Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Global System: World Distribution of
Uploaded by
Garcia AzirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Global System: World Distribution of
Uploaded by
Garcia AzirCopyright:
Available Formats
Global system
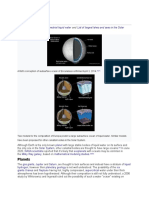
World Distribution of Mid-Oceanic Ridges; USGS
Three main types of plate boundaries.
The mid-ocean ridges of the world are connected and form a single global mid-oceanic ridge system
that is part of every ocean and the longest mountain range in the world. The continuous mountain
range is 65,000 km (40,000 mi) long (several times longer than the Andes, the longest continental
mountain range).[28]
Physical properties
Main article: Seawater
The total mass of the hydrosphere is about 1.4 quintillion tonnes (1.4×10 18 long tons or 1.5×1018 short
tons), which is about 0.023% of Earth's total mass. Less than 3% is freshwater; the rest is saltwater,
almost all of which is in the ocean. The area of the World Ocean is about 361.9 million square
kilometers (139.7 million square miles),[9] which covers about 70.9% of Earth's surface, and its
volume is approximately 1.335 billion cubic kilometers (320.3 million cubic miles). [9] This can be
thought of as a cube of water with an edge length of 1,101 kilometers (684 mi). Its average depth is
about 3,688 meters (12,100 ft),[9] and its maximum depth is 10,994 meters (6.831 mi) at the Mariana
Trench.[29] Nearly half of the world's marine waters are over 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) deep.[16] The vast
expanses of deep ocean (anything below 200 meters or 660 feet) cover about 66% of Earth's
surface.[30] This does not include seas not connected to the World Ocean, such as the Caspian Sea.
The bluish ocean color is a composite of several contributing agents. Prominent contributors include
dissolved organic matter and chlorophyll.[31] Mariners and other seafarers have reported that the
ocean often emits a visible glow which extends for miles at night. In 2005, scientists announced that
for the first time, they had obtained photographic evidence of this glow. [32] It is most likely caused
by bioluminescence.[33][34][35]
You might also like
- OceanDocument7 pagesOceanTsea CaronNo ratings yet
- Definitions and ApplicationDocument1 pageDefinitions and ApplicationŚáńtőśh MőkáśhíNo ratings yet
- Oceans and Coral ReefsDocument6 pagesOceans and Coral ReefsHarsh BajajNo ratings yet
- Ocean: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument2 pagesOcean: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchEllaineNo ratings yet
- 6 HydrosphereDocument11 pages6 HydrosphereAndrew GravesNo ratings yet
- Oceans Coastal Processes Notes Kean UniversityDocument43 pagesOceans Coastal Processes Notes Kean Universityapi-323312952100% (1)
- Earth 0Document14 pagesEarth 046m9yfrqmtNo ratings yet
- Database 3Document5 pagesDatabase 3Adrian WardNo ratings yet
- Ang Batas Sedisyon Ay Isang Batas Na Usa NG Kamatayan o Matagal Pagkakabilanggo Sa Mga Pilipino Sa PagsasalitaDocument5 pagesAng Batas Sedisyon Ay Isang Batas Na Usa NG Kamatayan o Matagal Pagkakabilanggo Sa Mga Pilipino Sa PagsasalitaThea Jill Roxas50% (2)
- Redemption OceanDocument19 pagesRedemption Oceanansari naseem ahmadNo ratings yet
- Natural Environment: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesNatural Environment: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediasabniezahmukrizNo ratings yet
- Ocean: The Ocean Covers 70% of The Earth, Sometimes Called The "Blue Planet"Document3 pagesOcean: The Ocean Covers 70% of The Earth, Sometimes Called The "Blue Planet"gabrielaNo ratings yet
- Gross Features of The EarthDocument6 pagesGross Features of The EarthPrince Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical OceanographyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Physical OceanographyM Farid Geonova100% (1)
- List of Lakes by AreaDocument8 pagesList of Lakes by AreaNoeroel HoedaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word 97 - 2003 DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word 97 - 2003 DocumentvishaldhandeNo ratings yet
- Earth Is The Third Planet From The Sun and The Only Astronomical Object Known To Harbor LifeDocument5 pagesEarth Is The Third Planet From The Sun and The Only Astronomical Object Known To Harbor LifePersonal Unit AccountNo ratings yet
