Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: Name of Patient: Attending Physician: Age: Impression/Diagnosis
Uploaded by
Melody B. Miguel0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views3 pagesThe nursing care plan addresses an asthma exacerbation in a client with a respiratory rate of 37 breaths per minute, nasal flaring, and use of accessory muscles. The nursing diagnosis is ineffective breathing pattern related to bronchospasm and decreased lung expansion. Interventions include assessing respiratory status, providing rest periods, positioning to improve breathing, teaching pursed-lip breathing and relaxation techniques, administering oxygen and nebulizer treatments, and anti-inflammatory medications. The goal is to establish an effective breathing pattern with a stabilized respiratory rate and decreased distress by the next evaluation.
Original Description:
Original Title
36580174-Ineffective-Breathing-Pattern-related-to-bronchospasm-decreased-lung-expansion.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing care plan addresses an asthma exacerbation in a client with a respiratory rate of 37 breaths per minute, nasal flaring, and use of accessory muscles. The nursing diagnosis is ineffective breathing pattern related to bronchospasm and decreased lung expansion. Interventions include assessing respiratory status, providing rest periods, positioning to improve breathing, teaching pursed-lip breathing and relaxation techniques, administering oxygen and nebulizer treatments, and anti-inflammatory medications. The goal is to establish an effective breathing pattern with a stabilized respiratory rate and decreased distress by the next evaluation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Name of Patient: Attending Physician: Age: Impression/Diagnosis
Uploaded by
Melody B. MiguelThe nursing care plan addresses an asthma exacerbation in a client with a respiratory rate of 37 breaths per minute, nasal flaring, and use of accessory muscles. The nursing diagnosis is ineffective breathing pattern related to bronchospasm and decreased lung expansion. Interventions include assessing respiratory status, providing rest periods, positioning to improve breathing, teaching pursed-lip breathing and relaxation techniques, administering oxygen and nebulizer treatments, and anti-inflammatory medications. The goal is to establish an effective breathing pattern with a stabilized respiratory rate and decreased distress by the next evaluation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
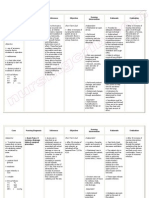
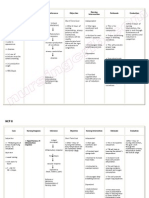
NURSING CARE PLAN
Name of Patient: Attending Physician:
Age: Impression/Diagnosis:
Clustered Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Outcome Criteria Interventions Rationale Evaluation
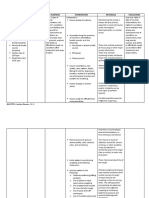
04/20/10 11:00 am INDEPENDENT: 04/20/10 3:00 p.m
Ineffective Breathing The physiologic changes The client will be able to
Client refrains from Pattern related to in lung ventilation that establish an effective 1. Frequently assess Early identification of GOAL PARTIALLY MET.
talking because he finds bronchospasm, occur during an acute respiratory pattern so as respiratory rate, pattern, ineffective respirations The client manifested
it hard to breathe while decreased lung asthma attack impair to provide adequate and breath sounds. Note allow timely initiation of decreasing respiratory
doing so. expansion both lung expansion and ventilation as manifested manifestations of interventions. rate, RR=22
emptying. Anxiety by stabilizing respiratory ineffective breathing. breaths/minute and
Client simply points out caused by hypoxia and rate, decreasing chest appeared less strained
objects he wants and dyspnea compounds the tightness, slight to no 2. Monitor vital signs and Tachypnea, tachycardia, and distressed upon
makes signs because he problem by increasing nasal flaring and laboratory results. an elevated blood breathing. However,
finds it difficult to the respiratory rate. decreasing usage of pressure, and increasing wheezes can still be
breath. accessory muscles by hypoxemia and auscultated from all lung
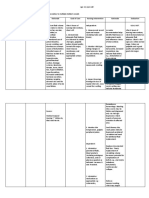
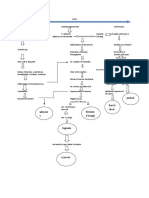
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 04/20/10 3:00 p.m. hypercapnia are signs of fields and there is still
Complains of tight When a trigger such as compromised respiratory usage of accessory
feeling in the chest inhalation of an allergen status. muscles and nasal
or irritant occurs, an flaring.
RR=37 breaths/minute acute or early response 3.Assist with self-care This conserves energy
develops in the activities. and reduces fatigue.
With rapid and shallow hyperreactive airways
respirations predisposed to 4. Provide rest periods Scheduled rest is
bronchospasm. between scheduled important to prevent
Uses accessory muscles Sensitized mast cells in activities and fatigue and reduce
to aid in breathing the bronchial mucosa treatments. oxygen demands. .
release inflammatory
Exhibits nasal flaring mediators such as 5. Place in Fowler’s, High These positions reduce
histamine, Fowler’s or orthopneic the work of breathing
ABG Results 04/20/10 prostaglandins and (with head and arms and increases lung
HCO3= 23.2 mmol/L leukotrienes. These supported on the expansion, especially the
O2 Sat= 97.9% mediators stimulate overbed table) position basilar areas.
pH= 7.501 parasympathetic to facilitate breathing
pCO2= 29.8 mmHg receptors and bronchial and lung expansion.
