Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DX Infective Endocarditis PDF
Uploaded by
Sherree HayesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DX Infective Endocarditis PDF
Uploaded by
Sherree HayesCopyright:
Available Formats
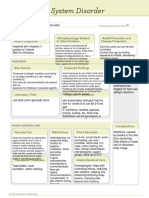
eNursing Care Plan 36-1
Patient with Infective Endocarditis
Nursing Diagnosis*
Impaired Cardiac Output
Etiology: Altered rhythm, valvular insufficiency, fluid overload
Supporting data: Heart murmur, S3, tachycardia, diminished peripheral pulses,
adventitious breath sounds, decreased urine output, unexplained weight gain, restlessness
(Outcomes and Interventions for this Nursing Diagnosis are presented in eNursing Care
Plan 36-2: Nursing Care Plan for the Patient with Valvular Heart Disease.)
Nursing Diagnosis
Activity Intolerance
Etiology: Insufficient oxygenation from decreased cardiac output
Supporting data: Fatigue, malaise, weakness, painful joints, myalgia, dyspnea,
dysrhythmias
(Outcomes and Interventions for this Nursing Diagnosis are presented in eNursing Care
Plan 36-2: Nursing Care Plan for the Patient with Valvular Heart Disease.)
Nursing Diagnosis
Hyperthermia
Etiology: Infection of heart tissue
Supporting data: Fever, diaphoresis, chills, malaise, tachycardia, tachypnea
Patient Goal
Maintains normal body temperature
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
Thermoregulation Fever Treatment
Sweating when hot _____ Monitor temperature and other vital signs, as
Shivering when cold _____ appropriate, to determine effectiveness of therapy and
Apical heart rate _____ to prevent complications.
Radial pulse rate _____ Administer medications or IV fluids (e.g.,
Reported thermal comfort antipyretics, antibacterial agents, and anti-shivering
_____ agents) to reduce fever and treat cause.
Monitor intake and output and be aware of changes in
Measurement Scale insensible fluid loss to monitor for signs and
1 = Severely compromised symptoms of dehydration.
2 = Substantially compromised Encourage fluid consumption to replace fluids lost as
3 = Moderately compromised a result of fever.
4 = Mildly compromised Monitor for fever-related complications and signs and
*
Nursing diagnoses listed in order of priority.
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
eNursing Care Plan 36-2
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
5 = Not compromised symptoms of fever-causing condition (e.g., seizure,
decreased level of consciousness, abnormal
electrolyte status, acid-base imbalance, dysrhythmia,
and abnormal cellular changes) to identify and treat
complications.
Avoid unnecessary exposure, drafts, overheating, or
chilling to control fever symptoms.
Nursing Diagnosis
Acute Pain
Etiology: Infection of heart tissue, embolization
Supporting data: Malaise, painful joints, myalgia, back pain, abdominal discomfort,
headache, backache
Patient Goal
Reports relief of pain
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
Pain Control Pain Management
Uses preventive Perform a comprehensive assessment of pain to include
measures ___ location, characteristics, onset/duration, intensity/severity
Uses analgesics of pain, and precipitating factors to plan appropriate
appropriately ___ interventions.
Reports uncontrolled Provide optimal pain relief with prescribed analgesics
symptoms to health care because pain exacerbates tachycardia and increases BP.
professional ___ Position patient (e.g., using principles of body alignment,
Reports pain controlled support with pillows, support joints during movement,
_____ splint over incisions and immobilize painful body parts to
facilitate comfort.
Measurement Scale Teach the use of nonpharmacologic techniques (e.g.,
1 = Never demonstrated relaxation, guided imagery, hot/cold application, and
2 = Rarely demonstrated massage) and along with other pain relief measures to
3 = Sometimes promote comfort.
demonstrated Encourage patient to monitor own pain and intervene
4 = Often demonstrated
appropriately to increase patient’s control over pain
5 = Consistently
demonstrated management.
Facilitate hygiene measures (e.g., wiping brow, applying
skin creams, or cleaning body, hair, and oral cavity) to
keep the patient comfortable.
