Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TOLLENS
Uploaded by
DDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TOLLENS
Uploaded by
DDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)Copyright:
Available Formats
TOLLEN’S TEST
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
A few drops of freshly prepared Tollen’s reagent was added to each of the 2 ml aqueous
solution of samples in a test tube, after that the solution was heated gently.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
TABLE B. 8 Tollen’s Test
SAMPLES RESULTS
Glucose
(C6H12O6)
Figure B. 8.a. Glucose (C6H12O6)
(+). Upon the addition of Tollen’s reagent and
gentle heating presence of silver color occurs
Arabinose
(C5H10O5)
Figure B. 8.b. Arabinose (C5H10O5)
(+). Upon the addition of Tollen’s reagent and
gentle heating presence of silver color occurs
Fructose
(C6H12O6)
Figure B. 8.c. Fructose (C6H12O6)
(+). Upon the addition of Tollen’s reagent and
gentle heating presence of silver color occurs
Starch
(C27H48O20)
Figure B. 8.d. Starch (C27H48O20)
(-). Upon the addition of Tollen’s reagent and
gentle heating, there was a formation of white
precipitate but absence of silver mirror complex
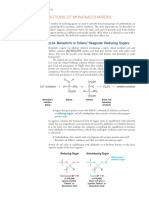
Tollen’s test was conducted to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone.
Monosaccharides containing the aldehyde group are classified as aldoses, and those
with a ketone group are classified as ketoses. Aldoses are reducing sugars; ketoses are
non-reducing sugars. This is important in understanding the reaction of sugars with
Tollen’s reagent (Chemistry for Biologist, n.d.).
In this test, four samples were subjected to Tollen’s reagent -Glucose (C6H12O6),
Arabinose (C5H10O5), Fructose (C6H12O6), and Starch (C27H48O20). The three
monosaccharide samples yielded a positive results. The positive result for this test was
the formation of a silver mirror. Only one sample gave a negative result, which is the
starch (C27H48O20). The monosaccharide samples reacts positively in this test due to the
fact that all monosaccharides are reducing sugars. It was also said earlier that Tollen’s
reagent only oxidizes those that contain aldehydes, but for sugars like fructose
(C6H12O6) which belong to sugars containing ketones, ketoses must first tautomerize to
aldoses before they can act as reducing sugars (Pratt & Cornely). According to Pearce
(2017), Tollens’ reagent and Benedict’s reagent react with a free aldehyde group.
Fructose (C6H12O6) is a ketose sugar, and does not itself have a free aldehydic group,
but under the alkaline conditions of the reaction it is partially converted to a mixture of
glucose (C6H12O6) and mannose (C6H12O6) which do react with the reagents.
Figure X. Reduction of Fructose
Only starch (C27H48O20) yielded a negative result because starch (C27H48O20),
whether it's in the form of amylose (C6H10O5) or amylopectin (C30H52O26), is not a reducing
sugar. Being a non-reducing sugar, it means that starch does not contain aldehydes,
which is the one that is reduced by the reagent. The first ring cannot open up because
there's no hydrogen on the circled oxygen to allow for ring opening. Similarly the next
ring, and the following rings cannot open up. So polysaccharides, such as starch
(C27H48O20), are not reducing sugars. They need to be hydrolyzed and broken down into
smaller units, such as glucose (C6H12O6) or perhaps maltose (C6H12O6), before the rings
can open up (Clackamas.edu, n.d.). Thus, the treatment of starch with Tollens’ reagent
in a glass test tube does not result in a silver mirror.
Chemistry for biologists (n.d.) stated that, sugars may be classified
as reducing or non-reducing based on their reactivity
with Tollens', Benedict's or Fehling's reagents. If a sugar is oxidized by these reagents it
is called reducing, since the oxidant (Ag+ ) is reduced in the reaction, as evidenced by
formation of a silver mirror. Tollens’ test, also known as silver-mirror test, is a qualitative
laboratory test, generally used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone, and for
carbohydrates it is a specific determines reducing sugar from non-reducing sugars.
Figure X. Oxidation by Tollen’s reagent.