Impression: Respiratory smooth muscle to
Alkalosis without produce 6. Teach and assist to use Pursed- lip breathing
compensation bronchoconstriction. techniques to control helps keep airways open
They also increase breathing pattern: by maintaining positive
capillary permeability, a. Pursed-lip breathing pressure, and abdominal
leading to mucosal b. Abdominal breathing breathing improves lung
edema, and stimulate c. Relaxation technique expansion. Relaxation
mucus production. including visualization, techniques reduce
The attack is prolonged meditation and others. anxiety and its effect on
by the late response the respiratory rate.
phase, which develops 4
to 12 hours after .
exposure to the trigger.
Inflammatory cells such DEPENDENT:
as basophils and
eosinophils are 7. Administer 2 liters per Supplemental oxygen
activated, which damage minute of oxygen as reduces hypoxemia.
airway epithelium, ordered.
produce musocsal
edema, impair 8. Administer nebulizers Adrenergic stimulants
mucociliary clearance, treatments as ordered: affect receptors on
and produce ro prolong Combivent 1 nebule smooth muscle cells of
bronchoconstriction. The Duavent 1 nebule the respiratory tract,
degree of hyperreactivity (with 15 minutes interval causing smooth muscle
depends on the extent of in between) relaxation and
inflammation, and bronchodilation.
mucous secretion
narrow the airway. These are used to
Airway resistance 9. Administer anti- suppress airway
increases, limiting inflammatory agents as inflammation and reduce
airflow and increasing ordered: asthma symptoms. It
work of breathing. Hydrocortisone 200 mg blocks late response to
IVTT inhaled allergens and
Source: reduce bronchial
LeMone, P. ,et.al. 2004. hyperresponsiveness.
Medical-Surgical
Nursing: Critical Thinking
in Client Care 3rd Edition
pp. 1106,1111-1112.
You might also like
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToFrudz OrjalezaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- NCP - CapDocument4 pagesNCP - CapSherryNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument2 pagesNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearancederic100% (13)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternPaolo Anthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP For CHDDocument2 pagesNCP For CHDMonica Rivera100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternNecheal BaayNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Document1 pageIneffective Airway Clearance (Retained Secretions)Danna Tan50% (2)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee Baluyot100% (2)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Document1 pageNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Constipation NCPDocument2 pagesConstipation NCPAbby GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Document8 pagesRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure NCPDocument1 pageRespiratory Failure NCPkyaw100% (1)
- CHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 5 Nursing Care PlanMiguelito Galagar GultianoNo ratings yet
- Risk For AspirationDocument2 pagesRisk For AspirationGly Mtg100% (6)
- NCP For TBDocument3 pagesNCP For TBNelle Agni100% (1)
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPRyan John Bito-onNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Imbalance NutritionDocument2 pagesNcp-Imbalance NutritionMariko BarbaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument3 pagesNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualNo ratings yet
- NCP FoodDocument1 pageNCP FoodAdrian ArdamilNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Impaire Spontaneous VentilationDocument4 pagesImpaire Spontaneous VentilationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationDocument2 pagesAnxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationmonaNo ratings yet
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPbjhilario100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaMarla NavarroNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking ExerciseDocument1 pageCritical Thinking ExerciseMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- NCP Actual and PotentialDocument4 pagesNCP Actual and PotentialKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainSatchiko Riko SakuraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Tarasoff CaseDocument2 pagesTarasoff Casealyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearancemichelle_010379No ratings yet
- Risk For Infection Related To Insufficient Knowledge To Avoid Exposure To Pathogens As Evidence by Dirty Nails.Document2 pagesRisk For Infection Related To Insufficient Knowledge To Avoid Exposure To Pathogens As Evidence by Dirty Nails.Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As VerbalizedDocument2 pagesAssessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalizedmayla_jordan3666No ratings yet
- NCP - Risk For InjuryDocument3 pagesNCP - Risk For InjuryMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisPanJan BalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - AnxietyDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - AnxietyPauPau100% (1)
- CARAGAN, Chantal Herpes Zoster Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument4 pagesCARAGAN, Chantal Herpes Zoster Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermChantal Caragan100% (2)
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- NCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeNica RespondoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Swallowing Related To Dysphagia Secondary To Dry Oral MucosaDocument3 pagesImpaired Swallowing Related To Dysphagia Secondary To Dry Oral MucosaJUN JUN PALISOC100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance (Bronchi)deric94% (17)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnossis Scientific Basis Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnossis Scientific Basis Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentPamela laquindanumNo ratings yet
- Chona NCP 1Document5 pagesChona NCP 1Jan Mark SotoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation (Baiae)Document10 pagesA Case Study of Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation (Baiae)Janina RojoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plans of Bronchial AsthmaKannanNo ratings yet