Evaluate effectiveness of pain control measures through
ongoing assessment of pain experience to ensure effective
pain managemen and facilitate comfort.
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
eNursing Care Plan 36-3
Nursing Diagnosis
Lack of Knowledge
Etiology: Lack of experience and exposure to information about disease and treatment
process
Supporting data: Questions about desired or prescribed health behaviors, requests
information
Patient Goal
Describes disease process, appropriate treatments, and measures to prevent recurrence of
disease
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
Knowledge: Disease Process Teaching: Disease Process
Characteristics of specific Assess the patient’s current level of knowledge
disease _____ related to specific disease process to identify teaching
Cause and contributing needs.
factors _____ Describe common signs and symptoms of the disease
Physiologic effects of so patient will notify health care provider and
disease _____ treatment can be initiated promptly.
Usual course of disease Discuss lifestyle changes that may be required to
process _____ prevent future complications and/or control the
Signs and symptoms of disease process to reduce the risk of recurrent
disease complications _____ infective endocarditis.
Precautions to prevent
complications _____ Teaching: Prescribed Medication
Provide the patient and caregiver with written
Measurement Scale information about the action, purpose, and side effects
1 = No knowledge of the medications to promote safe medication
2 = Limited knowledge therapy.
3 = Moderate knowledge
4 = Substantial knowledge
5 = Extensive knowledge
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
eNursing Care Plan 36-4
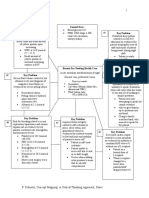
eNursing Care Plan 36-2
Patient with Valvular Heart Disease
Nursing Diagnosis*
Impaired Cardiac Output
Etiology: Valvular incompetence
Supporting data: Murmurs, dyspnea, dysrhythmias, peripheral edema
Patient Goal
Maintains adequate tissue and organ perfusion
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
Cardiac Pump Effectiveness Cardiac Care
Dysrhythmia ___ Monitor vital signs, cardiovascular status, and
Abnormal heart sounds ___ respiratory status to assess for manifestations of
Peripheral edema ___ decreased cardiac output (e.g., fatigue, malaise,
Dyspnea ___ shortness of breath, dyspnea on exertion, palpitations,
Pulmonary edema ___ angina, widened pulse pressure).
Monitor for dysrhythmias, including disturbances of
Measurement Scale both rhythm and conduction, to identify and treat
1 = Severe significant dysrhythmias.
2 = Substantial
3 = Moderate Hemodynamic Regulation
4 = Mild Administer positive inotropic and contractility
5 = None medications to increase myocardial contractility.
Elevate the head of the bed to reduce venous return
and optimize breathing.
Energy Management
Promote bedrest/activity limitation to decrease
cardiac workload and O2 demand.
Nursing Diagnosis
Fluid Imbalance
Etiology: Fluid retention from valvular-induced heart failure
Supporting data: Peripheral edema, weight gain, adventitious breath sounds, neck vein
distention
Patient Goal
Achieves fluid and electrolyte balance
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
*Nursing diagnoses listed in order of priority.
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
eNursing Care Plan 36-5
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
Fluid Balance Hypervolemia Management
Adventitious breath sounds Monitor for peripheral edema to detect hypervolemia
___ causing third spacing.
Neck vein distention ___ Monitor respiratory pattern for symptoms of
Peripheral edema ___ pulmonary edema (e.g., anxiety, air hunger,
orthopnea, dyspnea, tachypnea, cough, frothy sputum
Measurement Scale production, and shortness of breath) to assess for fluid
1 = Severe congestion in the lungs.
2 = Substantial Monitor hemodynamic status, including HR, BP,
3 = Moderate MAP, CVP, PAP, PCWP, CO, and CI, if available, to
4 = Mild assess hemodynamic response to and effectiveness of
5 = None
interventions.
Weigh daily at consistent times (e.g., after voiding,
before breakfast) and monitor trends to monitor for
signs of hypervolemia.
Administer prescribed medications to reduce preload
(e.g., furosemide, spironolactone, morphine, and
nitroglycerin) to assist with removal of fluid.