References:
Biology Dictionary. (2019). Monosaccharide. Retrieved from
https://biologydictionary.net/monosaccharide/
Chemistry for biologists. (n.d.). Carbohydrates. Retrieved from
https://www.rsc.org/Education/Teachers/Resources/cfb/carbohydrates.htm
Chemistry Libre Texts. (2019). Tollen’s test. Retrieved from
https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Organic_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules
_(Organic_Chemistry)/Aldehydes_and_Ketones/Reactivity_of_Aldehydes_and_Ket
ones/Tollens%E2%80%99_Test
Clackamas edu.(n.d.). Disaccharides and Polysaccharides. Retrieved from
http://dl.clackamas.edu/ch106-07/disaccha.htm
Exhibition chemistry.(n.d.). The silver mirror test. Retrieved from
https://edu.rsc.org/exhibition-chemistry/the-silver-mirror-test/2020077.article
Pearce, F. (2017). Why does fructose reduce tollen’s reagent?
https://www.chemistryonline.com/Why-does-Fructose-reduce-Tollens-reagent-
although-it-does-not-have-an-aldehydic-group
Pratt, C.W. & Cornely, K. (2013). Essential Biochemistry (Third ed.). Wiley.
p. 626. ISBN 978-1118083505.
PS: IHABOL KO NALANG PO YUNG ANILINE ACETATE TEST TAS DIKO MUNA
ISESEND YUNG SS NG REFERENCES KO DITO. THANKYOU.
You might also like
- Differential Equation LectureDocument6 pagesDifferential Equation LectureMeverlyn Roquero100% (1)
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehyde and KetonesDocument7 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehyde and KetonesJason Raquin Roque100% (1)
- Lecture 6 7 SNFR Course SlidesDocument93 pagesLecture 6 7 SNFR Course Slidesgreg100% (1)
- Hem Actsheet: Organic Chemistry 4: Carbonyl CompoundsDocument3 pagesHem Actsheet: Organic Chemistry 4: Carbonyl CompoundsDaniel C. WalshNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesOxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryTarun Lfc Gerrard100% (1)
- Isolation From Chicken Liver and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of GlycogenDocument2 pagesIsolation From Chicken Liver and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of GlycogenAngela ResicoNo ratings yet
- Liquid DosageDocument29 pagesLiquid DosageDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates WorksheetDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates WorksheetNatalie Pemberton86% (7)
- Ketones and AldehydesDocument10 pagesKetones and AldehydesManjeeta Mandlik0% (1)
- Classification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsDocument7 pagesClassification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsSamantha Hope SyNo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDocument7 pagesClassification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsSamantha Louise MondonedoNo ratings yet
- Scientific Paper Exp 7Document6 pagesScientific Paper Exp 7Brent TenorioNo ratings yet
- Acrolein Test: Identifying Lipids Using Chemical TestsDocument3 pagesAcrolein Test: Identifying Lipids Using Chemical TestsHenna TkNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Thermo ClsuDocument94 pagesThermo ClsuHermione SorianoNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Expt 8 Lab ReportDocument30 pagesChem 31.1 Expt 8 Lab ReportJohn Christian LopezNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry—VII: VIth International Symposium on Carbohydrate ChemistryFrom EverandCarbohydrate Chemistry—VII: VIth International Symposium on Carbohydrate ChemistryW. M. DoaneNo ratings yet
- BS1005 Wet Lab ReportDocument12 pagesBS1005 Wet Lab ReportDoug A. HoleNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8 (Carbonyl Compounds and Carbohydrates)Document9 pagesExercise 8 (Carbonyl Compounds and Carbohydrates)Wendell Kim Llaneta0% (1)
- Barfoed's, Tollen's, FehlingsDocument3 pagesBarfoed's, Tollen's, FehlingsAlgenne AmiruddinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - & Carbonyl-Containing CompoundsDocument8 pagesExperiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - & Carbonyl-Containing CompoundsPatricia Isabel Tayag100% (7)
- Experiment 16 IntroDocument1 pageExperiment 16 IntroJesclea EspinosaNo ratings yet
- CH102 Lab 5 Aldehydes and Ketones PDFDocument10 pagesCH102 Lab 5 Aldehydes and Ketones PDFAnonymous caERsANo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Test For Carbohydrates: CHY 47.1 Biochemistry LaboratoryDocument11 pagesExercise 4 Test For Carbohydrates: CHY 47.1 Biochemistry LaboratorycamilleNo ratings yet
- Test For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalDocument31 pagesTest For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalHasan RabyNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones: ResultsDocument7 pagesAldehydes and Ketones: ResultsStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Title: Aldehyde and Ketones: Characterization of An Unknown ObjectiveDocument7 pagesExperiment 9 Title: Aldehyde and Ketones: Characterization of An Unknown ObjectiveKristinne Daenielle GomezNo ratings yet