- Anaphylactic Shock ReaderDocument3 pagesAnaphylactic Shock ReaderzipheleleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanRachelleNo ratings yet
- CHN Complete NotesDocument237 pagesCHN Complete NotesMelody B. Miguel100% (1)
- Community Health NursingDocument23 pagesCommunity Health Nursingcoy008No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Nur 217 LeadershipDocument3 pagesNur 217 LeadershipMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Period: NUR 112 Lisa M. Dunn RN, MSN/EDDocument46 pagesPreoperative Period: NUR 112 Lisa M. Dunn RN, MSN/EDMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- How To Write An Incident ReportDocument5 pagesHow To Write An Incident ReportMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing ManagementDocument14 pagesPerioperative Nursing ManagementMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Tissue Practice TestDocument15 pagesCH 4 Tissue Practice TestMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease: Case StudyDocument9 pagesAlzheimer's Disease: Case StudyMelody B. Miguel100% (1)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case StudyDocument9 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: Case StudyMelody B. Miguel100% (1)
- Patient ConfidentialityDocument2 pagesPatient ConfidentialityMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- APA FormatDocument3 pagesAPA FormatMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Rle Disaster Season 8Document2 pagesRle Disaster Season 8Melody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Theories in Psychiatric Nursing (Addendum)Document27 pagesTheories in Psychiatric Nursing (Addendum)Melody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument16 pagesNursing Care PlanMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychiatric Nursing Phil HistoryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Psychiatric Nursing Phil HistoryMelody B. Miguel0% (1)
- Triage and Field ManagementDocument41 pagesTriage and Field ManagementMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Coping Mechanism and Stress Among Emergency Department Nurses After Unsuccessful Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument9 pagesCoping Mechanism and Stress Among Emergency Department Nurses After Unsuccessful Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- GAD Case Manuscript BSN 3Y2 1A Group 5 1Document25 pagesGAD Case Manuscript BSN 3Y2 1A Group 5 1Melody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Sign and SymptomsDocument4 pagesBehavioral Sign and SymptomsMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- A Career PathDocument3 pagesA Career PathMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Sas 11-17Document10 pagesSas 11-17Melody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Ventilator: IntegratedDocument10 pagesVentilator: IntegratedNaveed Abrar100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderBlessyl Mae EstenzoNo ratings yet
- Kine 2p90 l17Document7 pagesKine 2p90 l17baileyschaefer28No ratings yet
- Cap No GraphyDocument21 pagesCap No GraphyPrabhakar KumarNo ratings yet
- Child With Respiratory DisordersDocument12 pagesChild With Respiratory DisordersManju TalluriNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Exacerbation of Copd: Dr. Fanny WS KoDocument3 pagesManagement of Acute Exacerbation of Copd: Dr. Fanny WS KoCalca NeusNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System ProblemsDocument3 pagesRespiratory System ProblemsGman SupNo ratings yet
- Dirty DozenDocument23 pagesDirty DozenGeevine CansinoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledRafsan HossainNo ratings yet
- Enfermedad Pulmonar IntersticialDocument39 pagesEnfermedad Pulmonar IntersticialDanhi V. EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Circulation 4th Edition (2016) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFDocument773 pagesPulmonary Circulation 4th Edition (2016) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFpvs5155No ratings yet
- Care of Patient With Chest-Tube DrainageDocument60 pagesCare of Patient With Chest-Tube Drainageu0907593No ratings yet
- Activity 17 The Respiratory System and Pulmonary VentilationDocument5 pagesActivity 17 The Respiratory System and Pulmonary VentilationarmandNo ratings yet
- Acute Asthma ExacerbationDocument3 pagesAcute Asthma ExacerbationRoa Al-SajjanNo ratings yet
- Sputum Examination: Martey AlfredDocument28 pagesSputum Examination: Martey AlfredShazad Ahamed S NNo ratings yet
- Nice Neotech - HORN Puff - 14Document1 pageNice Neotech - HORN Puff - 14David Gnana DuraiNo ratings yet
- GINA 2018 Teaching Slide Set FullDocument190 pagesGINA 2018 Teaching Slide Set FullAndres Dobler0% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (3)
- Lab 06 SpirometryDocument28 pagesLab 06 SpirometryMâřâh MöHămmădNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis: Yuping GuoDocument75 pagesBronchiectasis: Yuping GuoAmeliaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory FailureDocument22 pagesRespiratory Failuresoni gurungNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DisordersDocument48 pagesRespiratory DisordersJean Cabigao100% (1)
- Respi SystemDocument65 pagesRespi Systemapi-373599567% (3)
- High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy in Adults PDFDocument8 pagesHigh-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy in Adults PDFIda_Maryani94No ratings yet
- BronchiectasisDocument61 pagesBronchiectasisRapid MedicineNo ratings yet
- COPD PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCOPD PathophysiologyJustin Ahorro-Dionisio33% (3)
- PulmonologyDocument175 pagesPulmonologyJohanna GarciaNo ratings yet
- Brochure Philips Respironics V60 Plus VentilatorDocument4 pagesBrochure Philips Respironics V60 Plus VentilatorKevin KasegerNo ratings yet
- Prehabilitation ChecklistDocument1 pagePrehabilitation ChecklistMuhammad AL Farisi SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Pneumothorax - UpToDateDocument40 pagesImaging of Pneumothorax - UpToDateTP RMadNo ratings yet