument40 pagesMobility and ImmobilityBabita DhruwNo ratings yet
- 1bobath TechniqueDocument24 pages1bobath Techniquekim100% (1)
- Pe2 PrelimsDocument3 pagesPe2 PrelimsMoira CatarrojaNo ratings yet
- Morallos, Jeomar Cruz: Objective of Physical EducationDocument19 pagesMorallos, Jeomar Cruz: Objective of Physical EducationElenita CruzNo ratings yet
- Orientación Postural y Equilibrio. Lo Que Se Necesita Saber Acerca Del Control Neural Del Balance para Prevenir Caídas.Document5 pagesOrientación Postural y Equilibrio. Lo Que Se Necesita Saber Acerca Del Control Neural Del Balance para Prevenir Caídas.Mauro Esban Obreque QuianNo ratings yet
- Neurophysiologyofbalance 200525080144Document45 pagesNeurophysiologyofbalance 200525080144İpek OMURNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Anatomy Posture and Body MechanicsDocument53 pagesChapter 2 - Anatomy Posture and Body MechanicsRogini Sindhu100% (6)
- Sajida Bibi NoonariDocument39 pagesSajida Bibi NoonariSajida Bibi NoonariNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 2Document20 pagesPathfit 2Gemmalyn AguilarNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercise 1 IntroductionDocument30 pagesTherapeutic Exercise 1 IntroductionMyrgen TingsonNo ratings yet
- A Simple Test For Gauging Recovery & Workout “Readiness” - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Ready For ActionFrom EverandA Simple Test For Gauging Recovery & Workout “Readiness” - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Ready For ActionNo ratings yet
- Archery Anatomy: An Introduction to Techniques for Improved PerformanceFrom EverandArchery Anatomy: An Introduction to Techniques for Improved PerformanceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)