Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry Reaction Pathways
Organic Chemistry Reaction Pathways
Uploaded by
amrhkmhCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Chemistry Reaction Pathways
Organic Chemistry Reaction Pathways
Uploaded by
amrhkmhCopyright:
Available Formats
SUMMARY OF REACTION PATHWAYS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
ALKANES POLYALKENES
PRIMARY AMINES
ALKENES DIHALOALKANES
HALOALKANES ALKYL
HYDROGEN EPOXYALKANES DIOLS
SULPHATES
ALCOHOLS
NITRILES
CARBONYLS
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
You need to know the equations, conditions, reagents and type of reaction for all these
reactions.
You need to know the mechanism for some of them.
1. Alkane chloroalkane
reagents: Cl 2
conditions: UV light
mechanism: free radical substitution
equation: RH + Cl 2 RCl + HCl
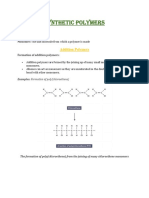
2. Alkene polyalkene
Conditions: low T, high p.
Equation:
C C
n C C
Type of reaction: addition polymerisation (free radical)
3. Alkene bromoalkane
Reagent: HX(g)
Conditions: room T
Equation:
C C + H Br C C
Br H
Type of reaction: electrophilic addition
4. Alkene dibromoalkane
Reagent: Br 2 in water or in an organic solvent
Conditions: room T
Equation:
C C + Br Br C C
Br Br
Mechanism: electrophilic addition
5. Alkene alkylhydrogensulphate
Reagent: concentrated sulphuric acid
Conditions: cold
Equation:
C C + H OSO3H C C
H OSO3H
Mechanism: electrophilic addition
6. Alkylhydrogensulphate alcohol
Reagent: water
Conditions: warm
Equation:
C C
C C +
+ H2O H OSO3H
H OSO3H
H OH
Type of reaction: hydrolysis
7. Alkene alcohol
Reagent: steam
Conditions: 300 oC, 60 atm, H 3 PO 4 catalyst
Equation:
H H
C C + O C C
OH H
Type of reaction: hydration
8. Haloalkane alcohol
Reagent: NaOH(aq) or KOH(aq)
Conditions: warm under reflux
Equation: R-X + OH- R-OH + X-
Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution
9. Haloalkane nitrile
Reagent: KCN in aqueous ethanol
Conditions: boil under reflux
Equation: R-X + CN- R-CN + X-
Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution
10. Haloalkane Amine
Reagent: ammonia in ethanol in a sealed tube
Conditions: heat
Equation: R-X + 2NH 3 R-NH 2 + NH 4 X
Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution
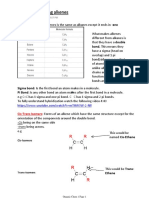
11. Haloalkane alkene
Reagent: KOH in ethanol
Conditions: heat
Equation:
H R R R
C C -
R C C X + X + H2O
R R
R R
Type of reaction: elimination
12. Primary alcohol aldehyde
Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions: warm, distillation
Equation: RCH 2 OH + [O] RCHO + H 2 O
Type of reaction: mild oxidation
13. Secondary alcohol ketone
Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions: heat, distillation
Equation: R 1 CH(OH)R 2 + [O] R 1 COR 2 + H 2 O
Type of reaction: oxidation
14. aldehyde carboxylic acid
Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions: heat, reflux
Equation: R-CHO + [O] R-COOH
Type of reaction: oxidation
15. Alcohols alkenes
Reagent: concentrated sulphuric acid
Conditions: heat
Equation:
C C H
C C + H2O
OH
Type of reaction: elimination
16. glucose ethanol
reagent: yeast
conditions: 35 – 55 oC, no air
equation: C 6 H 12 O 6 2C 2 H 5 OH + 2CO 2
type of reaction: fermentation
You might also like
- Reagent and The Reactions They CauseDocument3 pagesReagent and The Reactions They CauseChip Timmons100% (9)
- Aldehydes and Ketones - 1-MergedDocument94 pagesAldehydes and Ketones - 1-MergedseNo ratings yet
- Reagent TableDocument10 pagesReagent Tablebluebeary22No ratings yet
- AromaticityDocument24 pagesAromaticitymilindthakare75No ratings yet
- Summary of Important Organic ReactionsDocument41 pagesSummary of Important Organic ReactionsKathyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Fiitjee Flowcharts PDFDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry Fiitjee Flowcharts PDFTanishq VermaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesOxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryTarun Lfc Gerrard100% (1)
- Chemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic Chemistryhelixate100% (5)
- Experiments 3 Stage 2017-2018Document50 pagesExperiments 3 Stage 2017-2018Parawgay Danar100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 Dir+eff++keyDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry Midterm 1 Dir+eff++keyNorma Leticia RamosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Orgnic ChemistryDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Orgnic ChemistryladybugNo ratings yet