- 1152 Lab CarbohydratesDocument8 pages1152 Lab Carbohydratesanyss_afiezaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDocument8 pagesExperiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl Carbonyl Containing CompoundsLovelyrabbit26No ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Aldehydes and Ketones: Preparation and Qualitative AnalysisDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Aldehydes and Ketones: Preparation and Qualitative AnalysisRom PeDrazaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Solomon Periodic AcidDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Solomon Periodic AcidIqbal A Mir100% (1)
- Colorimetric Determination of Carbohydrate UnknownsDocument6 pagesColorimetric Determination of Carbohydrate Unknownsmogn8586% (7)
- Classification Test For Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing Compound ReferenceDocument6 pagesClassification Test For Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing Compound ReferenceErica OcheaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6-283gDocument11 pagesLab 6-283gAnonymous 4KuItFhNo ratings yet
- Names: Bryle Kristiann CamaroteDocument18 pagesNames: Bryle Kristiann CamaroteKateNo ratings yet
- Pre Laboratory AssignmentDocument44 pagesPre Laboratory AssignmentJr Montero100% (3)
- Brady's Tests Can Be Used To Qualitatively Detect The Carbonyl Functionality of ADocument6 pagesBrady's Tests Can Be Used To Qualitatively Detect The Carbonyl Functionality of AEdon EduinNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab #1Document9 pagesChem Lab #1EmmaNo ratings yet
- I. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument10 pagesI. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidLaily SafitriNo ratings yet
- Synthetic of CyclohexanoneDocument15 pagesSynthetic of CyclohexanoneRadiatul Awalia AmirNo ratings yet
- Practical 1Document6 pagesPractical 1DOUMBOUYA SIDIKINo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing Compounds AutosavedDocument9 pagesClassification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing Compounds AutosavedCamille OngchuanNo ratings yet
- Organic Lab 6Document19 pagesOrganic Lab 6badirmhammadNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document3 pagesExperiment 4atiqahNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules One Shot BouncebackDocument144 pagesBiomolecules One Shot Bouncebackmourya100% (1)
- Ketones Post LabDocument18 pagesKetones Post LabcorpuzxyleneyaraNo ratings yet
- Separation of The Colored Pigments Found in MalunggayDocument9 pagesSeparation of The Colored Pigments Found in MalunggayZxyl BasilioNo ratings yet
- Benz AldehydeDocument5 pagesBenz AldehydeRoni BaroesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondDocument2 pagesChemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondJAYLEN TRACEYNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 B.ODocument10 pagesExp 4 B.OUmmu Umar Wa Aisyah100% (2)
- Experiment 5a Pre Post LabDocument9 pagesExperiment 5a Pre Post LabRue Cheng Ma100% (1)
- Laporan IGF AlimDocument11 pagesLaporan IGF Alimppg.risdaniar99130No ratings yet
- Physical Properties and Identification of Acid-Base Properties of Representative Organic Compounds Using Simple Solubility TestsDocument6 pagesPhysical Properties and Identification of Acid-Base Properties of Representative Organic Compounds Using Simple Solubility TestsMatthew SA100% (1)
- Organic Chemical Tests (A2)Document3 pagesOrganic Chemical Tests (A2)Kevin The Chemistry TutorNo ratings yet
- Reflux and DistillationDocument1 pageReflux and Distillation06hoqueaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Kinetic Study of Co (Salen) (Revision)Document3 pagesSynthesis and Kinetic Study of Co (Salen) (Revision)Daniel Rodman50% (2)
- Exer2 PrelabDocument3 pagesExer2 Prelabkarinadegoma100% (1)
- Chemistrt r3 KeyDocument31 pagesChemistrt r3 KeyBharathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules Aldehydes and KetonesDocument8 pagesChapter 15 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules Aldehydes and KetonesinkheartkatNo ratings yet
- A. Title of Experiment B. The Aim of ExperimentDocument10 pagesA. Title of Experiment B. The Aim of ExperimentsitrahnurdiniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 10 - Most Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesChemistry Class 10 - Most Important QuestionsAditi PandyaNo ratings yet
- Class X Chapter4Document12 pagesClass X Chapter4kannan2030No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones-12cDocument12 pagesAldehydes and Ketones-12cAlmira Kaye CuadraNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesFrom EverandTransition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesNo ratings yet