Monitor for laboratory test results of
hemoconcentration (e.g., sodium, BUN, hematocrit,
urine specific gravity), if available, to assess for signs
of hypervolemia.
Fluid/Electrolyte Management
Provide prescribed diet as appropriate for specific
fluid or electrolyte imbalance (e.g., low-sodium, fluid-
restricted, and no added salt) to prevent fluid
retention.
Nursing Diagnosis
Activity Intolerance
Etiology: Insufficient oxygenation from decreased cardiac output and pulmonary
congestion
Supporting data: Weakness, fatigue, shortness of breath, increase or decrease in pulse
rate, BP changes
Patient Goal
Achieves optimal level of activity
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
Activity Tolerance Energy Management
Pulse rate with activity ___ Monitor cardiorespiratory response to activity
Ease of breathing with activity (e.g., tachycardia, other dysrhythmias, dyspnea,
___ diaphoresis, pallor, hemodynamic pressures,
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
eNursing Care Plan 36-6
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
Systolic BP with activity ___ respiratory rate) to plan appropriate interventions.
Diastolic BP with activity ___ Encourage alternate rest and activity periods to
conserve energy and decrease cardiac demands.
Measurement Scale Encourage patient to choose activities that
1 = Severely compromised gradually build endurance to increase cardiac
2 = Substantially compromised tolerance.
3 = Moderately compromised Assist the patient/caregiver to establish realistic
4 = Mildly compromised
activity goals to promote feelings of
5 = Not compromised
accomplishment.
Nursing Diagnosis
Lack of Knowledge
Etiology: Lack of experience and exposure to information about disease and treatment
process
Supporting data: Questions about measures to prevent complications, requests for
information
Patient Goal
Describes disease process and appropriate measures to prevent complications
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
Knowledge: Disease Process Teaching: Disease Process
Characteristics of specific Assess the patient’s current level of knowledge
disease ___ related to specific disease to develop teaching
Physiologic effects of disease plan.
___ Explain pathophysiology of the disease and how it
Signs and symptoms of disease relates to anatomy and physiology to ensure
___ knowledge base.
Strategies to minimize disease Describe common signs and symptoms of the
progression ___ disease.
Describe disease process. Instruct the patient on
Knowledge: Medication measures to control/minimize symptoms to
Medication therapeutic effects manage disease.
___ Discuss lifestyle changes that may be required to
Medication side effects ___ prevent complications and/or control the disease
Medication adverse effects ___ process (e.g., smoking cessation) to decrease
Potential medication cardiac workload and promote oxygenation.
interactions ___ Teach patient and caregiver signs and symptoms to
Correct use of prescribed report to health care provider to ensure
medication ___ appropriate interventions.
Measurement Scale Teaching: Prescribed Medication
1 = No knowledge Teach patient and/or caregiver purpose and action
2 = Limited knowledge
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
eNursing Care Plan 36-7
Outcomes (NOC) Interventions (NIC) and Rationales
3 = Moderate knowledge of each medication.
4 = Substantial knowledge Provide patient and/or caregiver with written
5 = Extensive knowledge information about action, purpose, and side effects
of each medication.
Teach the patient appropriate actions to take if side
effects occur to prevent complications and ensure
appropriate actions are taken.
Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Marquez - Case Study 4Document4 pagesMarquez - Case Study 4Caren MarquezNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderDocument1 pageSmall Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderMarina Wasem Netzlaff0% (1)
- Name of Student: - InstructionDocument31 pagesName of Student: - InstructionPaul Jackson50% (2)
- Carla Hernandez Clinical WorksheetDocument2 pagesCarla Hernandez Clinical WorksheetJasmyn RoseNo ratings yet
- System Disorder GHDDocument1 pageSystem Disorder GHDSariahNo ratings yet
- Case Simulation 118Document4 pagesCase Simulation 118Rica AvendañoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Case 1: Jackson Weber (Core) : Guided Reflection QuestionsDocument3 pagesPediatric Case 1: Jackson Weber (Core) : Guided Reflection QuestionsDai Nguyen100% (1)
- System Disorder CP CLDocument1 pageSystem Disorder CP CLSariahNo ratings yet
- Ati Medication Template HydrocortisoneDocument1 pageAti Medication Template HydrocortisoneSharee HaywoodNo ratings yet
- 2Document4 pages2Emmyr JohnNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Maternity Case 5: Fatime SanogoDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Maternity Case 5: Fatime SanogoNicole AngelNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 - Case Analysis - Nursing Care Plan of Heart FailureDocument2 pagesNCM 106 - Case Analysis - Nursing Care Plan of Heart FailureMarisol Jane JomayaNo ratings yet
- Fever Nursing Care PlanDocument30 pagesFever Nursing Care PlanAnuchithra Radhakrishnan100% (4)
- System Disorder ADDocument1 pageSystem Disorder ADSariahNo ratings yet
- MCN Exam 2 Study Guide - CompleteDocument87 pagesMCN Exam 2 Study Guide - CompleteColin MacKenzie100% (1)
- NCLEX Practice QuestionsDocument12 pagesNCLEX Practice QuestionsDane WrightNo ratings yet
- FundamentalsExam W RatioDocument13 pagesFundamentalsExam W RatioKeesha Mae Urgelles TimogNo ratings yet
- Cord Prolapse March 23Document2 pagesCord Prolapse March 23Kathleen Vargas100% (1)
- FundaDocument101 pagesFundaMelanieTriezlVillaseñorJosonNo ratings yet
- Drug Card SennaDocument1 pageDrug Card SennaAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- ClindamycinDocument3 pagesClindamycinShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic - Procedure DoyleDocument1 pageDiagnostic - Procedure Doylemp1757No ratings yet
- Common Medical Surgical MedicationsDocument36 pagesCommon Medical Surgical MedicationsAshley Etheredge100% (1)
- Nursing Concept MapDocument2 pagesNursing Concept MapMary Mann100% (1)
- Concept Map Worksheet Fatime Sanogo Jasgou1752Document1 pageConcept Map Worksheet Fatime Sanogo Jasgou1752Jasmyn RoseNo ratings yet
- LCPDDocument7 pagesLCPDakoismeNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaSteffanie Serrano100% (1)
- Post Assessment PediatricsDocument4 pagesPost Assessment Pediatricscuicuita100% (4)
- Concept Map RSV 4Document10 pagesConcept Map RSV 4api-546577761No ratings yet
- Completed Concept MapDocument4 pagesCompleted Concept Mapapi-607361848No ratings yet
- Rheumatic Joint Disease Study GuideDocument18 pagesRheumatic Joint Disease Study Guidechalinsammy1No ratings yet
- Care Plan FaringitisDocument63 pagesCare Plan FaringitisEnerolisa ParedesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Concept Map 1Document3 pagesNursing Concept Map 1Norah Okafor Ezike67% (3)
- NCLEX Questions PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCLEX Questions PneumoniaLovely Laranjo100% (1)
- Cap Grand Case PreDocument46 pagesCap Grand Case PreMatty FelNo ratings yet
- Care PlanDocument2 pagesCare PlanLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Board Questions 2009Document16 pagesBoard Questions 2009Erick EspinoNo ratings yet
- Sena, Zyrus Reoder ADocument4 pagesSena, Zyrus Reoder AAkoSiIngridNo ratings yet
- CASE SIMUlation 112Document6 pagesCASE SIMUlation 112Princess Levie CenizaNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Care PlanDocument2 pagesChest Pain Care Planapi-545292605No ratings yet
- Concept Map Due 04Document9 pagesConcept Map Due 04api-545711468No ratings yet