- Resonance and Inductive Effects PresentationDocument36 pagesResonance and Inductive Effects Presentationeagl33yeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Organic MoleculesDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Organic MoleculesJenny Vhie S. Vinagrera100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry-All Reaction MechanismsDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry-All Reaction MechanismsParameshwari kumar100% (1)
- 18 Aromatic SubstitutionsDocument67 pages18 Aromatic SubstitutionsJun LyNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsFrom EverandOrganometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ChartsDocument84 pagesOrganic Chemistry ChartsPRIYANSHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Chemistry Core Concepts 2nd Edition PDFDocument30 pagesEbook PDF Chemistry Core Concepts 2nd Edition PDFjames.riles871100% (42)
- Reaction MechanismDocument68 pagesReaction MechanismSiddarth Singh73% (11)
- Master Organic Chemistry SubstitutionDocument43 pagesMaster Organic Chemistry SubstitutionArsalan Khan GhauriNo ratings yet
- Retrosynthetic Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesRetrosynthetic Analysis PDFNoleNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument55 pagesAromatic CompoundsNadine Bacalangco100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry I: The Unofficial Reaction SheetDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry I: The Unofficial Reaction SheetKarl WilsonNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument28 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersDnyanesh Shinde100% (1)
- Experiments in Physical Chemistry: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionFrom EverandExperiments in Physical Chemistry: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionNo ratings yet
- CAPE Chemistry Syllabus Unit 2 Page 1 of 12: Structure and Formulae (Module 1)Document12 pagesCAPE Chemistry Syllabus Unit 2 Page 1 of 12: Structure and Formulae (Module 1)Fabian SealeyNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument20 pagesOrganic ChemistryGirish RaguvirNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions and MechanismDocument51 pagesOrganic Reactions and MechanismAbhay Kumar Nayak75% (8)
- Reaction SummaryDocument5 pagesReaction SummaryShafaqatRahmanNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alkyl Halides-GDocument37 pagesReactions of Alkyl Halides-Gnicole_oropezaNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil RefiniringDocument96 pagesCrude Oil RefiniringNamwangala Rashid Natindu100% (1)
- Aromatic HydrocarbonDocument45 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonPrashantNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document53 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIFrom EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- C F C CL C - BR: HalogenoalkanesDocument11 pagesC F C CL C - BR: HalogenoalkanesMufaro MutotiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Top 500 Question Bank For JEE Main by MathonGo PDFDocument65 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Top 500 Question Bank For JEE Main by MathonGo PDFDeepak BinwalNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Retrosynthesis: Organic Synthesis using Reaxys and SciFinderFrom EverandHybrid Retrosynthesis: Organic Synthesis using Reaxys and SciFinderNo ratings yet
- Problems On Named ReactionsDocument103 pagesProblems On Named ReactionsBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Vollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11Document58 pagesVollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11superfr3shmNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 @stereochemistry PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 @stereochemistry PDFMoulindu Kundu50% (2)
- Huckel Rule of Aromaticity 2 PDFDocument25 pagesHuckel Rule of Aromaticity 2 PDFUmar Farooq100% (1)
- Chapter12 WorkedExamplesDocument17 pagesChapter12 WorkedExamplesHalil EmreNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReactionDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReactionGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- IB Organic Reactions SummaryDocument2 pagesIB Organic Reactions SummaryUrim ParkNo ratings yet
- Hetero-Cyclic CompoundsDocument69 pagesHetero-Cyclic CompoundsNaveed SajidNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IIDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry IIRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of UnknownDocument10 pagesQualitative Analysis of UnknownJulie Edington100% (1)