- FAWECAFWECAWFFADocument7 pagesFAWECAFWECAWFFAMega ShowsNo ratings yet
- Enviornmental EngineeringDocument178 pagesEnviornmental EngineeringMatthew LiuNo ratings yet
- Earth 3Document4 pagesEarth 3Rey Jr. Cobel CababasadaNo ratings yet
- Ocean Chap 1Document32 pagesOcean Chap 1alimahrougNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesaidahjaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge of The UniverseDocument2 pagesKnowledge of The UniverseMichael Muhammad50% (2)
- Earth - Wikipedia2Document64 pagesEarth - Wikipedia2ROBLOX GAMERNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument3 pagesEarthIseg ProductionsNo ratings yet
- As An AI Language ModelDocument2 pagesAs An AI Language ModelSADAFAL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Ocean - LocationDocument1 pageOcean - Locationharmit1920No ratings yet
- EarthDocument4 pagesEarthgnoble30No ratings yet
- Physiography of OceanDocument4 pagesPhysiography of OceanMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Ageo Lopez Oceanography and GeologyDocument65 pagesAgeo Lopez Oceanography and GeologyQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Plate Tectonics and Earth's CrustDocument10 pagesLab 6 - Plate Tectonics and Earth's CrustBrian HoskinsonNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Q2 Module 10Document5 pagesEarth Science Q2 Module 10Jasmin grace BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Natural Environment: Land Management Hopetoun Falls AustraliaDocument4 pagesNatural Environment: Land Management Hopetoun Falls AustraliaNitinAgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Pacific Ocean - WikipediaDocument5 pagesPacific Ocean - WikipediatrianaNo ratings yet
- 56,000km Mid-Oceanic RidgeDocument3 pages56,000km Mid-Oceanic RidgeAfesoj BelirNo ratings yet
- Unit01 Lesson 1Document1 pageUnit01 Lesson 1Tongpin PengNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geography Earth Size and ShapeDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Geography Earth Size and ShapehrdepartmentemailsNo ratings yet
- Natural Environment: Navigation SearchDocument16 pagesNatural Environment: Navigation SearchChong Ru YinNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument45 pagesEarthBibithaNo ratings yet
- Seismic BeltsDocument14 pagesSeismic BeltsMaki OchonNo ratings yet
- Ocean: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia For Other Uses, See - Further InformationDocument4 pagesOcean: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia For Other Uses, See - Further InformationSarah SullivanNo ratings yet
- Earth Systems: Hydrosphere: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIA (E-Mail:)Document13 pagesEarth Systems: Hydrosphere: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIA (E-Mail:)Mangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- FSDAFASDFADocument7 pagesFSDAFASDFAMega ShowsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 ElsDocument44 pagesLesson 2 ElsJhellee AquinoNo ratings yet
- OceanDocument1 pageOceanBRIGHT TECH INDUSTRIALS INDIA PVT LTDNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Geology LECTURE 1Document18 pagesFundamental of Geology LECTURE 1rutendo ticharwaNo ratings yet
- FASDFASDFAFADocument7 pagesFASDFASDFAFAMega ShowsNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument11 pagesNarrative ReportStephanie Jean Magbanua CortezNo ratings yet
- OceanDocument39 pagesOceanNirmal BhowmickNo ratings yet
- PacificDocument1 pagePacificAserNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document11 pagesLecture 01Hilmi HasaniNo ratings yet
- OceanDocument8 pagesOceanEa RLNo ratings yet
- FAWEFEAWFAWEDocument8 pagesFAWEFEAWFAWESirf LaundeNo ratings yet