- Guide Mse For Vsim Sharon ColeDocument3 pagesGuide Mse For Vsim Sharon Cole002No ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument1 pagePeptic Ulcer DiseaseEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Medsurge RationaleDocument8 pagesMedsurge RationaleRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- Waiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Description: Congestive Heart FailureDocument22 pagesDescription: Congestive Heart FailurePinklet Arleena CubianNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ForDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan ForVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- ATI DRUG TABLES Module4 Respiratory Sympathomimetics PhenylephrineDocument1 pageATI DRUG TABLES Module4 Respiratory Sympathomimetics Phenylephrinenoeyeshaveseen100% (1)
- Sample Letter Templates (4th Year)Document49 pagesSample Letter Templates (4th Year)Yna LafuenteNo ratings yet
- Nursing AssessmentDocument4 pagesNursing AssessmentFlor SabaysabayNo ratings yet
- MicrocephalyDocument4 pagesMicrocephalykurei_bluflamedNo ratings yet
- Waiters Osteoarthritis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Osteoarthritis PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Desires - How Are You Feeling Today Sir? If Huminto Po Si PT, Iallow Po Natin Siya & Bigyan Siya NG Time To Fully Undertand What He Is Feeling Right Now.Document19 pagesDesires - How Are You Feeling Today Sir? If Huminto Po Si PT, Iallow Po Natin Siya & Bigyan Siya NG Time To Fully Undertand What He Is Feeling Right Now.melodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment 51-100 QuestionnaireDocument27 pagesHealth Assessment 51-100 QuestionnairetflorenzNo ratings yet
- Nur 1210 Pedia Concept Module 4B Alterations With Infectious, Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseDocument19 pagesNur 1210 Pedia Concept Module 4B Alterations With Infectious, Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseweissNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Management: BleomycinDocument1 pagePharmacologic Management: BleomycinKim ApuradoNo ratings yet
- Med SurgDocument3 pagesMed SurgharpayNo ratings yet
- Dhan Chan NCPDocument3 pagesDhan Chan NCPDhaneanne Marie ChanNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- DX Resp Failure PDFDocument5 pagesDX Resp Failure PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Stroke PDFDocument8 pagesDX Stroke PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Spine Injury PDFDocument5 pagesDX Spine Injury PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Hyperthyoidism PDFDocument10 pagesDX Hyperthyoidism PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Intracranial Pressure PDFDocument8 pagesDX Intracranial Pressure PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Prostate Surgery PDFDocument4 pagesDX Prostate Surgery PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Postop PT PDFDocument9 pagesDX Postop PT PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Diarrhea PDFDocument11 pagesDX Diarrhea PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Osteo Issue PDFDocument9 pagesDX Osteo Issue PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Hepatitis PDFDocument14 pagesDX Hepatitis PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX DM PDFDocument6 pagesDX DM PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Hysterectomy PDFDocument1 pageDX Hysterectomy PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Heart Failure PDFDocument4 pagesDX Heart Failure PDFSherree Hayes100% (1)
- DX Fracture PDFDocument8 pagesDX Fracture PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis / TBDocument11 pagesTuberculosis / TBSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Asthma PDFDocument6 pagesDX Asthma PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- COPD Concept MapDocument1 pageCOPD Concept MapSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Burns PDFDocument6 pagesDX Burns PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Viruses: Organisms Causing PneumoniaDocument17 pagesRespiratory Viruses: Organisms Causing PneumoniaSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- DX Alcohol Withdrawal PDFDocument3 pagesDX Alcohol Withdrawal PDFSherree Hayes100% (1)
- EKG/ECG Study GuideDocument13 pagesEKG/ECG Study GuideSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument11 pagesCOPDSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument19 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument17 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeSherree Hayes100% (2)