- Aromaticity 2019Document65 pagesAromaticity 2019Shreya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Electron Delocalization and ResonanceDocument9 pagesElectron Delocalization and ResonanceMariana LizethNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocument58 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionArjunNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument8 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethersmv7602456No ratings yet
- Reagent ListDocument9 pagesReagent ListArka MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesOrganic ChemistryAndré Brincat100% (1)
- Intro To Organic ChemDocument91 pagesIntro To Organic ChemMiguel Marquez GelacioNo ratings yet
- Comparing The SN1 and SN2 Reactions - Master Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesComparing The SN1 and SN2 Reactions - Master Organic Chemistryprince ranaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2021Document76 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2021Arah Mae BonillaNo ratings yet
- Halogenated Benzenes, Toluenes and Phenols with Water: Solubility Data SeriesFrom EverandHalogenated Benzenes, Toluenes and Phenols with Water: Solubility Data SeriesAri L. HorvathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Functional Group Analysis: International Series of Monographs on Analytical Chemistry, Volume 8From EverandOrganic Functional Group Analysis: International Series of Monographs on Analytical Chemistry, Volume 8No ratings yet
- General Organic Biological Chemistry Third Edition Janice G Smith Full ChapterDocument51 pagesGeneral Organic Biological Chemistry Third Edition Janice G Smith Full Chapterrichard.mowatt659100% (17)
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES - Practice Sheet & Solution - Vijeta 2023Document8 pagesHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES - Practice Sheet & Solution - Vijeta 20237H VENOM TMNo ratings yet
- 04 Organic ChemistryDocument17 pages04 Organic ChemistrysandeepNo ratings yet
- 2023 Specimen Paper 1Document18 pages2023 Specimen Paper 1maryy.army.77No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument52 pagesOrganic ChemistryThung LingNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl ReactionDocument34 pagesCarbonyl Reactionmichot feleguNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1St Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesOrganic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1St Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmisstepmonocarp1b69100% (8)
- c1 Revision Poster - Set 1 OnlyDocument3 pagesc1 Revision Poster - Set 1 Onlyapi-320022467No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument11 pagesHydrocarbonsPoorni RenuNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 13 HydrocarbonsDocument159 pagesClass 11 Chapter 13 HydrocarbonsAnkita ChandaNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument2 pagesAlkanesJohnNo ratings yet
- JEC CompanyDocument70 pagesJEC CompanyArdita Rizky Putri ArcanggiNo ratings yet
- 13 - Alcohol, Phynol, Ether (New) PDFDocument37 pages13 - Alcohol, Phynol, Ether (New) PDFthinkiit100% (2)
- General Organic and Biochemistry An Applied Approach 2nd Edition Armstrong Test BankDocument17 pagesGeneral Organic and Biochemistry An Applied Approach 2nd Edition Armstrong Test Bankhebediemran100% (31)
- Alkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)Document3 pagesAlkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)khalil rehman100% (2)
- Alkadienes & Its PropertiesDocument24 pagesAlkadienes & Its PropertiesShivam Gupta67% (3)
- MSC Chemistry PDFDocument76 pagesMSC Chemistry PDFVenkatraj GowdasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.3 Arenes BenzeneDocument22 pagesChapter 5.3 Arenes BenzeneMohamed NaaifNo ratings yet
- Energy Chemistry NotesDocument11 pagesEnergy Chemistry NotesClayton Feng100% (1)
- HydrocarbonDocument29 pagesHydrocarbongoswamiaddNo ratings yet
- TripleScenceOnly AlcoholsDocument10 pagesTripleScenceOnly AlcoholsKhadijahNo ratings yet
- CHEM 200 - Organic Chemistry (Lecture)Document7 pagesCHEM 200 - Organic Chemistry (Lecture)Madeline SibuloNo ratings yet
- Total Synthesis of Pederin, A Potent Insect Toxin: The Ef®cient Synthesis of The Right Half, (1) - BenzoylpedamideDocument7 pagesTotal Synthesis of Pederin, A Potent Insect Toxin: The Ef®cient Synthesis of The Right Half, (1) - BenzoylpedamideHY-11 Đỗ Quốc TiệpNo ratings yet
- Synthetic PolymersDocument7 pagesSynthetic PolymersHalal BoiNo ratings yet
- Unit - I APCDocument37 pagesUnit - I APCMani DeepNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry For Chemical EngineersDocument13 pagesOrganic Chemistry For Chemical EngineersavixNo ratings yet