- Domain ProjectDocument6 pagesDomain ProjectPatel AvaniNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument32 pagesEarthRoel AbricaNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument22 pagesGeographymaheshgullankiNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTDocument12 pagesENVIRONMENTrakesh yadavNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Origin of Water On Earth History of Water On Earth Properties of Water HistoryDocument1 pageEtymology: Origin of Water On Earth History of Water On Earth Properties of Water HistoryGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Water Is An: Water in Three States: (Ice), and (Here Mostly Invisible, Cooling and Condensing, Is Building Clouds)Document1 pageWater Is An: Water in Three States: (Ice), and (Here Mostly Invisible, Cooling and Condensing, Is Building Clouds)Garcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Classical MechanicsDocument5 pagesMathematics: Classical MechanicsGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Color and Appearance: Color of Water Electromagnetic Absorption by WaterDocument2 pagesColor and Appearance: Color of Water Electromagnetic Absorption by WaterGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Triple and Critical PointsDocument1 pageTriple and Critical PointsGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Immanuel Kant Knowledge: SyntheticDocument2 pagesImmanuel Kant Knowledge: SyntheticGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Galileo: Philosophy of SpaceDocument1 pageGalileo: Philosophy of SpaceGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Role of Sertoli CellsDocument2 pagesRole of Sertoli CellsGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Essay 72Document1 pageEssay 72Garcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Indigenous Peoples and Pre-Columbian HistoryDocument2 pagesEtymology: Indigenous Peoples and Pre-Columbian HistoryGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Matter Electromagnetic Radiation Mass-Energy AntimatterDocument2 pagesOrdinary Matter Electromagnetic Radiation Mass-Energy AntimatterGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Space and Time Gottfried Leibniz Isaac NewtonDocument2 pagesPhilosophy of Space and Time Gottfried Leibniz Isaac NewtonGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Independence and ExpansionDocument2 pagesIndependence and ExpansionGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Stages: SpermatocytogenesisDocument3 pagesStages: SpermatocytogenesisGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Essay 74Document1 pageEssay 74Garcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Oceanic Zones: The Major Oceanic Zones, Based On Depth and Biophysical ConditionsDocument2 pagesOceanic Zones: The Major Oceanic Zones, Based On Depth and Biophysical ConditionsGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Biology: Further Information: andDocument1 pageBiology: Further Information: andGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis Is The Process by Which: Seminiferous Tubule With Maturing Sperm.Document2 pagesSpermatogenesis Is The Process by Which: Seminiferous Tubule With Maturing Sperm.Garcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Oocyte Conception Zygote Sexual Reproduction Chromosomes Haploid Diploid SpeciesDocument1 pagePurpose: Oocyte Conception Zygote Sexual Reproduction Chromosomes Haploid Diploid SpeciesGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Exploration: Mariana Trench Northern Mariana Islands Mariana Trench Challenger Deep TriesteDocument2 pagesExploration: Mariana Trench Northern Mariana Islands Mariana Trench Challenger Deep TriesteGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Oceanic DivisionsDocument2 pagesEtymology: Oceanic DivisionsGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Extraterrestrial Oceans: Further Information: andDocument2 pagesExtraterrestrial Oceans: Further Information: andGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Essays 47Document1 pageEssays 47Garcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Space Speed of Light Expansion of SpaceDocument1 pageSpace Speed of Light Expansion of SpaceGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Astronomers Discovered Stars in The Galaxy That Are Almost 13.6 Billion Years OldDocument1 pageAstronomers Discovered Stars in The Galaxy That Are Almost 13.6 Billion Years OldGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Essays 53Document1 pageEssays 53Garcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Second Italo-Ethiopian War: Main ArticleDocument1 pageSecond Italo-Ethiopian War: Main ArticleGarcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Essays 50Document1 pageEssays 50Garcia AzirNo ratings yet
- Essays 51Document1 pageEssays 51Garcia AzirNo ratings yet