- Chapter 27: Lower Respiratory Problems Pleural Effusion With Thoracentesis and Chest TubeDocument3 pagesChapter 27: Lower Respiratory Problems Pleural Effusion With Thoracentesis and Chest TubeSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine Injury: Julie C. LeonardDocument15 pagesCervical Spine Injury: Julie C. LeonardCamilla CristinaNo ratings yet
- MEAL (Psychiatric Nursing 2)Document4 pagesMEAL (Psychiatric Nursing 2)Yucef Bahian-AbangNo ratings yet
- Smoking Poor Dietary Habits Sedentary Lifestyle: Lung Cancer Diabetes Heart DiseaseDocument2 pagesSmoking Poor Dietary Habits Sedentary Lifestyle: Lung Cancer Diabetes Heart DiseaseKien Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PSM LMRP 2019Document25 pagesPSM LMRP 2019skNo ratings yet
- Approach To Delay PubertyDocument33 pagesApproach To Delay PubertyRaja Iqbal Mulya HarahapNo ratings yet
- Viral Skin InfectionsDocument28 pagesViral Skin Infectionstolesadereje73No ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument4 pagesHead TraumaDaniel GeduquioNo ratings yet
- Step2ck Practice TestDocument67 pagesStep2ck Practice TestAlf CarlNo ratings yet
- Kshudra Roga Critical Understanding: Dr. Gaurav DesaiDocument39 pagesKshudra Roga Critical Understanding: Dr. Gaurav DesaiDrVikas100% (3)
- Bsped Dka Guidelines 2020Document23 pagesBsped Dka Guidelines 2020drsaleemNo ratings yet
- First Aid For Snake BiteDocument11 pagesFirst Aid For Snake BiteHenryVanDerSchyffNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis Update On Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and PDFDocument11 pagesPeritonitis Update On Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and PDFAnonymous InJS6aYZ100% (1)
- Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery: SciencedirectDocument3 pagesClinical Neurology and Neurosurgery: SciencedirectYubitza NaviaNo ratings yet
- Immunofluorescence Techniques: Ian D. Odell and Deborah CookDocument4 pagesImmunofluorescence Techniques: Ian D. Odell and Deborah CookbalamurugantNo ratings yet
- Diazoxide 50mg Tab DCC SummeryDocument1 pageDiazoxide 50mg Tab DCC SummeryarifpharmjuNo ratings yet
- Clinical Symptom Score of The Japanese Orthopaedic Association PDFDocument3 pagesClinical Symptom Score of The Japanese Orthopaedic Association PDFJoanne NgimNo ratings yet
- The Clinical, Environmental, and Behavioral Factors That Foster Early Childhood CariesDocument9 pagesThe Clinical, Environmental, and Behavioral Factors That Foster Early Childhood CariesRayhan DaneoNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous Mastitis: The Histological Differentials: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument13 pagesGranulomatous Mastitis: The Histological Differentials: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAsmara SyedNo ratings yet
- U.S. Patent 9,301,519, Entitled, Systems and Methods For Ex Vivo Organ Care, To Hassanein Et Al., Issued Apr. 5, 2016.Document106 pagesU.S. Patent 9,301,519, Entitled, Systems and Methods For Ex Vivo Organ Care, To Hassanein Et Al., Issued Apr. 5, 2016.Anonymous a7S1qyXNo ratings yet
- Medical and Surgical NursingDocument9 pagesMedical and Surgical NursingWilmaBongotanPadawilNo ratings yet
- 4 Life TestimoniesDocument87 pages4 Life TestimoniesBhavin VoraNo ratings yet
- Issues in TraumatologyDocument111 pagesIssues in TraumatologyDr VirenNo ratings yet
- Efektivitas Pemberian Ikan Gabus Kukus Terhadap Penyembuhan Laserasi Perineum Pada Ibu PostpartumDocument9 pagesEfektivitas Pemberian Ikan Gabus Kukus Terhadap Penyembuhan Laserasi Perineum Pada Ibu Postpartumjulimarni13No ratings yet
- List of Facility HeadDocument2 pagesList of Facility HeadShohel RanaNo ratings yet
- The History of PsychiatryDocument12 pagesThe History of PsychiatryMarkoff Chaney100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument35 pagesEndocrine SystemLinkNo ratings yet
- History Taking and Mental State Examination 2Document35 pagesHistory Taking and Mental State Examination 2Noreen Choudhri100% (2)
- Vein Artery Capillary: Thin Wall Wide Lumen Valve Thick Wall Narrow Lumen One Cell Thick WallDocument1 pageVein Artery Capillary: Thin Wall Wide Lumen Valve Thick Wall Narrow Lumen One Cell Thick WallHuiso RohNo ratings yet