- Acid Fast OioDocument1 pageAcid Fast OioDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- Bacillus (Rod-Shaped Bacterium)Document2 pagesBacillus (Rod-Shaped Bacterium)DDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- Turpentine OilDocument1 pageTurpentine OilDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- Test 2, 3Document3 pagesTest 2, 3DDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- Gs Capsule March 2016 Part I Part IIDocument24 pagesGs Capsule March 2016 Part I Part IIRaj DubeyNo ratings yet
- INCOMPATIBILITIESDocument49 pagesINCOMPATIBILITIESDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- Crystallisation and Physical Properties of Fats: EditorialDocument2 pagesCrystallisation and Physical Properties of Fats: EditorialDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- The Chinese Revolution of 1949Document5 pagesThe Chinese Revolution of 1949Al GaniNo ratings yet
- Acid Fast OioDocument1 pageAcid Fast OioDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- GMP Biologicals Acceptance CriteriaDocument20 pagesGMP Biologicals Acceptance CriteriaIgorDatamanagementNo ratings yet
- A. Isolation Via Steam DistillationDocument4 pagesA. Isolation Via Steam DistillationDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- 4.a 4. C OfrDocument1 page4.a 4. C OfrDDS (Dingdong Dantes Supporter)No ratings yet
- PROBLEMS DaltonsLaw PDFDocument1 pagePROBLEMS DaltonsLaw PDFFact aazNo ratings yet
- Iligan Medical Center College: Activity 1 (GC)Document4 pagesIligan Medical Center College: Activity 1 (GC)Krizza Gales DemecilloNo ratings yet
- Nonylphenol EthoxylatesDocument25 pagesNonylphenol EthoxylatesJakin RookNo ratings yet
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument3 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsNicole de LeonNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab PapersDocument3 pagesBiochem Lab Papersloreign sinocruzNo ratings yet
- Waves FormulasDocument2 pagesWaves FormulasHshs HshshNo ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-06) Based On AIATS-06 (TYM) - ChemistryDocument6 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-06) Based On AIATS-06 (TYM) - ChemistryDev SoniNo ratings yet
- Dap An Mock 4Document4 pagesDap An Mock 4KIMTHOANo ratings yet
- Figure R4-1: Vacuum Column FlowsheetDocument18 pagesFigure R4-1: Vacuum Column Flowsheetnico123456789No ratings yet
- Imc Pipelines Loop 1Document7 pagesImc Pipelines Loop 1Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- MSDS R6Document3 pagesMSDS R6jafarptrNo ratings yet
- Combustion Basics: Joseph Colannino, P.EDocument20 pagesCombustion Basics: Joseph Colannino, P.ErezaimamNo ratings yet
- 5.7-5.10 Naming Mixed Ionic and Covalent Compounds AnswersDocument2 pages5.7-5.10 Naming Mixed Ionic and Covalent Compounds AnswersAlan MartínNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2pointsDocument4 pagesChemistry 2pointsjovanniNo ratings yet
- ASTM F639-09 Standard Specification For Polyethylene Plastics For Medical ApplicationsDocument3 pagesASTM F639-09 Standard Specification For Polyethylene Plastics For Medical ApplicationsJoãoNo ratings yet
- Peter Atkins Julio de Paula Ron Friedman Physical Chemistry Quanta (0766-0816)Document51 pagesPeter Atkins Julio de Paula Ron Friedman Physical Chemistry Quanta (0766-0816)Administracion OTIC IVICNo ratings yet
- Opic Nergy Iagrams: E U: L O: E K: EDocument4 pagesOpic Nergy Iagrams: E U: L O: E K: Esyafr.e.424No ratings yet
- Datesheet For Diploma HSBTE Exam Jan 2024 - 22.12.23Document494 pagesDatesheet For Diploma HSBTE Exam Jan 2024 - 22.12.23ls8612869No ratings yet
- Sans 5839Document9 pagesSans 5839Sergio VianaNo ratings yet
- Sphalerite Leaching With H2SO4 and NaNO3Document11 pagesSphalerite Leaching With H2SO4 and NaNO3Ade SatriaNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange, Molecular Sieve, AffinityDocument11 pagesIon Exchange, Molecular Sieve, AffinityNofrizalNo ratings yet
- Oxalic Acid Vs Kmno4Document2 pagesOxalic Acid Vs Kmno4rajansen2005No ratings yet
- The Teacher's Guide: To The Corrosion ToolkitDocument42 pagesThe Teacher's Guide: To The Corrosion ToolkitCiceroNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: TUNASCRYL 140-50Document2 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: TUNASCRYL 140-50JosephNo ratings yet
- APAR Conductors BrochureDocument178 pagesAPAR Conductors BrochureAshish bhattNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual For Laboratory EquipmentDocument169 pagesMaintenance Manual For Laboratory EquipmentOumaima H'rNo ratings yet
- Liquid-Liquid Equilibrium Data For Three Ternary Systems of Aqueous Alcohol Solutions AND Applicability of The Analytical Solutions of GroupsDocument3 pagesLiquid-Liquid Equilibrium Data For Three Ternary Systems of Aqueous Alcohol Solutions AND Applicability of The Analytical Solutions of GroupsGINA PAOLA BERRÍO JULIONo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Antidiabetical Action of Myrus Communis Variegatha Essential OilDocument16 pagesAntioxidant Antidiabetical Action of Myrus Communis Variegatha Essential OilMarina MagninNo ratings yet